实验指南
运行环境:
Dev c++
算法思想:
将处理机的运行时间划分成等长的时间片,转轮式分配给各个就绪进程使用。
采用此算法的系统中,所有就绪进程按照先来先服务的原则排成一个队列,每次调度时将处理机分派给队首进程。如果进程在一个时间片内没有执行完,那么调度程序强行将该进程中止,进程由执行态变为就绪态,并把处理机分配给下一个就绪进程。
核心数据结构定义:
typedef struct data{
int hour;
int minute;
}time;
typedef struct node{
int id;//进程编号
char name[20];//进程名
time arrive;//到达就绪队列的时间
int zx;//执行时间
time start;//开始执行时间
time finish;//执行完成时间
int zz;//周转时间=执行完成时间-到达就绪队列时间
float zzxs;//带权周转时间=周转时间/执行时间
time current;//当前进程开始执行的时间
int ywcsj;//进程已经完成的时间
int sysj; //当前进程的剩余时间
struct node* next;
}Node;
typedef struct Queue{
Node* front = NULL;
Node* tail = NULL;
}Queue;
程序主体框架:
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
typedef struct data{
int hour;
int minute;
}time;
typedef struct node{
int id;//进程编号
char name[20];//进程名
time arrive;//到达就绪队列的时间
int zx;//执行时间
time start;//开始执行时间
time finish;//执行完成时间
int zz;//周转时间=执行完成时间-到达就绪队列时间
float zzxs;//带权周转时间=周转时间/执行时间
time current;//当前进程开始执行的时间
int ywcsj;//进程已经完成的时间
int sysj; //当前进程的剩余时间
struct node* next;
}Node;
typedef struct Queue{
Node* front = NULL;
Node* tail = NULL;
}Queue;
Queue* init(){
Queue* p = (Queue*)malloc(sizeof(Queue));
p->front = NULL;
p->tail = NULL;
return p;
}
//函数名:timecompare 函数参数:,tt(系统计时),p(当前进程的到达时间)
bool timecompare(time tt,time p){
//函数功能:比较时间大小,tt<p返回false,否则返回true
}
//函数名:Namecompare 函数参数:,s1(进程名称),s2(进程名称)
bool Namecompare(string s1,string s2){
//函数功能:比较名字大小,s1<s2返回true,否则返回false
}
//函数名:Choose 函数参数:,p(进程指针),q(进程指针),flag(选择标志)
bool Choose(Node* p, Node* q,int flag){
//函数功能:选择比较函数比较名字大小,flag==1返回时间比较结果取反,否则返回名字比较结果
}
//函数名:Time_or_Name_Sorted 函数参数:,que(队列指针),flag(选择标志)
void Time_or_Name_Sorted(Queue* que,int flag){
//函数功能:选择排序函数并对进程进行排序,flag==1返回时间排序,否则返回名字排序
}
//函数名:ComputeTime 函数参数:,tt(时间指针),q(结点指针),tp(时间片)
time ComputeTime(time* tt,Node* q,int tp){
//函数功能:
//进程还未开始,首次更新进程的开始时间,并且每次重新定义进程执行的当前时间
//根据剩余时间与时间片的关系进行讨论
//更新进程的完成时间和周转时间,带权周转时间 ,最后返回时间指针
//调用timecompare()函数来寻找已到达的进程
//调用ComputeTime()函数来计算相关时间并更新进程信息
}
//函数名:Print_Current 函数参数:,que(队列指针),tt(系统时间),i(时间轮转次数)
void Print_Current(Queue* que,time tt,int i){
//函数功能:输出第i次时间轮转的进程信息,置前进程开始执行的时间为0
}
//函数名:Time_Slice_Rotation 函数参数:,que(队列指针),tp(时间片)
Queue* Time_Slice_Rotation(Queue *que,int tp){
//函数功能:模拟时间片轮转算法,分三种情况讨论:
//当前进程执行完
//当前进程未执行完
//除当前进程以外就绪队列队列为空,当前进程继续执行
另外还要考虑就绪队列为空,诞下一个进程还未达到的情况。
}
//函数名:Print 函数参数:,que(队列指针),n(进程数)
void Print(Queue* que,int n){
//函数功能:输出所有进程完成后的信息以及系统平均周转时间和系统平均带权周转系数
}
//函数名:ScanIn 函数参数:,wait(队列指针),n(进程数)
void ScanIn(Queue* wait,int n){
//函数功能:输入相关进程及信息
}
int main(){
Queue* wait;
wait = init();
int flag,n,t;
time earlytime;
while(1){
printf("请输入操作:(1:开始进程;0:结束进程):");
scanf("%d",&flag);
if(flag == 0){
printf("\n操作结束!\n");
break;
}
else{
printf("请输入进程数量:\n");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("请输入时间片时间:\n");
scanf("%d",&t);
ScanIn(wait,n);
Time_or_Name_Sorted(wait,1);//timesort
wait = Time_Slice_Rotation(wait,t);
Time_or_Name_Sorted(wait,0);//namesort
Print(wait,n);
wait = init();
}
}
return 0;
}
测试用例:
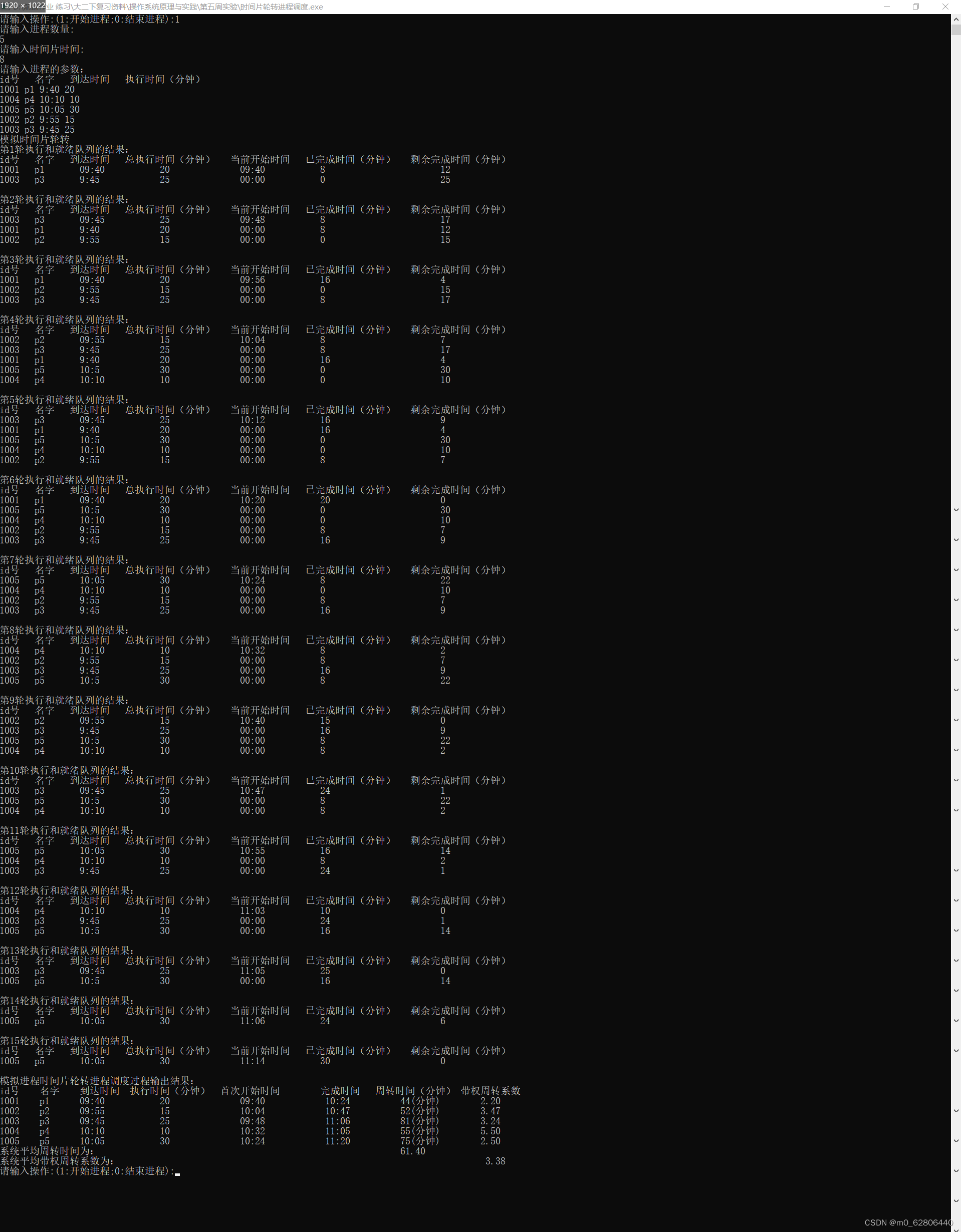
用例一:
1001 p1 9:40 20
1004 p4 10:10 10
1005 p5 10:05 30
1002 p2 9:55 15
1003 p3 9:45 25用例二:
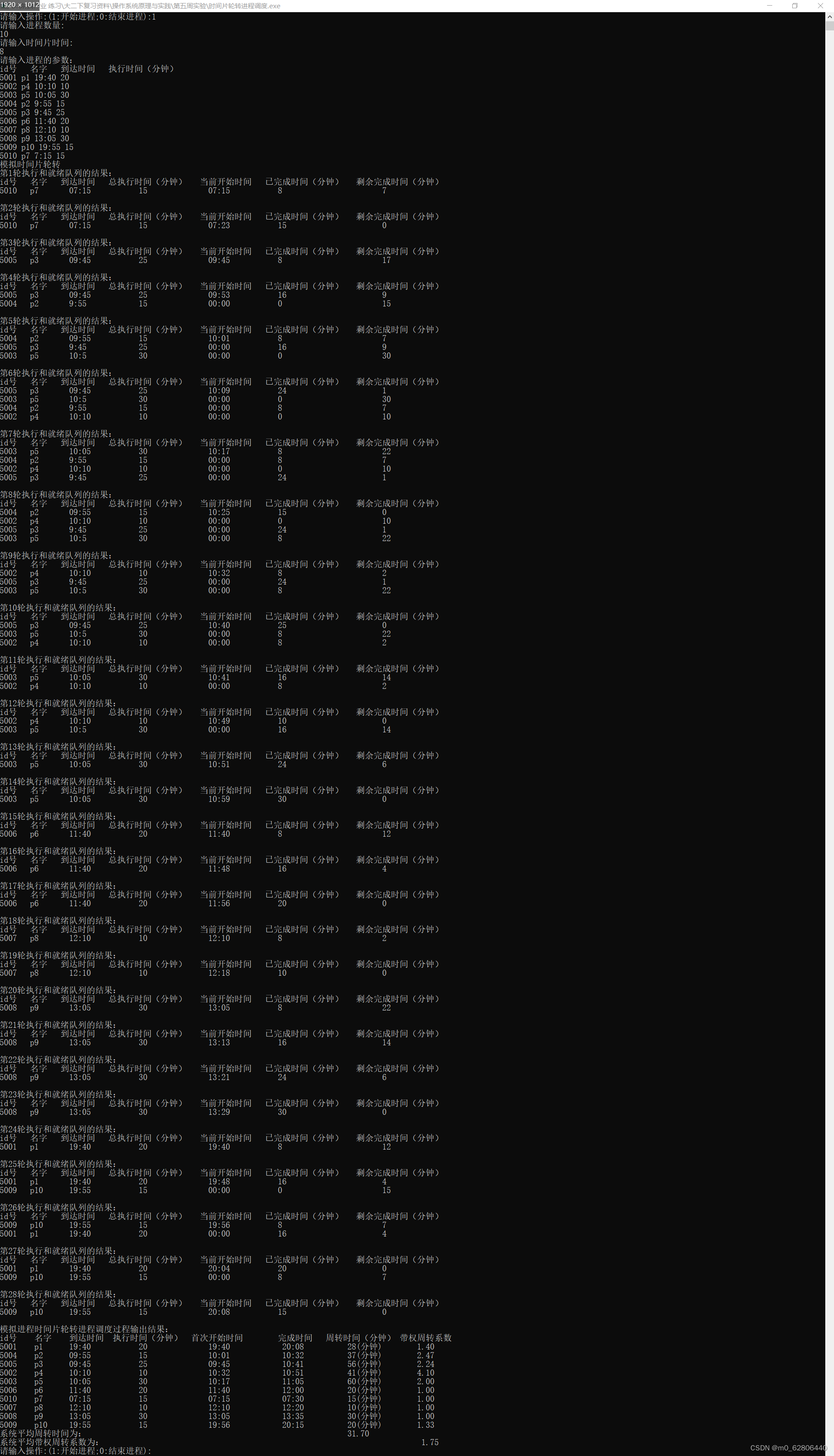
5001 p1 19:40 20
5002 p4 10:10 10
5003 p5 10:05 30
5004 p2 9:55 15
5005 p3 9:45 25
5006 p6 11:40 20
5007 p8 12:10 10
5008 p9 13:05 30
5009 p10 19:55 15
5010 p7 7:15 15
关键代码
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
typedef struct data{
int hour;
int minute;
}time;
typedef struct node{
int id;//进程编号
char name[20];//进程名
time arrive;//到达就绪队列的时间
int zx;//执行时间
time start;//开始执行时间
time finish;//执行完成时间
int zz;//周转时间=执行完成时间-到达就绪队列时间
float zzxs;//带权周转时间=周转时间/执行时间
time current;//当前进程开始执行的时间
int ywcsj;//进程已经完成的时间
int sysj; //当前进程的剩余时间
struct node* next;
}Node;
typedef struct Queue{
Node* front = NULL;
Node* tail = NULL;
}Queue;
Queue* init(){
Queue* p = (Queue*)malloc(sizeof(Queue));
p->front = NULL;
p->tail = NULL;
return p;
}
//函数名:timecompare 函数参数:,tt(系统计时),p(当前进程的到达时间)
bool timecompare(time tt,time p){
//函数功能:比较时间大小,tt<p返回false,否则返回true
if((tt.hour<p.hour)||((tt.hour==p.hour)&&(tt.minute<p.minute)))
return false;
else
return true;
}
//函数名:Namecompare 函数参数:,s1(进程名称),s2(进程名称)
bool Namecompare(string s1,string s2){
//函数功能:比较名字大小,s1<s2返回true,否则返回false
const char* p = s1.data();
const char* p2 = s2.data();
if(strlen(p)<strlen(p2))
return true;
else if(strlen(p)==strlen(p2))
{
if(strcmp(p,p2)<0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
else
return false;
}
//函数名:Choose 函数参数:,p(进程指针),q(进程指针),flag(选择标志)
bool Choose(Node* p, Node* q,int flag){
//函数功能:选择比较函数比较名字大小,flag==1返回时间比较结果取反,否则返回名字比较结果
}
//函数名:Time_or_Name_Sorted 函数参数:,que(队列指针),flag(选择标志)
void Time_or_Name_Sorted(Queue* que,int flag){
//函数功能:选择排序函数并对进程进行排序,flag==1返回时间排序,否则返回名字排序
Node *head=NULL,*pre,*q,*bl;
bl=que->front;
if(flag==1)
{
while(bl!=NULL)
{
Node *p=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
*p=*bl;
p->next=NULL;
q=head;
if(head==NULL)
{//printf("创建链表为空\n");
head=p;
q=head;
}
else
{//printf("创建链表不为空\n");
while(q!=NULL)
{
if(timecompare(p->arrive,head->arrive)==false)
{//printf("插头\n");
p->next=head;
head=p;
break;
}
else if(timecompare(p->arrive,q->arrive)==false)
{//printf("插中间\n");
p->next=q;
pre->next=p;
break;
}
else if(timecompare(p->arrive,q->arrive)&&q->next==NULL)
{//printf("插末尾\n");
q->next=p;
break;
}
pre=q;
q=q->next;
}
}
bl=bl->next;
}
}
else
{
string s1,s2,sh;
while(bl!=NULL)
{
Node *p=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
*p=*bl;
p->next=NULL;
q=head;
s1=p->name;
if(head==NULL)
{//printf("创建链表为空\n");
head=p;
q=head;
}
else
{//printf("创建链表不为空\n");
sh=head->name;
while(q!=NULL)
{ s2=q->name;
if(Namecompare(s1,sh))
{//printf("插头\n");
p->next=head;
head=p;//head就是头指针,没有next!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
break;
}
else if(Namecompare(s1,s2))
{//printf("插中间\n");
p->next=q;
pre->next=p;
break;
}
else if(!Namecompare(s1,s2)&&q->next==NULL)
{//printf("插末尾\n");
q->next=p;
break;
}
pre=q;
q=q->next;
}
}
bl=bl->next;
}
}
que->front=head;
que->tail=pre;
}
//函数名:ComputeTime 函数参数:,tt(时间指针),q(结点指针),tp(时间片)
time ComputeTime(time* tt,Node* q,int tp){
//函数功能:
//进程还未开始,首次更新进程的开始时间,并且每次重新定义进程执行的当前时间
//根据剩余时间与时间片的关系进行讨论
//更新进程的完成时间和周转时间,带权周转时间 ,最后返回时间指针
//调用timecompare()函数来寻找已到达的进程
//调用ComputeTime()函数来计算相关时间并更新进程信息
}
//函数名:Print_Current 函数参数:,que(队列指针),tt(系统时间),i(时间轮转次数)
void Print_Current(Queue* que,time tt,int i){
//函数功能:输出第i次时间轮转的进程信息,置前进程开始执行的时间为0
}
//函数名:Time_Slice_Rotation 函数参数:,que(队列指针),tp(时间片)
Queue* Time_Slice_Rotation(Queue *que,int tp){
//函数功能:模拟时间片轮转算法,分三种情况讨论:
//当前进程执行完
//当前进程未执行完
//除当前进程以外就绪队列队列为空,当前进程继续执行
//另外还要考虑就绪队列为空,诞下一个进程还未达到的情况。
printf("模拟时间片轮转\n");
int l=0;
Node *bl,*wait,*q,*bl1,*pre,*prep;
bl=que->front;
while(bl!=NULL)//设置剩余时间为执行的全部时间
{
bl->sysj=bl->zx;
bl->ywcsj=0;
bl->current.hour=0;
bl->current.minute=0;
bl=bl->next;
}
bl=que->front;
wait=NULL;
time tt;
tt.hour=bl->arrive.hour;
tt.minute=bl->arrive.minute;
while(!(bl==NULL&&wait==NULL))
{
if(wait==NULL)
{
//printf("如果就绪队列为空\n");
Node*p=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
*p=*bl;
p->next=NULL;
wait=p;
q=wait;
pre=wait;
bl=bl->next;
tt.hour=p->arrive.hour;
tt.minute=p->arrive.minute;
}
while(pre!=NULL)
{//printf("当前时间为%d:%d\n",tt.hour,tt.minute);
pre->current.hour=tt.hour;
pre->current.minute=tt.minute;
if(pre->ywcsj==0)//求最早执行时间
{
bl1=que->front;
while(bl1->id!=pre->id)
{
bl1=bl1->next;
}
bl1->start.hour=tt.hour;
bl1->start.minute=tt.minute;
}
if(pre->sysj-tp>0)//进程未完成
{
pre->sysj=pre->sysj-tp;
pre->ywcsj=pre->ywcsj+tp;
tt.hour=tt.hour+(tt.minute+tp)/60;
tt.minute=(tt.minute+tp)%60;
//printf("进程未完成,当前时间为%d:%d\n",tt.hour,tt.minute);
}
else if(pre->sysj-tp<=0)// 进程已完成
{
tt.hour=tt.hour+(tt.minute+pre->sysj)/60;
tt.minute=(tt.minute+pre->sysj)%60;
pre->sysj=0;
pre->ywcsj=pre->zx;
//printf("进程已完成,当前时间为%d:%d\n",tt.hour,tt.minute);
}
while(bl!=NULL)
{
//printf("找最小时间当前时间为%d:%d\n",tt.hour,tt.minute);
if(!timecompare(bl->arrive,tt))
{//printf("找到提前到达时间");
Node*p=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
*p=*bl;
p->next=NULL;
q->next=p;
q=p;
bl=bl->next;
}
else
break;
}
l++;
Node *c;
c=pre;
printf("第%d轮执行和就绪队列的结果:\n",l);
printf("id号 名字 到达时间 总执行时间(分钟) 当前开始时间 已完成时间(分钟) 剩余完成时间(分钟)\n");
printf("%d %s\t%02d:%02d\t\t%d\t\t%02d:%02d\t\t%d\t\t\t%d\n",c->id,c->name,c->arrive.hour,c->arrive.minute,c->zx,c->current.hour,c->current.minute,c->ywcsj,c->sysj);
c=c->next;
while(c!=NULL)
{
printf("%d %s\t%d:%d\t\t%d\t\t00:00\t\t%d\t\t\t%d\n",c->id,c->name,c->arrive.hour,c->arrive.minute,c->zx,c->ywcsj,c->sysj);
c=c->next;
}
printf("\n");
prep=pre;
pre=pre->next;
prep->next=NULL;
if(prep->sysj==0)
{
bl1=que->front;//求结束时间
while(bl1->id!=prep->id)
{
bl1=bl1->next;
}
bl1->finish.hour=tt.hour;
bl1->finish.minute=tt.minute;
free(prep);
}
else
{
q->next=prep;
q=prep;
}
wait=pre;
if(wait==NULL)
{
if(prep->sysj!=0)
{
wait=prep;
prep->next=NULL;
pre=wait;
}
}
}
}
Node *a;
a=que->front;
while(a!=NULL)
{
a->zz=a->finish.hour*60+a->finish.minute-a->arrive.hour*60-a->arrive.minute;
a->zzxs=a->zz*1.0/a->zx;
a=a->next;
}
return que;
}
//函数名:Print 函数参数:,que(队列指针),n(进程数)
void Print(Queue* que,int n){
//函数功能:输出所有进程完成后的信息以及系统平均周转时间和系统平均带权周转系数
float zzsj=0,dq=0;
Node *p;
p=que->front;
printf("模拟进程时间片轮转进程调度过程输出结果:\n");
printf("id号\t名字\t到达时间 执行时间(分钟) 首次开始时间\t完成时间 周转时间(分钟) 带权周转系数\n");
while(p!=NULL)
{
printf("%d\t%s\t%02d:%02d\t\t%d\t\t%02d:%02d\t\t %02d:%02d\t\t%d(分钟)\t%.2f\n",p->id,p->name,p->arrive.hour,p->arrive.minute,p->zx,p->start.hour,p->start.minute,p->finish.hour,p->finish.minute,p->zz,p->zzxs);
zzsj=zzsj+p->zz;
dq=dq+p->zzxs;
p=p->next;
}
printf("系统平均周转时间为:\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t%.2f\n",zzsj/n);
printf("系统平均带权周转系数为:\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t %.2f\n",dq*1.0/n);
}
//函数名:ScanIn 函数参数:,wait(队列指针),n(进程数)
void ScanIn(Queue* wait,int n){
//函数功能:输入相关进程及信息
int i=n;
printf("请输入进程的参数:\n");
printf("id号 名字 到达时间 执行时间(分钟)\n");
Node *head=NULL,*q;
while(i--)
{
Node *p=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
p->next=NULL;
scanf("%d %s %d:%d %d",&p->id,&p->name,&p->arrive.hour,&p->arrive.minute,&p->zx);
if(head==NULL)
{
head=p;
q=head;
}
else
{
q->next=p;
q=p;
}
}
wait->front=head;
wait->tail=q;
}
int main(){
Queue* wait;
wait = init();
int flag,n,t;
time earlytime;
while(1){
printf("请输入操作:(1:开始进程;0:结束进程):");
scanf("%d",&flag);
if(flag == 0){
printf("\n操作结束!\n");
break;
}
else{
printf("请输入进程数量:\n");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("请输入时间片时间:\n");
scanf("%d",&t);
ScanIn(wait,n);//函数功能:输入相关进程及信息
Time_or_Name_Sorted(wait,1);//timesort
wait = Time_Slice_Rotation(wait,t);//函数功能:模拟时间片轮转算法
Time_or_Name_Sorted(wait,0);//namesort
//函数功能:输出所有进程完成后的信息以及系统平均周转时间和系统平均带权周转系数
Print(wait,n);
wait = init();
}
}
return 0;
}
运行结果
实验总结
①一个重要的逻辑非常重要。
②链表指针的使用错误(如head->next)。
③还是不能运用队列来实现该算法;需要多加学习队列。
④对于这道题,有一些函数没有用上,比如void Print_Current(Queue* que,time tt,int i);time ComputeTime(time* tt,Node* q,int tp);bool Choose(Node* p, Node* q,int flag);因为我对函数的调用不是很理解和熟练,今后会慢慢改进该算法的。
⑤先有想法再实现,如果实在没有思路可以先写写看,不尝试就没有结果。