文章目录
- Part.I Introduction
- Chap.I 预备知识
- Chap.II 静态库与动态库区分
- Part.II 静态库的生成与使用 (newmat)
- Chap.I 生成静态库
- Chap.II 使用静态库
- Part.III 动态库的生成与使用 (newmat)
- Chap.I 生成动态库
- Chap.II 使用动态库
- Part.IV 文件内容
- Chap.I test.cpp (静态库)
- Chap.II test.cpp (动态库)
- Chap.III 测试文件下载
- Reference
Part.I Introduction
本文将详细地介绍 C++ 动态库和静态库,尽量让读者对他们有一个明晰的区分。然后基于一个实例(newmat 矩阵库)进行实际操作,以加深印象。

Chap.I 预备知识
在阅读下面的内容之前,首先需要了解如下概念和信息:
- 动态链接库(Dynamic Link Library)或叫共享库(Shared Object)(这就是
dll和so文件后缀的由来) - 静态链接库(Static Link Library
有关库的一些文件:
*.h文件:C++ 头文件(文本文件),一般会包含函数的声明。*.lib文件:库文件(二进制文件),它可能是完整的静态库,里面有函数代码本身,在编译时直接将代码加入程序当中,应用程序直接使用;也有可能是动态库的导出声明,只包含头部信息。里面只有函数所在的 DLL 文件和文件中函数位置的入口,代码由运行时加载在进程空间中的 DLL 提供*.dll文件:动态库文件(二进制文件),Windows 下的动态库文件。*.a文件:UNIX 下的静态库文件*.so文件:UNIX 下的动态库文件
Chap.II 静态库与动态库区分
我们写程序的时候会需要加载库,一般需要先include头文件,然后再调用库函数,而库又分为两种,静态库(lib)和动态库(dll),那么这两种库有什么区别呢?
- 静态库:我们的程序在链接时会把用到的静态库全部都链接进去,形成一个
exe,这也导致我们的exe很大(程序是先编译,再链接库,最后形成exe) - 动态库:程序在链接时在不再把整个库都链接进去,而是程序在运行过程中,用到哪个库,再加载哪个库,这就降低了
exe的大小,但同时,运行速度也会变慢。
动态库与静态库优缺点分析:
动态链接库:优点 包括可减少程序的磁盘空间占用、方便更新库文件、共享库文件、提高程序间的互操作性、降低内存占用;缺点 包括需要确保运行环境中库文件的可用性。
静态链接库:优点 包括编译后的可执行文件相对独立、移植性好、提高程序运行速度;缺点 包括每个可执行文件都包含一份静态库的拷贝、需要手动更新库文件。
静态链接库的使用
需要的文件:
*.h:头文件*.h中有函数的声明,使用静态链接库的项目需要引用(#include)文件才能编译通过*.lib:包含了实际执行代码、符号表等等
加载*.lib的方法:
- 用编译链接参数或者 VS 的配置属性来设置
- 使用 pragma 编译语句,例如
pragma comment(lib,"a.lib")
动态链接库的使用——隐式调用
需要的文件
*.h:头文件*.h中有函数的声明,使用静态链接库的项目需要引用(#include)文件才能编译通过*.lib:包含了函数所在的*.dll文件和文件中函数位置的信息。*.dll:包含了实际执行代码、符号表等等
*.lib文件是『链接』时用的,加载方法同样有:
- 用编译链接参数或者 VS 的配置属性来设置
- 使用 pragma 编译语句,例如
pragma comment(lib,"a.lib")
*.dll文件是程序『运行』时用的,链接了lib之后形成的EXE可执行文件中已经有了dll的信息,所以只要把dll放在和exe同一个目录下就可以了,运行时根据 EXE 需要自动加载dll中的函数。
动态链接库的使用——显示调用
需要的文件:只有动态链接库的 *.dll 文件,不需要*.h 文件和*.lib 文件。因为 LoadLibrary 之后可以使用 getProcAddress 来查找一个函数的地址从而调用该函数。
PS: 显式调用的前提是使用者需要知道想调用的函数的名字、参数、返回值信息,也就是说虽然编译链接用不上
.h头文件,但是调用者编程时可能还是要看.h文件作参考来知道函数名字、参数、返回值信息
显式调用动态库步骤
- 创建一个函数指针,其指针数据类型要与调用的
DLL引出函数相吻合。 - 通过 Win32 API 函数
LoadLibrary()显式的调用DLL,此函数返回DLL的实例句柄。 - 通过 Win32 API 函数
GetProcAddress()获取要调用的DLL的函数地址,把结果赋给自定义函数的指针类型。 - 使用函数指针来调用
DLL函数。 - 最后调用完成后,通过 Win32 API 函数
FreeLibrary()释放DLL函数。
下面将使用newmat矩阵库为例,基于 VS Studio 平台,详细介绍生成静态库和动态库的整个过程。newmat 戳我下载~
Part.II 静态库的生成与使用 (newmat)
Chap.I 生成静态库
1、新建一个『静态库』项目,名字取为LibNewmat_a

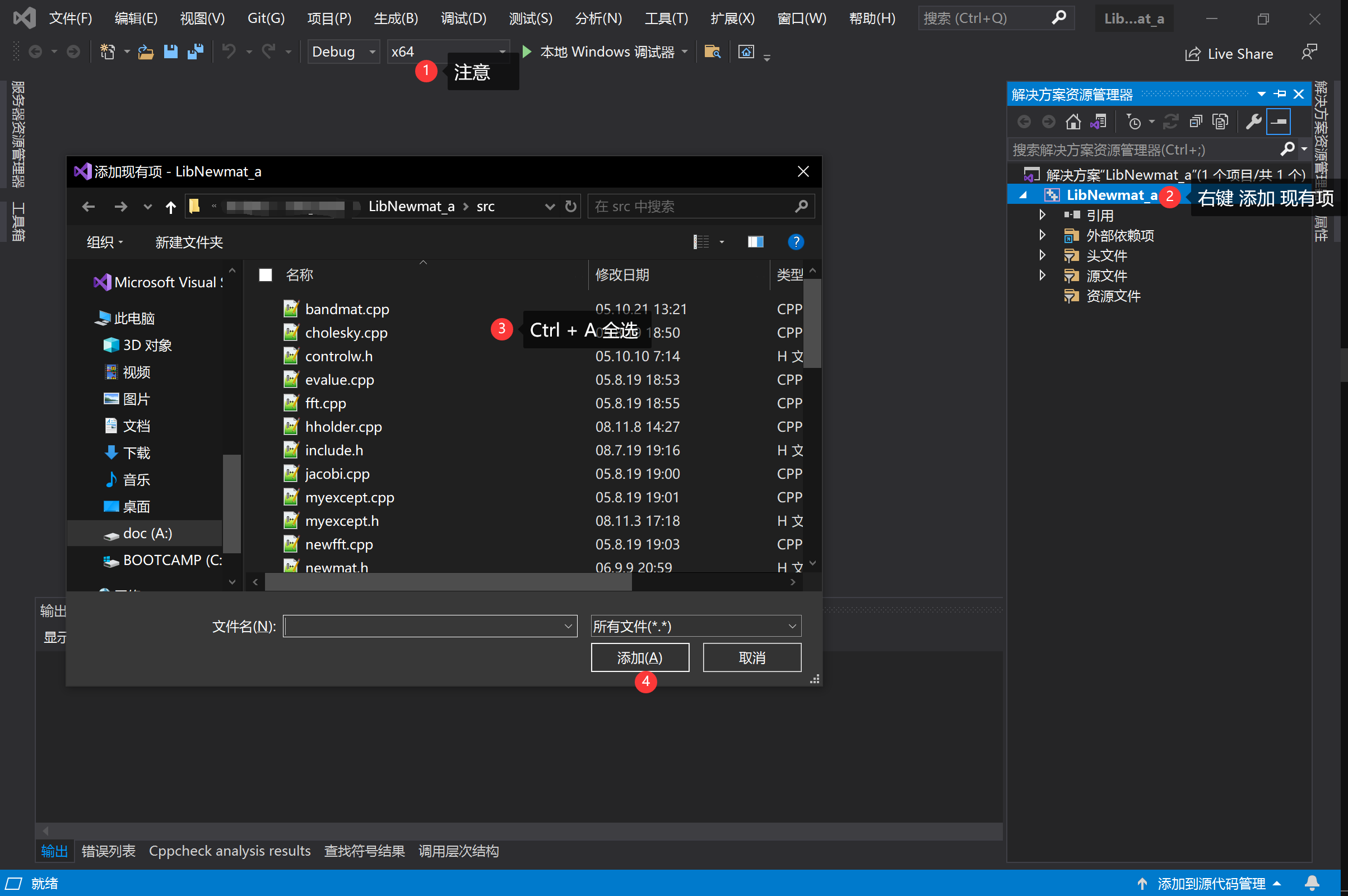
2、将默认创建的4个文件给排除掉,将 newmat 的 36 个文件复制到项目所在目录/src文件夹中。(注意x64)并将它们添加到项目中:右键项目→添加→现有项→进入src→Ctrl+A全选→添加
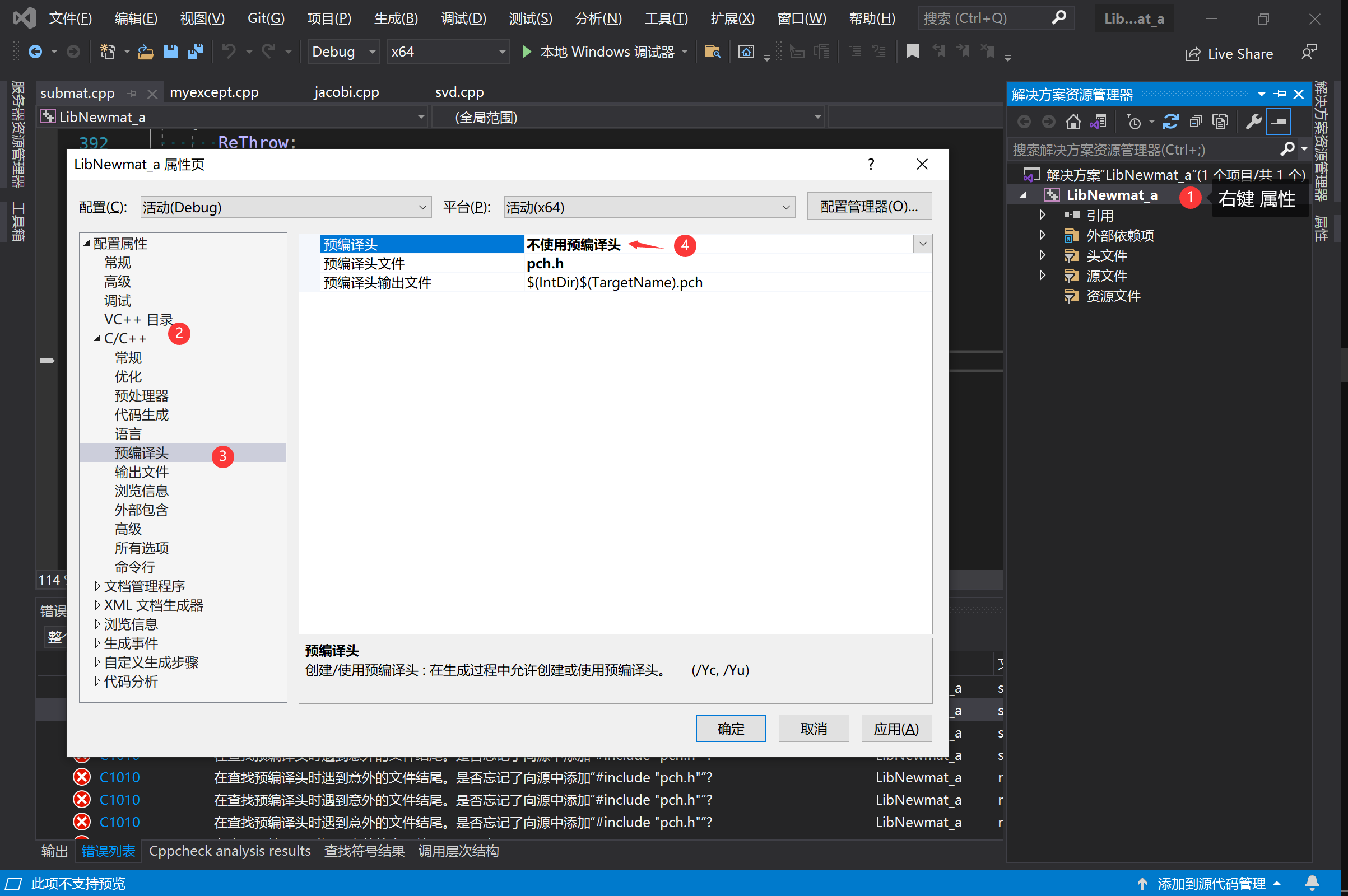
3、选中项目右键→属性→C/C++→预编译头→不使用预编译头→应用→确定
4、选中项目右键→属性→C/C++→预处理器→预处理器定义→下拉三角编辑→加入_CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS(这是针对newmat)进行的操作
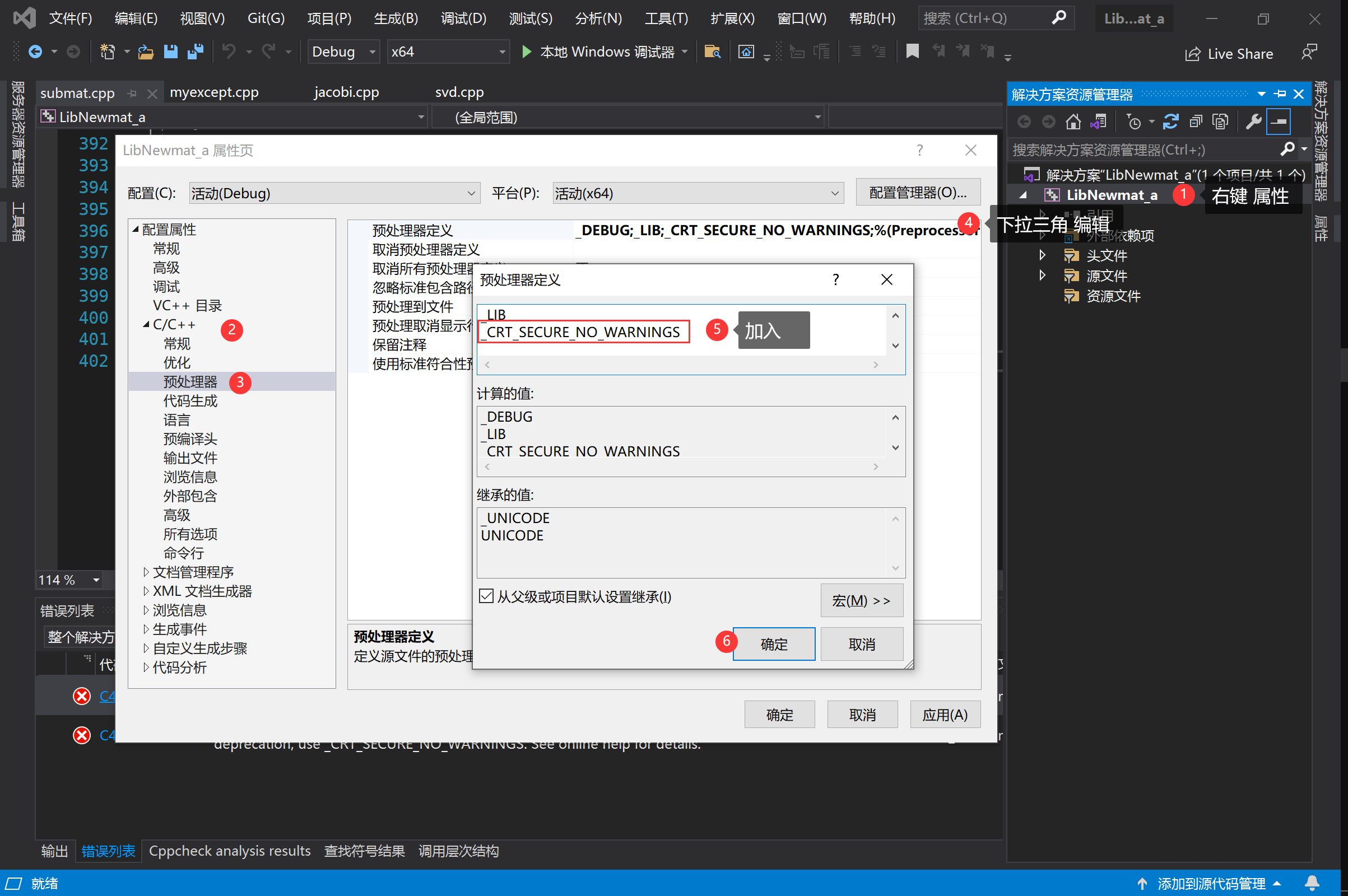
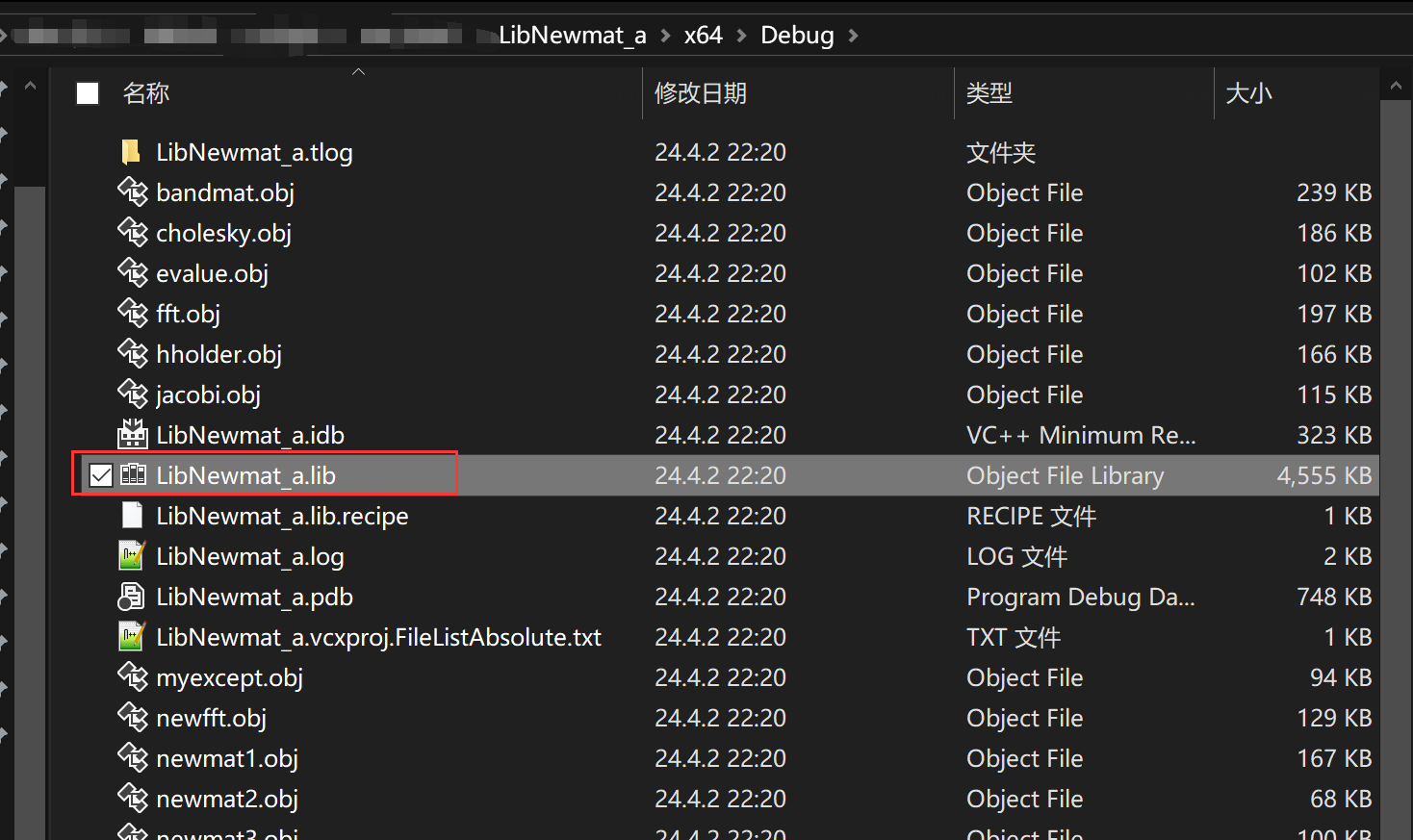
5、快捷键 F6 生成,在x64/Debug目录下就生成了我们需要的*.lib
Chap.II 使用静态库
1、创建一个空项目,名字叫做test_a,添加一个cpp文件test.cpp。
2、选中项目右键→属性→VC++ 目录→包含目录 把头文件所在目录贴进去;库目录把*.lib所在目录贴进去(看完下面的再决定要不要这样操作)
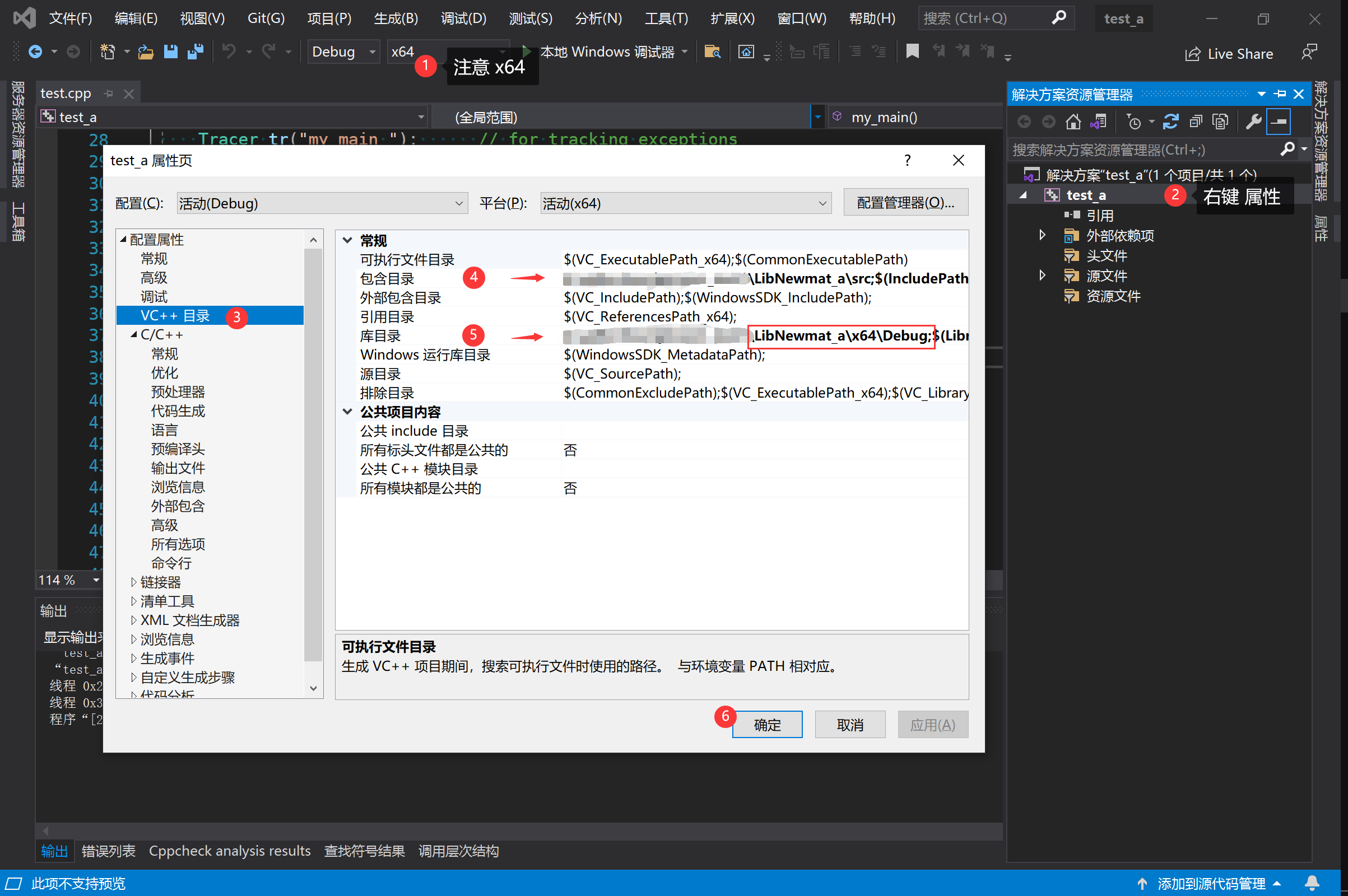
PS:最好不要在这里加包含目录和库目录,这里时全局的(我是为了截一个图,懒狗一个)。下面是比较合适的操作:
包含目录(头文件所在目录):右键『属性』→『C/C++』→『常规』→『附加包含目录』
库目录(lib 文件所在目录):右键『属性』→『链接器』→『常规』→『附加库目录』
3、将Part.IV__Chap.I test.cpp的内容复制到文件test.cpp中
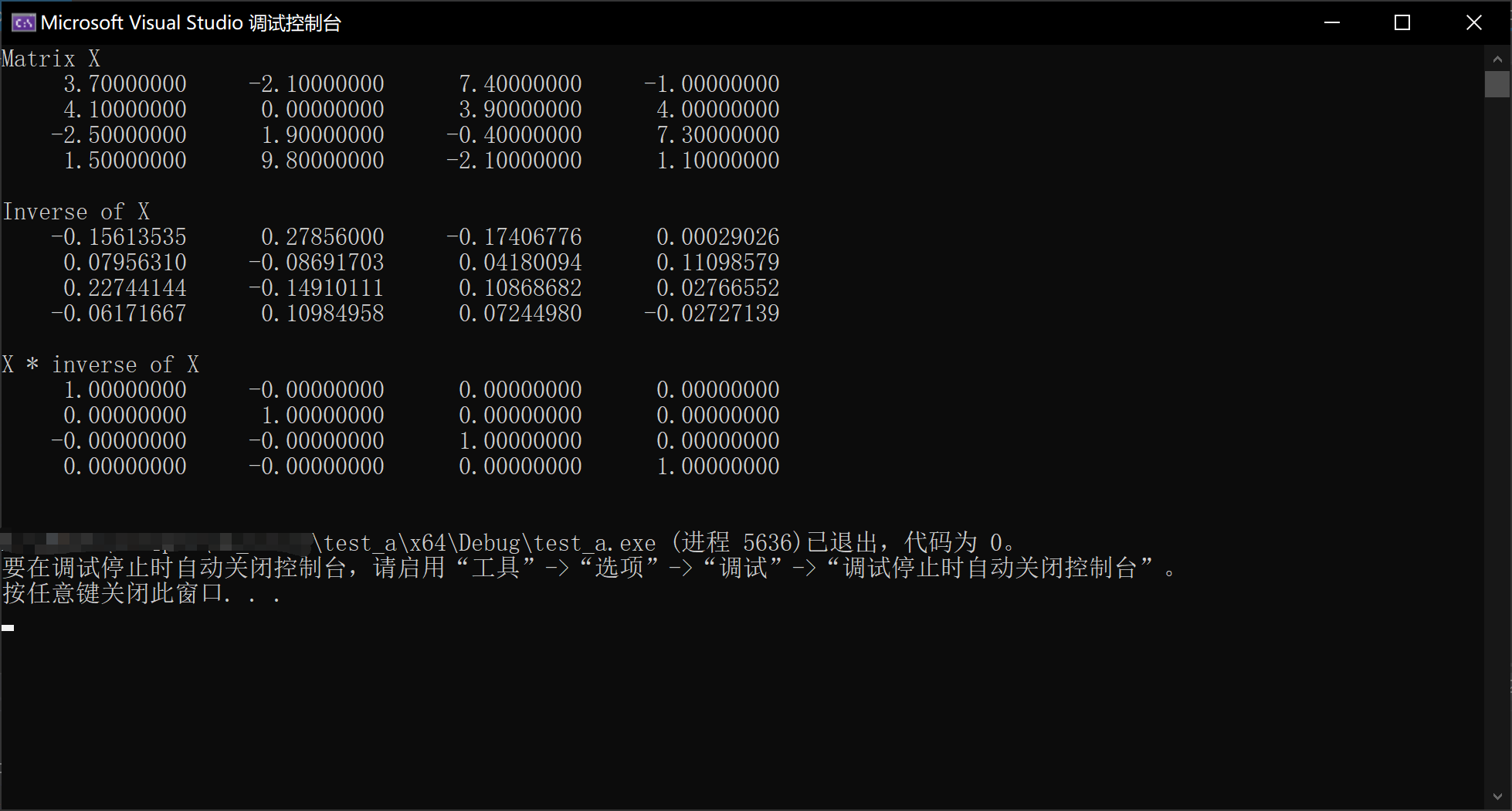
4、快捷键F5得到运行结果
Part.III 动态库的生成与使用 (newmat)
Chap.I 生成动态库
1、新建一个『动态库』项目,名字取为LibNewmat_so
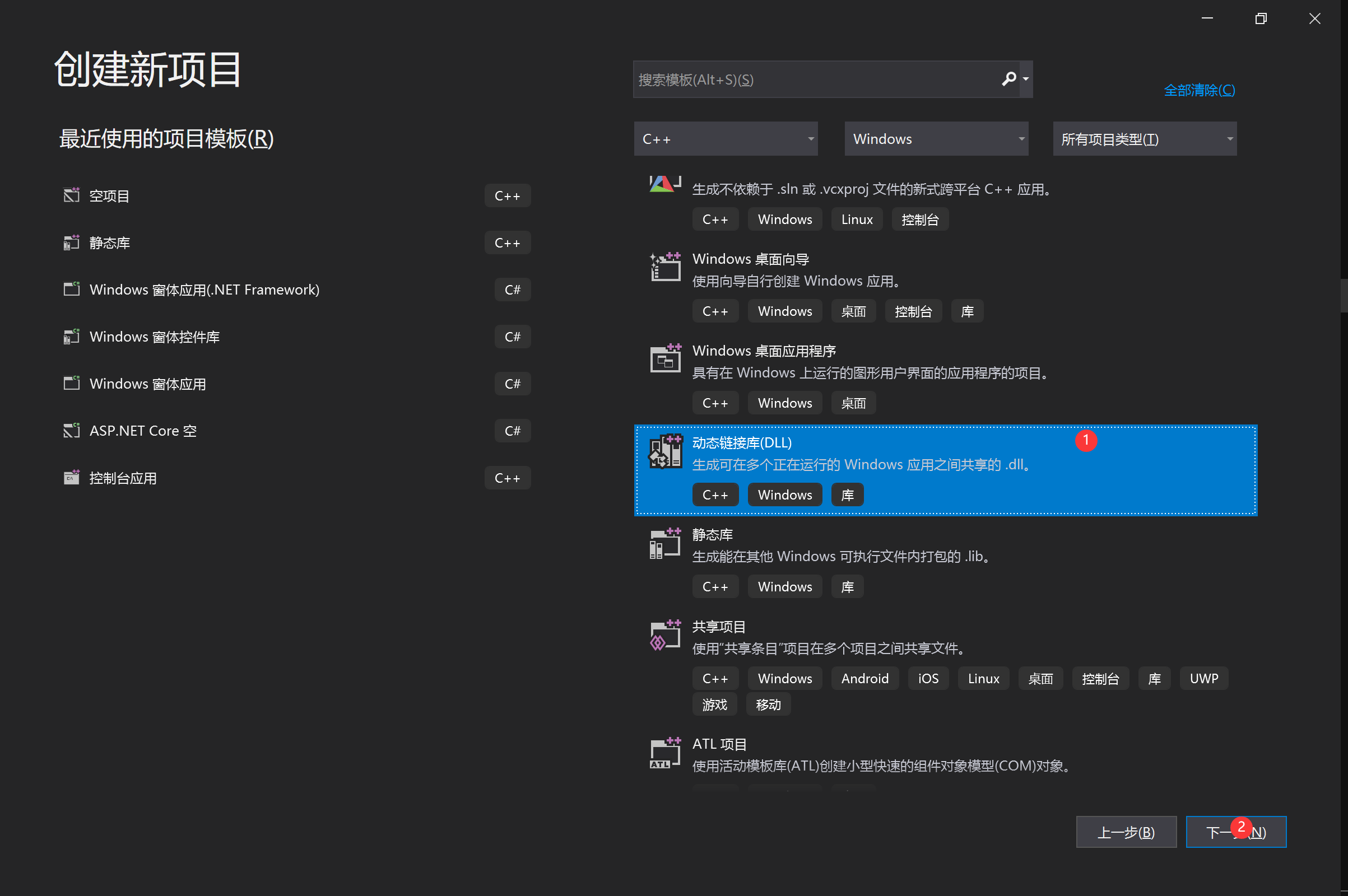
2、将默认创建的4个文件给排除掉,将 newmat 的 36 个文件复制到项目所在目录/src文件夹中。(注意x64)并将它们添加到项目中:右键项目→添加→现有项→进入src→Ctrl+A全选→添加
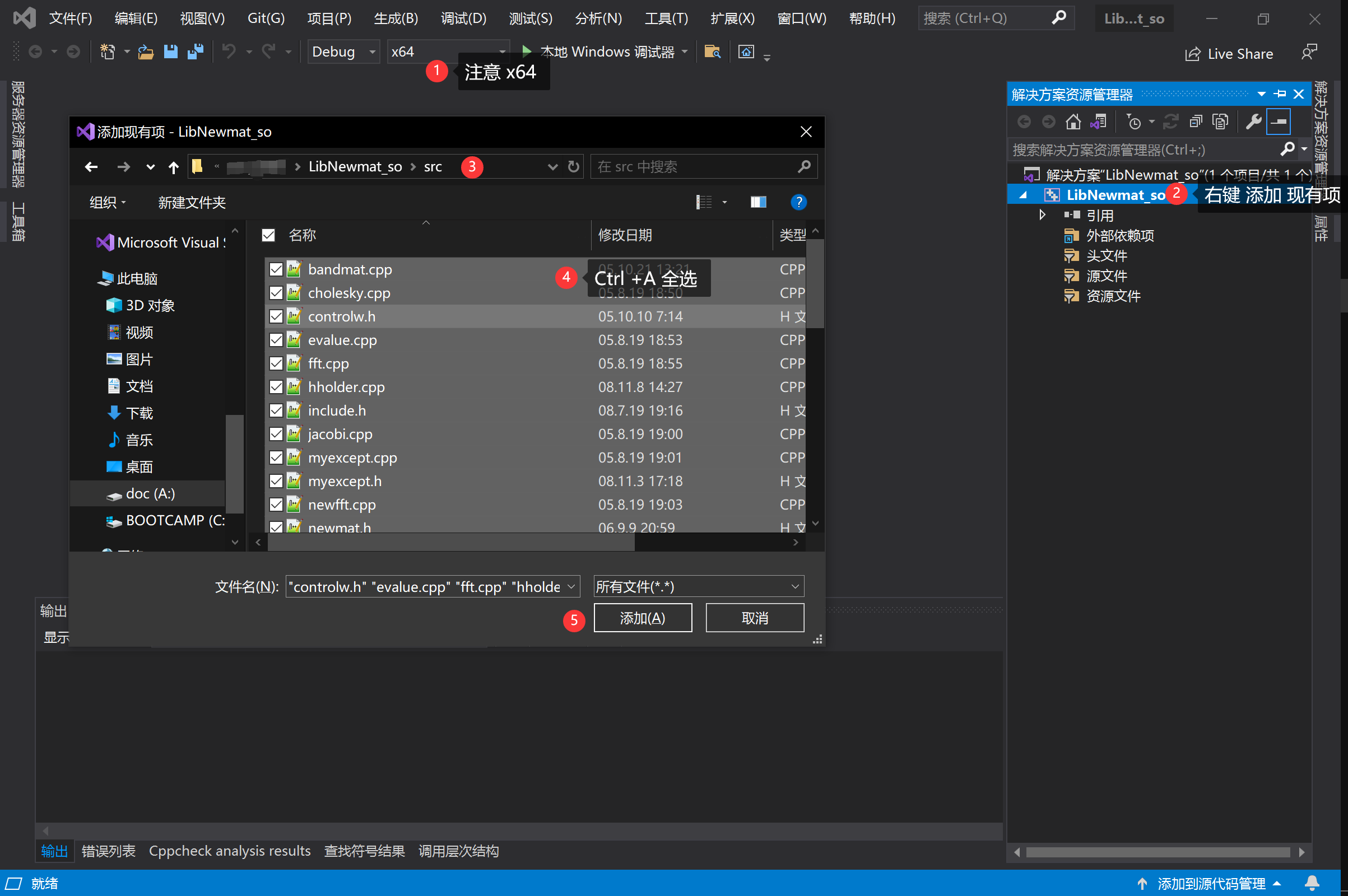
3、选中项目右键→属性→C/C++→预编译头→不使用预编译头→应用→确定
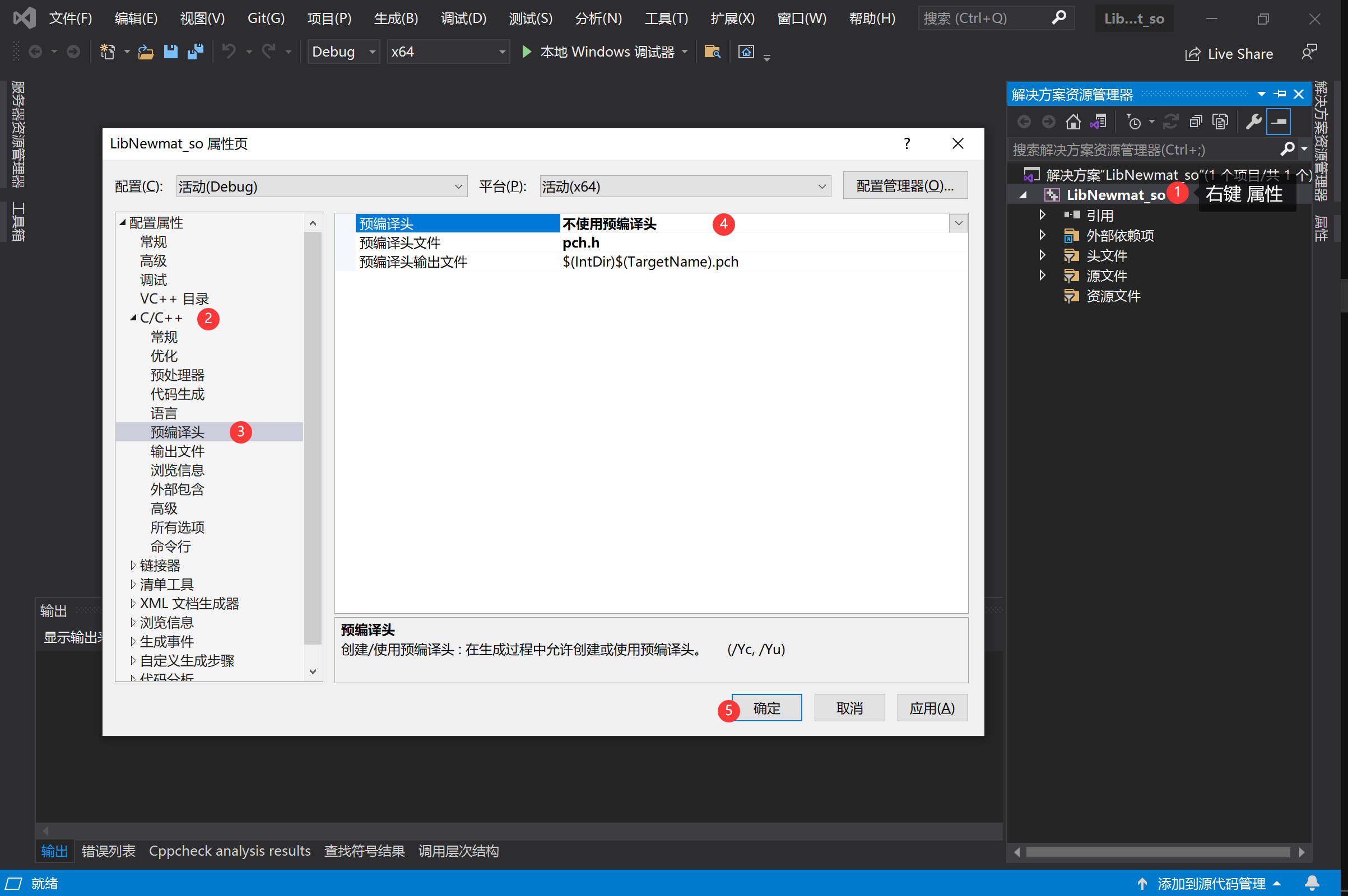
4、选中项目右键→属性→C/C++→预处理器→预处理器定义→下拉三角编辑→加入_CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS(这是针对newmat)进行的操作
5、快捷键 F6 生成,在x64/Debug目录下就生成了我们需要的*.dll
Chap.II 使用动态库
基于上面的操作我们可以看到:只生成了
dll文件,没有生成lib文件,这是因为newmat库本身没有导出 (__declspec(dllexport)) 任何方法、类等,所以生成的 DL L不需要lib文件来记载导出符号。那这种情况下只能显示调用了,如何操作呢?浅试了一下,不会比较复杂的显式调用,暂时放弃。所以本小节后面的部分不必看了
1、创建一个空项目,名字叫做test_so,添加一个cpp文件test.cpp。(注意x64)
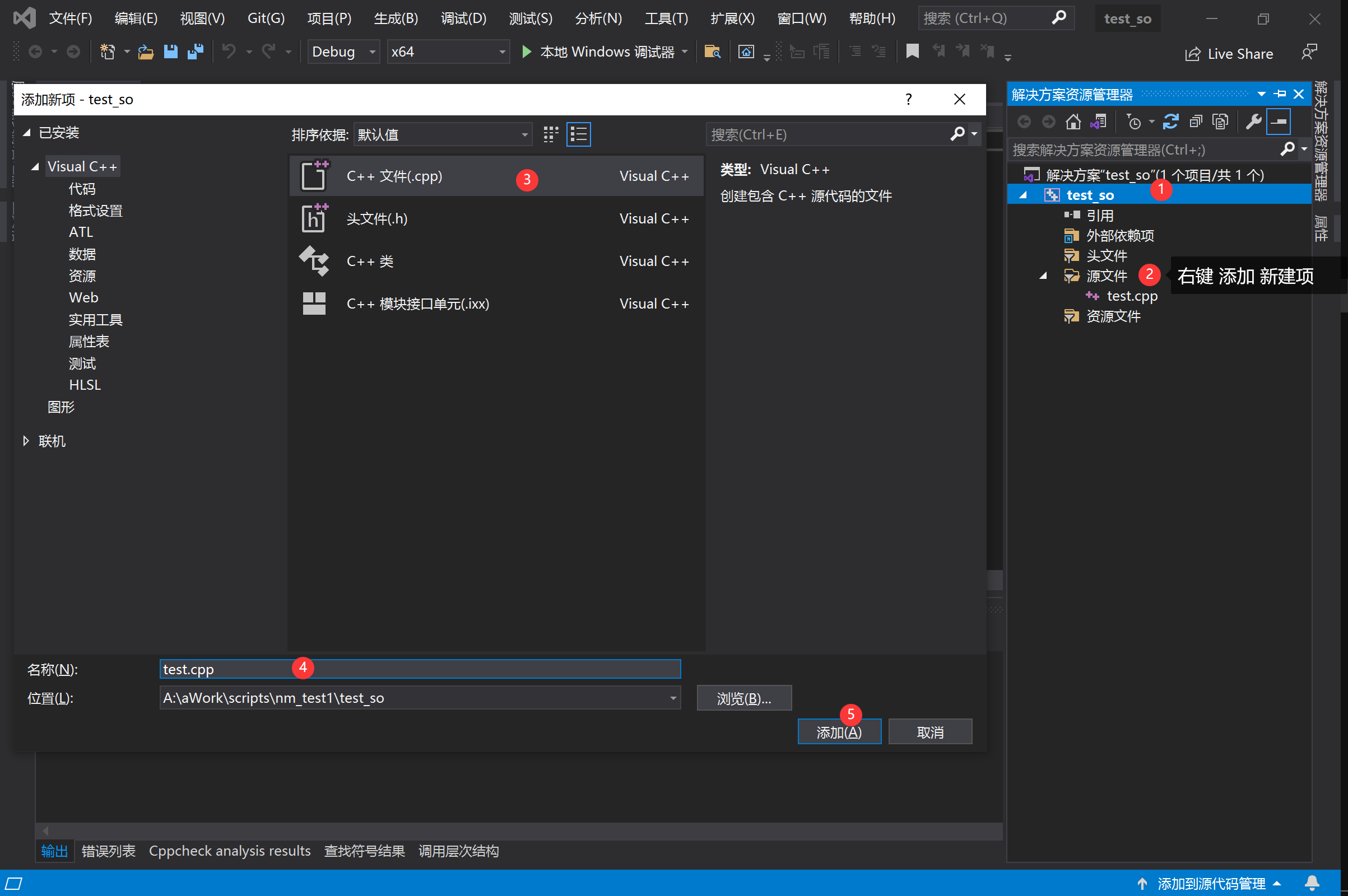
2、将Part.IV__Chap.II test.cpp的内容复制到文件test.cpp中
如何使用 dll 中的类型呢?求大佬指点!!
Part.IV 文件内容
Chap.I test.cpp (静态库)
/// \ingroup newmat
///@{
/// \file nm_ex1.cpp
/// Very simple example 1.
/// Invert a 4 x 4 matrix then check the result
#define WANT_STREAM // include iostream and iomanipulators
#include "newmatap.h" // newmat advanced functions
// should not be required for this example
// included because it seems to help MS VC6
// when you have namespace turned on
#include "newmatio.h" // newmat headers including output functions
#pragma comment(lib,"LibNewmat_a.lib")
#ifdef use_namespace
using namespace RBD_LIBRARIES;
#endif
int my_main() // called by main()
{
Tracer tr("my_main "); // for tracking exceptions
// declare a matrix
Matrix X(4, 4);
// load values row by row
X.row(1) << 3.7 << -2.1 << 7.4 << -1.0;
X.row(2) << 4.1 << 0.0 << 3.9 << 4.0;
X.row(3) << -2.5 << 1.9 << -0.4 << 7.3;
X.row(4) << 1.5 << 9.8 << -2.1 << 1.1;
// print the matrix
cout << "Matrix X" << endl;
cout << setw(15) << setprecision(8) << X << endl;
// calculate its inverse and print it
Matrix Y = X.i();
cout << "Inverse of X" << endl;
cout << setw(15) << setprecision(8) << Y << endl;
// multiply X by its inverse and print the result (should be near identity)
cout << "X * inverse of X" << endl;
cout << setw(15) << setprecision(8) << (X * Y) << endl;
return 0;
}
// call my_main() - use this to catch exceptions
// use macros for exception names for compatibility with simulated exceptions
int main()
{
Try{ return my_main(); }
Catch(BaseException) { cout << BaseException::what() << "\n"; }
CatchAll{ cout << "\nProgram fails - exception generated\n\n"; }
return 0;
}
///@}
Chap.II test.cpp (动态库)
半成品没有跑通
/// \ingroup newmat
///@{
/// \file nm_ex1.cpp
/// Very simple example 1.
/// Invert a 4 x 4 matrix then check the result
#define WANT_STREAM // include iostream and iomanipulators
#include <iostream>
#include <windows.h>
//#include "newmatap.h" // newmat advanced functions
// // should not be required for this example
// // included because it seems to help MS VC6
// // when you have namespace turned on
//
//#include "newmatio.h" // newmat headers including output functions
#ifdef use_namespace
using namespace RBD_LIBRARIES;
#endif
int my_main() // called by main()
{
HINSTANCE hInst = LoadLibrary(L"LibNewmat_so.dll"); //加载dll库
typedef void(*Sub)();//函数指针
Sub PrintHello = (Sub)GetProcAddress(hInst, "PrintHello");//加载库函数
Tracer tr("my_main "); // for tracking exceptions
// declare a matrix
Matrix X(4, 4);
// load values row by row
X.row(1) << 3.7 << -2.1 << 7.4 << -1.0;
X.row(2) << 4.1 << 0.0 << 3.9 << 4.0;
X.row(3) << -2.5 << 1.9 << -0.4 << 7.3;
X.row(4) << 1.5 << 9.8 << -2.1 << 1.1;
// print the matrix
cout << "Matrix X" << endl;
cout << setw(15) << setprecision(8) << X << endl;
// calculate its inverse and print it
Matrix Y = X.i();
cout << "Inverse of X" << endl;
cout << setw(15) << setprecision(8) << Y << endl;
// multiply X by its inverse and print the result (should be near identity)
cout << "X * inverse of X" << endl;
cout << setw(15) << setprecision(8) << (X * Y) << endl;
FreeLibrary(hInst); //释放库
return 0;
}
// call my_main() - use this to catch exceptions
// use macros for exception names for compatibility with simulated exceptions
int main()
{
Try{ return my_main(); }
Catch(BaseException) { cout << BaseException::what() << "\n"; }
CatchAll{ cout << "\nProgram fails - exception generated\n\n"; }
return 0;
}
///@}
Chap.III 测试文件下载
有关上面的测试文件,笔者进行了整理并上传至 CSDN 资源,感兴趣的朋友可戳我免费下载。文件树如下:
newmat_lib_dll
├─DLL_project
│ ├─LibNewmat_so // 生成的动态库 dll
│ └─test_so // 测试动态库 cpp 文件,半成品
├─LIB_project
│ ├─LibNewmat_a // 生成的静态库 lib
│ └─test_a // 测试静态库 cpp 文件
└─newmat_src // newmat 库源码
Reference
- C++ 静态库和动态库的创建和使用及区别
- 动态链接库和静态链接库的区别