nginx服务配置与配置优化
-
nginx服务脚本配置
mkdir wwwroot
cd wwwroot/
mkdir nginx1
touch index.php
vim index.php
<?php
echo $_SERVER["REMOTE_ADDR"];
vim conf/nginx.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
root /www/wwwroot/nginx1;
index index.php index.html;
location ~\.php$ {
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
}
sbin/nginx -s reload ##重载配置
-
nginx配置文件解释
-
影响nginx性能的配置
1. nginx服务脚本配置
服务配置脚本的主要作用是用于启动,重启,关闭,查看nginx服务是否正在运行,这样我们没必要在为了启动nginx而去找nginx的启动文件,通过启动文件的命令开启nginx服务了.
[root@localhost conf]# cd /etc/init.d [root@localhost init.d]# ll 总用量 40 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 18281 8月 24 2018 functions -rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 4569 8月 24 2018 netconsole -rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 7923 8月 24 2018 network -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1160 10月 31 2018 README [root@localhost init.d]# touch nginx [root@localhost init.d]# chmod -R 777 nginx
下面是脚本的具体内容:
简单版
#! /bin/bash #chkconfig:35 85 15 DAEMON=/www/server/nginx/sbin/nginx PID=/www/server/nginx/logs/nginx.pid case "$1" in start) echo "Starting nginx daemon..." $DAEMON && echo "SUCCESS" #开启nginx ;; stop) echo "Stopping nginx daemon..." $DAEMON -s quit && echo "SUCCESS" #从容的停止nginx ;; reload) echo "Reloading nginx daemon..." $DAEMON -s reload && echo "SUCCESS" #平滑重启nginx ;; restart) echo "Restarting nginx daemon..." $DAEMON -s quit #从容的停止nginx $DAEMON && echo "SUCCESS" #开启nginx ;; status) if [ ! -f "$PID" ]; then #因为nginx启动后会生成进程文件nginx.pid,这里通过判断进程文件是否存在,判断nginx是否启动 echo "Nginx is not running..." else echo "Nginx is running..." fi ;; *) echo "Usage:service nginx (start|stop|restart|reload|status)" exit 2 ;; esac
精细版
#! /bin/sh
# chkconfig: 2345 55 25
PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin
NAME=nginx
NGINX_BIN=/www/server/nginx/sbin/$NAME
CONFIGFILE=/www/server/nginx/conf/$NAME.conf
PIDFILE=/www/server/nginx/logs/$NAME.pid
ulimit -n 8192
case "$1" in
start)
echo -n "Starting $NAME... "
if [ -f $PIDFILE ];then
mPID=`cat $PIDFILE`
isStart=`ps ax | awk '{ print $1 }' | grep -e "^${mPID}$"`
if [ "$isStart" != '' ];then
echo "$NAME (pid `pidof $NAME`) already running. "
exit 1
fi
fi
$NGINX_BIN -c $CONFIGFILE
if [ "$?" != 0 ] ; then
echo " failed "
exit 1
else
echo " success "
fi
;;
stop)
echo -n "Stoping $NAME... "
if [ -f $PIDFILE ];then
mPID=`cat $PIDFILE`
isStart=`ps ax | awk '{ print $1 }' | grep -e "^${mPID}$"`
if [ "$isStart" = '' ];then
echo "$NAME is not running."
exit 1
fi
fi
$NGINX_BIN -s stop
if [ "$?" != 0 ] ; then
echo " failed. Use force-quit"
exit 1
else
echo " done"
fi
;;
status)
if [ -f $PIDFILE ];then
mPID=`cat $PIDFILE`
isStart=`ps ax | awk '{ print $1 }' | grep -e "^${mPID}$"`
if [ "$isStart" != '' ];then
echo "$NAME (pid `pidof $NAME`) already running."
exit 1
else
echo "$NAME is stopped"
exit 0
fi
else
echo "$NAME is stopped"
exit 0
fi
;;
restart)
$0 stop
sleep 1
$0 start
;;
reload)
echo -n "Reload service $NAME... "
if [ -f $PIDFILE ];then
mPID=`cat $PIDFILE`
isStart=`ps ax | awk '{ print $1 }' | grep -e "^${mPID}$"`
if [ "$isStart" != '' ];then
$NGINX_BIN -s reload
echo " done"
else
echo "$NAME is not running, can 't reload."
exit 1
fi
else
echo "$NAME is not running, can 't reload."
exit 1
fi
;;
configtest)
echo -n "Test $NAME configure files... "
$NGINX_BIN -t
;;
*)
echo "Usage: $0 {start|stop|restart|reload|status|configtest}"
exit 1
;;
esac
小星星版
#! /bin/sh
# chkconfig: 2345 55 25
PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin
NAME=nginx
NGINX_BIN=/www/server/nginx/sbin/$NAME
CONFIGFILE=/www/server/nginx/conf/$NAME.conf
PIDFILE=/www/server/nginx/logs/$NAME.pid
AUTHORNAME='xx'
SYSTEMNAME='小星星'
ulimit -n 8192
int=3
case "$1" in
start)
echo -e "\e[36m 亲爱的${AUTHORNAME}小朋友,你好 \e[0m"
echo -e "\e[36m ${SYSTEMNAME}正在为你启动$NAME \e[0m"
while(($int>=1))
do
echo -n "."
sleep 1
let "int--"
done
if [ -f $PIDFILE ];then
mPID=`cat $PIDFILE`
isStart=`ps ax | awk '{ print $1 }' | grep -e "^${mPID}$"`
if [ "$isStart" != '' ];then
echo -e "\e[31m 亲爱的${AUTHORNAME}小朋友,你好 \e[0m"
echo -e "\e[31m ${SYSTEMNAME}亲切的提醒你 你的$NAME (pid `pidof $NAME`) 已经启动了哦. \e[0m"
exit 1
fi
fi
$NGINX_BIN -c $CONFIGFILE
if [ "$?" != 0 ] ; then
echo -e "\e[31m 亲爱的${AUTHORNAME}小朋友,你好 \e[0m"
echo -e "\e[31m ${SYSTEMNAME}亲切的提醒你 你的$NAME 启动失败了哦. \e[0m"
exit 1
else
echo ""
echo -e "\e[32m 成功. \e[0m"
fi
;;
stop)
echo -e "\e[36m 亲爱的${AUTHORNAME}小朋友,你好 \e[0m"
echo -e "\e[36m ${SYSTEMNAME}正在为你停止$NAME \e[0m"
int=3
while(($int>=1))
do
echo -n "."
sleep 1
let "int--"
done
if [ -f $PIDFILE ];then
mPID=`cat $PIDFILE`
isStart=`ps ax | awk '{ print $1 }' | grep -e "^${mPID}$"`
if [ "$isStart" = '' ];then
echo -e "\e[31m 亲爱的${AUTHORNAME}小朋友 \e[0m"
echo -e "\e[31m 你好,${SYSTEMNAME}亲切的提醒你 你的$NAME 还没有启动哦. \e[0m"
exit 1
fi
fi
$NGINX_BIN -s stop
if [ "$?" != 0 ] ; then
echo -e "\e[31m 亲爱的${AUTHORNAME}小朋友,你好 \e[0m"
echo -e "\e[31m ${SYSTEMNAME}亲切的提醒你 你的$NAME 停止失败了哦. 细心检查下它的配置吧 \e[0m"
exit 1
else
echo ""
echo -e "\e[32m 停止成功,下次再来陪${SYSTEMNAME}玩哦 \e[0m"
fi
;;
status)
if [ -f $PIDFILE ];then
mPID=`cat $PIDFILE`
isStart=`ps ax | awk '{ print $1 }' | grep -e "^${mPID}$"`
if [ "$isStart" != '' ];then
echo -e "\e[31m 亲爱的${AUTHORNAME}小朋友,你好 \e[0m"
echo -e "\e[31m ${SYSTEMNAME}亲切的提醒你 你的$NAME (pid `pidof $NAME`) 已经启动了哦. \e[0m"
exit 1
else
echo -e "\e[31m 亲爱的${AUTHORNAME}小朋友,你好 \e[0m"
echo -e "\e[31m ${SYSTEMNAME}亲切的提醒你 你的$NAME 没有启动哦. \e[0m"
exit 0
fi
else
echo -e "\e[31m 亲爱的${AUTHORNAME}小朋友,你好 \e[0m"
echo -e "\e[31m ${SYSTEMNAME}亲切的提醒你 你的$NAME 没有启动哦. \e[0m"
exit 0
fi
;;
restart)
$0 stop
sleep 1
$0 start
;;
reload)
echo -e "\e[36m 亲爱的${AUTHORNAME}小朋友,你好 \e[0m"
echo -e "\e[36m ${SYSTEMNAME}正在为你更新$NAME 配置信息,请稍等 \e[0m"
int=3
while(($int>=1))
do
echo -n "."
sleep 1
let "int--"
done
if [ -f $PIDFILE ];then
mPID=`cat $PIDFILE`
isStart=`ps ax | awk '{ print $1 }' | grep -e "^${mPID}$"`
if [ "$isStart" != '' ];then
$NGINX_BIN -s reload
echo " done"
else
echo -e "\e[31m 亲爱的${AUTHORNAME}小朋友,你好 \e[0m"
echo -e "\e[31m ${SYSTEMNAME}亲切的提醒你 你的$NAME 没有启动哦, $NAME 没有启动不能更新配置信息. \e[0m"
exit 1
fi
else
echo -e "\e[31m 亲爱的${AUTHORNAME}小朋友,你好 \e[0m"
echo -e "\e[31m ${SYSTEMNAME}亲切的提醒你 你的$NAME 没有启动哦, $NAME 没有启动不能更新配置信息. \e[0m"
exit 1
fi
;;
configtest)
echo -n "Test $NAME configure files... "
$NGINX_BIN -t
;;
*)
echo "Usage: $0 {start|stop|restart|reload|status|configtest}"
exit 1
;;
esac
脚本使用的是shell进行编写,在我们解释上面的代码之前,我们应该先对nginx的程序以及相关命令参数有一个好的了解,我们先看到nginx的安装目录:
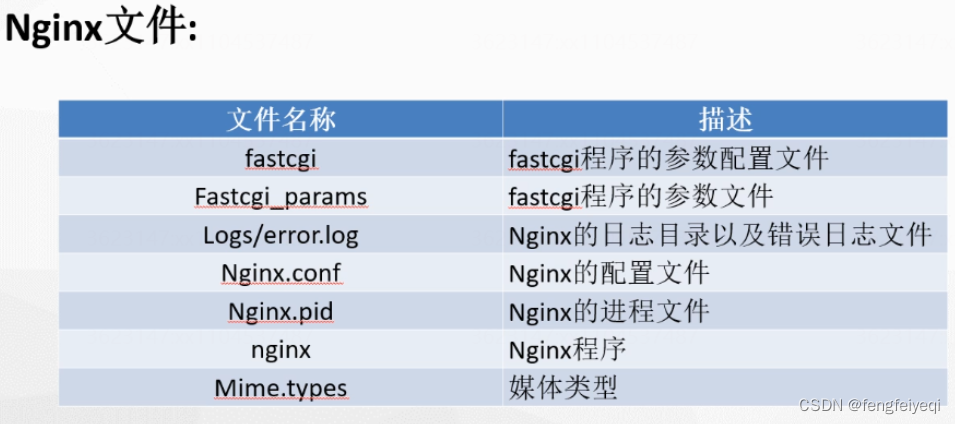
nginx nginx安装目录 ├── client_body_temp ├── fastcgi.conf fastcgi程序的参数配置文件 ├── fastcgi.conf.default fastcgi程序的初识默认配置文件 ├── fastcgi_params fastcgi程序的参数文件 ├── fastcgi_params.default fastcgi程序的初识默认参数文件 ├── fastcgi_temp fastcgi数据临时文件 ├── html nginx默认的站点目录 │ ├── 50x.html │ └── index.html ├── koi-utf ├── koi-win ├── logs nginx日志目录 │ ├── access.log 访问日志 │ └── error.log 错误日志 ├── mime.types 媒体类型 ├── mime.types.default ├── nginx nginx程序 ├── nginx.conf nginx主配置文件 ├── nginx.conf.default nginx初识默认配置文件 ├── nginx.pid nginx进程id文件 ├── proxy_temp 代理数据临时文件 ├── scgi_params ├── scgi_params.default ├── scgi_temp ├── uwsgi_params ├── uwsgi_params.default ├── uwsgi_temp └── win-utf
我们先看看上面的nginx程序,使用的时候nginx -h;
[root@localhost nginx]# ./nginx -h nginx version: nginx/1.18.0 Usage: nginx [-?hvVtTq] [-s signal] [-c filename] [-p prefix] [-g directives] Options: -?,-h : this help 查看帮助文档 -v : show version and exit 查看nginx版本信息 -V : show version and configure options then exit 查看nginx版本信息以及编译时的configure信息 -t : test configuration and exit 检查nginx的配置文件 -T : test configuration, dump it and exit 检查并输出nginx的配置文件内容 -q : suppress non-error messages during configuration testing 检查配置文件时,不输出异常信息 -s signal : send signal to a master process: stop, quit, reopen, reload nginx程序的启动,关闭等 -p prefix : set prefix path (default: /usr/local/nginx/) 设置nginx站点路径 -c filename : set configuration file (default: /usr/local/nginx/nginx.conf) 选择配置文件启动nginx -g directives : set global directives out of configuration file 设置全局配置
通过使用nginx程序加参数-h,我们能够看到nginx使用的帮助文档.
现在我们在来看前面的nginx服务启动代码:
#chkconfig:35 85 15
对于一个要经常使用的服务器而言,每次开机后,都需要用户手动开启一些服务较为麻烦。接下来,将通过chkconfig命令完成nginx开机自启动的功能,chkconfig命令的语法格式如下所示:
chlconfig [--add] [--del] [--list] [系统服务] 参数解释: --add:用于增加指定的系统服务(如nginx),设置该服务为开机自启动 --del:用于删除指定的系统服务,取消该服务的开机自启动 --list:用于列出系统所有的服务启动情况
代码解释:
#! /bin/bash:通常写在shell脚本的开头,需要使用特殊表示符号#!定义解释此脚本的shell路径。以上代码的意思是这个脚本将使用bash环境执行。
case语句:case语句通常用于多重分支语句匹配的情况,具体语法如下:
case $变量名 in
模式1)
命令序列1
;;
模式2)
命令序列2
;;
*)
默认执行的命令序列
;;
esac
case语句必须以case开始 in结尾,中间的变量表示用户输入的字符,每个模式必须以右括号")"结束,双分号";;"结束命令序列,且匹配模式中可以使用方括号表示一个连续的范围,如[0-9],使用树杠符号“|”表示“或”;最后的“*)”是默认模式,当使用前面的各种模式均无法匹配该变量时,将执行“*)”后的命令序列,最后case语句必须以esac结束。
2. nginx配置文件解释
本节我们学习的是nginx课程的第一节的第二小节,本小节我们将对nginx的配置文件做一个全面的解释,下面开始: 首先nginx的配置文件,我们安装之后的目录是在/usr/local/nginx/nginx.conf这个路径下,如果你不清楚你的nginx的配置文件在哪个下面,你可以使用nginx -t来进行查看,它能够告诉你你的nginx配置文件在哪里
[root@localhost nginx]# ./nginx -t nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
找到配置文件后,我们使用cat命令进行查看,cat /usr/local/nginx/nginx.conf:
worker_processes 1;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
root /www/php/blog;
index index.php index.html;
location ~ \.php$ {
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
}
include /usr/local/nginx/server/*.conf;
}
以上打印出来的是nginx的配置文件的少数内容,但是从这看我们依然可以将nginx的配置文件分为5个部分,分别是:
全局配置
配置影响`nginx`全局的指令。一般有运行nginx服务器的用户组,nginx进程pid存放路径,日志存放路径,配置文件引入,允许生成worker process数等。通常是一个核心占一个Nginx进程
events块
配置影响`nginx`服务器或与用户的网络连接。有每个进程的最大连接数,选取哪种事件驱动模型处理连接请求,是否允许同时接受多个网路连接,开启多个网络连接序列化等。
http块
可以嵌套多个`server`,配置代理,缓存,日志定义等绝大多数功能和第三方模块的配置。如文件引入,`mime-type`定义,日志自定义,是否使用`sendfile`传输文件,连接超时时间,单连接请求数等。
server块
配置虚拟主机的相关参数,一个`http`中可以有多个`server`。
location块
配置请求的路由,以及各种页面的处理情况。
user www www;
worker_processes auto;
error_log logs/nginx_error.log crit;
pid logs/nginx.pid;
worker_rlimit_nofile 51200;
events
{
use epoll;
worker_connections 51200;
multi_accept on;
}
http
{
include mime.types;
lua_package_path "/www/server/luaJIT/lib/lua/?.lua";
#include proxy.conf;
default_type application/octet-stream;
server_names_hash_bucket_size 512;
client_header_buffer_size 32k;
large_client_header_buffers 4 32k;
client_max_body_size 50m;
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
keepalive_timeout 60;
tcp_nodelay on;
fastcgi_connect_timeout 300;
fastcgi_send_timeout 300;
fastcgi_read_timeout 300;
fastcgi_buffer_size 64k;
fastcgi_buffers 4 64k;
fastcgi_busy_buffers_size 128k;
fastcgi_temp_file_write_size 256k;
fastcgi_intercept_errors on;
gzip on;
gzip_min_length 1k;
gzip_buffers 4 16k;
gzip_http_version 1.1;
gzip_comp_level 2;
gzip_types text/plain application/javascript application/x-javascript text/javascript text/css application/xml;
gzip_vary on;
gzip_proxied expired no-cache no-store private auth;
gzip_disable "MSIE [1-6]\.";
limit_conn_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=perip:10m;
limit_conn_zone $server_name zone=perserver:10m;
server_tokens off;
access_log off;
server
{
listen 888;
server_name phpmyadmin;
index index.html index.htm index.php;
root /www/server/phpmyadmin;
location ~ /tmp/ {
return 403;
}
#include enable-php.conf;
location ~ .*\.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|bmp|swf)$
{
expires 30d;
}
location ~ .*\.(js|css)?$
{
expires 12h;
}
location ~ /\.
{
deny all;
}
access_log logs/access.log;
}
include /www/server/nginx/vhost/*.conf;
}3.影响Nginx性能的配置
进程数: nginx进程数:建议设置为等于CPU总核心数(一般跟cPu核数相同或为它的倍数)。这里设置为多少,在进行top监控的时候就能看到高负载时就会打开多少个nginx进程。可通过Ilscpu命令查看服务器里有几个核(先看几个cPu,以及每个CPU是几核)。
连接数:
单个进程最大连接数:默认的值是1024,理论上每台Nginx服务器的最大连接数=worker_processes(最大进程个数) *worker_connections(单个进程最大连接数)
超时时间:
http连接超时时间:单位是秒,默认为60s,功能是使客户端到服务器端的连接在设定的时间(即:keepalive_timeout)内持续有效,当出现对服务器的后续请求时,该功能避免了建立或者重新建立连接。
Gzip on:
压缩文件的大小,提高文件传输速度;有效降低带宽的使用,加快响应速度
User epoll
在events标签中使用epoll的I/O模型,用这个模型用来高效处理异步事件。