SPI机制简介
SPI(Service Provider Interface),是从JDK6开始引入的,一种基于ClassLoader来发现并加载服务的机制。
一个标准的SPI,由3个组件构成,分别是:
- Service:是一个公开的接口或者抽象类,定义了一个抽象的功能模块;
- Service Provider:是Service接口的实现子类;
- ServiceLoader:是SPI机制的核心组件,负责在运行时发现并加载Service Provider。
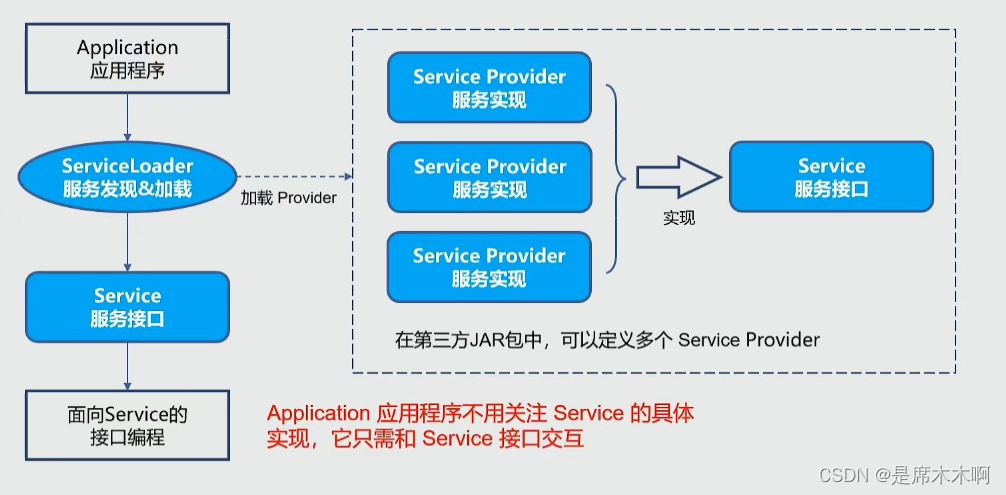
SPI运行流程
SPI运行流程如下图所示,
ServiceLoader类
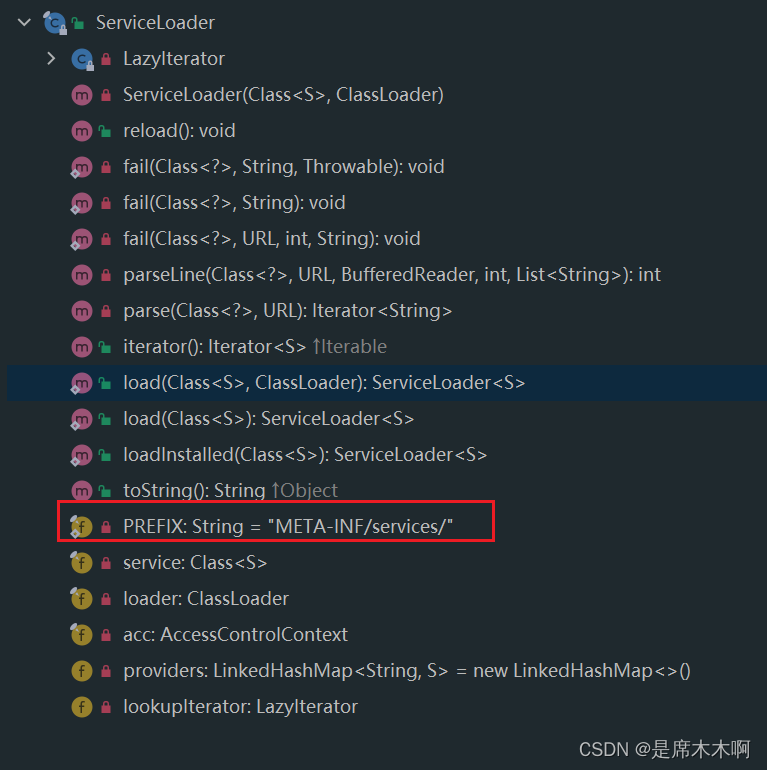
ServiceLoader是SPI机制的核心组件,负责在运行时发现并加载Service Provider。该类提供了load方法,用于在程序运行过程中去加载第三方提供的Service接口实现类,得到接口实例;后续过程中,只需要通过接口实例去执行对应的操作即可。
假设,我们有这样一个InternetService 接口,用来提供网络连接服务。
/**
* 网络连接服务接口SPI-Service
*/
public interface InternetService {
void connectInternet();
}然后为其提供接口实现子类,
package cn.mobile;
import spi.InternetService;
public class BeijingChinaMobileMobile implements InternetService {
@Override
public void connectInternet() {
System.out.println("connect internet By [Beijing China Mobile]");
}
}
这样写在单体项目中自然是可以的,但是,如果我们要让别人也能在项目中使用这个接口提供的网络连接服务,就有点难受了。好在SPI机制就是用来做服务发现和加载工作的,我们可以将其改造成符合SPI标准的一套通用工具。
service服务定义
接口就是在定义标准,而这个标准需要交由第三方进行实现。
1. 创建maven项目,
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>simple_spi_example</artifactId>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>simple-api</artifactId>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
</project>2.定义接口标准,
package spi;
/**
* 网络连接服务接口SPI-Service
*/
public interface InternetService {
void connectInternet();
}
service provider服务的第三方实现
service provider是Service接口的实现子类。以下我们提供两个第三方实现,分别命名为A、B。
第三方A实现
1. 创建Maven项目,引入接口标准依赖,
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>simple_spi_example</artifactId>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>simple-spi-mobile</artifactId>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<artifactId>simple-api</artifactId>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>2. 实现SPI接口,
package cn.mobile;
import spi.InternetService;
public class ChinaMobile implements InternetService {
@Override
public void connectInternet() {
System.out.println("connect internet By [China Mobile]");
}
}
package cn.mobile;
import spi.InternetService;
public class BeijingChinaMobileMobile implements InternetService {
@Override
public void connectInternet() {
System.out.println("connect internet By [Beijing China Mobile]");
}
}
3.提供service元数据,
在resources目录下,新建资源文件META-INF\services\spi.InternetService,文件名:spi.InternetService(父接口的全路径名称),
cn.mobile.ChinaMobile
cn.mobile.BeijingChinaMobileMobile 第三方B实现
1. 创建Maven项目,引入接口标准依赖,
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>simple_spi_example</artifactId>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>simple-spi-unicom</artifactId>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<artifactId>simple-api</artifactId>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>2. 实现SPI接口,
package cn.unicom;
import spi.InternetService;
public class ChinaUniCom implements InternetService {
@Override
public void connectInternet() {
System.out.println("connect internet By [ChinaUniCom]");
}
}
3.提供service元数据,
在resources目录下,新建资源文件META-INF\services\spi.InternetService,文件名:spi.InternetService(父接口的全路径名称),
cn.unicom.ChinaUniComServiceLoader服务发现和服务加载
1. 在主项目中引入service服务的第三方实现相关依赖,
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>simple_spi_example</artifactId>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>smaple-company</artifactId>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<artifactId>simple-api</artifactId>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>simple-spi-unicom</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>simple-spi-mobile</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>2. 通过ServiceLoader发现并加载服务
package com.company;
import spi.InternetService;
import java.util.ServiceLoader;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ServiceLoader<InternetService> load = ServiceLoader.load(InternetService.class);
for (InternetService provider : load) {
provider.connectInternet();
}
}
}
3.执行结果如下
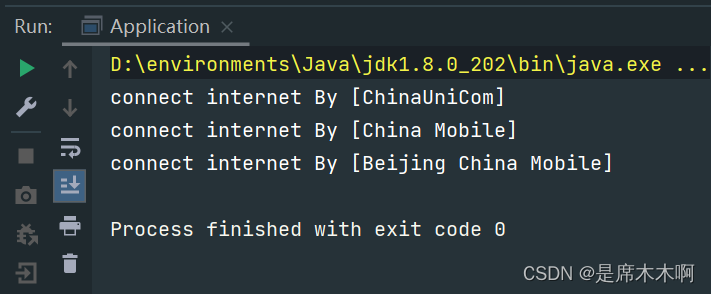
ServiceLoader源码分析
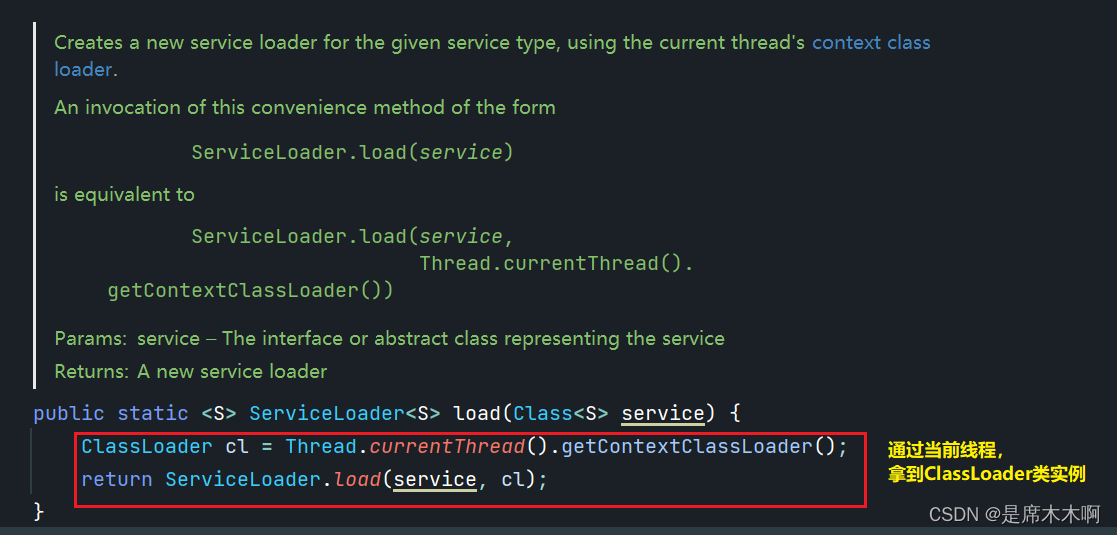
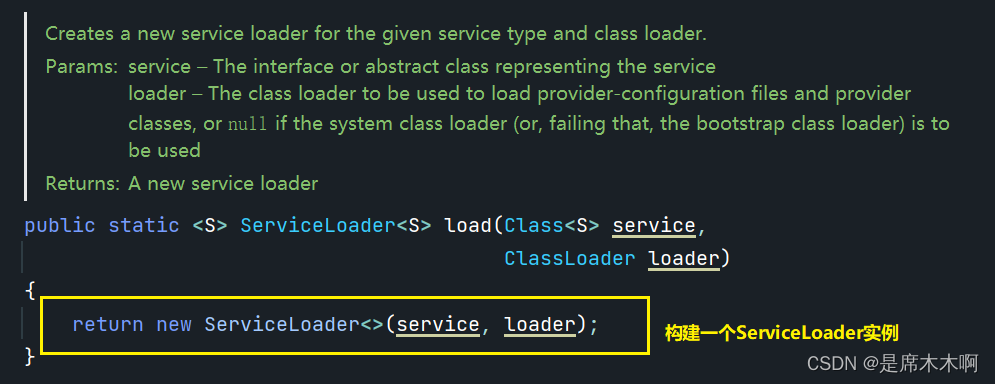
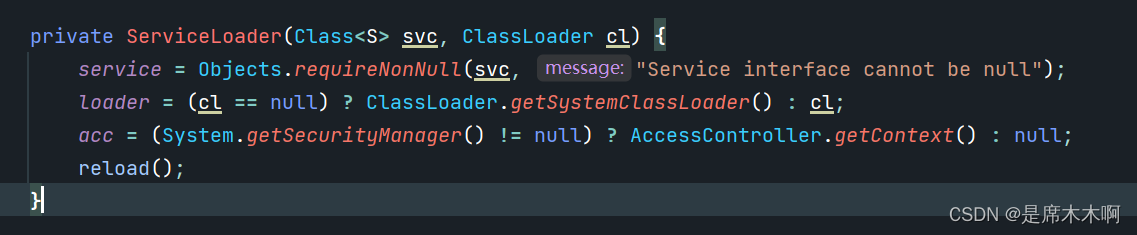
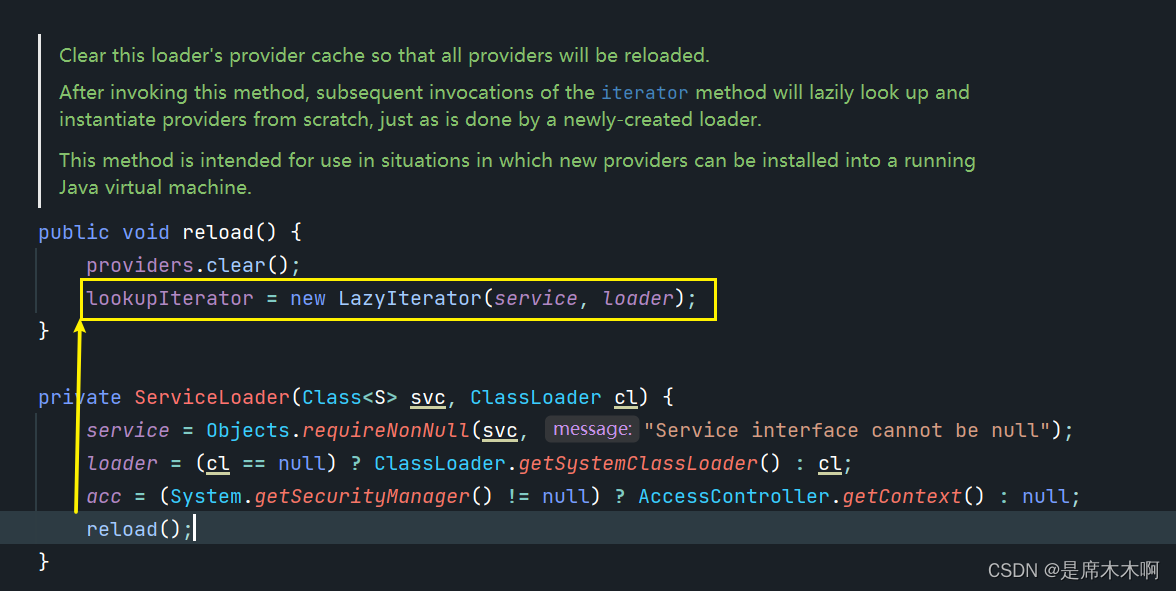
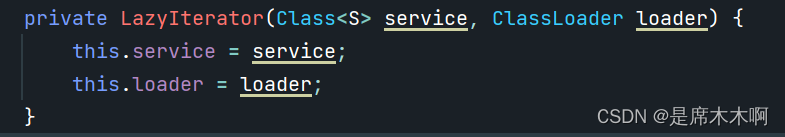
分析,
// ServiceLoader实现了Iterable接口,可以遍历所有的服务实现者
public final class ServiceLoader<S> implements Iterable<S>
{
// 查找配置文件的目录
private static final String PREFIX = "META-INF/services/";
// 表示要被加载的服务的类或接口
private final Class<S> service;
// 这个ClassLoader用来定位,加载,实例化服务提供者
private final ClassLoader loader;
// 访问控制上下文
private final AccessControlContext acc;
// 缓存已经被实例化的服务提供者,按照实例化的顺序存储
private LinkedHashMap<String,S> providers = new LinkedHashMap<>();
// 迭代器
private LazyIterator lookupIterator;
}
// 服务提供者查找的迭代器
public Iterator<S> iterator() {
return new Iterator<S>() {
Iterator<Map.Entry<String,S>> knownProviders
= providers.entrySet().iterator();
// hasNext方法
public boolean hasNext() {
if (knownProviders.hasNext())
return true;
return lookupIterator.hasNext();
}
// next方法
public S next() {
if (knownProviders.hasNext())
return knownProviders.next().getValue();
return lookupIterator.next();
}
};
}
// 服务提供者查找的迭代器
private class LazyIterator implements Iterator<S> {
// 服务提供者接口
Class<S> service;
// 类加载器
ClassLoader loader;
// 保存实现类的url
Enumeration<URL> configs = null;
// 保存实现类的全名
Iterator<String> pending = null;
// 迭代器中下一个实现类的全名
String nextName = null;
public boolean hasNext() {
if (nextName != null) {
return true;
}
if (configs == null) {
try {
String fullName = PREFIX + service.getName();
if (loader == null)
configs = ClassLoader.getSystemResources(fullName);
else
configs = loader.getResources(fullName);
} catch (IOException x) {
fail(service, "Error locating configuration files", x);
}
}
while ((pending == null) || !pending.hasNext()) {
if (!configs.hasMoreElements()) {
return false;
}
pending = parse(service, configs.nextElement());
}
nextName = pending.next();
return true;
}
public S next() {
if (!hasNext()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
String cn = nextName;
nextName = null;
Class<?> c = null;
try {
c = Class.forName(cn, false, loader);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException x) {
fail(service,"Provider " + cn + " not found");
}
if (!service.isAssignableFrom(c)) {
fail(service, "Provider " + cn + " not a subtype");
}
try {
S p = service.cast(c.newInstance());
providers.put(cn, p);
return p;
} catch (Throwable x) {
fail(service, "Provider " + cn + " could not be instantiated: " + x, x);
}
throw new Error(); // This cannot happen
}
}SPI应用场景举例
在JDBC4.0之前,连接数据库的时候,通常会用
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver")这句先加载数据库相关的驱动,然后再进行获取连接等的操作。而JDBC4.0之后不需要Class.forName来加载驱动,直接获取连接即可,这里使用了Java的SPI扩展机制来实现。
注册数据库连接驱动就是一个典型的例子,以PostGreSQL数据库连接驱动为例,我们知道:java中定义了接口java.sql.Driver,但是并没有提供具体的实现,具体的实现都是由不同厂商来提供的,所以我们实际开发时,需要先去找到对应的数据库连接驱动,把驱动加载到应用中,然后才能去执行数据库的种种操作。
查看postgresql依赖jar包,会发现在META-INFO下的services路径下,也提供了java.sql.Driver驱动类的实现子类信息,
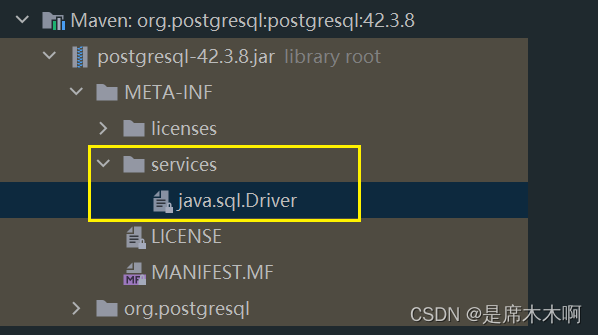
文件内容如下,
org.postgresql.Driver这样,就可以基于SPI机制,动态加载第三方提供的Driver数据库连接驱动,实现数据库相关的操作。