39. 组合总和
- 刷题
 https://leetcode.cn/problems/combination-sum/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/combination-sum/description/ - 文章讲解
 https://programmercarl.com/0039.%E7%BB%84%E5%90%88%E6%80%BB%E5%92%8C.html
https://programmercarl.com/0039.%E7%BB%84%E5%90%88%E6%80%BB%E5%92%8C.html - 视频讲解
 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1KT4y1M7HJ/?vd_source=af4853e80f89e28094a5fe1e220d9062
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1KT4y1M7HJ/?vd_source=af4853e80f89e28094a5fe1e220d9062 -
回溯树图示:
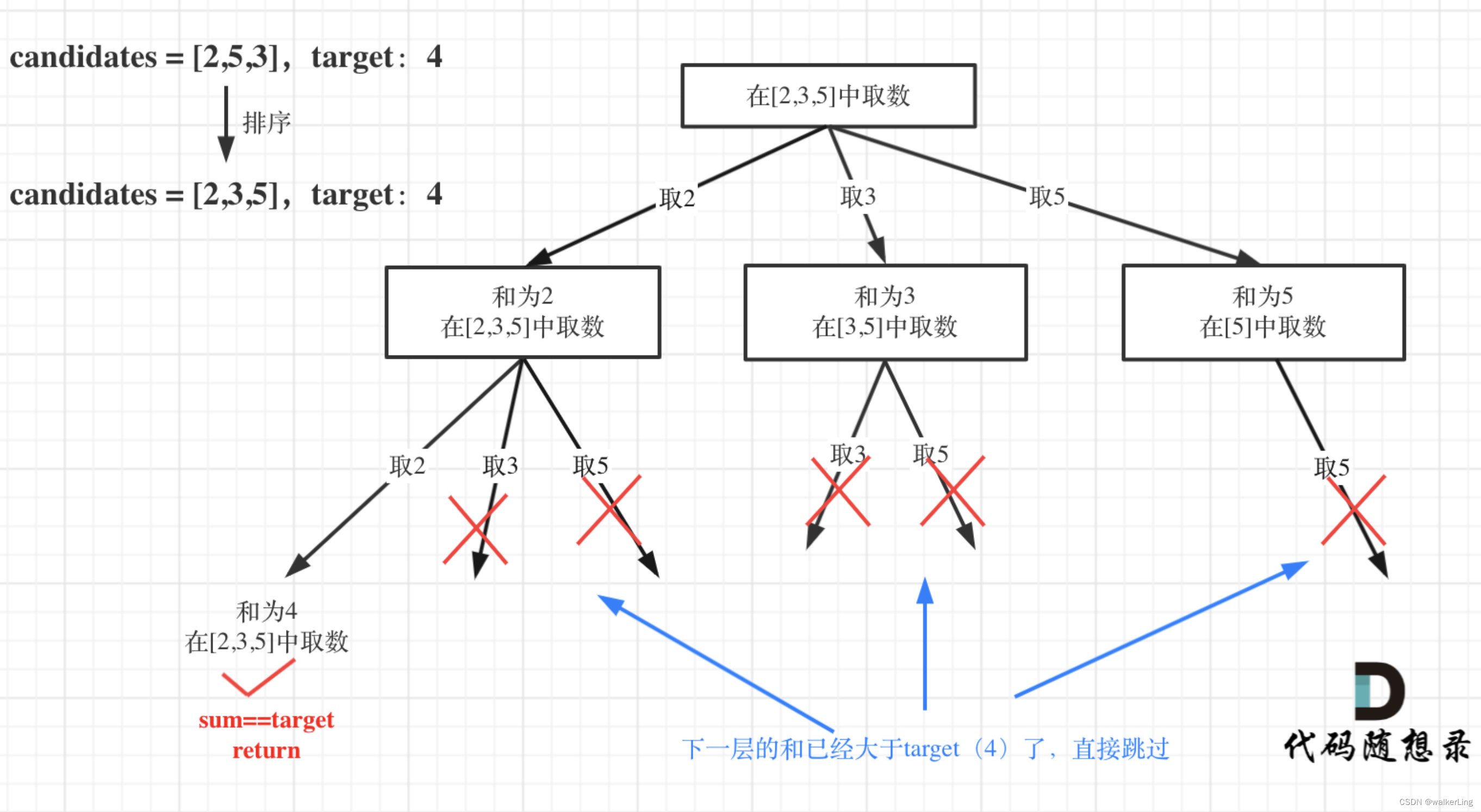
class Solution {
//与之前组合总和的问题的区别在于:
//之前的问题限制了元素个数k,本题中却未限制单个集合中元素个数
//且因为可以无限被选取,所以排除0,均为正整数
//这就表明本题回溯树的高度的控制条件只有sum,高度不能确定
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
//存储最终的结果序列
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
//为了进行合适的剪枝,需要对原始序列进行预排序
Arrays.sort(candidates);
combinationSum1(result, new ArrayList<>(), candidates, target, 0, 0);
return result;
}
//参数1:传入最终结果列表
//参数2:传入存储单个结果的列表
//参数3:传入原始序列
//参数4:传入目标总和
//参数5:传入当前总和
//参数6:传入控制for循环遍历的起始
public void combinationSum1(List<List<Integer>> result, List<Integer> path, int[] candidates, int target, int sum, int startIndex){
//递归出口,此时找到了和为target的组合,直接返回
//由于元素可以无限选取,所以递归结束的情况只有两种:
//1、总和恰好等于目标值,递归结束
//2、总和大于目标值,递归结束
if(sum == target){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
//递归回溯部分
//横向遍历,回溯树宽度即为原序列长度
for(int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length; i++){
//剪枝,若当前sum再加上当前值大于目标值,则直接终止当前的遍历
//因为原序列都是经过递增排序的,当前值已经大于目标值了,再接着遍历的话会更大于目标值
//所以需要结束当前遍历,进入下一个上级结点的遍历
if(sum + candidates[i] > target){
break;
}
//若加上当前值小于目标值,则可将当前值加入path序列
path.add(candidates[i]);
//递归部分
//因为二级递归不需要和一级递归避免重复,因为题目中某个元素可以重复使用不限制使用次数
//所以二级递归和一级递归一样仍然以i开始
combinationSum1(result, path, candidates, target, sum + candidates[i], i);
//回溯部分
//移除最后一个
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}
40.组合总和II
- 刷题
 https://leetcode.cn/problems/combination-sum-ii/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/combination-sum-ii/description/ - 文章讲解
 https://programmercarl.com/0040.%E7%BB%84%E5%90%88%E6%80%BB%E5%92%8CII.html
https://programmercarl.com/0040.%E7%BB%84%E5%90%88%E6%80%BB%E5%92%8CII.html - 视频讲解
 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV12V4y1V73A/?vd_source=af4853e80f89e28094a5fe1e220d9062
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV12V4y1V73A/?vd_source=af4853e80f89e28094a5fe1e220d9062 -
回溯树图示:
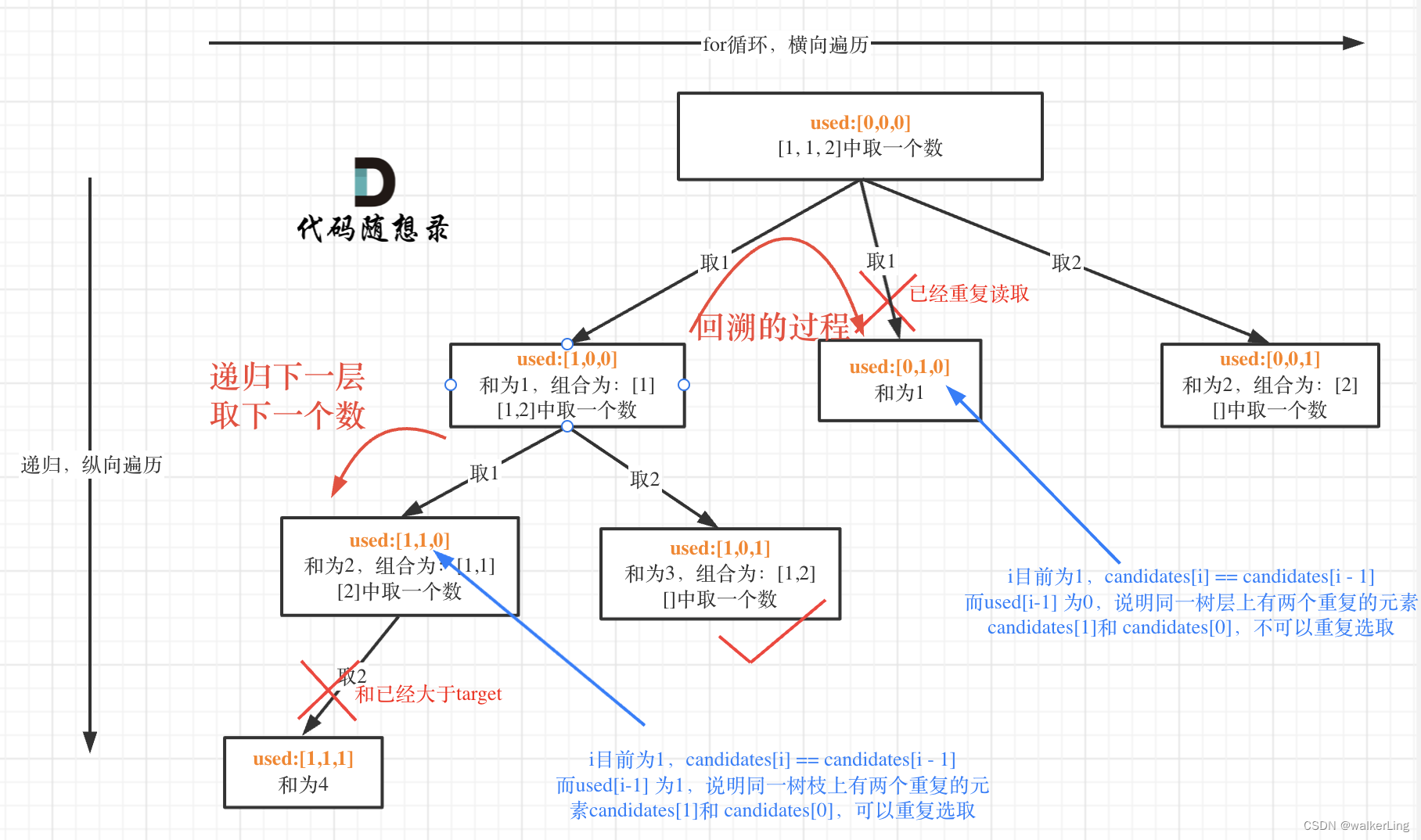
class Solution {
//标记used数组去重法
//记录最终结果
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
//记录单趟结果
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
//标记当前元素当前分支是否使用过
boolean[] used;
//记录当前总和
int sum = 0;
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
//创建和原始序列等长的used标记序列
used = new boolean[candidates.length];
//为了将重复元素放在一起进行的排序操作
Arrays.sort(candidates);
combinationSum21(candidates, target, 0);
return result;
}
//树枝去重和树层去重
//树枝可以使用两个值相等的不同元素,树层则不可以(经分析)
//所以我们需要通过used数组进行树层去重
public void combinationSum21(int[] candidates, int target, int startIndex){
//递归出口
if(sum == target){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
//递归回溯部分
for(int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length; i++){
if(sum + candidates[i] > target){
break;
}
//进行树层去重
//debug点:防止 i-1 < 0 下标越界,需要再加限制条件i > 0
if(i>=1 && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1] && !used[i - 1]){
//继续进行该层后序元素的遍历
continue;
}
used[i] = true;
sum += candidates[i];
path.add(candidates[i]);
//递归部分
//因为题中要求candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用一次,
//则下次递归startIndex从i+1开始
combinationSum21(candidates, target, i + 1);
//回溯部分
used[i] = false;
sum -= candidates[i];
path.removeLast();
}
}
}
131.分割回文串
- 刷题
 https://leetcode.cn/problems/palindrome-partitioning/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/palindrome-partitioning/description/ - 文章讲解
 https://programmercarl.com/0131.%E5%88%86%E5%89%B2%E5%9B%9E%E6%96%87%E4%B8%B2.html
https://programmercarl.com/0131.%E5%88%86%E5%89%B2%E5%9B%9E%E6%96%87%E4%B8%B2.html - 视频讲解
 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1c54y1e7k6/?vd_source=af4853e80f89e28094a5fe1e220d9062
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1c54y1e7k6/?vd_source=af4853e80f89e28094a5fe1e220d9062 -
回溯树图示:
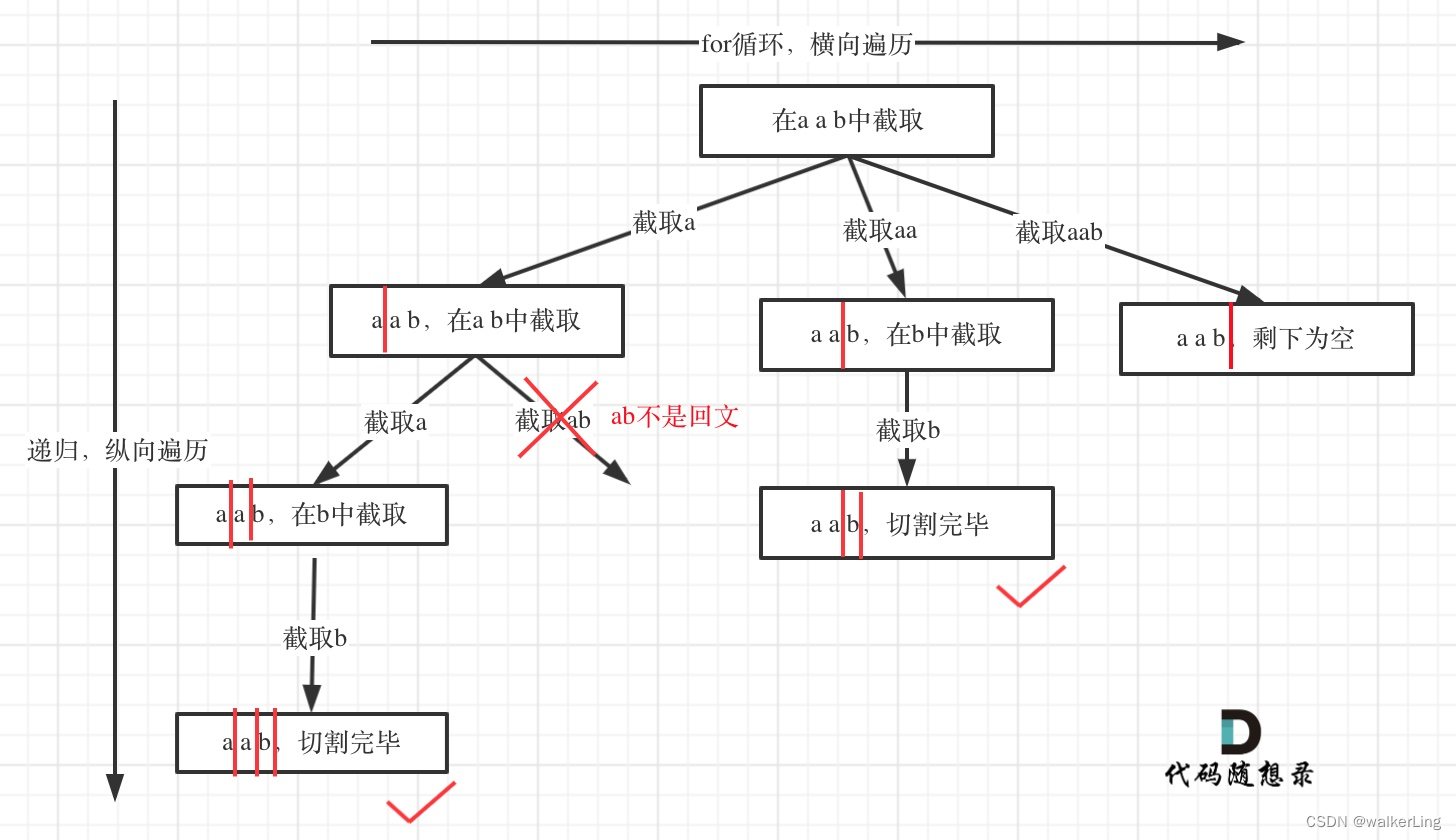
class Solution {
//存放整体结果
List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList<>();
//存放单趟结果
Deque<String> deque = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
partition1(s, 0);
return result;
}
//关键点在于:
//1、判断的合理区间在[startIndex, i]左闭右闭区间内
//2、分割线即为每次递归或者回溯后的startIndex
public void partition1(String s, int startIndex){
//递归出口
if(startIndex >= s.length()){
result.add(new ArrayList(deque));
return;
}
//递归回溯部分
for(int i = startIndex; i < s.length(); i++){
//若是回文子串,则记录结果
if(isHuiwen(s, startIndex, i)){
//因为substring左闭右开,而目标区间是左闭右闭,所以右边界加了1
String str = s.substring(startIndex, i + 1);
deque.addLast(str);
}else{
//若不是回文子串,则继续向后遍历即可
continue;
}
//递归
//因为需要保证不重复,则起始位置后移
partition1(s, i + 1);
//回溯
deque.removeLast();
}
}
//判断是否为回文子串
public boolean isHuiwen(String s, int startIndex, int end){
for(int i = startIndex, j = end; i < j; i++, j--){
if(s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(j)){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
 https://leetcode.cn/problems/combination-sum/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/combination-sum/description/ https://programmercarl.com/0039.%E7%BB%84%E5%90%88%E6%80%BB%E5%92%8C.html
https://programmercarl.com/0039.%E7%BB%84%E5%90%88%E6%80%BB%E5%92%8C.html https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1KT4y1M7HJ/?vd_source=af4853e80f89e28094a5fe1e220d9062
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1KT4y1M7HJ/?vd_source=af4853e80f89e28094a5fe1e220d9062
 https://leetcode.cn/problems/combination-sum-ii/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/combination-sum-ii/description/ https://programmercarl.com/0040.%E7%BB%84%E5%90%88%E6%80%BB%E5%92%8CII.html
https://programmercarl.com/0040.%E7%BB%84%E5%90%88%E6%80%BB%E5%92%8CII.html https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV12V4y1V73A/?vd_source=af4853e80f89e28094a5fe1e220d9062
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV12V4y1V73A/?vd_source=af4853e80f89e28094a5fe1e220d9062
 https://leetcode.cn/problems/palindrome-partitioning/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/palindrome-partitioning/description/ https://programmercarl.com/0131.%E5%88%86%E5%89%B2%E5%9B%9E%E6%96%87%E4%B8%B2.html
https://programmercarl.com/0131.%E5%88%86%E5%89%B2%E5%9B%9E%E6%96%87%E4%B8%B2.html https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1c54y1e7k6/?vd_source=af4853e80f89e28094a5fe1e220d9062
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1c54y1e7k6/?vd_source=af4853e80f89e28094a5fe1e220d9062