课程地址
Mybatis 是一个优秀的持久层框架,用于简化 JDBC 操作
快速入门

POJO = Plain Old Java Object
建表
create database mybatis;
use mybatis;
drop table if exists tb_user;
create table tb_user(
id int primary key auto_increment,
username varchar(20),
password varchar(20),
gender char(1),
addr varchar(30)
);
INSERT INTO tb_user VALUES (1, 'zhangsan', '123', '男', '北京');
INSERT INTO tb_user VALUES (2, '李四', '234', '女', '天津');
INSERT INTO tb_user VALUES (3, '王五', '11', '男', '西安');
添加项目依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.5</version>
</dependency>
<!--mysql 驱动-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.46</version>
</dependency>
<!--junit 单元测试-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- 添加slf4j日志api -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>1.7.20</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 添加logback-classic依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.2.3</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 添加logback-core依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-core</artifactId>
<version>1.2.3</version>
</dependency>
添加 logback.xml 配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration>
<!--
CONSOLE :表示当前的日志信息是可以输出到控制台的。
-->
<appender name="Console" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder>
<pattern>[%level] %cyan([%thread]) %boldGreen(%logger{15}) - %msg %n</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<logger name="com.itheima" level="DEBUG" additivity="false">
<appender-ref ref="Console"/>
</logger>
<!--
level:用来设置打印级别,大小写无关:TRACE, DEBUG, INFO, WARN, ERROR, ALL 和 OFF
, 默认debug
<root>可以包含零个或多个<appender-ref>元素,标识这个输出位置将会被本日志级别控制。
-->
<root level="DEBUG">
<appender-ref ref="Console"/>
</root>
</configuration>
添加 mybatis-config.xml 配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<typeAliases>
<package name="com.itheima.pojo"/>
</typeAliases>
<!--
environments:配置数据库连接环境信息。可以配置多个environment,通过default属性切换不同的environment
-->
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!--数据库连接信息-->
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://192.168.93.12/itcast?useSSL=false"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="1234"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<!--加载sql映射文件-->
<mapper resource="UserMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
添加 UserMapper.xml sql 映射文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper>
<!--statement-->
<select id="selectAll" resultType="user">
select *
from tb_user;
</select>
</mapper>
创建 POJO 类
public class User {
private int id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String gender;
private String addr;
// setters and getters...
}
测试代码
public class MybatisDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
List<User> all_users = sqlSession.selectList("selectAll");
System.out.println(all_users);
sqlSession.close();
}
}
解决警告
警告:Idea 没有与数据库连接,无法识别数据库,不能给出字段提示
解决:在右侧边栏配置 Datebase 连接到数据库,然后将 File -> Languages & Frameworks -> SQL Dialects 配置为 MySQL
Mapper 代理开发
目的:解决原生方式中的硬编码;简化后期执行 SQL
将使用 sqlID 选择 SQL 执行并获取结果的方式改为使用接口的特定方法:
List<User> all_users = sqlSession.selectList("selectAll");
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
List<User> users = userMapper.selectAll();

让 resources 和 java 保持同样的目录结构,构建后配置文件和字节码就在同一目录下了
设置 namespace:
<mapper namespace="com.itheima.mapper.UserMapper">
在 Mapper 接口中定义方法,方法名与 SQL 映射文件中 SQL 语句的 id 相同:
public interface UserMapper {
List<User> selectAll();
}
修改 mybatis-config.xml 中 mappers 配置路径:
<mappers>
<!--加载sql映射文件-->
<mapper resource="com/itheima/mapper/UserMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
编码:
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
List<User> all_users = userMapper.selectAll();
System.out.println(all_users);
Mybatis 核心配置文件
enviroments
environments:配置数据库连接环境信息。可以配置多个environment,通过default属性切换不同的environment
typeAliases
类型别名可为 Java 类型设置一个缩写名字。 它仅用于 XML 配置,意在降低冗余的全限定类名书写
使用“包扫描”机制,用于简化映射文件中的 resultType
<typeAliases>
<package name="com.itheima.pojo"/>
</typeAliases>
上面配置好后,在 SQL 映射文件中的 resultType 就可以使用缩写类型名称:
<select id="selectAll" resultType="User">
配置文件完成增删改查
环境准备
建表:
drop table if exists tb_brand;
create table tb_brand (
id int primary key auto_increment,
brand_name varchar(20),
company_name varchar(20),
ordered int,
description varchar(100),
status int
);
insert into tb_brand (brand_name, company_name, ordered, description, status)
values ('三只松鼠', '三只松鼠股份有限公司', 5, '好吃不上火', 0),
('华为', '华为技术有限公司', 100, '华为致力于把数字世界带入每个人、每个家庭、每个组织,构建万物互联的智能世界', 1),
('小米', '小米科技有限公司', 50, 'are you ok', 1);
创建实体类:
public class Brand {
private Integer id; // 在实体类中,建议使用其对应的包装类型
private String brandName;
private String companyName;
private Integer ordered;
private String description;
private Integer status;
// setters and getters...
}
安装 MybatisX 插件,实现在接口和 xml 文件中的跳转
查询所有
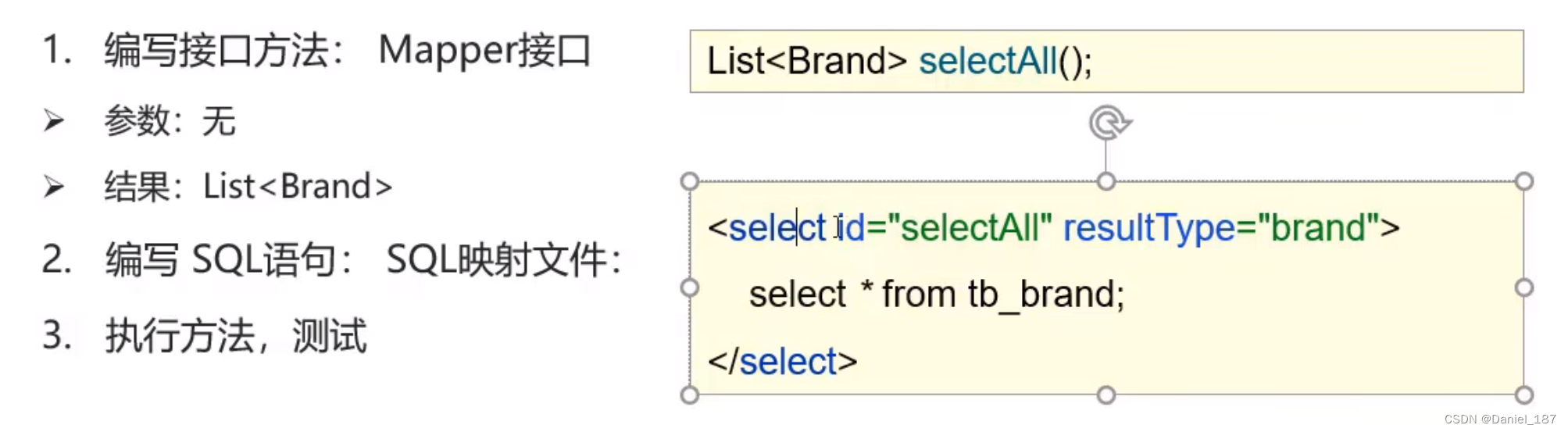
创建映射文件 BrandMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.itheima.mapper.BrandMapper">
<select id="selectAll" resultType="com.itheima.pojo.Brand">
select * from tb_brand
</select>
</mapper>
编写 BrandMapper 接口:
public interface BrandMapper {
List<Brand> selectAll();
}
在 mybatis-config.xml 中添加映射文件:
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/itheima/mapper/BrandMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
测试代码:
public class MybatistTest {
@Test
public void testSelectAll() throws Exception {
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
BrandMapper brandMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(BrandMapper.class);
List<Brand> all_brands = brandMapper.selectAll();
System.out.println(all_brands);
sqlSession.close();
}
}
数据库表的字段名称和实体类的属性名称不一致,则不能自动封装数据。解决方法:
- 方法一:对查询语句 as 起别名,让别名和实体类的属性名一致
<select id="selectAll" resultType="com.itheima.pojo.Brand">
select id, brand_name as brandName, company_name as companyName, ordered, description, status
from tb_brand
</select>
- 方法二:使用 sql 片段:
<sql id="brand_column">
id, brand_name as brandName, company_name as companyName, ordered, description, status
</sql>
<select id="selectAll" resultType="com.itheima.pojo.Brand">
select <include refid="brand_column"></include>
from tb_brand
</select>
- 方法三:使用 resultMap,维护列名和属性名之间的映射:
<resultMap id="brandResultMap" type="Brand">
<result column="brand_name" property="brandName"></result>
<result column="company_name" property="companyName"></result>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectAll" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select *
from tb_brand
</select>
根据 id 查询

编写 Mapper 接口:
public interface BrandMapper {
List<Brand> selectAll();
Brand selectById(int id);
}
编写 Mapper 配置:
<select id="selectById" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select * from tb_brand where id=#{id}
</select>
测试代码:
Brand b = brandMapper.selectById(2);
System.out.println(b);
参数占位符:
- #{}:会将其替换为
?:select * from tb_brand where id=? - ${}:会将其替换为实际的 id:
select * from tb_brand where id=2
为了防止 SQL 注入,建议使用 #{}
特殊字符处理:
- 转义字符:
< - CDATA 区
参数占位符:
#{}:执行 SQL 时,会将 #{} 占位符替换为 ?,将来自动设置参数值(参数传递时使用)
${}:拼 SQL,会存在 SQL 注入的问题(需要对表名,列名进行动态设置时使用)
条件查询
多条件查询
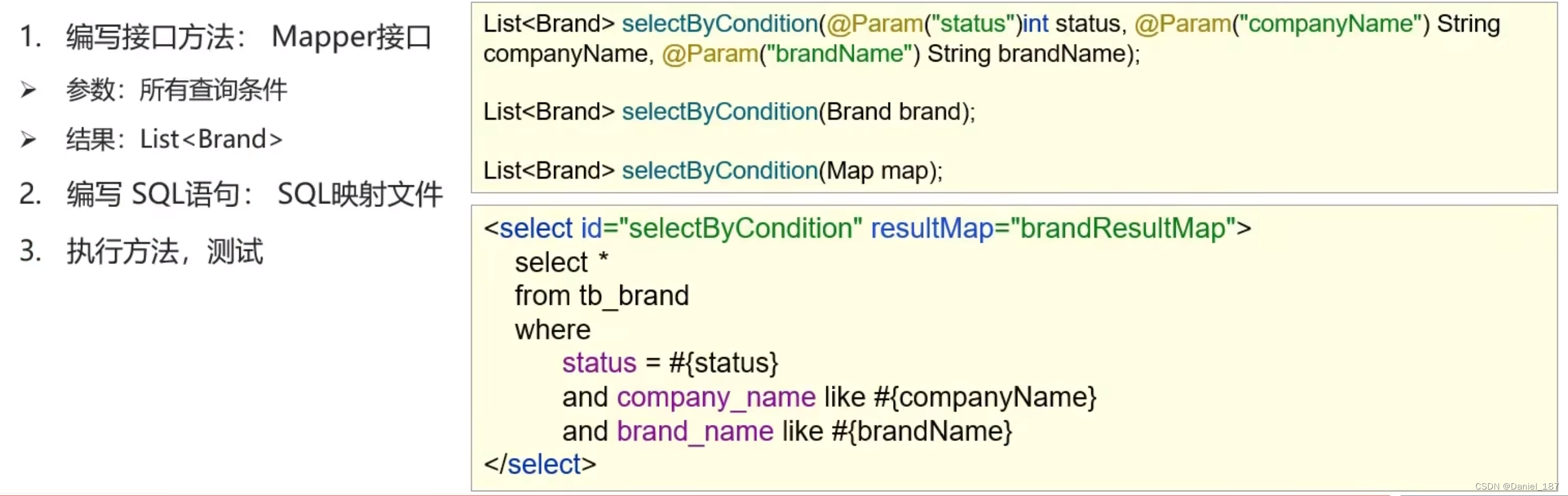
编写 3 种多条件查询接口:
public interface BrandMapper {
List<Brand> selectAll();
Brand selectById(int id);
List<Brand> selectByCondition(@Param("status")int status, @Param("companyName")String companyName, @Param("brandName")String brandName);
List<Brand> selectByCondition(Brand brand);
List<Brand> selectByCondition(Map map);
}
创建映射文件:
<select id="selectByCondition" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select *
from tb_brand
where
status = #{status}
and company_name like #{companyName}
and brand_name like #{brandName}
</select>
测试代码:
// 散装参数查询
List<Brand> brands1 = brandMapper.selectByCondition(1, "%华为%", "%华为%");
System.out.println(brands1);
// 实体类封装参数
Brand brand = new Brand();
brand.setStatus(1);
brand.setCompanyName("%华为%");
brand.setBrandName("%华为%");
List<Brand> brands2 = brandMapper.selectByCondition(brand);
System.out.println(brands2);
// 根据 map 查询
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("status", 1);
map.put("companyName", "%华为%");
map.put("brandName", "%华为%");
List<Brand> brands3 = brandMapper.selectByCondition(map);
System.out.println(brands3);
SQL 语句设置多个参数的方式:
- 散装参数:使用 @Param(“SQL 中的参数占位符名称”)
- 实体类封装参数:SQL 中的参数名和实体类属性名对应上
- map 集合:SQL 中的参数名和 map 集合的键的名称对应上
动态条件查询
上面程序的问题在于,每次查询需要用户输入所有的条件,不符合用户的使用习惯

使用 if 进行条件判断:
<select id="selectByCondition" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select *
from tb_brand
where 1 = 1
<if test="status != null">
and status = #{status}
</if>
<if test="companyName != null and companyName != '' ">
and company_name like #{companyName}
</if>
<if test="brandName != null and brandName != '' ">
and brand_name like #{brandName}
</if>
</select>
或者使用 where 标签连接多个条件,避免为了满足 and 而加的冗余条件 1 = 1:
<select id="selectByCondition" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select *
from tb_brand
<where>
<if test="status != null">
and status = #{status}
</if>
<if test="companyName != null and companyName != '' ">
and company_name like #{companyName}
</if>
<if test="brandName != null and brandName != '' ">
and brand_name like #{brandName}
</if>
</where>
</select>
if:用于判断参数是否有值,使用 test 属性进行条件判断
存在的问题:第一个条件不需要逻辑运算符
解决方案:使用恒等式 1 = 1 让所有条件格式都一样;使用 <where> 标签替换 where 关键字
单条件动态条件查询:

编写接口:
List<Brand> selectBySingleCondition(Brand brand);
生成 statement:
<select id="selectBySingleCondition" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select *
from tb_brand
where
<choose>
<when test="status != null">
status = #{status}
</when>
<when test="companyName != null">
company_bame like #{companyName}
</when>
<when test="brandName != null">
brand_name like #{brandName}
</when>
<otherwise>
1 = 1
</otherwise>
</choose>
</select>
单条件查询测试代码:
Brand b = new Brand();
b.setStatus(0);
List<Brand> brands = brandMapper.selectBySingleCondition(b);
System.out.println(brands);
添加&修改
添加
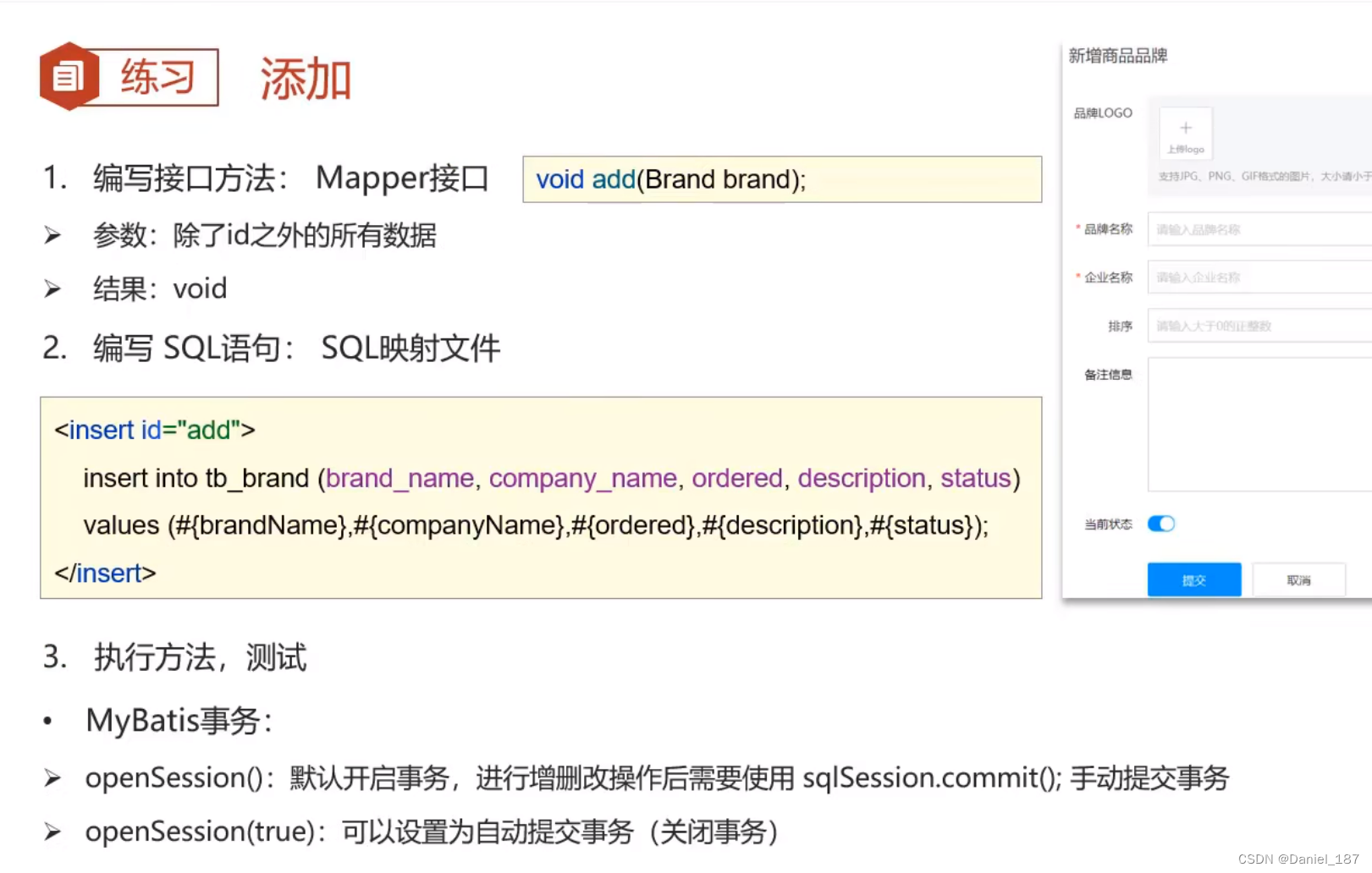
编写接口:
void add(Brand brand);
生成 statement:
<insert id="add">
insert into tb_brand(brand_name, company_name, ordered, description, status)
values (#{brandName}, #{companyName}, #{ordered}, #{description}, #{status})
</insert>
编写测试代码:
Brand b = new Brand();
b.setStatus(1);
b.setCompanyName("波导手机");
b.setBrandName("波导");
b.setDescription("手机中的战斗机");
b.setOrdered(100);
brandMapper.add(b);
sqlSession.commit(); // 手动提交事务
// 或者在获取 sqlsession 时设置自动提交事务
// SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
主键返回:
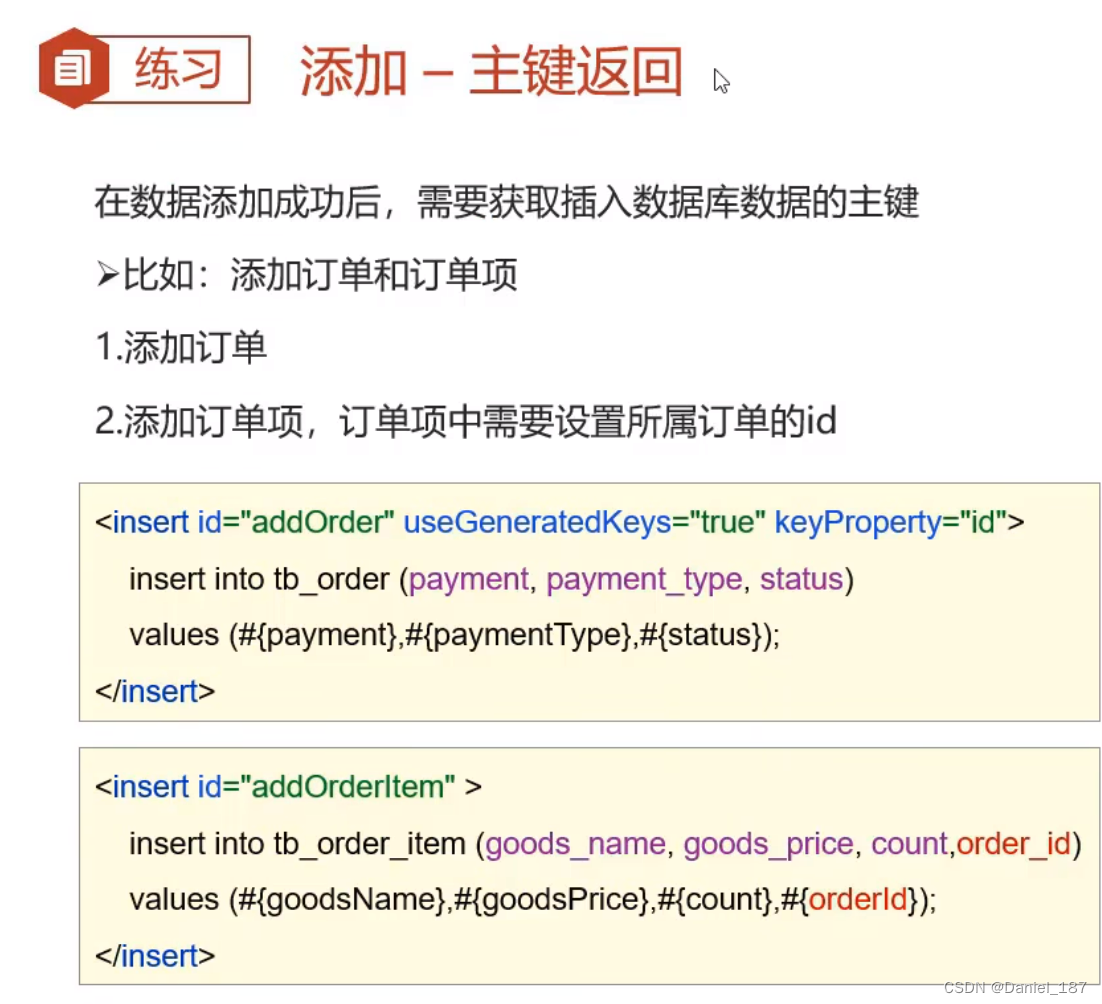
设置 useGeneratedKeys 和 keyProperty:
<insert id="add" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
insert into tb_brand(brand_name, company_name, ordered, description, status)
values (#{brandName}, #{companyName}, #{ordered}, #{description}, #{status})
</insert>
在测试程序获取 id:
Brand b = new Brand();
b.setStatus(1);
b.setCompanyName("波导手机");
b.setBrandName("波导");
b.setDescription("手机中的战斗机");
b.setOrdered(100);
brandMapper.add(b);
sqlSession.commit(); // 手动提交事务
System.out.println(b.getId()); // 获取 id
修改

编写接口:
int update(Brand brand);
生成 statement:
<update id="update">
update tb_brand
set brand_name = #{brandName}, company_name = #{companyName}, ordered = #{ordered}, description = #{description}, status = #{status}
where id = #{id}
</update>
编写测试代码:
Brand b = new Brand();
b.setId(5);
b.setStatus(1);
b.setCompanyName("波导手机");
b.setBrandName("波导");
b.setDescription("波导手机,手机中的战斗机");
b.setOrdered(200);
int res = brandMapper.update(b);
sqlSession.commit();
System.out.println(res);
修改动态字段:
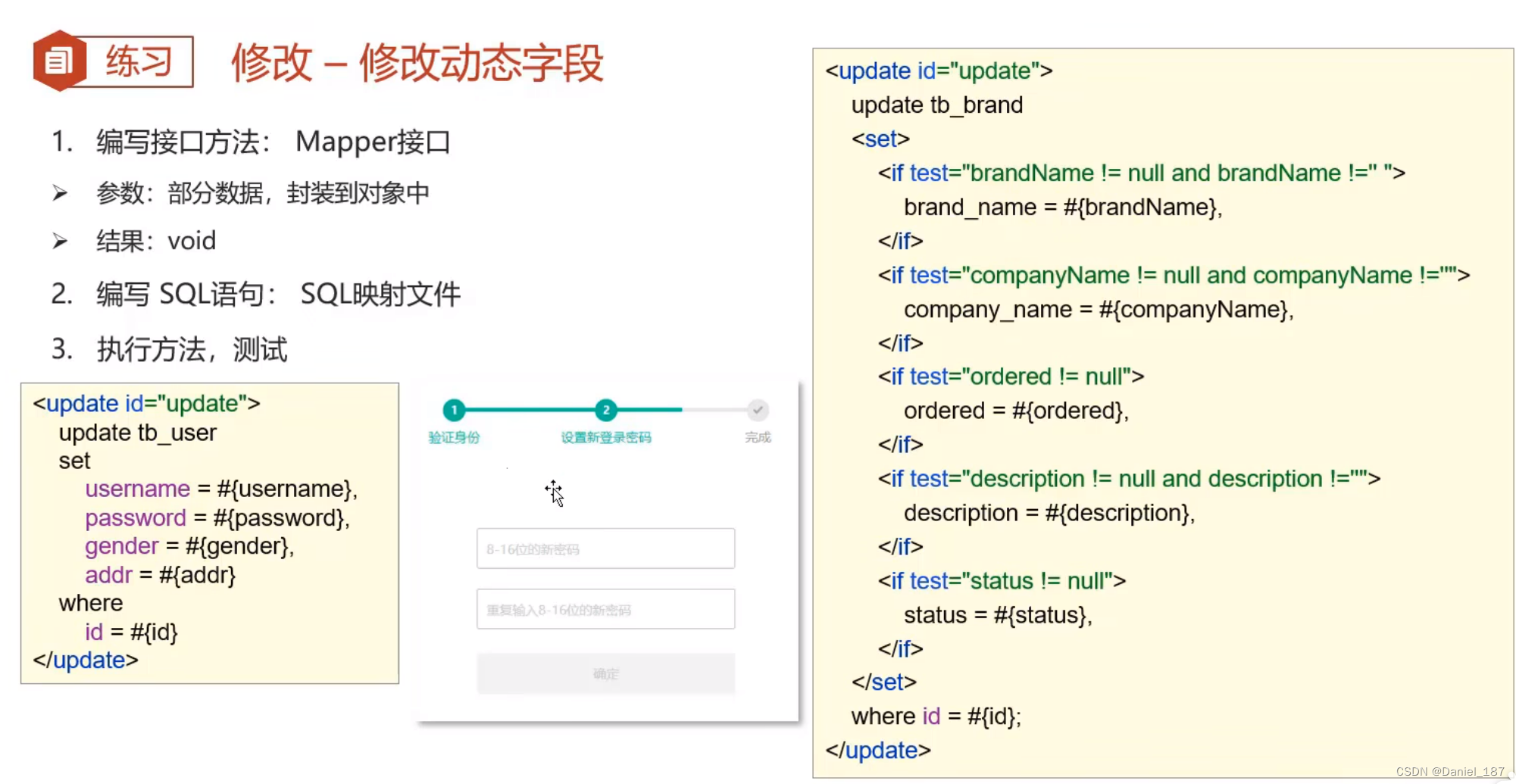
修改 statement:
<update id="update">
update tb_brand
<set>
<if test="brandName != null and brandName != '' ">
brand_name = #{brandName}
</if>
<if test="companyName != null and companyName != '' ">
company_name = #{companyName}
</if>
<if test="ordered != null">
ordered = #{ordered}
</if>
<if test="description != null and description != '' ">
description = #{description}
</if>
<if test="status != null and status != '' ">
status = #{status}
</if>
</set>
where id = #{id};
</update>
测试代码:
Brand b = new Brand();
b.setId(5);
b.setOrdered(300);
int res = brandMapper.update(b);
sqlSession.commit();
删除
删除一个
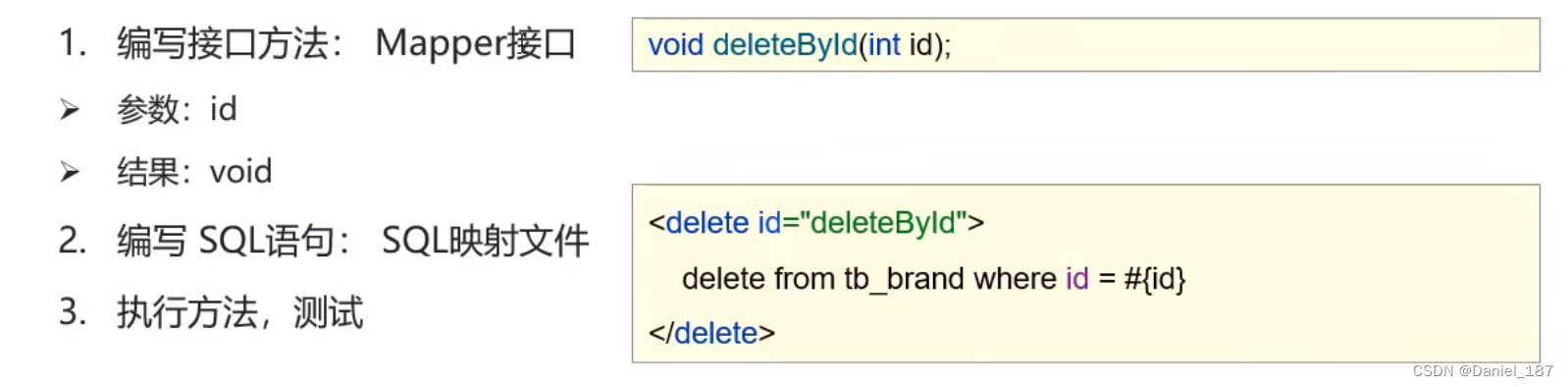
添加接口:
void deleteById(int id);
编写 SQL 映射:
<delete id="deleteById">
delete from tb_brand where id = #{id}
</delete>
测试代码:
brandMapper.deleteById(6);
sqlSession.commit();
批量删除
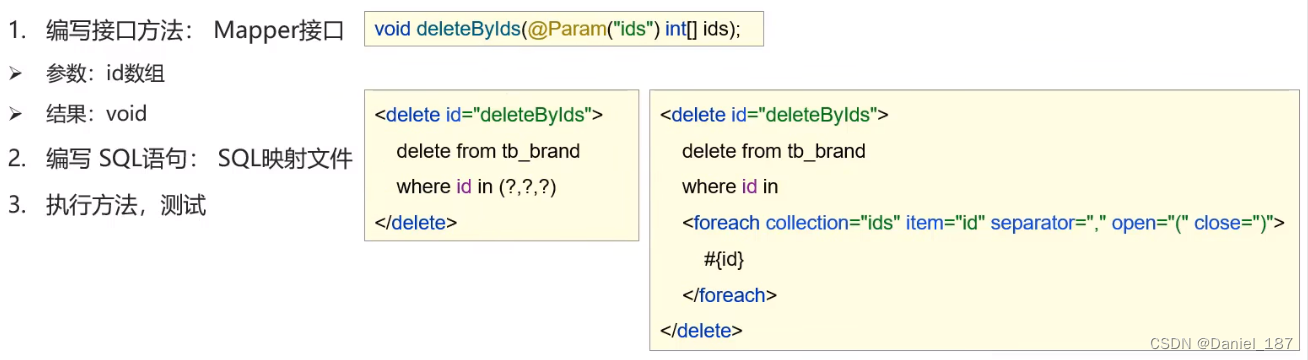
添加接口:
void deleteByIds(@Param("ids")int[] ids);
编写 SQL 映射:
<delete id="deleteByIds">
delete from tb_brand
where id in
<foreach collection="ids" item="id" separator="," open="(" close=")">
#{id}
</foreach>
</delete>
测试代码:
int[] ids = {3, 5};
brandMapper.deleteByIds(ids);
sqlSession.commit();
参数传递
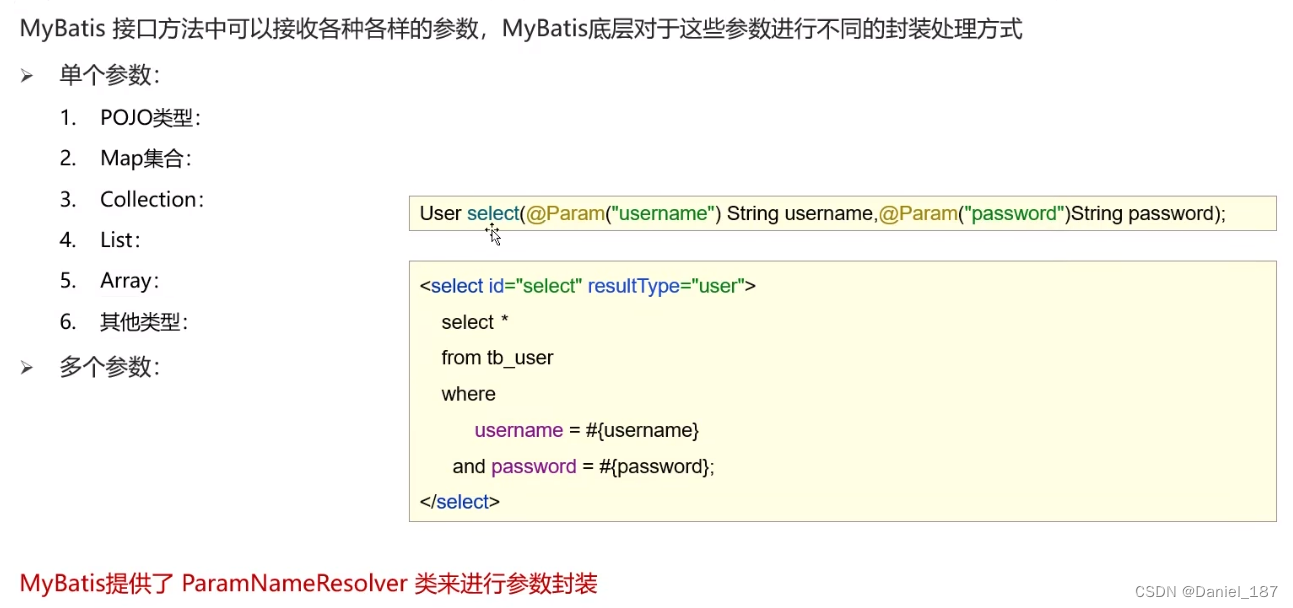
对于多个参数,会封装为 Map 集合

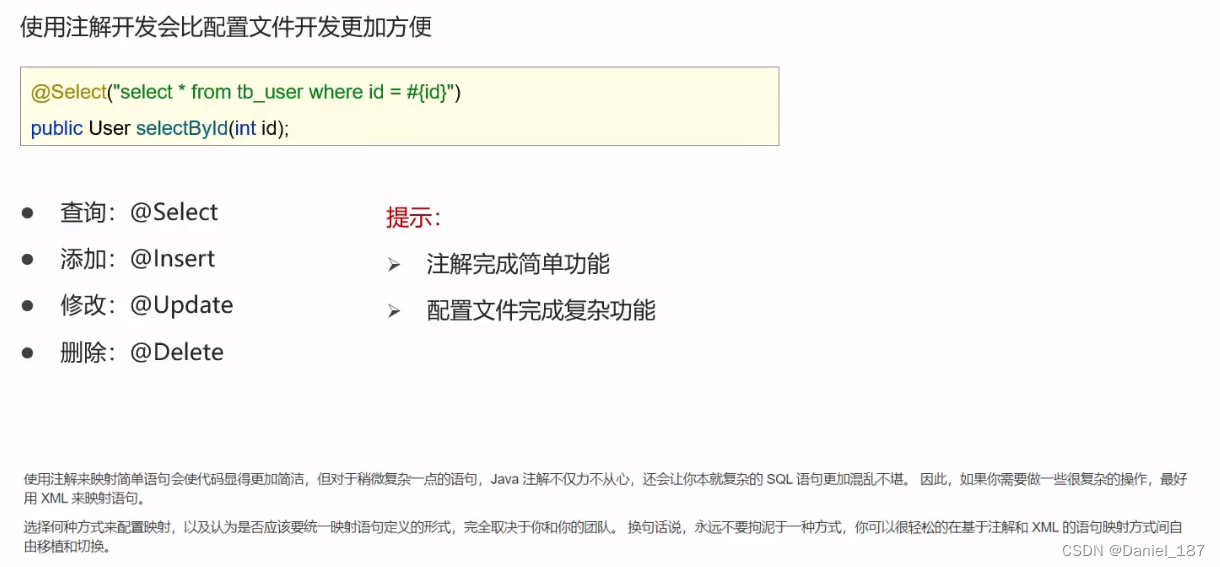
注解完成增删改查





![[ Linux ] git工具的基本使用(仓库的构建,提交)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/de62670ec55642ab9df947e560494b08.png)