手动分页
非mybatis 自动分页
service 层
@Override
public PageInfo<CfLogVo> cfLogList(CfLogQuery cfLogQuery) {
if (StrUtil.isNotBlank(cfLogQuery.getRequest()) && cfLogQuery.getRequest().length() >100){
throw new ServiceException("请求报文长度不能大于100个字符!");
};
if (StrUtil.isNotBlank(cfLogQuery.getResponse()) && cfLogQuery.getResponse().length() >100){
throw new ServiceException("响应报文长度不能大于100个字符!");
};
if (ObjectUtil.isEmpty(cfLogQuery.getBeginTime()))
throw new ServiceException("开始时间不能为空!");
if (ObjectUtil.isEmpty(cfLogQuery.getEndTime()))
throw new ServiceException("结束时间不能为空!");
//PageHelper.startPage(cfLogQuery.getPage(), cfLogQuery.getLimit());
cfLogQuery.setPage((cfLogQuery.getPage() - 1) * cfLogQuery.getLimit());
//Integer listLogsByCount = cfLogDao.findListLogsByCount(cfLogQuery);
Integer listLogsByCount = 1000;
List<CfLogVo> listLogs = cfLogDao.findListLogs(cfLogQuery);
PageInfo pageInfo = new PageInfo<CfLogVo>(listLogs);
pageInfo.setPageNum(cfLogQuery.getPage());
pageInfo.setPageSize(cfLogQuery.getLimit());
pageInfo.setTotal(listLogsByCount == null ? 0 : listLogsByCount);
return pageInfo;
}
maper
<select id="findListLogs" resultType="com.kamowl.kamo.cloud.third.open.vo.CfLogVo" parameterType="com.kamowl.kamo.cloud.third.open.query.report.cf.CfLogQuery">
SELECT * from cf_log
<include refid="where"/>
order by create_time desc
limit ${page},${limit}
</select>
<select id="findListLogsByCount" resultType="integer" parameterType="com.kamowl.kamo.cloud.third.open.query.report.cf.CfLogQuery">
SELECT count(1) from cf_log
<include refid="where"/>
</select>
<sql id="where">
<where>
<if test="type != null and type != ''">
and type = #{type}
</if>
<if test="response != null and response != ''">
and response like concat('%', #{response}, '%')
</if>
<if test="request != null and request != ''">
and request like concat('%', #{request}, '%')
</if>
<if test="url != null and url != ''">
and url like concat('%', #{url}, '%')
</if>
<if test="state != null ">
and state = #{state}
</if>
<if test="beginTime != null">
and create_time>=#{beginTime}
</if>
<if test="endTime != null">
and #{endTime}>=create_time
</if>
</where>
</sql>
事务@Transactional(rollbackFor=Exception.class)
当作用于类上时,该类的所有 public 方法将都具有该类型的事务属性,同时,我们也可以在方法级别使用该标注来覆盖类级别的定义。
在项目中,@Transactional(rollbackFor=Exception.class),如果类加了这个注解,那么这个类里面的方法抛出异常,就会回滚,数据库里面的数据也会回滚。
在@Transactional注解中如果不配置rollbackFor属性,那么事物只会在遇到RuntimeException的时候才会回滚,加上rollbackFor=Exception.class,可以让事物在遇到非运行时异常时也回滚
| 属性 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| value | String | 可选的限定描述符,指定使用的事务管理器 |
| propagation | enum: Propagation | 可选的事务传播行为设置 |
| isolation | enum: Isolation | 可选的事务隔离级别设置 |
| readOnly | boolean | 读写或只读事务,默认读写 |
| timeout | int (in seconds granularity) | 事务超时时间设置 |
| rollbackFor | Class对象数组,必须继承自Throwable | 导致事务回滚的异常类数组 |
| rollbackForClassName | 类名数组,必须继承自Throwable | 导致事务回滚的异常类名字数组 |
| noRollbackFor | Class对象数组,必须继承自Throwable | 不会导致事务回滚的异常类数组 |
| noRollbackForClassName | 类名数组,必须继承自Throwable | 不会导致事务回滚的异常类名字数组 |
注释权限@PreAuthorize
Spring-Security@PreAuthorize(“hasAuthority(‘’)”)源码分析
连接
Spring-Security@PreAuthorize(“hasAuthority(’’)”)源码分析
@PreAuthorize(“hasAuthority(‘xxx’)”)用来鉴别当前登录用户所拥有的角色是否有xxx权限访问该接口。
点进去看看security是如何来鉴权的。
这里authority即为我们传入的权限,比如prod:create,接下来再看this.hasAnyAuthority如何处理这个权限字符串吧。
翻看源码的话会发现其实hasAnyAuthority方法就在hasAuthority方法的下面,该访问hasAnyAuthorityName了,我们传入的权限字符串(prod:create)就像皮球一样被踢到了hasAnyAuthorityName脚下了~
该方法终于要射门了!
首行为 Set roleSet = this.getAuthoritySet(); 点进去getAuthorityeSet()方法看到
该方法为获取当前用户所拥有角色的所有权限,Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> userAuthorities = this.authentication.getAuthorities();此行为登录操作时应访问数据库将用户权限放入authentication中,也就是说,这一行将会把该用户所持角色的所有权限都查询出来。
此时我们的鉴权字符串(“prod:create”)被守门员getRoleWithDefaultPrefix()拿下,来看看守门员是怎么守住这球的:
原来是判断一下这球是不是假动作啊,该方法会对传入的(prod:create)进行组装,前面传入的这个defaultRolePrefix为null,所以直接返回role即可,也就是我们一开始传入的“prod:create”。
该比对了,prod:create字符串在权限集合roleSet中,即该用户有访问该接口的权限。
总的来说,鉴权过程为:从数据库中查询出当前登录用户的所有权限并交给security管理;注解@PreAuthorize(“hasAuthority(‘xxx’)”)来判断“xxx”是否在当前登录用户的权限集合中,在则200,不在则403。
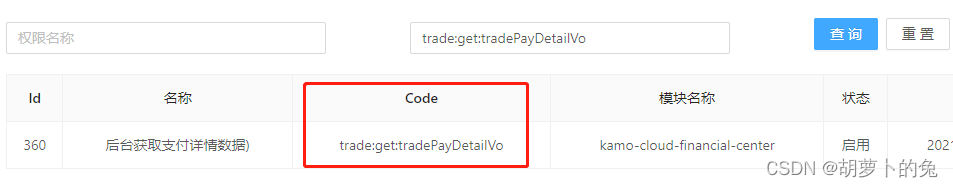
@GetMapping("/adm/adminTradeController/detail")
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('trade:get:tradePayDetailVo')")
@ApiOperation(value = "后台获取支付详情数据)")
@ApiImplicitParams({
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "tradeId", value = "订单ID", required = true, dataType = "int", example = "0"),
})
@LogAnnotation
public Result<TradePayDetailVo> tradePayDetailVo(@RequestParam("tradeId") Integer tradeId) {
return tradeService.getTradePayDetailVo(tradeId);
}
@PreAuthorize(“hasAuthority(‘trade:get:tradePayDetailVo’)”)
@Component注解的作用
Spring自带的@Component注解及扩展:
@Component:定义Spring管理Bean(也就是将标注@Component注解的类交由spring管理)
@AspectJ风格的切面可以通过@Compenent注解标识其为Spring管理Bean,而@Aspect注解不能被Spring自动识别并注册为Bean,必须通过@Component注解来完成
@Component
@Aspect
@Order(5)
@Slf4j
public class ReportAspect {
@Autowired
private ThirdFeignClient thirdFeignClient;
@Pointcut("@within(com.kamowl.kamo.cloud.third.open.annotation.Report) || @annotation(com.kamowl.kamo.cloud.third.open.annotation.Report)")
public void pointCut() {
}
@AfterReturning(pointcut = "pointCut() && @annotation(report)", returning = "methodResult")
public void doAfterAdvice(JoinPoint joinPoint, Report report, Object methodResult) {
Result result = (Result) methodResult;
ReportChannel[] channels = report.channel();
for (ReportChannel channel : channels) {
thirdFeignClient.upload(assembleReport(channel, report.type(), result.getData() + ""));
}
}
private ReportDto assembleReport(ReportChannel channel, ReportType type, String uniqueId) {
ReportDto reportDto = new ReportDto();
reportDto.setChannel(channel);
reportDto.setType(type);
reportDto.setUniqueId(uniqueId);
return reportDto;
}
}
springboot2 valid @RequestBody @Valid 校验失效
https://blog.csdn.net/xxpxxpoo8/article/details/127551926