TRUNCATE和DELETE都是用来删除表中数据的SQL命令,但它们的工作方式和使用场景有所不同:
-
DELETE命令:DELETE命令用于从表中删除一行、多行或所有行。你可以添加WHERE子句来指定要删除的行。例如,DELETE FROM table_name WHERE condition;。使用DELETE命令时,每一行都会被单独删除,并且触发器会被触发。此外,DELETE命令会记录下每个删除的行,因此你可以在事务中使用ROLLBACK命令来撤销DELETE操作。 -
TRUNCATE命令:TRUNCATE命令用于删除表中的所有行。与DELETE不同,TRUNCATE会删除表的数据并重置表的身份计数器(如果存在)。TRUNCATE操作更快,因为它不会记录每个删除的行,也不会触发触发器。然而,你不能在事务中撤销TRUNCATE操作。
总的来说,如果你需要删除表中的所有数据,并且不需要撤销操作,那么TRUNCATE是一个好选择。如果你需要删除特定的行,或者需要在事务中撤销删除操作,那么你应该使用DELETE命令。
CREATE DEFINER=`root`@`%` PROCEDURE `proc_test_date`() BEGIN #Routine body goes here... start TRANSACTION; INSERT into temp_test_date(type,create_time) select 'sysdate',sysdate(); INSERT into temp_test_date(type,create_time) select 'now',NOW(); select SLEEP(10); INSERT into temp_test_date(type,create_time) select 'sysdate',sysdate(); INSERT into temp_test_date(type,create_time) select 'now',NOW(); commit; END
执行truncate
call proc_test_date(); select * from temp_test_date; truncate table temp_test_date; call proc_test_date(); select * from temp_test_date;
然后发现
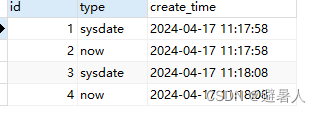
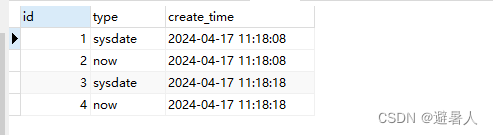
两次的执行结果id都是续上的,
执行delete
call proc_test_date(); select * from temp_test_date; delete from temp_test_date; call proc_test_date(); select * from temp_test_date;
查看结果

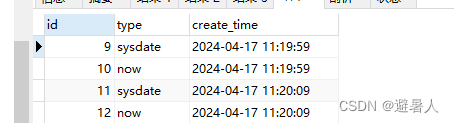
发现两次的查询结果,id并没有续上
这就是truncate,和delete的区别
需要注意的是在什么情况下id会不会连续呢?
在一个添加事务执行时,若是事务没有提交,那么其实以及申请了id
后面插入的数据会默认id以及有了,然后就会越过这个不存在的id
执行函数
##在事务提交之前结束
call proc_test_date();
##等待事务提交
call proc_test_date();
select * from temp_test_date; 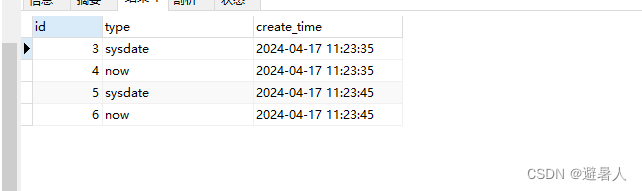
发现id1,2的数据并不存在
![[Win11·Copilot] Win11 系统更新重启后任务栏 Copilot 图标突然消失 | 解决方案](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/fca89418431140539a24f3f6ad80b7e4.jpeg#pic_center)