区间和
题目描述
假定有一个无限长的数轴,数轴上每个坐标上的数都是0。
现在,我们首先进行 n 次操作,每次操作将某一位置x上的数加c。
接下来,进行 m 次询问,每个询问包含两个整数l和r,你需要求出在区间[l, r]之间的所有数的和。
输入格式
第一行包含两个整数n和m。
接下来 n 行,每行包含两个整数x和c。
再接下里 m 行,每行包含两个整数l和r。
输出格式
共m行,每行输出一个询问中所求的区间内数字和。
数据范围
$ −109≤x≤109,$
$ 1≤n,m≤10^5,$
$ −109≤l≤r≤109,$
$ −10000≤c≤10000$
输入样例:
3 3
1 2
3 6
7 5
1 3
4 6
7 8
输出样例:
8
0
5
Solution
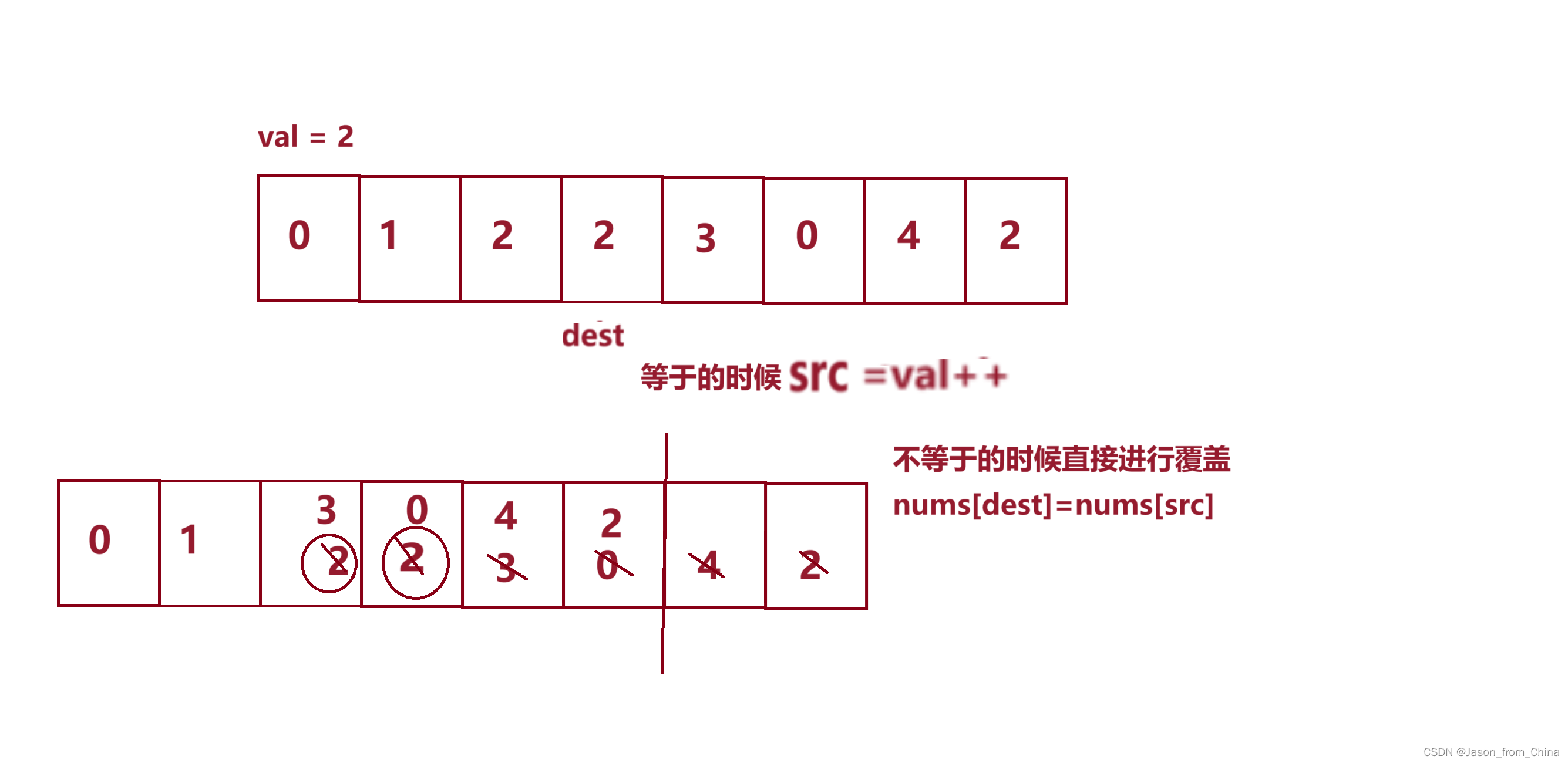
- 用题目中会用到的数字最多有 3 * 10^5,可以用来离散化表示 10^9
- alls 存所有用到的下标,adds 存所有添加操作,querys 存所有查询操作
- a 存执行添加操作之后的下标的值,q 存前缀和
用二维数组代替 Pairs,用数组代替 List,速度快了一倍
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class Main{
static final int N = 100010;
static int[] a = new int[3 * N];
static int[] q = new int[3 * N];
static int[][] adds = new int[N][2];
static int[][] querys = new int[N][2];
static int[] alls = new int[3 * N];
public static int unique(int[] alls, int n){
// 双指针
int j = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(i == 0 || alls[i] != alls[i - 1]){
alls[j] = alls[i];
j++;
}
}
return j;
}
public static int bsearch(int[] alls, int n, int x){
int low = 0, high = n - 1;
while(low <= high){
int mid = low + high >> 1;
if(alls[mid] > x) high = mid - 1;
else if(alls[mid] < x) low = mid + 1;
else return mid + 1;
}
return low;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
String[] s = br.readLine().split(" ");
int n = Integer.parseInt(s[0]);
int m = Integer.parseInt(s[1]);
// 下标
int idx = 0, idx1 = 0;
// 存插入
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
s = br.readLine().split(" ");
int x = Integer.parseInt(s[0]);
int c = Integer.parseInt(s[1]);
alls[idx++] = x;
adds[i][0] = x;
adds[i][1] = c;
}
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
s = br.readLine().split(" ");
int l = Integer.parseInt(s[0]);
int r = Integer.parseInt(s[1]);
alls[idx++] = l;
alls[idx++] = r;
querys[i][0] = l;
querys[i][1] = r;
}
// alls(0, idx - 1) 排序
Arrays.sort(alls, 0, idx);
// 去重
int end = unique(alls, idx);
// 添加操作
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
// 二分查找找到 x 在 alls 数组中的下标
int t = bsearch(alls, end, adds[i][0]);
a[t] += adds[i][1];
}
// 计算前缀和
for(int i = 1; i <= end; i++){
q[i] = q[i - 1] + a[i];
}
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
int l = bsearch(alls, end, querys[i][0]);
int r = bsearch(alls, end, querys[i][1]);
bw.write(q[r] - q[l - 1] + "\n");
}
bw.close();
br.close();
}
}
用了 List 和 Pairs,效率不高
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main{
static class Pairs{
int first, second;
public Pairs(int first, int second){
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter out = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
String[] s = in.readLine().split(" ");
int n = Integer.parseInt(s[0]);
int m = Integer.parseInt(s[1]);
// 数据范围为 10 的 9 次方,如果直接一个数组来存,空间就会超出限制
// 但是操作数和查询数只有 10 的 5 次方
// 想到用离散化的方式,用 10 的 5 次方的长度表示 10 的 9 次方的量级
// 申请的数组长度 n + m + m + 10 就可以,加个 10 防止边界问题
int N = n + m + m + 10;
// a[] 去重,离散化之后的数组
int[] a = new int[N];
// p[] a的前缀和
int[] p = new int[N];
// adds 记录添加操作
List<Pairs> adds = new ArrayList<>();
// querys 记录查询操作
List<Pairs> querys = new ArrayList<>();
// alls 记录所有在数轴上出现过的坐标
List<Integer> alls = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
s = in.readLine().split(" ");
int x = Integer.parseInt(s[0]);
int c = Integer.parseInt(s[1]);
adds.add(new Pairs(x, c));
alls.add(x);
}
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
s = in.readLine().split(" ");
int l = Integer.parseInt(s[0]);
int r = Integer.parseInt(s[1]);
querys.add(new Pairs(l, r));
alls.add(l);
alls.add(r);
}
// 排序
Collections.sort(alls);
// 去重
int end = unique(alls);
alls = alls.subList(0, end);
// 离散化,就是找到要插入或者查询的数字在 alls 的位置
// 可以用二分查找
// 插入
// 返回值以 1 开始计数
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int index = bsearch(adds.get(i).first, alls);
a[index] += adds.get(i).second;
}
// 计算前缀和
for(int i = 1; i < N; i++){
p[i] = p[i - 1] + a[i];
}
// 开始查询输出
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
int l = bsearch(querys.get(i).first, alls);
int r = bsearch(querys.get(i).second, alls);
int res = p[r] - p[l - 1];
out.write(res + "\n");
out.flush();
}
}
public static int unique(List<Integer> list){
int j = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++){
if(i == 0 || list.get(i) != list.get(i - 1)){
list.set(j, list.get(i));
j++;
}
}
return j;
}
public static int bsearch(int x, List<Integer> list){
int l = 0, r = list.size() - 1;
while(l <= r){
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if(list.get(mid) > x) r = mid - 1;
else if(list.get(mid) < x) l = mid + 1;
else return mid + 1;
}
return 1;
}
}
yxc
- 离散化