文章目录
- 1. 类和结构体
- 1.1 类的定义
- 1.2 类的使用
- 1.3 结构体
- 1.4 构造函数
- 2. 指针和引用
- 2.1 指针
- 2.2 数组
- 2.3 引用
- 2.4 查询地址
- 3. 链表
-
1. 类和结构体
1.1 类的定义
class Person
{
private:
int age, height;
double money;
string books[100];
public:
string name;
void say()
{
cout << "I'm " << name << endl;
}
int get_age
{
return age;
}
void add_money(double x)
{
money += x;
}
);
- 类中的变量和函数被统一称为类的成员变量
- private后面的内容是私有成员变量,在类的外部不能访问;public后面的内容是公有成员变量,在类的外部可以访问
1.2 类的使用
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1000010;
class Person
{
private:
int age, height;
double money;
string books[100];
public:
string name;
void say()
{
cout << "I'm " << name << endl;
}
int set_age(int a)
{
age = a;
}
int get_age()
{
return age;
}
void add_money(double x)
{
money += x;
}
} person_a, person_b, persons[100];
int main()
{
Person persons[100];
Person c;
c.name = "yxc";
c.age = 18;
c.set_age(18);
c.add_money(100);
c.say();
cout << c.get_age() << endl;
return 0;
}
- 结构体和类的作用是一样的。不同点在于类默认是private,结构体默认是public
1.3 结构体
- 结构体和类的作用是一样的。不同点在于类默认是private,结构体默认是public
struct Person
{
private:
int age, height;
double money;
string books[100];
int get_height()
{
return height;
}
public:
string name;
void say()
{
cout << "I'm " << name << endl;
}
int get_age
{
return age;
}
void add_money(double x)
{
money += x;
}
)person_a, person_b, persons[100];
1.4 构造函数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Person
{
int age, height;
double money;
Person() {}
Person (int _age. int _height) : age(_age), hight(_hight) {}
Person(int _age, int _height, double _money)
{
age = _age;
height = _height;
money = _money;
}
Person(int _age, int _height, double _money) : age(_age), hight(_hight), money(_money){}
};
int main()
{
Person p;
Person p(18, 180, 100.0);
Person p = {18, 180, 100.0};
return 0;
}
2. 指针和引用
2.1 指针
- 指针指向存放变量的值的地址,因此我们可以通过指针来修改变量的值
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = 10;
int* p = &a;
*p += 5;
cout << *p << endl;
return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = 10;
int* p = &a;
int** q = &p;
cout << q << endl;
cout << *p << endl;
*p = 12;
cout << *p << endl;
cout << a << endl;
return 0;
}
2.2 数组
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[5] = {1,2,3,4,5};
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) cout << *(a + i) << endl;
return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char c;
int a[5] = {1,2,3,4,5};
int* p = &a[0], *q = &a[1];
cout << q - p << endl;
return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
char a, b;
int main()
{
char c;
int a[5] = {1,2,3,4,5};
cout << (void*)&c << endl;
cout << a << endl;
for(int i = 0;i < 5;i++)
cout << (void*)&a[i] << endl;
return 0;
}
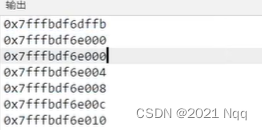
- 数组地址间隔4个字节,int型是4个字节
2.3 引用
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = 10;
int &p = a;
p += 5;
cout << p << endl;
return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = 10;
int* p = a;
int& p = a;
p += 5;
cout << p << endl;
return 0;
}
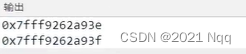
2.4 查询地址
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char c = 'a', b;
cout << (void*)&c << endl;
cout << (void*)&b << endl;
return 0;
}
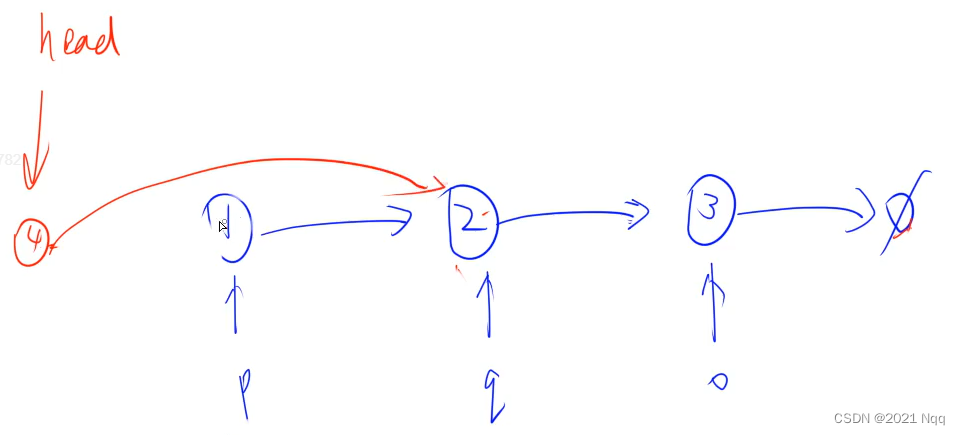
3. 链表
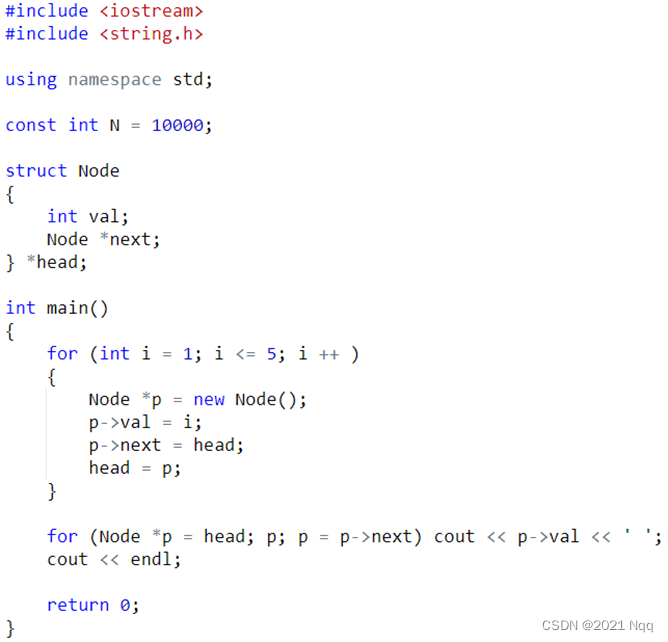
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int val;
Node* next;
Node(int _val) : val(_val), next(NULL) {}
}*head;
int main()
{
Node* p = new Node(1);
Node* q = new Node(2);
auto o = new Node(3);
p->next = q;
q->next = o;
Node* u = new Node(4);
u->next = head;
head = u;
head->next = head->next->next;
Node* head = p;
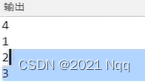
for(Node* i = head; i != 0; i = i->next)
cout << i->val << endl;
return 0;
}
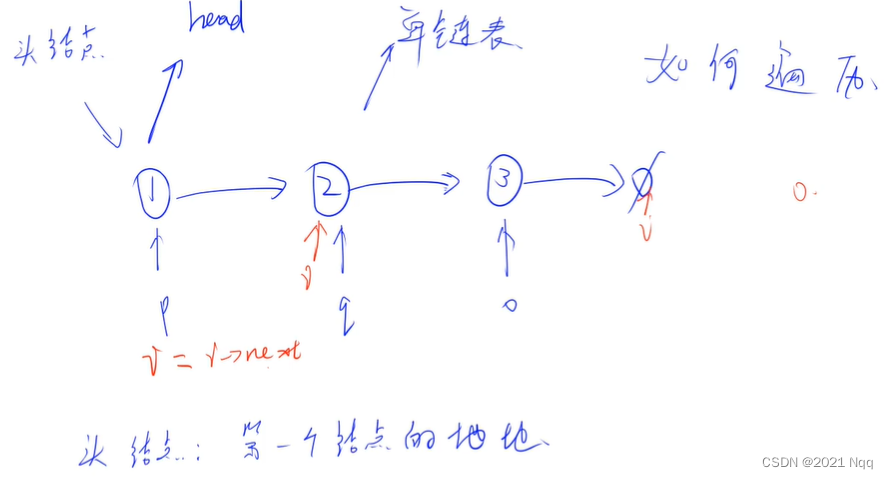
3.1 添加结点
Node* u = new Node(4);
u->next = head;
head = u;
- u->next = head; 将head赋值给u->next
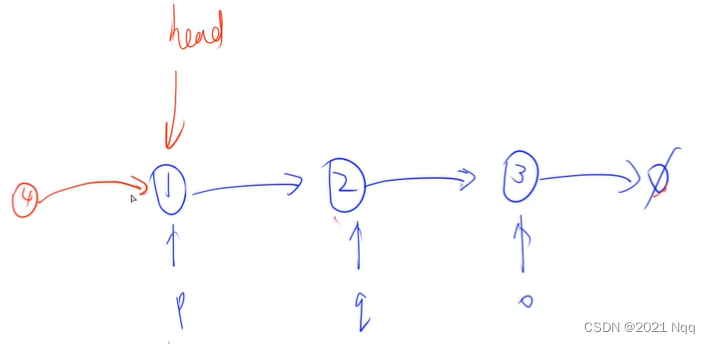
- head = u; 将结点u赋值给head
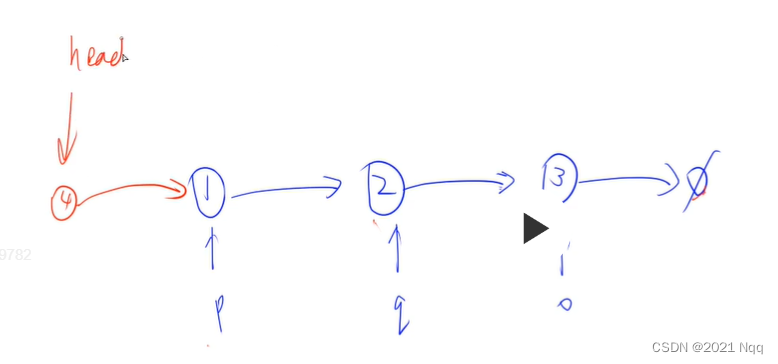
3.2 删除结点

head->next = head->next->next;