创建证书
不管是单向tls还是双向tls(mTLS),都需要创建证书。
创建证书可以使用openssl或者keytool,openssl 参考 mTLS: openssl创建CA证书
单向/双向tls需要使用到的相关文件:
| 文件 | 单向tls | 双向tls | Server端 | Client端 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ca.key | - | - | - | - | 需要保管好,后面ca.crt续期或者生成server/client证书时需要使用它进行签名 |
| ca.crt | 可选 | 需要 | 可选 | 可选 | CA 证书 |
| server.key | 需要 | 需要 | 需要 | - | 服务端密钥,与 pkcs8_server.key 任选一个使用 |
| pkcs8_server.key | 需要 | 需要 | 需要 | - | PK8格式的服务端密钥,与 server.key 任选一个使用 |
| server.crt | 需要 | 需要 | 需要 | - | 服务端证书 |
| client.key | - | 需要 | - | 需要 | 客户端密钥,与 pkcs8_client.key 任选一个使用 |
| pkcs8_client.key | - | 需要 | - | 需要 | PK8格式的客户端密钥,与 client.key 任选一个使用 |
| client.crt | - | 需要 | - | 需要 | 客户端证书 |
netty单向/双向TLS
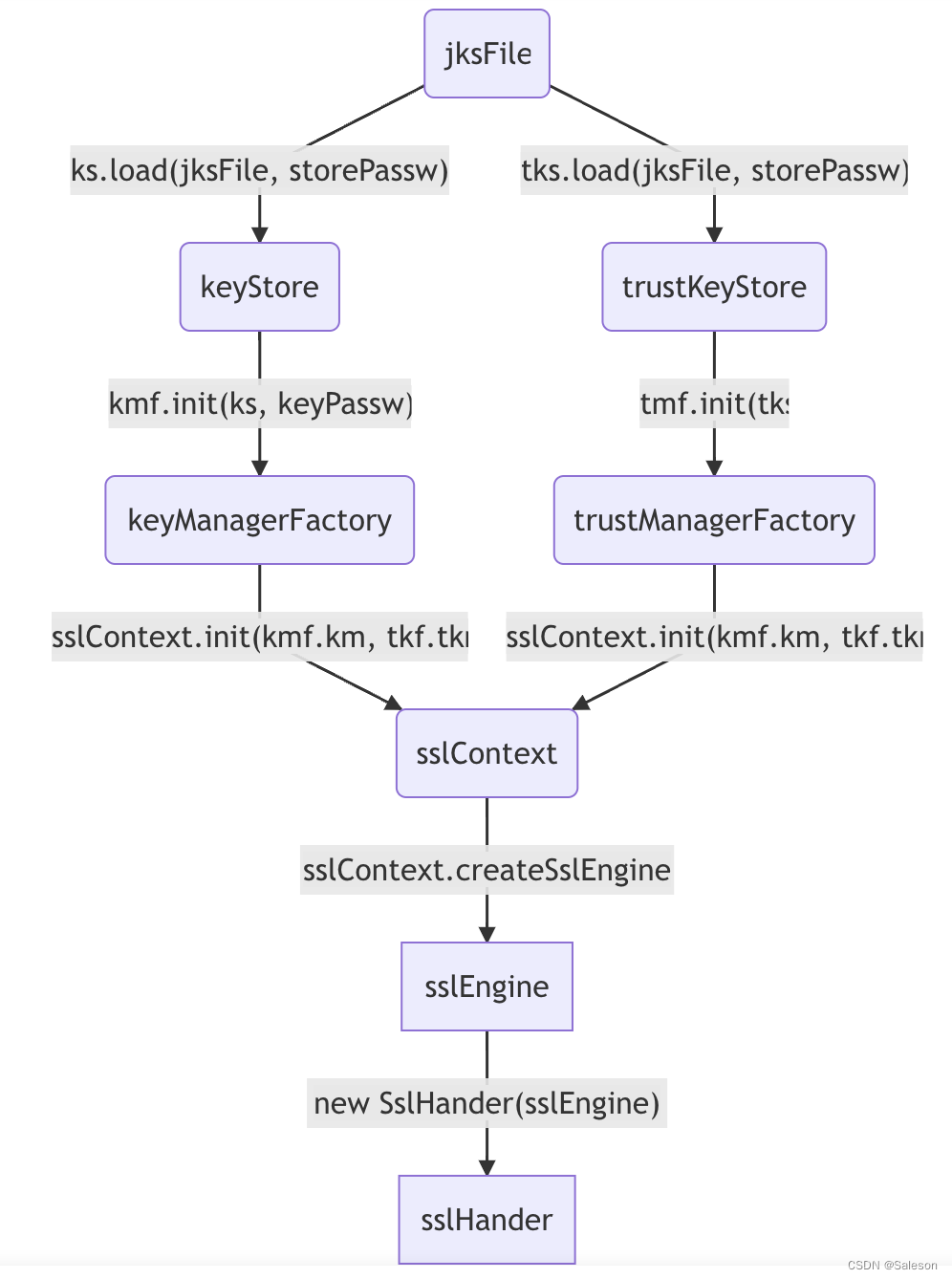
在netty中tls的处理逻辑是由SslHandler完成的,SslHandler对象创建方式有两种:
- 通过Java Ssl相关接口+jks密钥库创建SslEngine,再将SslEngine做为构造参数创建SslHandler对象。
- 通过netty 的SslContextBuilder创建SslContext对象,再由SslContext对象创建SslHandler对象。
ava Ssl相关接口+jks密钥库生成SslHandler的流程如下图所示:
SslContextBuidler创建SslHandler的方法相对简单,如下:
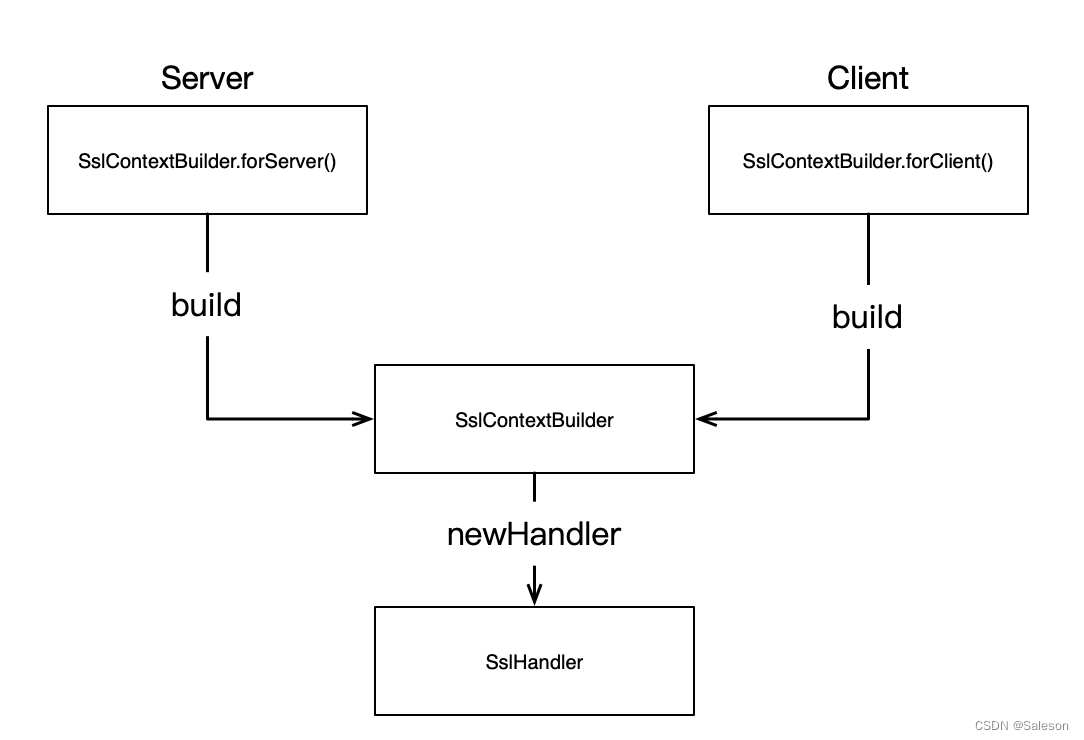
关于SslContextBuidler创建SslContext对象和SslHandler对象的方式是本篇文章的重点,后面详细描述。
创建Server端和Client的BootStrap
先是将Server端的ServerBootStrap和Client端的BootStrap对象创建好,并初始化完成,能够在非tls场景下正常通信。
Server端ServerBootstrap
Server端创建ServerBootstrap, 添加编解码器和业务逻辑Handler,监听端口。代码如下:
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.buffer.PooledByteBufAllocator;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.channel.epoll.EpollServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.LineBasedFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringEncoder;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.netty.NettyHelper;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.security.cert.CertificateException;
@Slf4j
public class NettyTLSServer {
private InetSocketAddress bindAddress;
private ServerBootstrap bootstrap;
private EventLoopGroup bossGroup;
private EventLoopGroup workerGroup;
public NettyTLSServer() {
this(8080);
}
public NettyTLSServer(int bindPort) {
this("localhost", bindPort);
}
public NettyTLSServer(String bindIp, int bindPort) {
bindAddress = new InetSocketAddress(bindIp, bindPort);
}
private void init() throws CertificateException, SSLException {
bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bossGroup = NettyHelper.eventLoopGroup(1, "NettyServerBoss");
workerGroup = NettyHelper.eventLoopGroup(Math.min(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() + 1, 32), "NettyServerWorker");
bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NettyHelper.shouldEpoll() ? EpollServerSocketChannel.class : NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_REUSEADDR, Boolean.TRUE)
.childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, Boolean.TRUE)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, Boolean.TRUE)
.childOption(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT)
.childOption(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, 10000);
bootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
log.info("accept client: {} {}", ch.remoteAddress().getHostName(), ch.remoteAddress().getPort());
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline
//添加字节消息解码器
.addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(1024))
//添加消息解码器,将字节转换为String
.addLast(new StringDecoder())
//添加消息编码器,将String转换为字节
.addLast(new StringEncoder())
//业务逻辑处理Handler
.addLast(new ChannelDuplexHandler() {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
log.info("received message from client: {}", msg);
ctx.writeAndFlush("server response: " + msg);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
log.info("occur exception, close channel:{}.", ctx.channel().remoteAddress(), cause);
ctx.channel().closeFuture()
.addListener(future -> {
log.info("close client channel {}: {}",
ctx.channel().remoteAddress(),
future.isSuccess());
});
}
});
}
});
}
public void bind(boolean sync) throws CertificateException, SSLException {
init();
try {
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.bind(bindAddress).sync();
if (channelFuture.isDone()) {
log.info("netty server start at house and port: {} ", bindAddress.getPort());
}
Channel channel = channelFuture.channel();
ChannelFuture closeFuture = channel.closeFuture();
if (sync) {
closeFuture.sync();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("netty server start exception,", e);
} finally {
if (sync) {
shutdown();
}
}
}
public void shutdown() {
log.info("netty server shutdown");
log.info("netty server shutdown bossEventLoopGroup&workerEventLoopGroup gracefully");
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
Client端BootStrap
Client端创建Bootstrap, 添加编解码器和业务逻辑Handler,建立连接。代码如下:
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.buffer.PooledByteBufAllocator;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.codec.LineBasedFrameDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringEncoder;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.netty.NettyHelper;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
@Slf4j
public class NettyTLSClient {
private InetSocketAddress serverAddress;
private Bootstrap bootstrap;
private EventLoopGroup workerGroup;
private Channel channel;
public NettyTLSClient(String severHost, int serverPort) {
serverAddress = new InetSocketAddress(severHost, serverPort);
}
public void init() throws SSLException {
bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
workerGroup = NettyHelper.eventLoopGroup(1, "NettyClientWorker");
bootstrap.group(workerGroup)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.option(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT)
.option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, 10000)
.remoteAddress(serverAddress)
.channel(NettyHelper.socketChannelClass());
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline
//添加字节消息解码器
.addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(1024))
//添加消息解码器,将字节转换为String
.addLast(new StringDecoder())
//添加消息编码器,将String转换为字节
.addLast(new StringEncoder())
//业务逻辑处理Handler
.addLast(new ChannelDuplexHandler() {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
log.info("received message from server: {}", msg);
super.channelRead(ctx, msg);
}
});
}
});
}
public ChannelFuture connect() throws SSLException {
init();
//开始连接
final ChannelFuture promise = bootstrap.connect(serverAddress.getHostName(), serverAddress.getPort());
// final ChannelFuture promise = bootstrap.connect();
promise.addListener(future -> {
log.info("client connect to server: {}", future.isSuccess());
});
channel = promise.channel();
return promise;
}
public void shutdown() {
log.info("netty client shutdown");
channel.closeFuture()
.addListener(future -> {
log.info("netty client shutdown workerEventLoopGroup gracefully");
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
});
}
public Channel getChannel() {
return channel;
}
}
工具类: NettyHelper
主要用是创建EventLoopGroup和判断是否支持Epoll,代码如下:
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.epoll.Epoll;
import io.netty.channel.epoll.EpollEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.epoll.EpollSocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import io.netty.util.concurrent.DefaultThreadFactory;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadFactory;
public class NettyHelper {
static final String NETTY_EPOLL_ENABLE_KEY = "netty.epoll.enable";
static final String OS_NAME_KEY = "os.name";
static final String OS_LINUX_PREFIX = "linux";
public static EventLoopGroup eventLoopGroup(int threads, String threadFactoryName) {
ThreadFactory threadFactory = new DefaultThreadFactory(threadFactoryName, true);
return shouldEpoll() ? new EpollEventLoopGroup(threads, threadFactory) :
new NioEventLoopGroup(threads, threadFactory);
}
public static boolean shouldEpoll() {
if (Boolean.parseBoolean(System.getProperty(NETTY_EPOLL_ENABLE_KEY, "false"))) {
String osName = System.getProperty(OS_NAME_KEY);
return osName.toLowerCase().contains(OS_LINUX_PREFIX) && Epoll.isAvailable();
}
return false;
}
public static Class<? extends SocketChannel> socketChannelClass() {
return shouldEpoll() ? EpollSocketChannel.class : NioSocketChannel.class;
}
}
构建单向tls
创建SslContext
自签名证书的SslContext(测试场景)
Server 端
在单向tls场景中,主要是server端需要证书,所以在Server侧需要SelfSignedCertificate对象来生成密钥和证书,同时创建并返回netty的SslContextBuilder构造器创建SslContext对象。代码如下:
public class SslContextUtils {
/**
* 创建server SslContext
* 会自动创建一个临时自签名的证书 -- Generates a temporary self-signed certificate
*
* @return
* @throws CertificateException
* @throws SSLException
*/
public static SslContext createTlsServerSslContext() throws CertificateException, SSLException {
SslProvider provider = SslProvider.isAlpnSupported(SslProvider.OPENSSL) ? SslProvider.OPENSSL : SslProvider.JDK;
SelfSignedCertificate cert = new SelfSignedCertificate();
return SslContextBuilder.forServer(cert.certificate(), cert.privateKey())
.sslProvider(provider)
.protocols("TLSv1.3", "TLSv1.2")
.build();
}
}
在netty ChannelPipeline的初始化Channel逻辑中,通过SslContext生成SslHandler对象,并将其添加到ChannelPipeline中。
Client 端
客户端简单很多,可以不需要证书,因为在单向tls中只在client验证验证服务端的证书是否合法。代码如下:
public class SslContextUtils {
public static SslContext createTlsClientSslContext() throws SSLException {
SslProvider provider = SslProvider.isAlpnSupported(SslProvider.OPENSSL) ? SslProvider.OPENSSL : SslProvider.JDK;
return SslContextBuilder.forClient()
.sslProvider(provider)
.trustManager(InsecureTrustManagerFactory.INSTANCE)
.protocols("TLSv1.3", "TLSv1.2")
.build();
}
}
openssl证书创建SslContext
使用openssl 生成证书, 需要的文件如下:
| 文件 | Server端 | Client端 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ca.crt | 可选 | 可选 | CA 证书 |
| server.key | 需要 | - | 服务端密钥,与 pkcs8_server.key 任选一个使用 |
| pkcs8_server.key | 需要 | - | PK8格式的服务端密钥,与 server.key 任选一个使用 |
| server.crt | 需要 | - | 服务端证书 |
SslContextUtils将文件转InputStream
如果出现文件相关的报错,可以尝试先将文件将流。
SslContextUtils中文件转InputStream的方法如下:
public class SslContextUtils {
}public static InputStream openInputStream(File file) {
try {
return file == null ? null : file.toURI().toURL().openStream();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Could not find certificate file or the certificate is invalid.", e);
}
}
private static void safeCloseStream(InputStream stream) {
if (stream == null) {
return;
}
try {
stream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
log.warn("Failed to close a stream.", e);
}
}
Server 端
逻辑跟自签名证书创建SslContext是一样的,只是将服务端密钥和证书换成了使用openssl生成。
在生成服务端证书时,会用到ca证书,所以也可以把ca证书加入到TrustManager中 ,当然这一步骤是可选的。
代码如下:
public class SslContextUtils {
public static SslContext createServerSslContext(File keyCertChainFile, File keyFile, String keyPassword, File trustCertFile){
try (InputStream keyCertChainInputStream = openInputStream(keyCertChainFile);
InputStream keyInputStream = openInputStream(keyFile);
InputStream trustCertFileInputStream = openInputStream(trustCertFile)) {
SslContextBuilder builder;
if (keyPassword != null) {
builder = SslContextBuilder.forServer(keyCertChainInputStream, keyInputStream, keyPassword);
} else {
builder = SslContextBuilder.forServer(keyCertChainInputStream, keyInputStream);
}
if (trustCertFile != null) {
builder.trustManager(trustCertFileInputStream);
}
try {
SslProvider provider = SslProvider.isAlpnSupported(SslProvider.OPENSSL) ? SslProvider.OPENSSL : SslProvider.JDK;
return builder
.sslProvider(provider)
.protocols("TLSv1.3", "TLSv1.2")
.build();
} catch (SSLException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Build SslSession failed.", e);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Could not find certificate file or the certificate is invalid.", e);
}
}
}
Client 端
client端的逻辑是同自签名证书创建SslContext是一样的,不过要支持ca证书需要稍做调整:
public class SslContextUtils {
public static SslContext createClientSslContext(File trustCertFile) {
try (InputStream trustCertFileInputStream = openInputStream(trustCertFile)) {
SslProvider provider = SslProvider.isAlpnSupported(SslProvider.OPENSSL) ? SslProvider.OPENSSL : SslProvider.JDK;
SslContextBuilder builder = SslContextBuilder.forClient()
.sslProvider(provider)
.protocols("TLSv1.3", "TLSv1.2");
if (trustCertFile != null) {
builder.trustManager(InsecureTrustManagerFactory.INSTANCE);
} else {
builder.trustManager(trustCertFileInputStream);
}
return builder.build();
} catch (SSLException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Build SslSession failed.", e);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Could not find certificate file or the certificate is invalid.", e);
}
}
}
添加SslHandler,完成ssl handshake
在服务端和客户端的BootStrap对Channel的初始化逻辑做些调整,添加SslHandler和TlsHandler。
它们的用途分别如下:
- SslHandler是netty提供用来建立tls连接和握手。
- TlsHandler用于检查ssl handshake,如果是在客户端场景,会将服务端的证书信息打印出来。
Server端
在NettyTLSServer.init()方法中,对Channel的初始化逻辑做调整,添加SslHandler和TlsHandler。
Channel的初始化方法在ChannelInitializer中,代码如下:
@Slf4j
public class NettyTLSServer {
public void init() throws CertificateException, SSLException {
...
//创建一个临时自签名证书的SslContext对象
// SslContext sslContext = SslContextUtils.createServerSslContext();
//使用openssl 生成的私钥和证书创建SslContext对象, 不传ca.crt
SslContext sslContext = SslContextUtils.createServerSslContext(
new File("./cert/server.crt"),
new File("./cert/server.key"),
null,
null);
//使用openssl 生成的私钥和证书创建SslContext对象,传ca.crt
// SslContext sslContext = SslContextUtils.createServerSslContext(
// new File("./cert/server.crt"),
// new File("./cert/server.key"),
// null,
// new File("./cert/ca.crt"));
//创建TlsHandler对象,该Handler会进行ssl handshake检查
TlsHandler tlsHandler = new TlsHandler(true);
//将ChannelInitializer设置为ServerBootstrap对象的childHandler
bootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
// SocketChannel 初始化方法,该方法在Channel注册后只会被调用一次
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
log.info("accept client: {} {}", ch.remoteAddress().getHostName(), ch.remoteAddress().getPort());
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline
// 添加SslHandler
.addLast(sslContext.newHandler(ch.alloc()))
// 添加TslHandler
.addLast(tlsHandler)
//添加字节消息解码器
.addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(1024))
//添加消息解码器,将字节转换为String
.addLast(new StringDecoder())
//添加消息编码器,将String转换为字节
.addLast(new StringEncoder(){
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, CharSequence msg, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
super.encode(ctx, msg + "\n", out);
}
})
//业务逻辑处理Handler
.addLast(new ChannelDuplexHandler() {
...
});
}
});
}
}
Client端
在NettyTLSClient.init()方法中,对Channel的初始化逻辑做调整,添加SslHandler和TlsHandler。
Channel的初始化方法在ChannelInitializer中,代码如下:
public class NettyTLSClient {
public void init() throws SSLException {
...
// 创建SslContext对象,不传ca.crt
SslContext sslContext = SslContextUtils.createClientSslContext();
// 使用openssl 生成的Ca证书创建SslContext对象,传ca.crt
// SslContext sslContext = SslContextUtils.createClientSslContext(new File("./cert/ca.crt"));
//创建TlsHandler对象,该Handler会进行ssl handshake检查,并会将服务端的证书信息打印出来
TlsHandler tlsHandler = new TlsHandler(false);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline
// 添加ssl Handler
.addLast(sslContext.newHandler(ch.alloc()))
// 添加TslHandler
.addLast(tlsHandler)
//添加字节消息解码器
.addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(1024))
//添加消息解码器,将字节转换为String
.addLast(new StringDecoder())
//添加消息编码器,将String转换为字节
.addLast(new StringEncoder(){
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, CharSequence msg, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
super.encode(ctx, msg + "\n", out);
}
})
//业务逻辑处理Handler
.addLast(new ChannelDuplexHandler() {
...
});
}
});
}
}
TlsHandler
代码如下:
import io.netty.channel.Channel;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelDuplexHandler;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandler;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.ssl.SslHandler;
import io.netty.util.concurrent.Future;
import io.netty.util.concurrent.GenericFutureListener;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLSession;
import javax.security.cert.X509Certificate;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
@Slf4j
public class TlsHandler extends ChannelDuplexHandler {
private boolean serverSide;
public TlsHandler(boolean serverSide) {
this.serverSide = serverSide;
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.pipeline()
.get(SslHandler.class)
.handshakeFuture()
.addListener(
new GenericFutureListener<Future<Channel>>() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(Future<Channel> future) throws Exception {
if (future.isSuccess()) {
log.info("[{}] {} 握手成功", getSideType(), ctx.channel().remoteAddress());
SSLSession ss = ctx.pipeline().get(SslHandler.class).engine().getSession();
log.info("[{}] {} cipherSuite: {}", getSideType(), ctx.channel().remoteAddress(), ss.getCipherSuite());
if (!serverSide) {
X509Certificate cert = ss.getPeerCertificateChain()[0];
String info = null;
// 获得证书版本
info = String.valueOf(cert.getVersion());
System.out.println("证书版本:" + info);
// 获得证书序列号
info = cert.getSerialNumber().toString(16);
System.out.println("证书序列号:" + info);
// 获得证书有效期
Date beforedate = cert.getNotBefore();
info = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd").format(beforedate);
System.out.println("证书生效日期:" + info);
Date afterdate = (Date) cert.getNotAfter();
info = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd").format(afterdate);
System.out.println("证书失效日期:" + info);
// 获得证书主体信息
info = cert.getSubjectDN().getName();
System.out.println("证书拥有者:" + info);
// 获得证书颁发者信息
info = cert.getIssuerDN().getName();
System.out.println("证书颁发者:" + info);
// 获得证书签名算法名称
info = cert.getSigAlgName();
System.out.println("证书签名算法:" + info);
}
} else {
log.warn("[{}] {} 握手失败,关闭连接", getSideType(), ctx.channel().remoteAddress());
ctx.channel().closeFuture().addListener(closeFuture -> {
log.info("[{}] {} 关闭连接:{}", getSideType(), ctx.channel().remoteAddress(), closeFuture.isSuccess());
});
}
}
});
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) ctx.channel();
}
private String getSideType() {
return serverSide ? "SERVER" : "CLIENT";
}
}
构建双向tls (mTLS)
创建MTls的SslContext
在SslContextUtils中添加两个方法,分别是:
- 创建服务端MTls SslContext的对象
- 创建客户端MTls 的SslContext
代码如下:
public class SslContextUtils {
/**
* 创建服务端MTls 的SslContext
*
* @param keyCertChainFile 服务端证书
* @param keyFile 服务端私钥
* @param keyPassword 服务端私钥加密密码
* @param trustCertFile CA证书
* @return
*/
public static SslContext createServerMTslContext(File keyCertChainFile, File keyFile, String keyPassword, File trustCertFile) {
SslContextBuilder builder;
try (InputStream keyCertChainInputStream = openInputStream(keyCertChainFile);
InputStream keyInputStream = openInputStream(keyFile);
InputStream trustCertFileInputStream = openInputStream(trustCertFile)) {
if (keyPassword != null) {
builder = SslContextBuilder.forServer(keyCertChainInputStream, keyInputStream, keyPassword);
} else {
builder = SslContextBuilder.forServer(keyCertChainInputStream, keyInputStream);
}
builder.trustManager(trustCertFileInputStream);
builder.clientAuth(ClientAuth.REQUIRE);
try {
SslProvider provider = SslProvider.isAlpnSupported(SslProvider.OPENSSL) ? SslProvider.OPENSSL : SslProvider.JDK;
return builder
.sslProvider(provider)
.protocols("TLSv1.3", "TLSv1.2")
.build();
} catch (SSLException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Build SslSession failed.", e);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Could not find certificate file or the certificate is invalid.", e);
}
}
/**
* 创建客户端MTls 的SslContext
*
* @param keyCertChainFile 客户端证书
* @param keyFile 客户端私钥
* @param keyPassword 客户端私钥加密密码
* @param trustCertFile CA证书
* @return
*/
public static SslContext createClientMTslContext(File keyCertChainFile, File keyFile, String keyPassword, File trustCertFile) {
try (InputStream keyCertChainInputStream = openInputStream(keyCertChainFile);
InputStream keyInputStream = openInputStream(keyFile);
InputStream trustCertFileInputStream = openInputStream(trustCertFile)) {
SslContextBuilder builder = SslContextBuilder.forClient();
builder.trustManager(trustCertFileInputStream);
if (keyPassword != null) {
builder.keyManager(keyCertChainInputStream, keyInputStream, keyPassword);
} else {
builder.keyManager(keyCertChainInputStream, keyInputStream);
}
try {
SslProvider provider = SslProvider.isAlpnSupported(SslProvider.OPENSSL) ? SslProvider.OPENSSL : SslProvider.JDK;
return builder
.sslProvider(provider)
.protocols("TLSv1.3", "TLSv1.2")
.build();
} catch (SSLException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Build SslSession failed.", e);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Could not find certificate file or the certificate is invalid.", e);
}
}
}
BootStrap对Channel的初始化逻辑
同单向Tls一样,要服务端和客户端的BootStrap对Channel的初始化逻辑做些调整,主要是SslContext的调整。所以在单向ssl的代码基础上做些调整就可以了。
服务端在NettyTLSServer.init()方法中将SslContext改成调用SslContextUtils.createServerMTslContext()创建。
代码如下:
public class NettyTLSServer {
public void init() throws CertificateException, SSLException {
...
//使用openssl 生成的私钥和证书创建支持mtls的SslContext对象
SslContext sslContext = SslContextUtils.createServerMTslContext(
new File("./cert/server.crt"),
new File("./cert/pkcs8_server.key"),
null,
new File("./cert/ca.crt"));
//创建TlsHandler对象,该Handler会进行ssl handshake检查,会将对端的证书信息打印出来
TlsHandler tlsHandler = new TlsHandler(true, true);
//将ChannelInitializer设置为ServerBootstrap对象的childHandler
bootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
// SocketChannel 初始化方法,该方法在Channel注册后只会被调用一次
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
log.info("accept client: {} {}", ch.remoteAddress().getHostName(), ch.remoteAddress().getPort());
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline
// 添加SslHandler
.addLast(sslContext.newHandler(ch.alloc()))
// 添加TslHandler
.addLast(tlsHandler)
//添加字节消息解码器
.addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(1024))
//添加消息解码器,将字节转换为String
.addLast(new StringDecoder())
//添加消息编码器,将String转换为字节
.addLast(new StringEncoder(){
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, CharSequence msg, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
super.encode(ctx, msg + "\n", out);
}
})
//业务逻辑处理Handler
.addLast(new ChannelDuplexHandler() {
...
});
}
});
}
}
客户端在NettyTLSClient.init()方法中将SslContext改成调用SslContextUtils.createClientMTslContext()创建。
代码如下:
```java
public class NettyTLSClient {
public void init() throws SSLException {
...
//使用openssl 生成的私钥和证书创建支持mtls的SslContext对象
SslContext sslContext = SslContextUtils.createClientMTslContext(
new File("./cert/client.crt"),
new File("./cert/pkcs8_client.key"),
null,
new File("./cert/ca.crt"));
//创建TlsHandler对象,该Handler会进行ssl handshake检查,并会将对端的证书信息打印出来
TlsHandler tlsHandler = new TlsHandler(true, false);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline
// 添加ssl Handler
.addLast(sslContext.newHandler(ch.alloc()))
// 添加TslHandler
.addLast(tlsHandler)
//添加字节消息解码器
.addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(1024))
//添加消息解码器,将字节转换为String
.addLast(new StringDecoder())
//添加消息编码器,将String转换为字节
.addLast(new StringEncoder(){
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, CharSequence msg, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
super.encode(ctx, msg + "\n", out);
}
})
//业务逻辑处理Handler
.addLast(new ChannelDuplexHandler() {
...
});
}
});
}
}
调整TlsHandler,支持mtls场景下打印对端的证书信息
在TlsHandler中添加一个名为mtls的boolean类型成员变量,通过这个成员变量判断是否使用mtls,如果是则打印对端的证书信息,否则在client打印服务端的证书信息。
代码如下:
import io.netty.channel.Channel;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelDuplexHandler;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.handler.ssl.SslHandler;
import io.netty.util.concurrent.Future;
import io.netty.util.concurrent.GenericFutureListener;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLSession;
import javax.security.cert.X509Certificate;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
@Slf4j
public class TlsHandler extends ChannelDuplexHandler {
private boolean serverSide;
private boolean mtls;
public TlsHandler(boolean serverSide, boolean mtls) {
this.serverSide = serverSide;
this.mtls = mtls;
}
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.pipeline().get(SslHandler.class).handshakeFuture().addListener(
new GenericFutureListener<Future<Channel>>() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(Future<Channel> future) throws Exception {
if (future.isSuccess()) {
log.info("[{}] {} 握手成功", getSideType(), ctx.channel().remoteAddress());
SSLSession ss = ctx.pipeline().get(SslHandler.class).engine().getSession();
log.info("[{}] {} cipherSuite: {}", getSideType(), ctx.channel().remoteAddress(), ss.getCipherSuite());
if (mtls || !serverSide) {
X509Certificate cert = ss.getPeerCertificateChain()[0];
String info = null;
// 获得证书版本
info = String.valueOf(cert.getVersion());
System.out.println("证书版本:" + info);
// 获得证书序列号
info = cert.getSerialNumber().toString(16);
System.out.println("证书序列号:" + info);
// 获得证书有效期
Date beforedate = cert.getNotBefore();
info = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd").format(beforedate);
System.out.println("证书生效日期:" + info);
Date afterdate = (Date) cert.getNotAfter();
info = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd").format(afterdate);
System.out.println("证书失效日期:" + info);
// 获得证书主体信息
info = cert.getSubjectDN().getName();
System.out.println("证书拥有者:" + info);
// 获得证书颁发者信息
info = cert.getIssuerDN().getName();
System.out.println("证书颁发者:" + info);
// 获得证书签名算法名称
info = cert.getSigAlgName();
System.out.println("证书签名算法:" + info);
}
} else {
log.warn("[{}] {} 握手失败,关闭连接", getSideType(), ctx.channel().remoteAddress());
ctx.channel().closeFuture().addListener(closeFuture -> {
log.info("[{}] {} 关闭连接:{}", getSideType(), ctx.channel().remoteAddress(), closeFuture.isSuccess());
});
}
}
});
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) ctx.channel();
System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date()) + " conn:");
System.out.println("IP:" + channel.localAddress().getHostString());
System.out.println("Port:" + channel.localAddress().getPort());
}
private String getSideType() {
return serverSide ? "SERVER" : "CLIENT";
}
}
创建Main类进行测试
测试Main Class:
import javax.net.ssl.SSLException;
import java.security.cert.CertificateException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class NettyMTlsMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CertificateException, SSLException {
String serverHost = "localhost";
int serverPort = 10001;
NettyTLSServer server = new NettyTLSServer(serverHost, serverPort);
server.bind(false);
NettyTLSClient client = new NettyTLSClient(serverHost, serverPort);
client.connect().addListener(future -> {
if (future.isSuccess()) {
client.getChannel().writeAndFlush("--test--");
}
});
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
System.out.println("waiting input");
String line = scanner.nextLine();
if ("exit".equals(line) || "eq".equals(line) || "quit".equals(line)) {
client.shutdown();
server.shutdown();
return;
}
client.getChannel().writeAndFlush(line);
}
}
}
参考
netty实现TLS/SSL双向加密认证
Netty+OpenSSL TCP双向认证证书配置
基于Netty的MQTT Server实现并支持SSL
Netty tls验证
netty使用ssl双向认证
netty中实现双向认证的SSL连接
记一次TrustAnchor with subject异常解决
SpringBoot (WebFlux Netty) 支持动态更换https证书
手动实现CA数字认证(java)
java编程方式生成CA证书
netty https有什么方式根据域名设置证书?

![[计算机网络]--五种IO模型和select](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/9c5200a6465b49a7a53f66f56710f8ab.png)