一、注意事项
- explicit
c++中,一个参数的构造函数(或者除了第一个参数外其余参数都有默认值的多参构造函数),承担了两个角色,构造器、类型转换操作符,
c++提供关键字explicit,阻止转换构造函数进行的隐式转换的发生,声明explicit的构造函数不能在隐式转换中使用。 - c++ 函数前面和后面 使用const 的作用
前面使用const 表示返回值为const;
后面加 const表示函数不可以修改class的成员;
const成员函数可以被非const对象和const对象调用;
非const成员函数只能被非const对象调用; - 类外补充函数的定义要加作用域限定符::
二、重要知识:cmake
在QT中选择cmake方式构建c++项目,最好提前了解cmake相关知识,以方便理解如何导入外部库,推荐学习视频链接:B站:爱编程的大丙
重要细节:静态库的链接要放在add_executable之前
三、c++代码调用python步骤
- 设置python配置
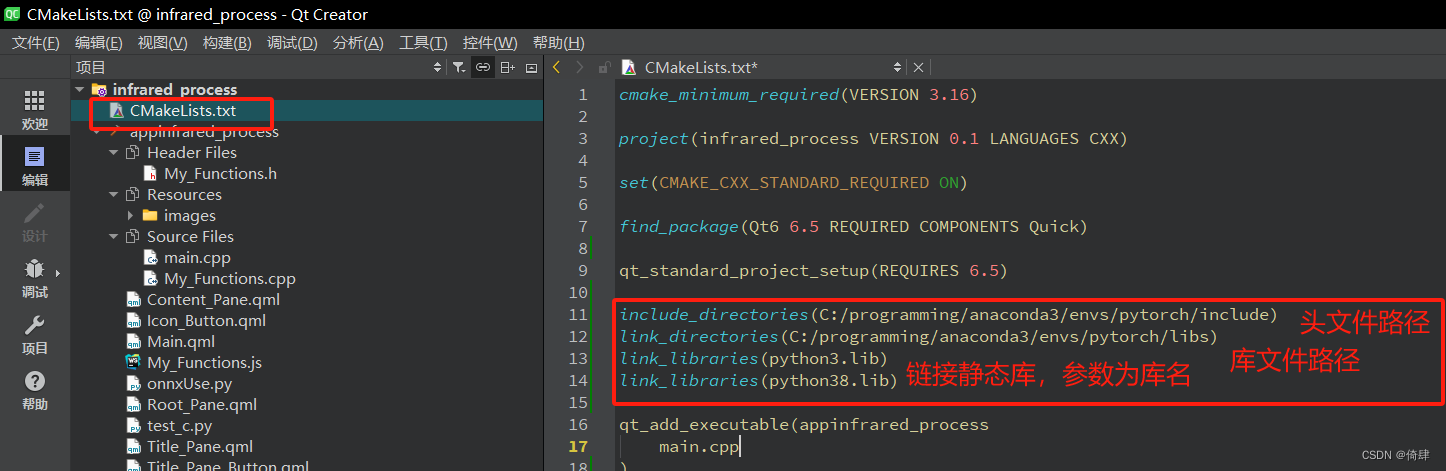
CMakeList.txt文件中输入python文件的相关信息:头文件夹路径、库文件夹路径、需要连接的库文件名称(有没有.lib后缀都可)
include_directories(C:/programming/anaconda3/envs/pytorch/include)
link_directories(C:/programming/anaconda3/envs/pytorch/libs)
link_libraries(python3)
link_libraries(python38)
2. c++代码(.cpp)中调用python(注:下面代码中功函数invokePython的调用只可执行一次,再次调用程序会崩溃)
#include "My_Functions.h"
#include <QDir>
#include <Python.h>
My_Functions::My_Functions(QObject *parent) : QObject(parent){}
My_Functions:: ~My_Functions(){}
bool My_Functions :: invokePython(){
QDir dir;
const char* pythonFilePath = (dir.currentPath().append("/").append(dir.currentPath().split("/").last().split("-")[1])).toUtf8();
Py_SetPythonHome(L"C:/programming/anaconda3/envs/pytorch");
//调用前必须初始化python解释器
Py_Initialize();
if(!Py_IsInitialized()){qDebug()<<"初始化失败"; return 0;}
// 将路径转换为Python对象
PyObject *py_path_str = PyUnicode_FromWideChar(Py_DecodeLocale(pythonFilePath, NULL), -1);
// 加载 python 脚本
// 获取sys模块以进行项目.py文件的搜索
PyObject *sys_module = PyImport_ImportModule("sys");
// 获取sys.path
PyObject *sys_path = PyObject_GetAttrString(sys_module, "path");
if (!PyList_Check(sys_path)) {
// sys.path不是列表,错误处理
qDebug()<<"获取py搜索路径失败" ;
// 释放python所用内存
Py_Finalize();
return 0;
} else {
// 将自定义路径添加到sys.path
int appended = PyList_Append(sys_path, py_path_str);
if (appended == -1) {
// 错误处理
qDebug()<<"添加py搜索路径失败" ;
// 释放python所用内存
Py_Finalize();
return 0;
}
}
PyObject *pModule = PyImport_ImportModule("onnxUse");
if (pModule == NULL) {
// 模块导入失败,处理错误
qDebug() << "脚本加载失败";
// 释放python所用内存
Py_Finalize();
return 0;
} else {
qDebug() << "脚本加载成功";
}
// 创建函数指针
PyObject* pFunc = PyObject_GetAttrString(pModule, "detect_images"); // 方法名称
if (pFunc == NULL) {
// 函数导入失败,处理错误
qDebug() << "函数创建失败";
// 释放python所用内存
Py_Finalize();
return 0;
}else {
qDebug() << "函数创建成功";
}
// 调用有参函数
// 创建函数参数
// s 将C字符串转换成Python对象,如果C字符串为空,返回NONE
// z: 类似于 s,但允许转换为 NULL(Python 的 None)
// c 将C类型的char转换成长度为1的Python字符串对象
// b: C unsigned char,将布尔值转换为 0 或 1
// i 将一个C类型的int转换成Python int对象
// k: C unsigned long,转换为无符号长整数
// l 将C类型的long转换成Pyhon中的int对象
// f 将C类型的float转换成python中的浮点型对象
// d 将C类型的double转换成python中的浮点型对象
// O 通用对象引用,接收任意 Python 对象而不转换
// O!: 类型对象和转换标志,用于接收特定类型的 Python 对象
// O&: 自定义回调函数,用于自定义对象转换
// (ii):两个 C 整型变量构成的元组或列表
// [ii]:两个 C 整型变量构成的列表
// {ss}:键值对都是 C 字符串的字典
// #:s, #i, #d 等:带有长度指示的字符串、整数或浮点数
// n: 接收 None,检查参数是否为 None
// PyObject* args = Py_BuildValue("(i,s)", 110, "hello"); // 参数为整数 110 和字符串 "hello"
// PyObject *result = PyObject_CallObject(pFunc, args);
// 调用无参函数
PyObject *result = PyObject_CallObject(pFunc, NULL);
// 检查并处理有参函数调用的返回结果
if (result == NULL) {
// 处理错误
qDebug() << "函数调用失败";
// 释放python所用内存
Py_Finalize();
return 0;
} else {
// 使用返回值
qDebug() << "函数调用成功";
// const char *result_str;
// if (!PyArg_Parse(result, "s", &result_str)) {
// // 错误处理:无法将Python对象转换为字符串
// qDebug() << "函数返回值处理失败";
// // 释放python所用内存
// Py_Finalize();
// return 0;
// } else {
// // 使用result_str
// }
}
// 释放引用计数
Py_DECREF(result);
// // 释放参数元组
// Py_DECREF(args);
// 释放函数指针
Py_DECREF(pFunc);
// 不再需要模块时,减少引用计数
Py_DECREF(pModule);
// 释放python所用内存
Py_Finalize();
qDebug()<<"调用完成";
return false;
}
- 局部多次调用python脚本
改造 invokePython 函数
bool My_Functions :: invokePython(){
PyGILState_STATE gil_state; // 用以保存获取的Global Interpreter Lock (GIL)
gil_state = PyGILState_Ensure(); // 获取GIL,只有拥有GIL的线程才可以执行python代码
PyObject *pModule = PyImport_ImportModule("onnxUse");
if (pModule == NULL) {
// 模块导入失败,处理错误
qDebug() << "脚本加载失败";
return 0;
} else {
qDebug() << "脚本加载成功";
}
// 创建函数指针
PyObject* pFunc = PyObject_GetAttrString(pModule, "detect_images"); // 方法名称
if (pFunc == NULL) {
// 函数导入失败,处理错误
qDebug() << "函数创建失败";
PyErr_Print();
return 0;
}else {
qDebug() << "函数创建成功";
}
// 调用无参函数
PyObject *result = PyObject_CallObject(pFunc, NULL);
// 检查并处理有参函数调用的返回结果
if (result == NULL) {
// 处理错误
qDebug() << "函数调用失败";
return 0;
} else {
// 使用返回值
qDebug() << "函数调用成功";
// const char *result_str;
// if (!PyArg_Parse(result, "s", &result_str)) {
// // 错误处理:无法将Python对象转换为字符串
// qDebug() << "函数返回值处理失败";
// // 释放python所用内存
// Py_Finalize();
// return 0;
// } else {
// // 使用result_str
// }
}
// 释放引用计数
Py_DECREF(result);
// // 释放参数元组
// Py_DECREF(args);
// 释放函数指针
Py_DECREF(pFunc);
// 不再需要模块时,减少引用计数
Py_DECREF(pModule);
PyGILState_Release(gil_state); // 释放GIL,释放前确保获取到了GIL,同时最好主动释放各计数,以防发生内存泄漏
return false;
}
同时不要忘记初始化python解释器(注:整个程序只可初始化一次,结束程序前再释放,否则再次初始化程序会崩溃),下面是改造后的初始化函数
头文件:
#ifndef INVOKE_PYTHON_INIT_H
#define INVOKE_PYTHON_INIT_H
#include <QObject>
#include <Python.h>
class Invoke_Python_Init
{
public:
Invoke_Python_Init();
~Invoke_Python_Init();
private:
QString pythonDirectoryPath;
bool init();
void initPythonDirectoryPath();
bool pythonDirectoryIsInit = false;
bool pythonIsInited = false;
};
#endif // INVOKE_PYTHON_INIT_H
源码文件:
#include "invoke_python_init.h"
#include <qDebug>
#include <QDir>
Invoke_Python_Init :: Invoke_Python_Init() {init();}
Invoke_Python_Init :: ~Invoke_Python_Init() {
// 释放python所用内存
Py_Finalize();
qDebug()<<"释放python解释器完成";
}
bool Invoke_Python_Init :: init() {
initPythonDirectoryPath();
if (!pythonDirectoryIsInit) {qDebug()<<"路径初始化失败" ; return 0;}
Py_SetPythonHome(L"C:/programming/anaconda3/envs/pytorch");
//调用前必须初始化python解释器
Py_Initialize();
if(!Py_IsInitialized()){qDebug()<<"python解释器初始化失败"; return 0;}
// 将路径转换为Python对象
PyObject *py_path_str = PyUnicode_FromWideChar(Py_DecodeLocale(pythonDirectoryPath.toLocal8Bit().constData(), NULL), -1);
// 加载 python 脚本
// 获取sys模块以进行项目.py文件的搜索
PyObject *sys_module = PyImport_ImportModule("sys");
// 获取sys.path
PyObject *sys_path = PyObject_GetAttrString(sys_module, "path");
if (!PyList_Check(sys_path)) {
// sys.path不是列表,错误处理
qDebug()<<"获取py搜索路径失败\n" ;
return 0;
} else {
// 将自定义路径添加到sys.path
int appended = PyList_Append(sys_path, py_path_str);
if (appended == -1) {
// 错误处理
qDebug()<<"添加py搜索路径失败" ;
return 0;
}
// 将sys.path转换为QStringList
QStringList pythonPathList;
// 遍历sys.path列表
for (Py_ssize_t i = 0; i < PyList_Size(sys_path); ++i) {
PyObject *path_item = PyList_GetItem(sys_path, i);
// 将路径元素转换为QString
QString path_str = QString::fromUtf8(PyUnicode_AsUTF8(path_item));
// 添加到QStringList
pythonPathList.append(path_str);
// 减少引用计数
Py_DECREF(path_item);
}
// 输出所有搜索路径到QDebug
foreach (const QString &path, pythonPathList) {
qDebug() << path<< "\n";
}
}
PyEval_ReleaseThread(PyThreadState_Get());
pythonIsInited = true;
qDebug("Python解释器初始化成功");
return true;
}
void Invoke_Python_Init :: initPythonDirectoryPath(){
QDir dir;
// 构建新的路径
QString Path = dir.currentPath().append("/").append(dir.currentPath().split("/").last().split("-")[1]);
// 将QString赋值给pythonFilePath
pythonDirectoryPath = Path;
pythonDirectoryIsInit = true;
}
在认为合适的地方初始化 Invoke_Python_Init 类,初始化完成后便可重复调用 invokePython 函数,即重复调用 python 脚本。
未完待续




![nginx: [emerg] stream directive is duplicate in /etc/nginx/nginx.conf:56](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/3fe89b9d19b0426d8b50bcd9c4dbfdf8.png)