栈和队列报错调试
1.用栈实现队列
232. 用栈实现队列 - 力扣(LeetCode)
此题解题思路如下:
先将数据放在pushst栈里面,popst栈为空再把pushst栈里面的数据放进popst栈里面去,不为空则不执行。不为空时候直接拿取栈顶数据。
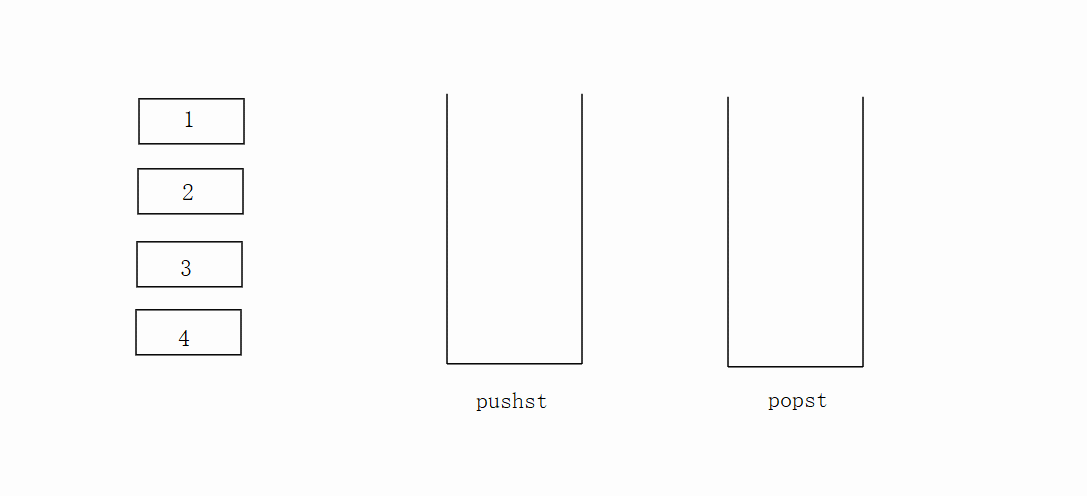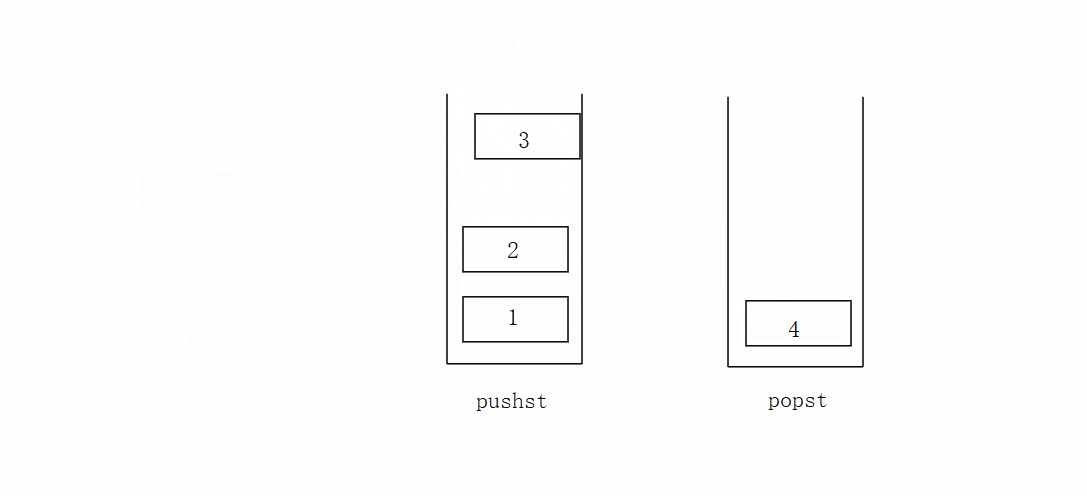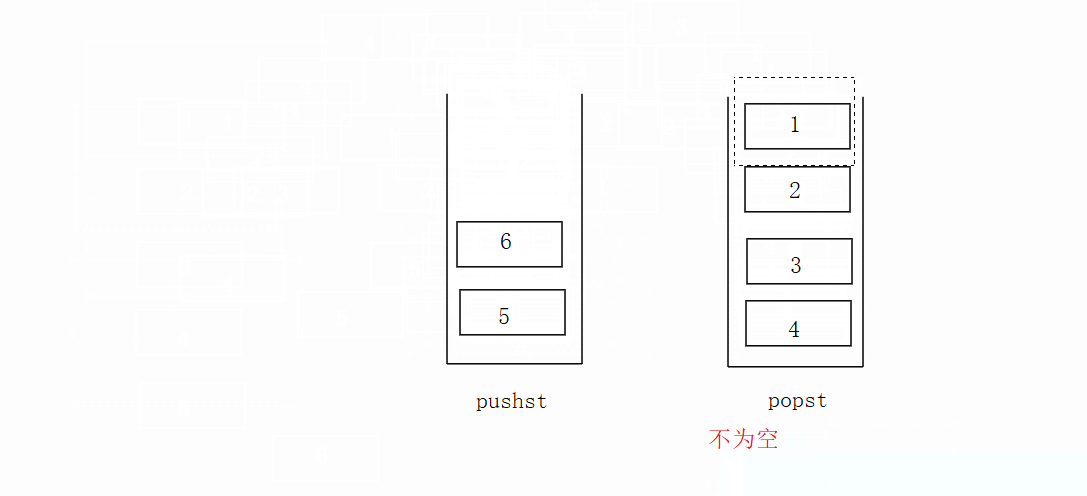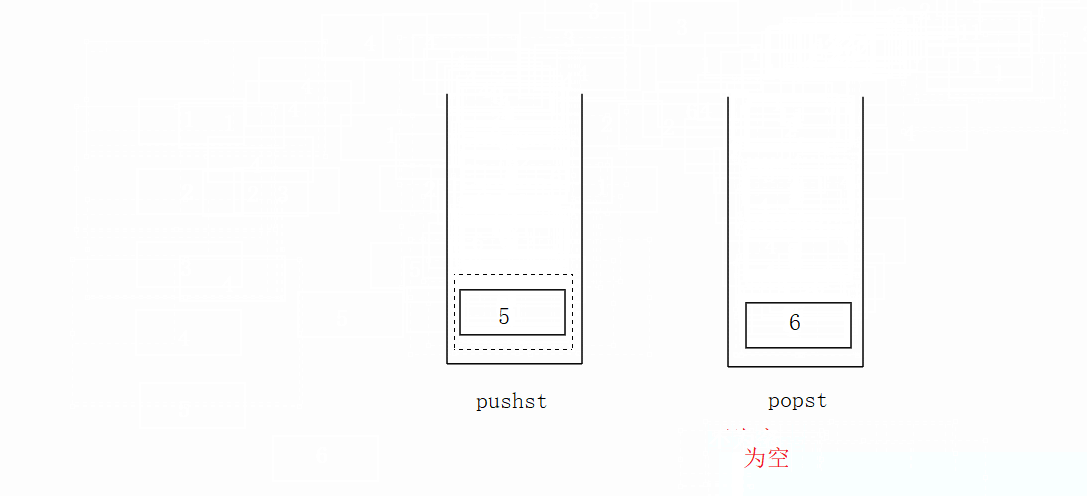
代码如下:
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;
void STInit(ST* pst);
void STDestroy(ST* pst);
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x);
void STPop(ST* pst);
STDataType STTop(ST* pst);//拿取栈顶数据
bool STEmpty(ST* pst);
int STSize(ST* pst);
void STInit(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->capacity = 0;
//表示top指向栈顶元素的下一个位置
pst->top = 0;
}
void STDestroy(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
free(pst->a);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->capacity = pst->top = 0;
}
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x)
{
assert(pst);
if (pst->top == pst->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newcapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
pst->a = tmp;
pst->capacity = newcapacity;
}
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
pst->top++;
}
void STPop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst->top >0);
pst->top--;
}
STDataType STTop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst->top > 0);
return pst->a[pst->top-1];
}
bool STEmpty(ST* pst)//判断真假
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top == 0;
}
int STSize(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top;
}
typedef struct
{
ST pushst;
ST popst;
} MyQueue;
MyQueue* myQueueCreate()
{
MyQueue* obj=(MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
STInit(&obj->pushst);
STInit(&obj->popst);
return obj;
}
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x)
{
STPush(&obj->pushst, x);
}
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj)
{
int tmp=myQueuePeek(&obj->popst);
STPop(&obj->popst);
return tmp;
}
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj)
{
if(STEmpty(&obj->popst))
{
while(!STEmpty(&obj->pushst))
{
STPush(&obj->popst, STTop(&obj->pushst));
STPop(&obj->pushst);
}
}
return STTop(&obj->popst);
}
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj)
{
return STEmpty(&obj->pushst)&&STEmpty(&obj->popst);
}
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj)
{
STDestroy(&obj->popst);
STDestroy(&obj->pushst);
free(obj);
obj =NULL;
}
/**
* Your MyQueue struct will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue* obj = myQueueCreate();
* myQueuePush(obj, x);
* int param_2 = myQueuePop(obj);
* int param_3 = myQueuePeek(obj);
* bool param_4 = myQueueEmpty(obj);
* myQueueFree(obj);
*/
报错1如下:
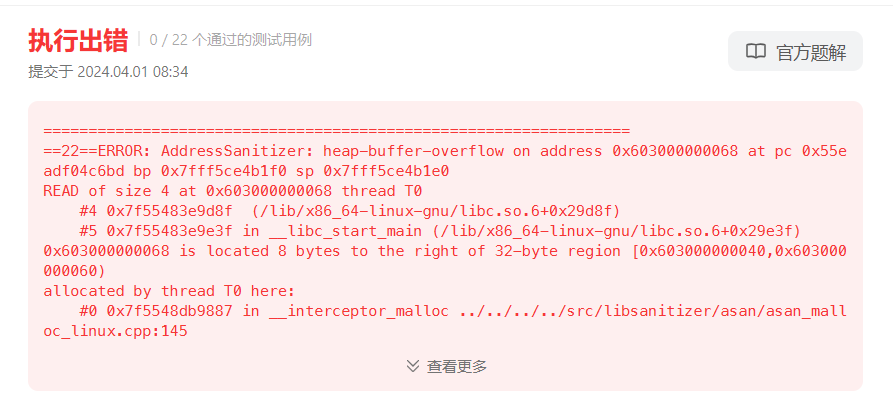
错误原因分析:
编译出错是运行问题,执行出错是代码逻辑问题,没有报结果大概率是头部出错。以此为基础推导出错原因,思路如下:
将上面代码拷贝至VS调试按照力扣所提供的测试样例进行传参,这道题我是使用栈实现代码进行解题,所以直接使用之前的实现代码进行调试,如果不知道栈的实现方法请观看这篇文章:
我们观察力扣所提供的测试样例:
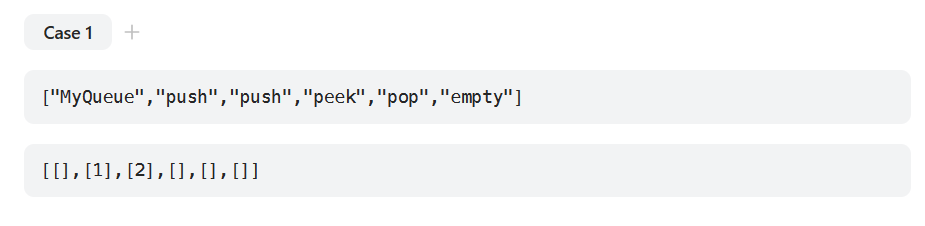
我们先看力扣对这几个函数的传参设置:

函数"MyQueue"无传参值设置只需要一个返回值接受它,所以无需传参。调用两次"push"函数传结构体指针然后分别给x传1,2。剩下的"peek",“pop”,"empty"只需要传结构体指针。
但一般调试无需调用这么多函数,我调用了两个函数进行调试,调用如下:
int main()
{
MyQueue* obj = myQueueCreate();
myQueuePush(&obj, 1);
return 0;
}
运行时候realloc函数会报错,出现内存不足的问题:
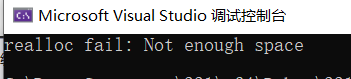
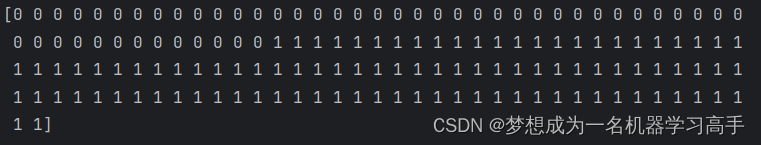
首先排除栈实现代码问题,因为实现时候调试过,没有报错,我们将问题范围缩小在实现队列部分,而初始化问题我前面已经解决了,那么排除初始化问题。因为是开辟空间报错,我们监视栈的结构体值变化,如图所示发现运行STPush函数的时候,栈的结构体里面的指针会变成野指针:
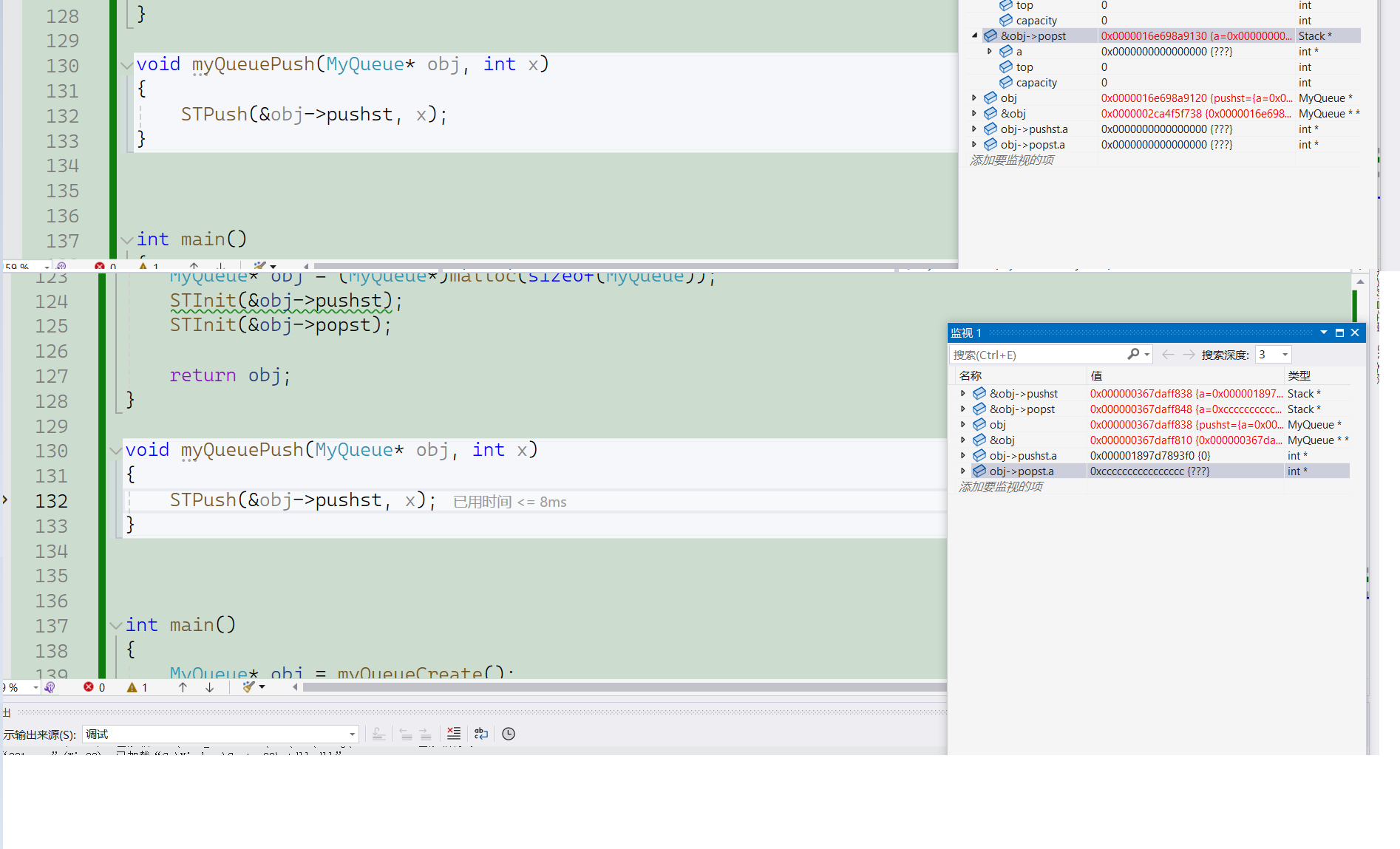
我们查看所有调用STPush的函数:

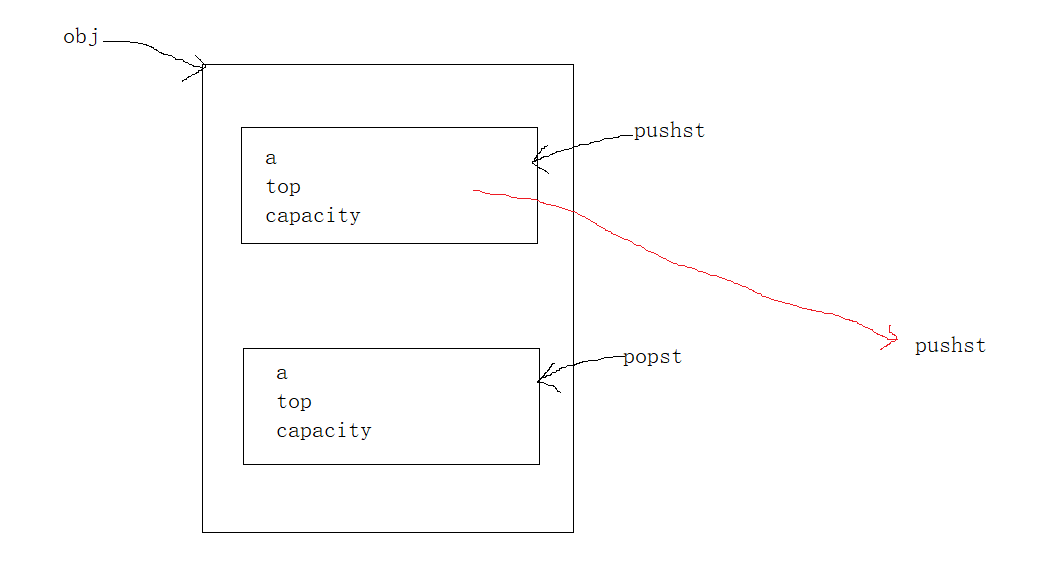
按思路走读一下代码,发现myQueuePop函数调用myQueuePeek函数时候我们想传的是出栈函数的地址给myQueuePeek函数进行调用,myQueuePeek函数调用STPush的函数我们想传的是出栈函数的地址给STPush函数进行调用,我们将此代码的思路图画出来,发现obj访问pushst结构体后再访问里面的pushst结构体,所以是传参错误,因为myQueuePeek函数里面已经传pushst的地址给STPush函数了,所以myQueuePop函数调用myQueuePeek函数只需要传obj指针调用即可。
报错2如下:
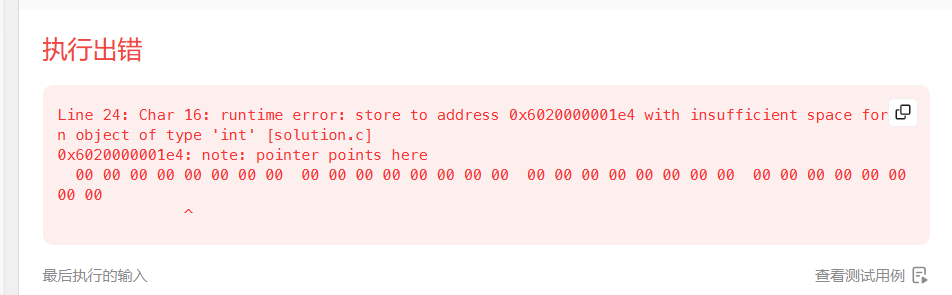
实现代码如下:
typedef struct
{
ST* pushst;
ST* popst;
} MyQueue;
MyQueue* myQueueCreate()
{
MyQueue* obj=(MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
STInit(&obj->pushst);
STInit(&obj->popst);
return obj;
}
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x)
{
STPush(&obj->pushst, x);
}
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj)
{
int tmp=myQueuePeek(obj);
STPop(&obj->popst);
return tmp;
}
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj)
{
if(STEmpty(&obj->popst))
{
while(!STEmpty(&obj->pushst))
{
STPush(&obj->popst, STTop(&obj->pushst));
STPop(&obj->pushst);
}
}
return STTop(&obj->popst);
}
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj)
{
return STEmpty(&obj->pushst)&&STEmpty(&obj->popst);
}
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj)
{
STDestroy(&obj->popst);
STDestroy(&obj->pushst);
free(obj);
obj =NULL;
}
我们观察这段代码:

malloc函数开辟出来的指针只为MyQueue结构体开辟空间。但是MyQueue结构体里存放了两个结构体指针,不初始化就为空指针,初始化了为空指针,在栈实现的代码中assert(pst)会报错。不初始化会出现野指针访问报错,如果要写两个指针,需要再为这两个指针开辟空间。
STDestroy(&obj->popst);
STDestroy(&obj->pushst);
free(obj);
obj =NULL;
}
我们观察这段代码:
[外链图片转存中...(img-RbuGxtYJ-1712389444934)]
malloc函数开辟出来的指针只为MyQueue结构体开辟空间。但是MyQueue结构体里存放了两个结构体指针,不初始化就为空指针,初始化了为空指针,在栈实现的代码中assert(pst)会报错。不初始化会出现野指针访问报错,如果要写两个指针,需要再为这两个指针开辟空间。