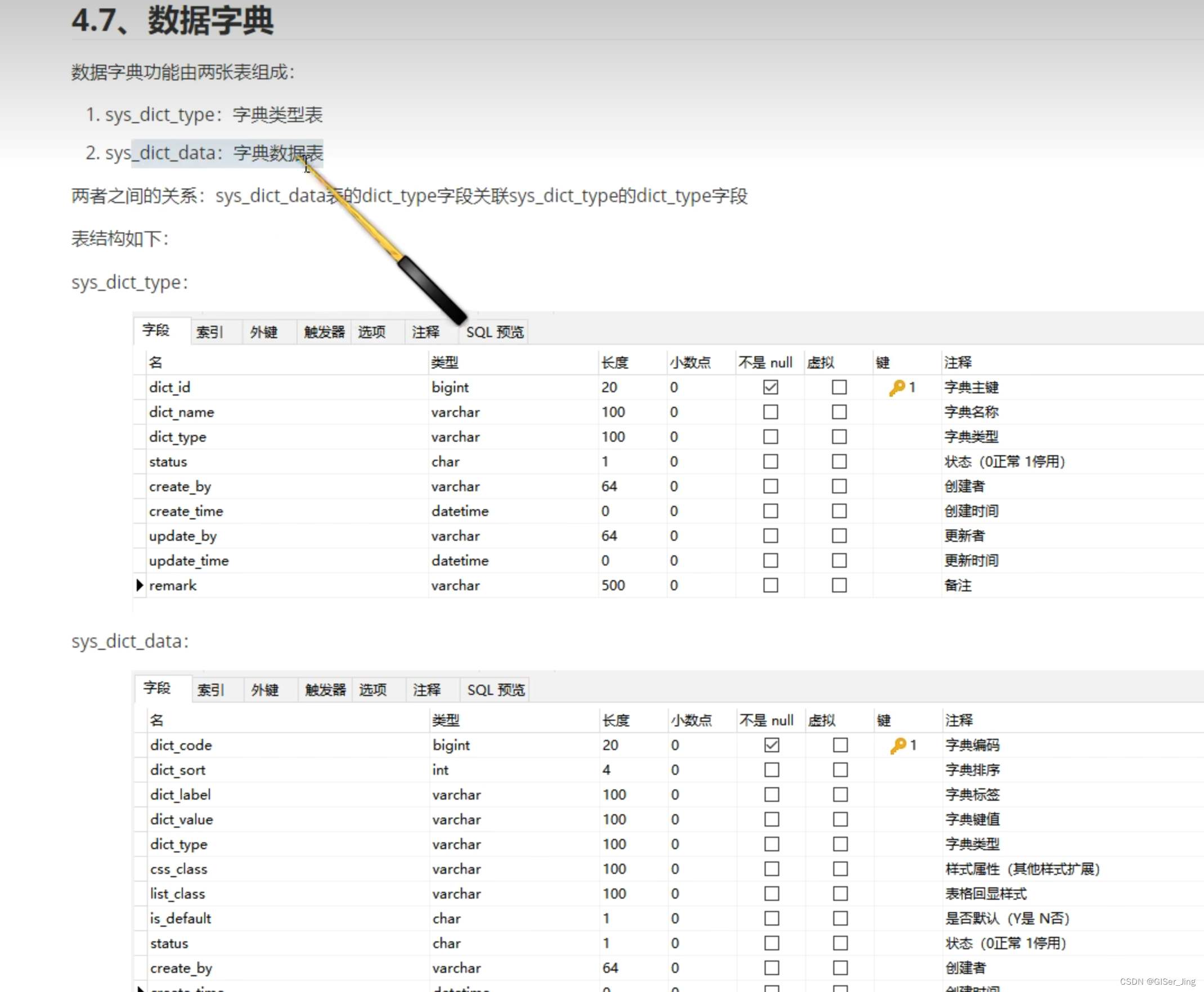
什么是虚拟Dom
虚拟 DOM 基于虚拟节点 VNode,VNode 本质上是一个对象,VDOM 就是VNode 组成的
废话,js 中所有的东西都是对象
虚拟DOM 为什么快,做了哪些优化
- 批量更新
- 多个DOM合并更新
- 减少浏览器的重排和重绘
- 局部更新
- 通过新VDOM对比,diff 算法
- 只更新需要重新渲染的真实 DOM
- 减少开销
- 跨平台支持
- node、浏览器、移动端、小程序都可以支持
虚拟DOM一定更快吗,不一定
- 额外的内存占用
- 虚拟DOM需要维护一个表示整个组件树的数据结构,这可能会占用额外的内存。
- VDOM 生成、对比,渲染都有额外的开销
- VDOM 适合中大型项目
- 简单的程序不适合VDOM,直接操作真实DOM更好
- 有些框架不用VDOM也很快
- 使用异步渲染技术
- requestAnimationFrame
- MutationObserver
- 使用异步渲染技术
实现VDOM
vue3 源码 runtime-core/src/vnode.ts 有关于 VNode 的定义
export interface VNode<
HostNode = RendererNode,
HostElement = RendererElement,
ExtraProps = { [key: string]: any },
> {
/**
* @internal
*/
__v_isVNode: true
/**
* @internal
*/
[ReactiveFlags.SKIP]: true
type: VNodeTypes
props: (VNodeProps & ExtraProps) | null
key: string | number | symbol | null
ref: VNodeNormalizedRef | null
/**
* SFC only. This is assigned on vnode creation using currentScopeId
* which is set alongside currentRenderingInstance.
*/
scopeId: string | null
/**
* SFC only. This is assigned to:
* - Slot fragment vnodes with :slotted SFC styles.
* - Component vnodes (during patch/hydration) so that its root node can
* inherit the component's slotScopeIds
* @internal
*/
slotScopeIds: string[] | null
children: VNodeNormalizedChildren
component: ComponentInternalInstance | null
dirs: DirectiveBinding[] | null
transition: TransitionHooks<HostElement> | null
// DOM
el: HostNode | null
anchor: HostNode | null // fragment anchor
target: HostElement | null // teleport target
targetAnchor: HostNode | null // teleport target anchor
/**
* number of elements contained in a static vnode
* @internal
*/
staticCount: number
// suspense
suspense: SuspenseBoundary | null
/**
* @internal
*/
ssContent: VNode | null
/**
* @internal
*/
ssFallback: VNode | null
// optimization only
shapeFlag: number
patchFlag: number
/**
* @internal
*/
dynamicProps: string[] | null
/**
* @internal
*/
dynamicChildren: VNode[] | null
// application root node only
appContext: AppContext | null
/**
* @internal lexical scope owner instance
*/
ctx: ComponentInternalInstance | null
/**
* @internal attached by v-memo
*/
memo?: any[]
/**
* @internal __COMPAT__ only
*/
isCompatRoot?: true
/**
* @internal custom element interception hook
*/
ce?: (instance: ComponentInternalInstance) => void
}使用 createVNode 创建虚拟节点
虚拟 dom 就是虚拟 node 节点的结合,每个 Vnode 都有一个 children 属性,children 的每个元素也是一个 VNode,他们有共同的根节点,就形成了一个虚拟的树结构。
自己实现虚拟 DOM 的重点步骤
- 定义一个 VNode 数据结构【这个如果是用 js,没有接口类型定义,就不用在代码中直接体现】
- 类中有 children 属性【用来存储子节点】
- 有 tag 代表标签【用来存储真实 html 的标签, div, p, span 等】
- 有 props 节点的属性【用来存储 html 元素的各种属性,style, class 等】
- 定义一个创建 VNode 的函数或类【createVNode】
- 定义一个渲染函数,将 VDOM 转成真实节点【render】
下面是我根据上面的步骤自己实现的:
// 创建虚拟节点函数
function createVNode(tag, props, children) {
// 虚拟节点必须包含的三个属性
return {
isVnode: true, // 用来判断是否是虚拟节点,也不可不用这个
tag,
props,
children // 数组
}
}
function render(VNode) {
const { tag, props, children } = VNode
// 创建真实 Dom 元素
const element = document.createElement(tag)
// 给 dom 元素增加属性
for(let key in props) {
element.setAttribute(key, props[key])
}
for(let i =0; i < children.length; i ++) {
let child = children[i]
// 如果子节点还是虚拟节点,就递归调用渲染函数
if (child.isVnode ) {
element.appendChild(render(child))
} else {
// 最终的真实节点
element.appendChild(document.createTextNode(child))
}
}
return element
}
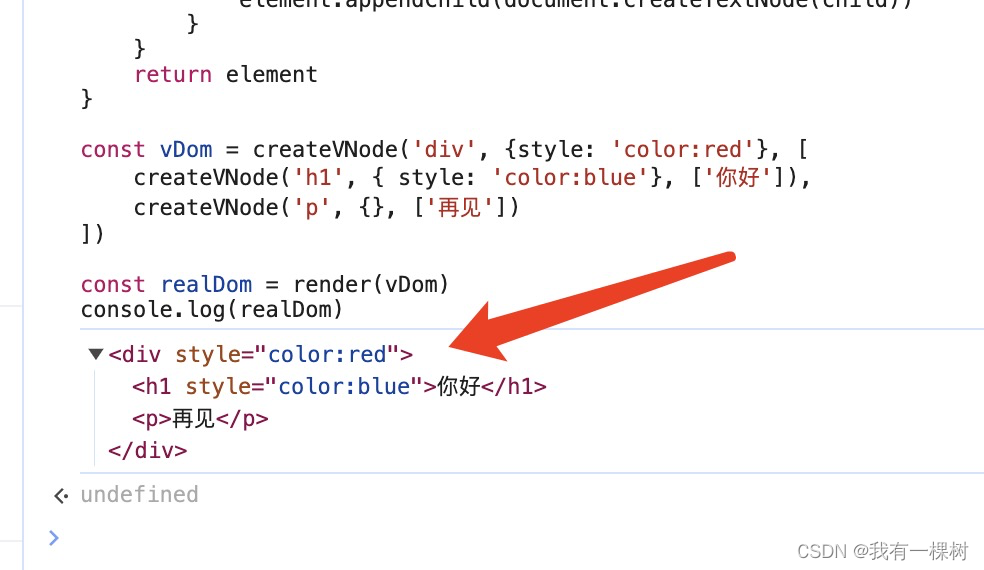
const vDom = createVNode('div', {style: 'color:red'}, [
createVNode('h1', { style: 'color:blue'}, ['你好']),
createVNode('p', {}, ['再见'])
])
const realDom = render(vDom)
console.log(realDom)复制上面代码到浏览器开发者工具中可以直接运行
下面 chatgpt 给的答案,使用了一个 vnode类,看起来更好一些:
// 定义虚拟DOM节点的数据结构
class VNode {
constructor(tag, props, children) {
this.tag = tag;
this.props = props;
this.children = children;
}
// 渲染虚拟DOM为真实DOM
render() {
const element = document.createElement(this.tag);
// 设置属性
for (const key in this.props) {
element.setAttribute(key, this.props[key]);
}
// 渲染子节点
this.children.forEach(child => {
if (child instanceof VNode) {
element.appendChild(child.render());
} else {
element.appendChild(document.createTextNode(child));
}
});
return element;
}
}
// 创建虚拟DOM
const virtualDOM = new VNode('div', { class: 'container' }, [
new VNode('h1', {}, ['Hello, Virtual DOM!']),
new VNode('p', {}, ['This is a paragraph.']),
]);
// 将虚拟DOM渲染到页面中
const root = document.getElementById('root');
root.appendChild(virtualDOM.render());