原文链接:Gemma模型论文详解(附源码)
1. 背景介绍
Gemma模型是在2023.2.21号Google新发布的大语言模型, Gemma复用了Gemini相同的技术(Gemini也是Google发布的多模态模型),Gemma这次发布了了2B和7B两个版本的参数,不仅提供了预训练的checkpoints,还提供了用于对话、指令跟随等fine-tune的checkpoints。在QA问答、常识。在11

2. 模型介绍
2.1 模型结构
Gemma模型使用了transformer decoder结构进行训练,训练的上下文大小为8192个token,模型参数如下:
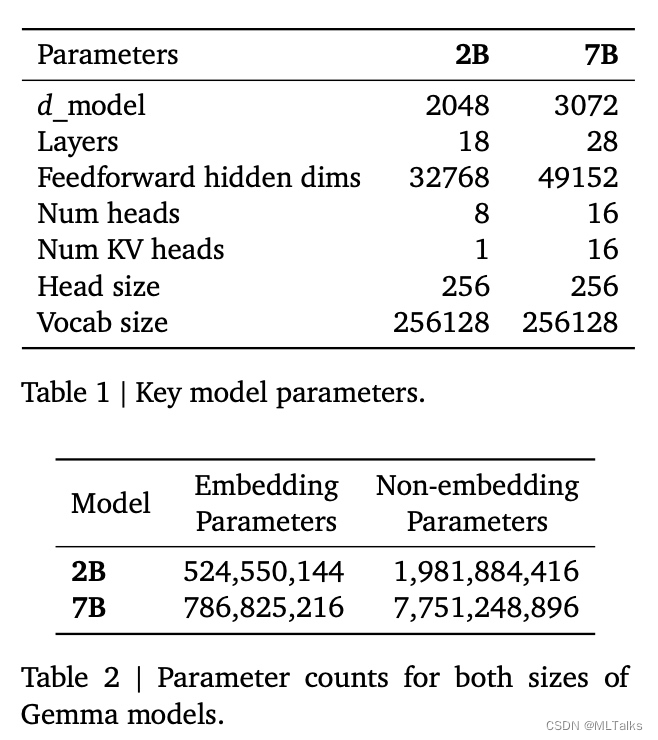
相比原始transformer结构的区别:
-
Multi-Query Attention:7B模型使用了
multi-head attention,2B模型使用了multi-query attention (with 𝑛𝑢𝑚_𝑘𝑣_ℎ𝑒𝑎𝑑𝑠 = 1)。对比llama2中用了group-query attention。

-
RoPE Embeddings: 不使用绝对位置编码,在每一层前加下
RoPE Embedding,同时共享输入与输出层的embedding权重。 -
GeGLU Activations: ReLU的激活替换为GeGLU的激活。对比llama中用了swiglu。
-
Normalizer Location: 在transformer的每一层layer的前后都进行规一化,这里使用
RMSNorm做为规一化层。
2.2 训练搭建
Gemma使用TPUv5e进行训练;一个pod中有256块TPUv5e芯片,256块芯片被设计为16X16的2D拓扑;Gemma-7B使用16个pods(4096块卡)进行训练,Gemma-2B使用2个pods(512块卡)。7B模型在一个pod内使用16路模型并行和16路数据并行,2B模型在一个pod内使用256路数据并行。优化器状态使用ZeRO-3进行切分,减少显存占用。在pod外使用类似Pathways的方式减少数据复制的成本。
和Gemini模型训练一样,综合了Jax和Pathways的单控制器single controller编程范式,使用单个python进程编排整个训练; 使用GSPMD partitioner用于训练step的计算,使用XLA compiler减少中间结果的大小。
2.3 训练数据
Gemma 2B和7B分别基于2T和6T个token进行训练,token来源于纯英文的文本,内容包括网页、数学、代码等。使用SentencePiece的tokenizer,字典大小有256K个token。数据过滤使用基于模型的分类器去除有害的、低质量的内容。最后采用类似Gemini的方式进行训练数据的混合,提升高质量数据的占比。
2.4 指令微调(Instruction Tuning)
2B和7B进行有监督微调(SFT)训练中使用混合生成数据和人工标注的prompt文本对,同时进行RLHF训练。在SFT阶段,基于给定的一个prompt,通过测试模型生成多个响应的回答结果,通过一个更大更好的模型进行结果的好坏判断。基于不同的侧重方向(指令跟随/事实/创造性/安全等)构建不同的prompt。使用多种基于LM的自动判断方法,比如chain-of-thought prompting。
训练和推理过程中使用相同的数据格式,格式的设计重点在于两点,一个是确定多轮对话中的角色,一个是确定一轮对话的开始结束。对应格式标记和示例的训练数据如下:
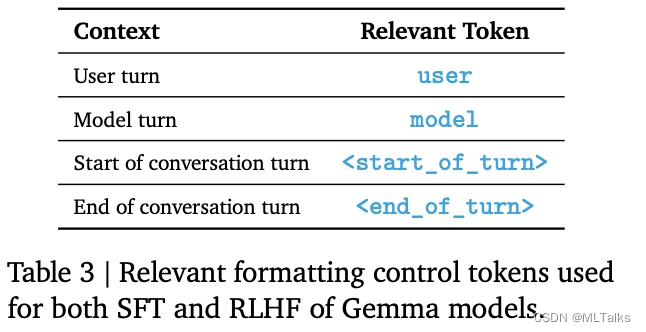
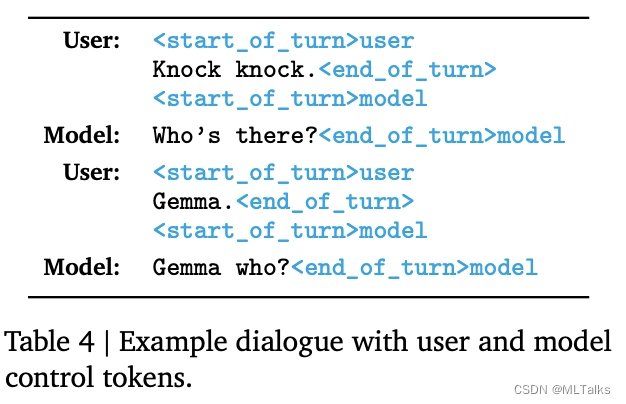
3. 源码
-
Tensorflow实现的源码在github google-deepmind/gemma中,PyTorch实现的源码在github google/gemma_pytorch。
-
模型的配置在gemma/config.py文件中, 7B与2B区别主要在于
num_hidden_layers/num_attention_heads/num_key_value_heads/hidden_size/intermediate_size。
@dataclasses.dataclass
class GemmaConfig:
# The number of tokens in the vocabulary.
vocab_size: int = 256000
# The maximum sequence length that this model might ever be used with.
max_position_embeddings: int = 8192
# The number of blocks in the model.
num_hidden_layers: int = 28
# The number of attention heads used in the attention layers of the model.
num_attention_heads: int = 16
# The number of key-value heads for implementing attention.
num_key_value_heads: int = 16
# The hidden size of the model.
hidden_size: int = 3072
# The dimension of the MLP representations.
intermediate_size: int = 24576
# The number of head dimensions.
head_dim: int = 256
# The epsilon used by the rms normalization layers.
rms_norm_eps: float = 1e-6
# The dtype of the weights.
dtype: str = 'bfloat16'
# Whether a quantized version of the model is used.
quant: bool = False
# The path to the model tokenizer.
tokenizer: Optional[str] = 'tokenizer/tokenizer.model'
def get_dtype(self) -> Optional[torch.dtype]:
"""Gets the torch dtype from the config dtype string."""
return _STR_DTYPE_TO_TORCH_DTYPE.get(self.dtype, None)
def get_config_for_7b() -> GemmaConfig:
return GemmaConfig()
def get_config_for_2b() -> GemmaConfig:
return GemmaConfig(
num_hidden_layers=18,
num_attention_heads=8,
num_key_value_heads=1,
hidden_size=2048,
intermediate_size=16384
)
- 模型定义在gemma/model.py文件中,
GemmaDecoderLayer的定义如下:
class GemmaDecoderLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
config: gemma_config.GemmaConfig,
):
super().__init__()
self.self_attn = GemmaAttention(
hidden_size=config.hidden_size,
num_heads=config.num_attention_heads,
num_kv_heads=config.num_key_value_heads,
head_dim=config.head_dim,
quant=config.quant,
)
self.mlp = GemmaMLP(
hidden_size=config.hidden_size,
intermediate_size=config.intermediate_size,
quant=config.quant,
)
self.input_layernorm = RMSNorm(config.hidden_size,
eps=config.rms_norm_eps)
self.post_attention_layernorm = RMSNorm(config.hidden_size,
eps=config.rms_norm_eps)
- GeGLU的实现跟llama的swiglu不同,geglu相比glu区是采用了gelu的激活,以下是glu的计算示例图:
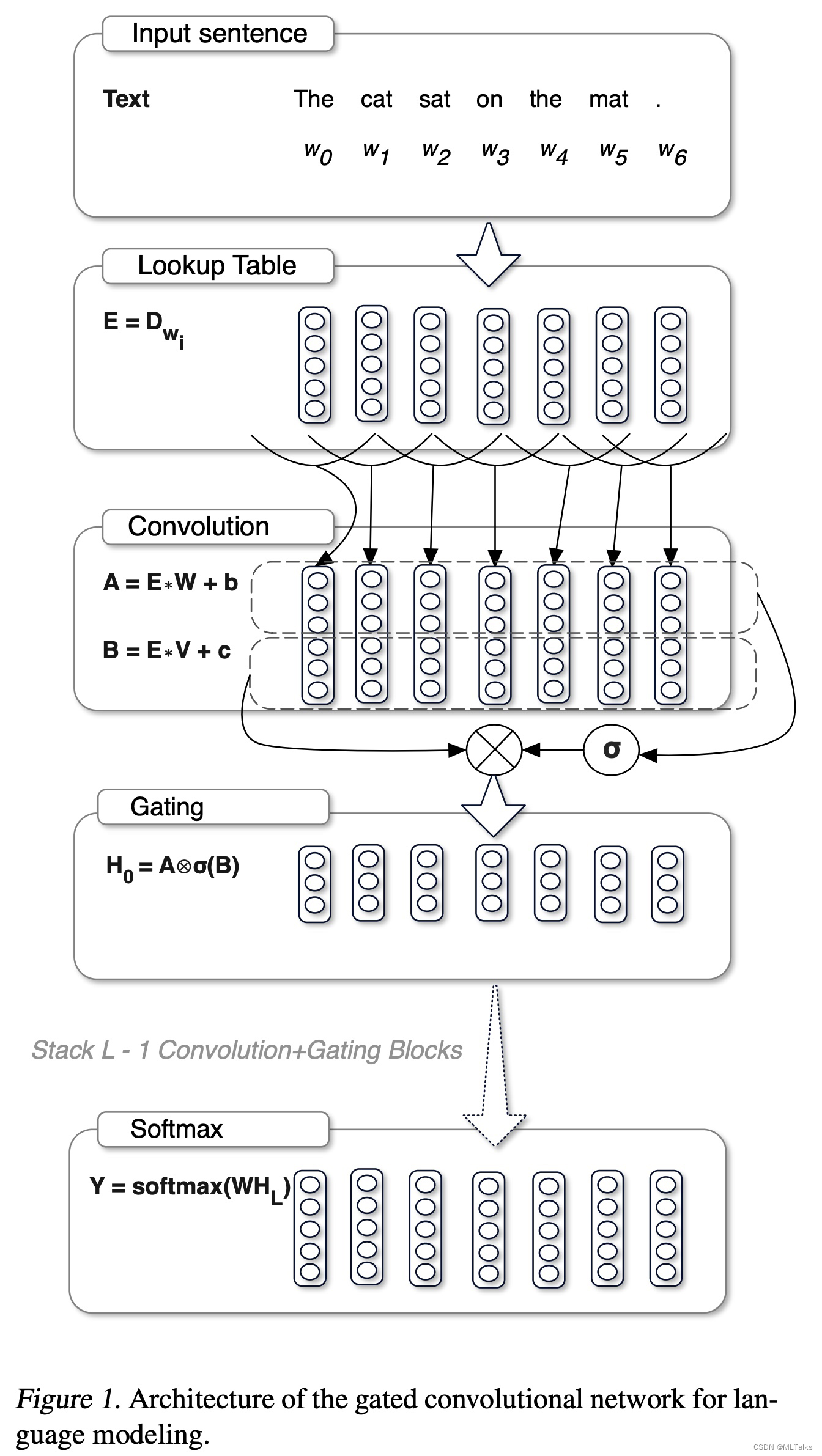
代码参考如下,代码中self.gate_proj对应上图中的B矩阵,gate相当于
σ
(
B
)
\sigma(B)
σ(B),self.up_proj对应上图中的A矩阵.
class GemmaMLP(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
hidden_size: int,
intermediate_size: int,
quant: bool,
):
super().__init__()
self.gate_proj = Linear(hidden_size, intermediate_size, quant)
self.up_proj = Linear(hidden_size, intermediate_size, quant)
self.down_proj = Linear(intermediate_size, hidden_size, quant)
def forward(self, x):
gate = self.gate_proj(x)
gate = F.gelu(gate)
up = self.up_proj(x)
fuse = gate * up
outputs = self.down_proj(fuse)
return outputs
4. 参考
- google-deepmind/gemma
- Gemma 开放模型
- Gemma: Open Models Based on Gemini Research and Technology
- gemma-open-models
- github google/gemma_pytorch
- github google-deepmind/gemma
- Grouped Query Attention论文阅读
- SwiGLU论文阅读








![[hgame 2024 week3] crypto/pwn](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/f5cf191d46de4d4aad270b0d4e617ecd.png)