目录
一、继承体系
二、HandlerMapping
三、AbstractHandlerMapping
四、AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
4.1 成员属性
4.1.1 MappingRegistry内部类
4.2 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的初始化
4.3 getHandlerInternal()方法:根据当前的请求url,获取对应的处理器HandlerMathod
五、RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping
5.1 成员属性和构造方法
5.2 该类复写了一些方法
5.2.1 getMappingPathPatterns
5.2.2 getMatchingMapping
5.2.3 getMappingComparator
5.2.4 handleMatch,handleNoMatch
六、RequestMappingHandlerMapping
6.1 成员属性
6.2 主要方法
6.2.1 覆写了afterPropertiesSet()
6.2.2 isHandler()
6.2.3 getMappingForMethod()
我们现在最流行的就是使用注解实现Controller,那这就会涉及到AbstractHandlerMethodMapping,这个类在我们分析处理请求的源码中非常重要,所以这里单独拿出来分析。
一、继承体系
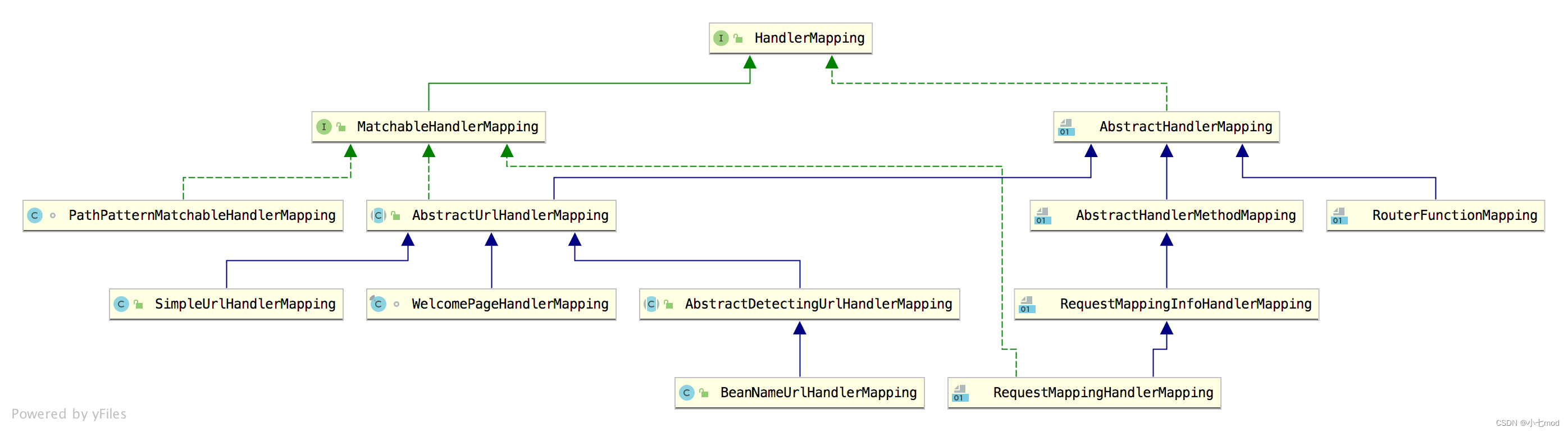
二、HandlerMapping
HandlerMapping是处理器映射器的顶层接口,只声明了1个方法–>getHandler–>调用getHandler实际上返回的是一个HandlerExecutionChain,这是典型的command的模式(命令模式)的使用,这个HandlerExecutionChain不但持有Handler本身,还包括了处理这个HTTP请求相关的拦截器,方法原型如下:
HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception;三、AbstractHandlerMapping
实现HandlerMapping的抽象实现,模板方法模式,将一些共性的方法抽象成1个类。其实现了getHandler。如下:
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 首先根据request获取handler
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
// 如果没有指定handler,就使用默认的
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
// 获取到了handler之后,再去获取拦截器,将两者封装到处理器执行链中返回
return getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
}
流程:
- 根据request获取对应的handler,该方法是1个抽象方法,由子类来实现,如下:
protected abstract Object getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception;- 如果没有对应的handler,就是要默认的handler
- 如果没有默认的handler,返回null
- 如果获取到的handler是一个字符串,说明这个是Bean名,则通过名称取出对应的 handler bean
- 把handler 封装到HandlerExecutionChain中并加上拦截器。如下:
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) {
// 1. 获得HandlerExecutionChain
HandlerExecutionChain chain = (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ?
(HandlerExecutionChain) handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler));
// 2. 根据请求获得对应的Path
String lookupPath = this.urlPathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request);
// 3. 遍历adaptedInterceptors
for (HandlerInterceptor interceptor : this.adaptedInterceptors) {
// 3.1 如果是MappedInterceptor,并且匹配当前的path,则加入到HandlerExecutionChain中
if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) {
MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = (MappedInterceptor) interceptor;
if (mappedInterceptor.matches(lookupPath, this.pathMatcher)) {
chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor());
}
}
// 3.2 否则,直接加入到HandlerExecutionChain
else {
chain.addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
}
return chain;
}- 获得HandlerExecutionChain
- 根据请求获得对应的Path
- 遍历adaptedInterceptors(拦截器)
- 如果是MappedInterceptor,并且匹配当前的path,则加入到HandlerExecutionChain中
- 否则,直接加入到HandlerExecutionChain
四、AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping是一个泛型类,其泛型参数T–>用来代表匹配handler的条件专门使用的一种类,这里的条件就不只是url了,还可以有很多其他条件,如request的类型,请求的参数,header等都可以作为匹配的HandlerMethod的条件。默认使用的是RequestMappingInfo,这个也是最常见的情况(只要是用注解实现Controller一般都是用RequestMappingInfo作为匹配条件类)。AbstractHandlerMethodMapping实现了InitializingBean接口。
4.1 成员属性
// scpoed 代理 bean的name的前缀。用来去除handler method的判断
private static final String SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX = "scopedTarget.";
// cors请求并且是options类型的请求并且请求头中含有Access-Control-Request-Method时返回的HandlerMethod
private static final HandlerMethod PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH =
new HandlerMethod(new EmptyHandler(), ClassUtils.getMethod(EmptyHandler.class, "handle"));
private static final CorsConfiguration ALLOW_CORS_CONFIG = new CorsConfiguration();
static {
ALLOW_CORS_CONFIG.addAllowedOrigin("*");
ALLOW_CORS_CONFIG.addAllowedMethod("*");
ALLOW_CORS_CONFIG.addAllowedHeader("*");
ALLOW_CORS_CONFIG.setAllowCredentials(true);
}
// 如果为true,则在当前applicationContext和祖先applicationContext中获取所有的bean,如果为false,则在当前上下文获得所有的bean
private boolean detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts = false;
// 向MappingRegistry中的nameLookup进行注册时用来生成beanName,这里默认使用的是RequestMappingInfoHandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy
// 其规则为:类名里的大写字母组合+"#"+方法名.
private HandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy<T> namingStrategy;
// 用来存储各种映射关系
private final MappingRegistry mappingRegistry = new MappingRegistry();
4.1.1 MappingRegistry内部类
这里有必要说明一下MappingRegistry类,它是AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的内部类,其成员属性如下:
class MappingRegistry {
private final Map<T, MappingRegistration<T>> registry = new HashMap<T, MappingRegistration<T>>();
// 保存着匹配条件(也就是RequestMappingInfo)和HandlerMethod的对应关系
private final Map<T, HandlerMethod> mappingLookup = new LinkedHashMap<T, HandlerMethod>();
// 保存着url与匹配条件(也就是RequestMappingInfo)的对应关系,当然这里的url是pattren式的,可以使用通配符。
// 由于RequestMappingInfo可以同时使用多种不同的匹配方式而不只是url一种,所以反过来说同一个url就可能有多个RequestMappingInfo与之对应
// 这里的RequestMappingInfo其实就是在@RequestMapping中注释的内容
private final MultiValueMap<String, T> urlLookup = new LinkedMultiValueMap<String, T>();
// 这个Map是spring mvc 4 新增的,保存着name(Controller中处理请求的方法名)与HandlerMethod的对应关系,这个name是从HandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy的实现类从
// HandlerMethod中解析处理的,默认使用的是RequestMappingInfoHandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy,解析规则是:
// 类名里的大写字母组合+"#"+方法名。这个在正常的匹配过程不需要使用,它主要用在MvcUriComponentsBuilder里,可以根据name获取相应的url
private final Map<String, List<HandlerMethod>> nameLookup =
new ConcurrentHashMap<String, List<HandlerMethod>>();
private final Map<HandlerMethod, CorsConfiguration> corsLookup =
new ConcurrentHashMap<HandlerMethod, CorsConfiguration>();
private final ReentrantReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
...
}注意:带有通配符的路径匹配不在urlLookup属性参数中,只存在了registry。直接匹配所有的参数路径中,才会两者都存。
4.2 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的初始化
由于AbstractHandlerMethodMapping实现了InitializingBean,因此在其初始化过程中,会调用afterPropertiesSet方法,如下:
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
initHandlerMethods();
}
这里我们就可以看出,在初始化AbstractHandlerMethodMapping类的时候,就自动调用了initHandlerMethods方法。这个方法其实就帮我们提前建立起了url和method之间的映射关系。在后面处理请求的时候可以根据url直接找到要处理该请求的method。
protected void initHandlerMethods() {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Looking for request mappings in application context: " + getApplicationContext());
}
// 获取ApplicationContext中的所有bean的name
String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts ?
BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(getApplicationContext(), Object.class) :
getApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class));
// 遍历所有的bean name
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
// 如果bean nanme 不是 scopedTarget开头的,则获得其类型
if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) {
Class<?> beanType = null;
try {
// 获取bean的类型
beanType = getApplicationContext().getType(beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An unresolvable bean type, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not resolve target class for bean with name '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
// 如果beanType不为空,并且是一个处理器,则进行处理
if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) {
detectHandlerMethods(beanName);
}
}
}
// 所有的处理器方法都初始化完成后,调用子类的方法
handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods());
}
流程:
- 获得ApplicationContext中的所有bean的name
- 遍历
- 如果bean name 不是 scopedTarget开头的,则获得其类型
- 如果该bean是一个handler(处理器),则调用detectHandlerMethods()对其进行注册。detectHandlerMethods()方法源码如下:
protected void detectHandlerMethods(final Object handler) {
// 获得handler的类型
Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ?
getApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass());
// 如果是cglib代理的子对象类型,则返回父类型,否则直接返回传入的类型
final Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
// 获取当前bean里所有符合Handler要求的Method(也就是获取当前Controller中所有的用来处理请求的方法)
Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,
new MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>() {
@Override
public T inspect(Method method) {
try {
return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" +
userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex);
}
}
});
// 将符合要求的methods注册到mappingRegistry中,也就是保存到mappingRegistry的3个map中
for (Map.Entry<Method, T> entry : methods.entrySet()) {
Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(entry.getKey(), userType);
T mapping = entry.getValue();
registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);
}
}
- 获得handler的类型,如果是cglib代理的子对象类型,则返回父类型,否则直接返回传入的类型。
- 获取当前bean里所有符合Handler要求的Method,其中会回调getMappingForMethod方法,该方法是个抽象方法,由子类实现。
- 将符合要求的methods注册,代码如下:
protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, T mapping) {
// 将method注册到mappingRegistry中
this.mappingRegistry.register(mapping, handler, method);
}
MappingRegistry#register()将url和handler之间的映射关系进行了注册,实现如下:
public void register(T mapping, Object handler, Method method) {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();
try {
// 根据传入的handler和method创建HandlerMethod处理器类型的对象
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method);
// 检查是否在mappingLookup已经存在,如果存在而且和现在传入的不同则抛出异常
assertUniqueMethodMapping(handlerMethod, mapping);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Mapped \"" + mapping + "\" onto " + handlerMethod);
}
// 添加到mappingLookup中
this.mappingLookup.put(mapping, handlerMethod);
// 添加到urlLookup
List<String> directUrls = getDirectUrls(mapping);
for (String url : directUrls) {
this.urlLookup.add(url, mapping);
}
// 添加到nameLookup
String name = null;
if (getNamingStrategy() != null) {
name = getNamingStrategy().getName(handlerMethod, mapping);
addMappingName(name, handlerMethod);
}
// 实例化CorsConfiguration
CorsConfiguration corsConfig = initCorsConfiguration(handler, method, mapping);
if (corsConfig != null) {
this.corsLookup.put(handlerMethod, corsConfig);
}
this.registry.put(mapping, new MappingRegistration<T>(mapping, handlerMethod, directUrls, name));
}
finally {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
步骤:
- 创建HandlerMethod,代码如下:
protected HandlerMethod createHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method) {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod;
// 如果handler是String类型,那么就是beanName
if (handler instanceof String) {
String beanName = (String) handler;
// 根据beanName获取对应的bean
handlerMethod = new HandlerMethod(beanName,
getApplicationContext().getAutowireCapableBeanFactory(), method);
}
else {
handlerMethod = new HandlerMethod(handler, method);
}
return handlerMethod;
}
- 检查是否在mappingLookup已经存在,如果存在而且和现在传入的不同则抛出异常。代码如下:
private void assertUniqueMethodMapping(HandlerMethod newHandlerMethod, T mapping) {
// 检查是否有重复的映射
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = this.mappingLookup.get(mapping);
if (handlerMethod != null && !handlerMethod.equals(newHandlerMethod)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Ambiguous mapping. Cannot map '" + newHandlerMethod.getBean() + "' method \n" +
newHandlerMethod + "\nto " + mapping + ": There is already '" +
handlerMethod.getBean() + "' bean method\n" + handlerMethod + " mapped.");
}
}
- 添加到mappingLookup中。
- 添加到urlLookup,其中getDirectUrls–>获得mapping的Path,如果不含有*或者含有?的话,则添加到结果集中。代码如下:
private List<String> getDirectUrls(T mapping) {
List<String> urls = new ArrayList<String>(1);
for (String path : getMappingPathPatterns(mapping)) {
if (!getPathMatcher().isPattern(path)) {
urls.add(path);
}
}
return urls;
}AntPathMatcher#isPattern,如下:
public boolean isPattern(String path) {
return (path.indexOf('*') != -1 || path.indexOf('?') != -1);
}
- 添加到nameLookup。
- 实例化CorsConfiguration,如果不为null,则添加到corsLookup。此处默认返回null,由子类复写。
- 添加到registry中。
handlerMethodsInitialized()是模板方法,空实现。
4.3 getHandlerInternal()方法:根据当前的请求url,获取对应的处理器HandlerMathod
getHandlerInternal()是一个很重要的方法,它的实现如下(删去多余代码):
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 1.利用request截取用于匹配的url有效路径(获取当前的请求路径)
String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
// 2. 使用lookupHandlerMethod方法通过lookupPath和request找对应的HandlerMethod
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
// 3. 如果可以找到handlerMethod则调用createWithResolvedBean方法创建新的HandlerMethod
return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);
}
- 利用request对象截取用于匹配的url有效路径。
- 使用lookupHandlerMethod方法通过lookupPath和request找HandlerMethod。代码如下:
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// match是内部类,用于保存匹配条件和HandlerMethod
List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<Match>();
// 根据请求路径lookupPath获取到匹配条件
List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByUrl(lookupPath);
if (directPathMatches != null) {
// 将匹配到的条件添加到matches
addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
// 如果不能直接使用lookupPath得到匹配条件,则将所有匹配条件加入到matches
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
// No choice but to go through all mappings...
addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), matches, request);
}
// 对matches进行排序,并取第一个作为bestMatch。如果前面两个排序相同则抛出异常
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request));
Collections.sort(matches, comparator);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Found " + matches.size() + " matching mapping(s) for [" +
lookupPath + "] : " + matches);
}
Match bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (matches.size() > 1) {
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH;
}
// 如果matches有多个匹配的,则将第2个和第一个进行比较,看顺序是否一样,如果是一样的话,则抛出异常
Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1);
if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) {
Method m1 = bestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
Method m2 = secondBestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
throw new IllegalStateException("Ambiguous handler methods mapped for HTTP path '" +
request.getRequestURL() + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}");
}
}
// 在返回前做一些处理,handleMatch方法的默认实现是将lookupPath设置到request的属性,将更多的参数设置到了request,主要是为了以后使用时方便
handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);
// 返回匹配的HandlerMethod
return bestMatch.handlerMethod;
}
else {
// 如果没有匹配的,则调用handleNoMatch方法,子类RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping进行了重写
return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), lookupPath, request);
}
}
Match内部类讲解:
- 根据lookupPath获取到匹配条件,将匹配到的条件添加到matches
- 如果不能直接使用lookupPath得到匹配条件,则将所有匹配条件加入到matches
- 如果matches非空
- 对matches进行排序,并取第一个作为bestMatch,如果前面两个排序相同则抛出异常
- 在返回前做一些处理。默认实现是将lookupPath设置到request的属性,子类RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping进行了重写,将更多的参数设置到了request。主要是为了以后使用时方便
- 否则,调用handleNoMatch,默认返回null。
- 如果可以找到handlerMethod则调用createWithResolvedBean方法创建新的HandlerMethod。代码如下:
// 该方法用于创建一个HandlerMethod对象
// 此时handlerMethod中只有匹配条件,还没有handler处理器,这个方法就是要将处理器和匹配条件绑定在一起,创建HandlerMethod对象
public HandlerMethod createWithResolvedBean() {
Object handler = this.bean;
if (this.bean instanceof String) {
String beanName = (String) this.bean;
handler = this.beanFactory.getBean(beanName);
}
return new HandlerMethod(this, handler);
}
五、RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping
RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping–> 继承自AbstractHandlerMethodMapping。
5.1 成员属性和构造方法
// 对OPTIONS请求的处理时用到
private static final Method HTTP_OPTIONS_HANDLE_METHOD;
static {
try {
HTTP_OPTIONS_HANDLE_METHOD = HttpOptionsHandler.class.getMethod("handle");
}
catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
// Should never happen
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to retrieve internal handler method for HTTP OPTIONS", ex);
}
}
// 构造方法
protected RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping() {
setHandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy(new RequestMappingInfoHandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy());
}5.2 该类复写了一些方法
5.2.1 getMappingPathPatterns
protected Set<String> getMappingPathPatterns(RequestMappingInfo info) {
return info.getPatternsCondition().getPatterns();
}
该方法是在hander注册的时候调用,如下:

5.2.2 getMatchingMapping
检查给定的RequestMappingInfo是否匹配当前的请求,返回RequestMappingInfo,代码如下:
protected RequestMappingInfo getMatchingMapping(RequestMappingInfo info, HttpServletRequest request) {
return info.getMatchingCondition(request);
}
5.2.3 getMappingComparator
返回1个比较RequestMappingInfo的Comparator,在有多个Handler匹配当前请求时用到。代码如下:
protected Comparator<RequestMappingInfo> getMappingComparator(final HttpServletRequest request) {
return new Comparator<RequestMappingInfo>() {
@Override
public int compare(RequestMappingInfo info1, RequestMappingInfo info2) {
return info1.compareTo(info2, request);
}
};
}
5.2.4 handleMatch,handleNoMatch
比较简单,这里就不再贴出
六、RequestMappingHandlerMapping
RequestMappingHandlerMapping–> 继承自RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping。根据在实现Controller接口或者被@Controller注解的类中的在类和方法上声明的@RequestMapping,创建一个 RequestMappingInfo。
6.1 成员属性
// 是否使用后缀匹配(.*)当对请求进行模式匹配时,如果可用时,则/users 对/users.*也匹配.默认是true.
private boolean useSuffixPatternMatch = true;
// 是否后缀匹配应该只对ContentNegotiationManager中注册的扩展符匹配时生效.这一般建议减少歧义和避免问题比如当.出现在路径的情况下
private boolean useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch = false;
// 是否有无斜杠都匹配,如果启用的化,则/users 也匹配 /users/.默认是true
private boolean useTrailingSlashMatch = true;
// 内容协商
private ContentNegotiationManager contentNegotiationManager = new ContentNegotiationManager();
// 这里使用的是EmbeddedValueResolver
private StringValueResolver embeddedValueResolver;
// RequestMappingInfo的Builder类,用来创建RequestMappingInfo的
private RequestMappingInfo.BuilderConfiguration config = new RequestMappingInfo.BuilderConfiguration();6.2 主要方法
6.2.1 覆写了afterPropertiesSet()
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
this.config = new RequestMappingInfo.BuilderConfiguration();
this.config.setUrlPathHelper(getUrlPathHelper());
this.config.setPathMatcher(getPathMatcher());
this.config.setSuffixPatternMatch(this.useSuffixPatternMatch);
this.config.setTrailingSlashMatch(this.useTrailingSlashMatch);
this.config.setRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch(this.useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch);
this.config.setContentNegotiationManager(getContentNegotiationManager());
super.afterPropertiesSet();
}
6.2.2 isHandler()
protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) {
return (AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) ||
AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class));
}
调用链如下:

6.2.3 getMappingForMethod()
使用在类和方法上声明的@RequestMapping来创建RequestMappingInfo。代码如下:
protected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType) {
// 1. 根据Method上的@RequestMapping创建RequestMappingInfo
RequestMappingInfo info = createRequestMappingInfo(method);
if (info != null) {
// 2. 根据类上的@RequestMapping创建RequestMappingInfo
RequestMappingInfo typeInfo = createRequestMappingInfo(handlerType);
if (typeInfo != null) {
// 3. 合并
info = typeInfo.combine(info);
}
}
return info;
}createRequestMappingInfo(),如下:
private RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(AnnotatedElement element) {
// 获取@RequestMapping 注解
RequestMapping requestMapping = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(element, RequestMapping.class);
// 此处返回的都是null
RequestCondition<?> condition = (element instanceof Class ?
getCustomTypeCondition((Class<?>) element) : getCustomMethodCondition((Method) element));
return (requestMapping != null ? createRequestMappingInfo(requestMapping, condition) : null);
}
- 获取@RequestMapping 注解
- 获得RequestCondition,此处返回的都是null
- 如果requestMapping等于null,则返回null,否则根据RequestMapping创建RequestMappingInfo。代码如下:
protected RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(
RequestMapping requestMapping, RequestCondition<?> customCondition) {
return RequestMappingInfo
.paths(resolveEmbeddedValuesInPatterns(requestMapping.path()))
.methods(requestMapping.method())
.params(requestMapping.params())
.headers(requestMapping.headers())
.consumes(requestMapping.consumes())
.produces(requestMapping.produces())
.mappingName(requestMapping.name())
.customCondition(customCondition)
.options(this.config)
.build();
}
相关文章:【Spring MVC】Spring MVC框架的介绍及其使用方法
【Spring MVC】Spring MVC的执行流程与源码分析