1.块设备驱动概念
块设备驱动是针对存储设备,例如SD卡、EMMC、NAND FLASH、NOR FLSASH。
块设备驱动以块为单位进行访问、最小寻址单位是扇区、一个块中包含多个扇区、支持随机访问、带缓冲区,,当发生写入操作时,并不会立马操作硬盘,因为写之前要擦除,擦写频繁影响flash寿命。对于flash设备而言,顺序读写扇区能极大提升效率,所以对于不对存储设备,Linux里有实现不同的I/O调度算法。
而字符设备以字节为单位,不需要缓冲,只能被顺序读写。
借鉴一张在网上找到的图片,框架图当然是学习中必不可备的东西,一眼便能有个清晰的认识
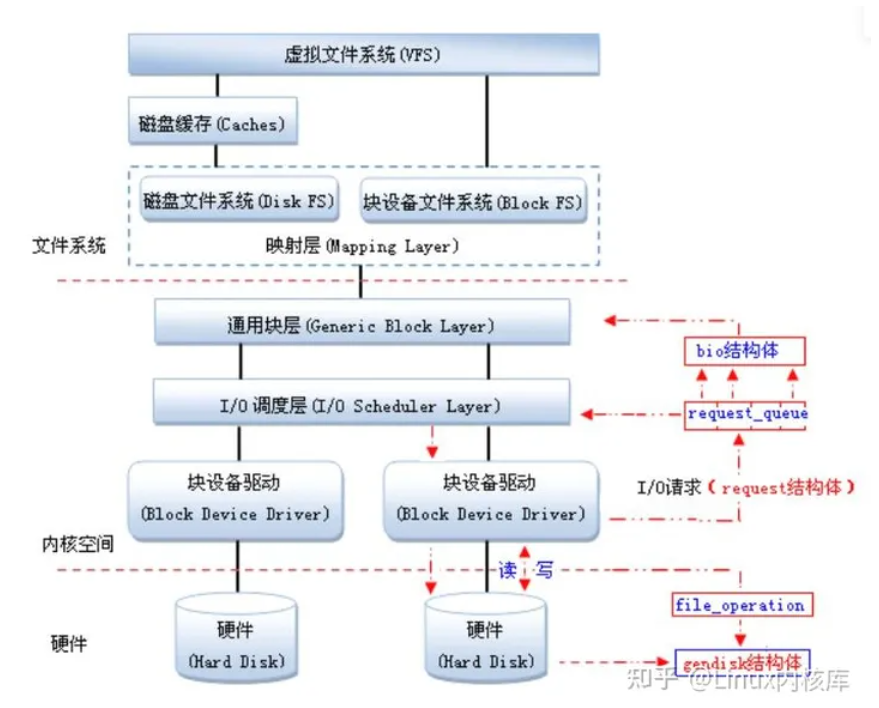
其中块设备驱动请求有两种形式,使用requeset_queue请求队列,以及不使用请求队列的。
2.常用结构体
2.1 block_device结构体
linux内核使用 block_device结构体表示块设备对象, 定义在include/linux/fs.h文件。
struct block_device {
dev_t bd_dev; /* not a kdev_t - it's a search key */
int bd_openers;
struct inode * bd_inode; /* will die */
struct super_block * bd_super;
struct mutex bd_mutex; /* open/close mutex */
struct list_head bd_inodes;
void * bd_claiming;
void * bd_holder;
int bd_holders;
bool bd_write_holder;
#ifdef CONFIG_SYSFS
struct list_head bd_holder_disks;
#endif
struct block_device * bd_contains;
unsigned bd_block_size;
struct hd_struct * bd_part;
/* number of times partitions within this device have been opened. */
unsigned bd_part_count;
int bd_invalidated;
struct gendisk * bd_disk;
struct request_queue * bd_queue;
struct list_head bd_list;
/*
* Private data. You must have bd_claim'ed the block_device
* to use this. NOTE: bd_claim allows an owner to claim
* the same device multiple times, the owner must take special
* care to not mess up bd_private for that case.
*/
unsigned long bd_private;
/* The counter of freeze processes */
int bd_fsfreeze_count;
/* Mutex for freeze */
struct mutex bd_fsfreeze_mutex;
};
2.2 gendisk结构体
linux 内核使用 gendisk 来描述一个磁盘设备,定义include/linux/genhd.h。
struct gendisk {
/* major, first_minor and minors are input parameters only,
* don't use directly. Use disk_devt() and disk_max_parts().
*/
int major; /* major number of driver */
int first_minor;
int minors; /* maximum number of minors, =1 for
* disks that can't be partitioned. */
char disk_name[DISK_NAME_LEN]; /* name of major driver */
char *(*devnode)(struct gendisk *gd, umode_t *mode);
unsigned int events; /* supported events */
unsigned int async_events; /* async events, subset of all */
/* Array of pointers to partitions indexed by partno.
* Protected with matching bdev lock but stat and other
* non-critical accesses use RCU. Always access through
* helpers.
*/
struct disk_part_tbl __rcu *part_tbl;
struct hd_struct part0;
const struct block_device_operations *fops;
struct request_queue *queue;
void *private_data;
int flags;
struct device *driverfs_dev; // FIXME: remove
struct kobject *slave_dir;
struct timer_rand_state *random;
atomic_t sync_io; /* RAID */
struct disk_events *ev;
#ifdef CONFIG_BLK_DEV_INTEGRITY
struct blk_integrity *integrity;
#endif
int node_id;
};
major:主设备号
first_minor:第一个次设备号
minors:次设备号数量
part_tbl:磁盘对应的分区表
fops:块设备操作集
queue:磁盘对应的请求队列
2.3 block_device_operations 结构体
struct block_device_operations {
int (*open) (struct block_device *, fmode_t);
void (*release) (struct gendisk *, fmode_t);
int (*rw_page)(struct block_device *, sector_t, struct page *, int rw);
int (*ioctl) (struct block_device *, fmode_t, unsigned, unsigned long);
int (*compat_ioctl) (struct block_device *, fmode_t, unsigned, unsigned long);
long (*direct_access)(struct block_device *, sector_t,
void **, unsigned long *pfn, long size);
unsigned int (*check_events) (struct gendisk *disk,
unsigned int clearing);
/* ->media_changed() is DEPRECATED, use ->check_events() instead */
int (*media_changed) (struct gendisk *);
void (*unlock_native_capacity) (struct gendisk *);
int (*revalidate_disk) (struct gendisk *);
int (*getgeo)(struct block_device *, struct hd_geometry *);
/* this callback is with swap_lock and sometimes page table lock held */
void (*swap_slot_free_notify) (struct block_device *, unsigned long);
struct module *owner;
};
open :打开指定的块设备
release:释放指定块设备
rw_page :数用于读写指定的页
ioctl:块设备IO控制
compat_ioctl:32位设备调用的ioctl函数
getgeo:获取磁盘信息,包括磁头、柱面和扇区
owner:标明属于哪个模块
3.块设备操作常用API
3.1块设备操作
1)注册块设备
int register_blkdev(unsigned int major, const char *name)
2)注销块设备
void unregister_blkdev(unsigned int major, const char *name)
major:主设备号
name:块设备名字
3.2gendisk相关操作
1)申请gendisk
struct gendisk *alloc_disk(int minors)
minors:次设备号数量、即gendisk对应的分区数量
2)删除 gendisk
void del_gendisk(struct gendisk *gp)
3)将 gendisk 添加到内核
void add_disk(struct gendisk *disk)
disk:要添加的gendisk结构体
4)设置 gendisk 容量
void set_capacity(struct gendisk *disk, sector_t size)
size:扇区数量大小,块设备驱动之间的扇区固定512字节,无论物理扇区是多大
5)增加gendisk 引用计数
struct kobject *get_disk(struct gendisk *disk)
5)减小gendisk 引用计数
void put_disk(struct gendisk *disk)
4.块设备IO请求过程
4.1 请求队列 request_queue
内核将块设备的读写,都放入到请求队列request_queue中,通过request请求,其中包含块设备从哪个地址读取,读取的数据长度,读取到哪里等。每个gendisk结构体中都有一个requeset_queue,即每个磁盘gendisk都会分配一个request_queue。
初始化请求队列之后,赋值给gendisk的queue成员变量
1)初始化请求队列(使用默认IO调度器)
当访问外部硬件、光盘、磁盘等,需要控制访问顺序来提升访问效率,则需要使用默认IO调度器,即需要使用这个API。
request_queue *blk_init_queue(request_fn_proc *rfn, spinlock_t *lock)
rfn:请求处理函数指针
lcok:自旋锁指针
2)删除请求队列
void blk_cleanup_queue(struct request_queue *q)
q:删除的请求队列
3)分配请求队列(不使用默认IO调度器),并绑定制造请求函数
当访问简单的SD卡等,可以进行随机访问,不需要控制访问顺序来提升访问效率,则不需要设置IO调度器,即可直接使用这个API。
struct request_queue *blk_alloc_queue(gfp_t gfp_mask)
gfp_mask : 内存分配的方式。 GFP_KERNEL和GFP_ATOMIC,
GFP_ATOMIC: 用来从中断处理和进程上下文之外的其他代码中分配内存. 从不睡眠
GFP_KERNEL: 内核内存的正常分配. 可能睡眠
void blk_queue_make_request(struct request_queue *q, make_request_fn *mfn)
mfs:make_request_fn函数指针
blk_alloc_queue不使用默认IO调度器,需要自己实现mfs函数。上层代码向请求队列发生请求,调用make_request_fn函数。
4.2 请求request
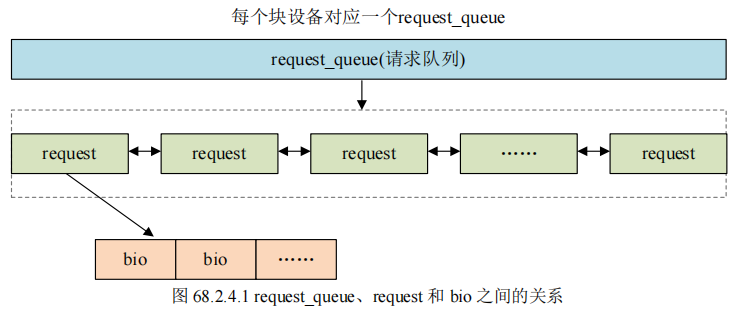
请求队列(request_queue)里面包含的就是一系列的请求(request),其中的bio成员变量保存真正的数据。
1)获取请求
从request_queue中依次获取每个request
request *blk_peek_request(struct request_queue *q)
q:指定request_queue
返回值:request_queue 中下一个要处理的请求(request)
2)开启请求
从request_queue中获取到request后,调用该函数开始处理这个request
void blk_start_request(struct request *req)
**req:**要开始处理的请求
3)获取并处理请求
一次性完成请求的获取和开启
struct request *blk_fetch_request(struct request_queue *q)
4)其他API
blk_end_request() //请求中指定字节数据被处理完成。
blk_end_request_all() //请求中所有数据全部处理完成。
blk_end_request_cur() //当前请求中的 chunk。
blk_end_request_err() //处理完请求,直到下一个错误产生。
__blk_end_request() //和 blk_end_request 函数一样,但是需要持有队列锁。
__blk_end_request_all() //和 blk_end_request_all 函数一样,但是需要持有队列锁。
__blk_end_request_cur() //和 blk_end_request_cur 函数一样,但是需要持有队列锁。
__blk_end_request_err() //和 blk_end_request_err 函数一样,但是需要持有队列锁
4.3 bio结构
每个 request 里面会有多个 bio,bio 保存着最终要读写的数据、地址等信息。
从 request_queue 中取出一个一个的 request,然后再从每个 request 里面取出 bio, 最后根据 bio 的描述讲数据写入到块设备,或者从块设备中读取数据
源码如下:
struct bio {
struct bio *bi_next; /* request queue link */
struct block_device *bi_bdev;
unsigned long bi_flags; /* status, command, etc */
unsigned long bi_rw; /* bottom bits READ/WRITE,
* top bits priority
*/
struct bvec_iter bi_iter;
/* Number of segments in this BIO after
* physical address coalescing is performed.
*/
unsigned int bi_phys_segments;
/*
* To keep track of the max segment size, we account for the
* sizes of the first and last mergeable segments in this bio.
*/
unsigned int bi_seg_front_size;
unsigned int bi_seg_back_size;
atomic_t bi_remaining;
bio_end_io_t *bi_end_io;
void *bi_private;
#ifdef CONFIG_BLK_CGROUP
/*
* Optional ioc and css associated with this bio. Put on bio
* release. Read comment on top of bio_associate_current().
*/
struct io_context *bi_ioc;
struct cgroup_subsys_state *bi_css;
#endif
union {
#if defined(CONFIG_BLK_DEV_INTEGRITY)
struct bio_integrity_payload *bi_integrity; /* data integrity */
#endif
};
unsigned short bi_vcnt; /* how many bio_vec's */
/*
* Everything starting with bi_max_vecs will be preserved by bio_reset()
*/
unsigned short bi_max_vecs; /* max bvl_vecs we can hold */
atomic_t bi_cnt; /* pin count */
struct bio_vec *bi_io_vec; /* the actual vec list */
struct bio_set *bi_pool;
/*
* We can inline a number of vecs at the end of the bio, to avoid
* double allocations for a small number of bio_vecs. This member
* MUST obviously be kept at the very end of the bio.
*/
struct bio_vec bi_inline_vecs[0];
};
struct bvec_iter {
sector_t bi_sector; /* I/O 请求的设备起始扇区(512 字节) */
unsigned int bi_size; /* 剩余的 I/O 数量 */
unsigned int bi_idx; /* blv_vec 中当前索引 */
unsigned int bi_bvec_done; /* 当前 bvec 中已经处理完成的字节数 */
};
struct bio_vec {
struct page *bv_page; /* 页 */
unsigned int bv_len; /* 长度 */
unsigned int bv_offset; /* 偏移 */
};
其中的bio与bio_iter 与 bio_vec之间的关系如下图所示,他们协同完成描述了数据源、数据长度以及数据目的地。
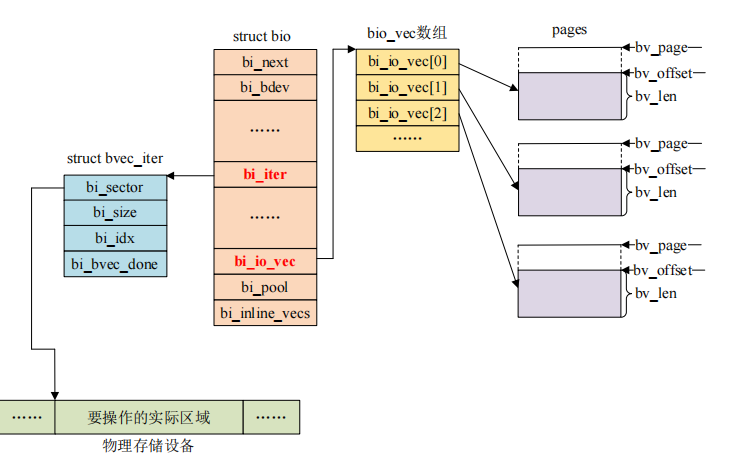
4.3.1 bio操作API
/// 遍历bio请求
#define __rq_for_each_bio(_bio, rq) \
if ((rq->bio)) \
for (_bio = (rq)->bio; _bio; _bio = _bio->bi_next)
/// 遍历bio中的段
#define bio_for_each_segment(bvl, bio, iter) \
__bio_for_each_segment(bvl, bio, iter, (bio)->bi_iter)
/// 通知bio处理函数
/// 当不使用默认IO调度器,而使用blk_alloc_queue 自己实现制造请求
/// 则在bio处理完成后要通知内核bio处理完成
bvoid bio_endio(struct bio *bio, int error);
![[2024-03-09 19:55:01] [42000][1067] Invalid default value for ‘create_time‘【报错】](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/3434d33fe79644ccb392a322885281c3.png)