优质博文:IT-BLOG-CN
一、粘包出现的原因
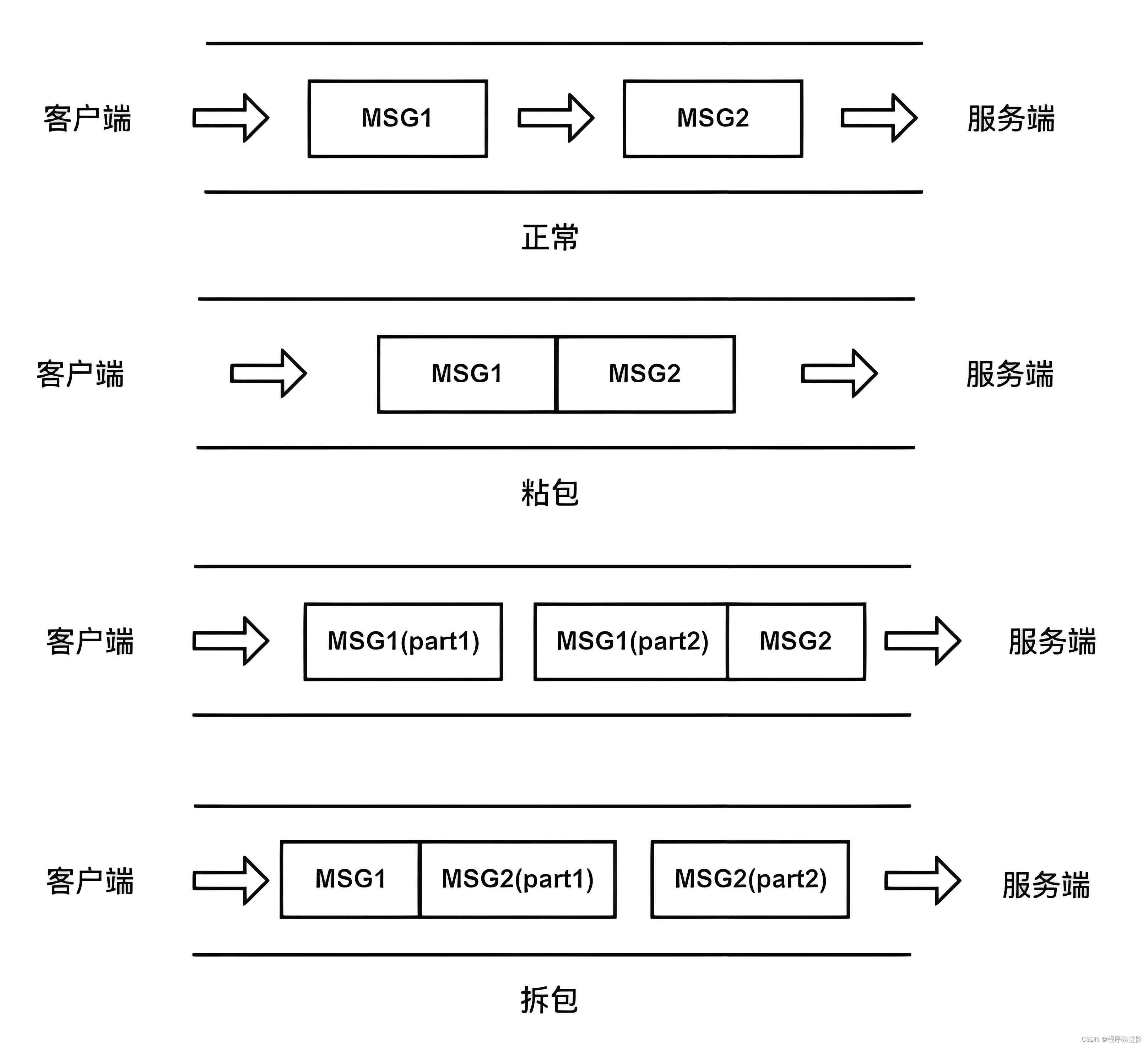
服务端与客户端没有约定好要使用的数据结构。Socket Client实际是将数据包发送到一个缓存buffer中,通过buffer刷到数据链路层。因服务端接收数据包时,不能断定数据包1何时结束,就有可能出现数据包2的部分数据结合数据包1发送出去,导致服务器读取数据包1时包含了数据包2的数据。这种现象称为粘包。
二、案例展示
【1】服务端代码如下,具体注释说明
package com.server;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.Channel;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringEncoder;
/**
* Netty5服务端
* @author zhengzx
*
*/
public class ServerSocket {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建服务类
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
//boss和worker
NioEventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup();
NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
//设置线程池
serverBootstrap.group(boss,worker);
//设置socket工厂,Channel 是对 Java 底层 Socket 连接的抽象
serverBootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
//设置管道工厂
serverBootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
//设置后台转换器(二进制转换字符串)
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringEncoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ServerSocketHandler());
}
});
//设置TCP参数
serverBootstrap.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 2048);//连接缓冲池大小
serverBootstrap.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);//维持连接的活跃,清除死连接
serverBootstrap.childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true);//关闭超时连接
ChannelFuture future = serverBootstrap.bind(10010);//绑定端口
System.out.println("服务端启动");
//等待服务端关闭
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//释放资源
boss.shutdownGracefully();
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
【2】ServerSocketHandler处理类展示:
package com.server;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler;
public class ServerSocketHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<String>{
@Override
protected void messageReceived(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println(msg);
}
}
【3】客户端发送请求代码展示:
package com.client;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException, IOException {
//创建连接
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 10010);
//循环发送请求
for(int i=0;i<1000;i++){
socket.getOutputStream().write("hello".getBytes());
}
//关闭连接
socket.close();
}
}
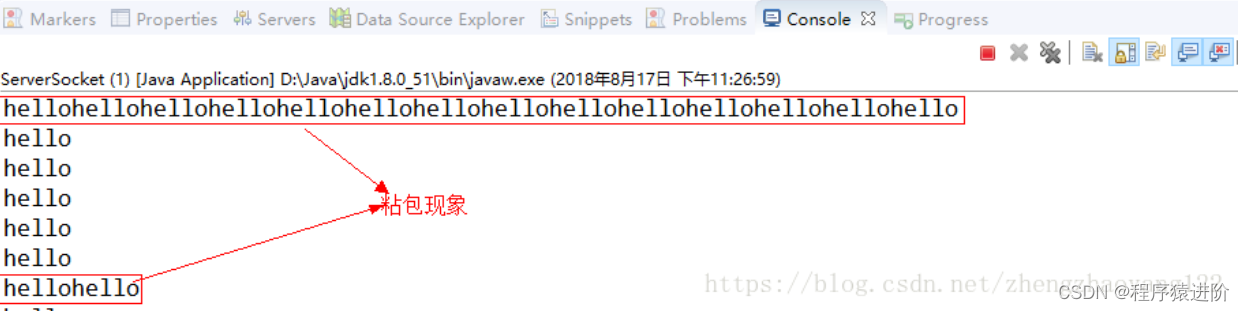
【4】打印结果。(正常情况应为一行一个hello打印)
三、分包
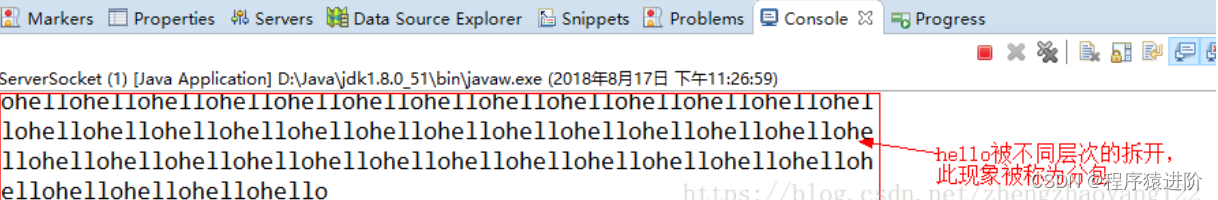
数据包数据被分开一部分发送出去,服务端一次读取数据时可能读取到完整数据包的一部分,剩余部分被第二次读取。具体情况如下图展示:
四、解决办法
方案一:定义一个稳定的结构:
【1】包头+length+数据包: 客户端代码展示:包头用来防止socket攻击,length用来获取数据包的长度。
package com.server;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import org.omg.CORBA.PRIVATE_MEMBER;
import org.omg.CORBA.PUBLIC_MEMBER;
/**
* @category 通过长度+数据包的方式解决粘包分包问题
* @author zhengzx
*
*/
public class Client {
//定义包头
public static int BAO = 24323455;
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException, IOException {
//创建连接
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 10010);
//客户端发送的消息
String msg = "hello";
//获取消息的字节码
byte[] bytes = msg.getBytes();
//初始化buffer的长度:4+4表示包头长度+存放数据长度的整数的长度
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(8+bytes.length);
//将长度和数据存入buffer中
buffer.putInt(BAO);
buffer.putInt(bytes.length);
buffer.put(bytes);
//获取缓冲区中的数据
byte[] array = buffer.array();
//循环发送请求
for(int i=0;i<1000;i++){
socket.getOutputStream().write(array);
}
//关闭连接
socket.close();
}
}
【2】服务端: 需要注意的是,添加了MyDecoder类,此类具体下面介绍
package com.server;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import org.jboss.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.ChannelPipelineFactory;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.Channels;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannelFactory;
import org.jboss.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
import org.jboss.netty.handler.codec.string.StringEncoder;
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//服务类
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
//boss线程监听端口,worker线程负责数据读写
ExecutorService boss = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
ExecutorService worker = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
//设置niosocket工厂
bootstrap.setFactory(new NioServerSocketChannelFactory(boss, worker));
//设置管道的工厂
bootstrap.setPipelineFactory(new ChannelPipelineFactory() {
@Override
public ChannelPipeline getPipeline() throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = Channels.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast("decoder", new MyDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("handler1", new HelloHandler());
return pipeline;
}
});
bootstrap.bind(new InetSocketAddress(10101));
System.out.println("start!!!");
}
}
【3】MyDecode类: 需要继承FrameDecoder类。此类中用ChannelBuffer缓存没有读取的数据包,等接收到第二次发送的数据包时,会将此数据包与缓存的数据包进行拼接处理。当return一个String时,FarmedDecoder通过判断返回类型,调用相应的sendUpStream(event)向下传递数据。源码展示:
public static void fireMessageReceived(
ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object message, SocketAddress remoteAddress) {
ctx.sendUpstream(new UpstreamMessageEvent(
ctx.getChannel(), message, remoteAddress));
}
}
当返回null时,会进行break,不处理数据包中的数据,源码展示:
while (cumulation.readable()) {
int oldReaderIndex = cumulation.readerIndex();
Object frame = decode(context, channel, cumulation);
if (frame == null) {
if (oldReaderIndex == cumulation.readerIndex()) {
// Seems like more data is required.
// Let us wait for the next notification.
break;
} else {
// Previous data has been discarded.
// Probably it is reading on.
continue;
}
}
}
我们自己写的MyDecoder类,代码展示:(包含socket攻击的校验)
package com.server;
import org.jboss.netty.buffer.ChannelBuffer;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.Channel;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import org.jboss.netty.handler.codec.frame.FrameDecoder;
public class MyDecoder extends FrameDecoder{
@Override
protected Object decode(ChannelHandlerContext arg0, Channel arg1, ChannelBuffer buffer) throws Exception {
//buffer.readableBytes获取缓冲区中的数据 需要 大于基本长度
if(buffer.readableBytes() > 4) {
//防止socket攻击,当缓冲区数据大于2048时,清除数据。
if(buffer.readableBytes() > 2048) {
buffer.skipBytes(buffer.readableBytes());
}
//循环获取包头,确定数据包的开始位置
while(true) {
buffer.markReaderIndex();
if(buffer.readInt() == Client.BAO) {
break;
}
//只读取一个字节
buffer.resetReaderIndex();
buffer.readByte();
if(buffer.readableBytes() < 4) {
return null;
}
}
//做标记
buffer.markReaderIndex();
//获取数据包的发送过来时的长度
int readInt = buffer.readInt();
//判断buffer中剩余的数据包长度是否大于单个数据包的长度(readInt)
if(buffer.readableBytes() < readInt) {
//返回到上次做标记的地方,因为此次数据读取的不是一个完整的数据包。
buffer.resetReaderIndex();
//缓存当前数据,等待剩下数据包到来
return null;
}
//定义一个数据包的长度
byte[] bt = new byte[readInt];
//读取数据
buffer.readBytes(bt);
//往下传递对象
return new String(bt);
}
//缓存当前数据包,等待第二次数据的到来
return null;
}
}
【4】服务端: 处理请求的handler。
package com.server;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.MessageEvent;
import org.jboss.netty.channel.SimpleChannelHandler;
public class HelloHandler extends SimpleChannelHandler {
private int count = 1;
@Override
public void messageReceived(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, MessageEvent e) throws Exception {
System.out.println(e.getMessage() + " " +count);
count++;
}
}
【5】结果展示(按顺序打印):

方案二: 在消息的尾部加一些特殊字符,那么在读取数据的时候,只要读到这个特殊字符,就认为已经可以截取一个完整的数据包了,这种情况在一定的业务情况下实用。
方案三:LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder与LengthFieldPrepender
LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder与LengthFieldPrepender需要配合起来使用,这两者一个是解码,一个是编码的关系。它们处理粘拆包的主要思想是在生成的数据包中添加一个长度字段,用于记录当前数据包的长度。LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder会按照参数指定的包长度偏移量数据对接收到的数据进行解码,从而得到目标消息体数据;而LengthFieldPrepender则会在响应的数据前面添加指定的字节数据,这个字节数据中保存了当前消息体的整体字节数据长度。
关于 LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder,这里需要对其构造函数参数进行介绍:
public LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(int maxFrameLength, //指定了每个包所能传递的最大数据包大小;
int lengthFieldOffset, //指定了长度字段在字节码中的偏移量;
int lengthFieldLength, //指定了长度字段所占用的字节长度;
int lengthAdjustment, //对一些不仅包含有消息头和消息体的数据进行消息头的长度的调整,这样就可以只得到消息体的数据,这里的 lengthAdjustment 指定的就是消息头的长度;
int initialBytesToStrip) //对于长度字段在消息头中间的情况,可以通过 initialBytesToStrip 忽略掉消息头以及长度字段占用的字节。
我们以json序列化为例对LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder和LengthFieldPrepender的使用方式进行说明。如下是EchoServer的源码:
public class EchoServer {
public void bind(int port) throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024)
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
// 这里将LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder添加到pipeline的首位,因为其需要对接收到的数据
// 进行长度字段解码,这里也会对数据进行粘包和拆包处理
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(1024, 0, 2, 0, 2));
// LengthFieldPrepender是一个编码器,主要是在响应字节数据前面添加字节长度字段
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LengthFieldPrepender(2));
// 对经过粘包和拆包处理之后的数据进行json反序列化,从而得到User对象
ch.pipeline().addLast(new JsonDecoder());
// 对响应数据进行编码,主要是将User对象序列化为json
ch.pipeline().addLast(new JsonEncoder());
// 处理客户端的请求的数据,并且进行响应
ch.pipeline().addLast(new EchoServerHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(port).sync();
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
new EchoServer().bind(8080);
}
}
EchoServer主要是在pipeline中添加了两个编码器和两个解码一器,编码器主要是负责将响应的User对象序列化为json对象,然后在其字节数组前面添加一个长度字段的字节数组;解码一器主要是对接收到的数据进行长度字段的解码,然后将其反序列化为一个User对象。下面是JsonDecoder的源码:
public class JsonDecoder extends MessageToMessageDecoder<ByteBuf> {
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf buf, List<Object> out)
throws Exception {
byte[] bytes = new byte[buf.readableBytes()];
buf.readBytes(bytes);
User user = JSON.parseObject(new String(bytes, CharsetUtil.UTF_8), User.class);
out.add(user);
}
}
JsonDecoder首先从接收到的数据流中读取字节数组,然后将其反序列化为一个User对象。下面我们看看JsonEncoder的源码:
public class JsonEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder<User> {
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, User user, ByteBuf buf)
throws Exception {
String json = JSON.toJSONString(user);
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.wrappedBuffer(json.getBytes()));
}
}
JsonEncoder将响应得到的User对象转换为一个json对象,然后写入响应中。对于EchoServerHandler,其主要作用就是接收客户端数据,并且进行响应,如下是其源码:
public class EchoServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<User> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, User user) throws Exception {
System.out.println("receive from client: " + user);
ctx.write(user);
}
}
对于客户端,其主要逻辑与服务端的基本类似,这里主要展示其pipeline的添加方式,以及最后发送请求,并且对服务器响应进行处理的过程:
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(1024, 0, 2, 0, 2));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new LengthFieldPrepender(2));
ch.pipeline().addLast(new JsonDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new JsonEncoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new EchoClientHandler());
}
这里客户端首先会在连接上服务器时,往服务器发送一个User对象数据,然后在接收到服务器响应之后,会打印服务器响应的数据。
public class EchoClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<User> {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.write(getUser());
}
private User getUser() {
User user = new User();
user.setAge(27);
user.setName("zhangxufeng");
return user;
}
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, User user) throws Exception {
System.out.println("receive message from server: " + user);
}
}
方案四:自定义粘包与拆包器:
对于一些更加复杂的协议,可能有一些定制化的需求。通过继承LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder和LengthFieldPrepender来实现粘包和拆包的处理。
如果用户确实需要不通过继承的方式实现自己的粘包和拆包处理器,这里可以通过实现MessageToByteEncoder和ByteToMessageDecoder来实现。这里MessageToByteEncoder的作用是将响应数据编码为一个ByteBuf对象,而ByteToMessageDecoder则是将接收到的ByteBuf数据转换为某个对象数据。通过实现这两个抽象类,用户就可以达到实现自定义粘包和拆包处理的目的。如下是这两个类及其抽象方法的声明:
public abstract class ByteToMessageDecoder extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
protected abstract void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out)
throws Exception;
}
public abstract class MessageToByteEncoder<I> extends ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter {
protected abstract void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, I msg, ByteBuf out)
throws Exception;
}
![[Electron]中的BrowserView](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/3dee076419304dff9e328c5e11bfcce7.png)
![[服务器]RTSP服务与ffmpeg推送-简单搭建-Windows与Linux](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/52a97ddc940b5922702ff38fc58aabbf.png)