【LetMeFly】106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树:分治(递归)——五彩斑斓的题解(若不是彩色的可以点击原文链接查看)
力扣题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-inorder-and-postorder-traversal/
给定两个整数数组 inorder 和 postorder ,其中 inorder 是二叉树的中序遍历, postorder 是同一棵树的后序遍历,请你构造并返回这颗 二叉树 。
示例 1:
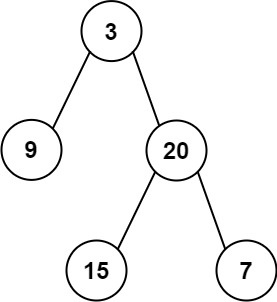
输入:inorder = [9,3,15,20,7], postorder = [9,15,7,20,3] 输出:[3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
示例 2:
输入:inorder = [-1], postorder = [-1] 输出:[-1]
提示:
1 <= inorder.length <= 3000postorder.length == inorder.length-3000 <= inorder[i], postorder[i] <= 3000inorder和postorder都由 不同 的值组成postorder中每一个值都在inorder中inorder保证是树的中序遍历postorder保证是树的后序遍历
方法一:分治(递归)
类似于从前序与中序建树,我们知道:
- 中序遍历:左子树 根 右子树
- 后序遍历:左子树 右子树 根
写一个函数dfs接收中序遍历数组和后序遍历数组作为参数:
- 根据
后序遍历数组的最后一个元素为根节点建立节点- 找到
根节点在中序遍历数组中的位置以此可得到左子树和右子树的长度信息
以此可确定左子树和右子树在两个数组中的位置
- 递归建立左子树和右子树
递归的终止条件为“中序遍历数组为空”,此时返回空节点。
Tips: 可以在预处理时建立一个哈希表,以便能快速地找到根节点在中序遍历数组中的位置。
- 时间复杂度 O ( N ) O(N) O(N),其中 N N N是节点个数
- 空间复杂度 O ( N ) O(N) O(N)
AC代码
C++
class Solution {
private:
unordered_map<int, vector<int>::iterator> ma;
TreeNode* dfs(vector<int>::iterator inLeft, vector<int>::iterator inRight, vector<int>::iterator postLeft, vector<int>::iterator postRight) {
if (inLeft >= inRight) {
return nullptr;
}
TreeNode* thisNode = new TreeNode(*(postRight - 1));
vector<int>::iterator loc = ma[*(postRight - 1)];
thisNode->left = dfs(inLeft, loc, postLeft, postLeft + (loc - inLeft));
thisNode->right = dfs(loc + 1, inRight, postLeft + (loc - inLeft), postRight - 1);
return thisNode;
}
public:
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {
for (vector<int>::iterator it = inorder.begin(); it != inorder.end(); it++) {
ma[*it] = it;
}
return dfs(inorder.begin(), inorder.end(), postorder.begin(), postorder.end());
}
};
Python
# from typing import List, Optional
# # Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def dfs(self, inorder: List[int], inLeft: int, inRight: int, postorder: List[int], postLeft: int, postRight: int) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
if inLeft >= inRight:
return None
thisNode = TreeNode(postorder[postRight - 1])
loc = self.ma[postorder[postRight - 1]]
thisNode.left = self.dfs(inorder, inLeft, loc, postorder, postLeft, postLeft + (loc - inLeft))
thisNode.right = self.dfs(inorder, loc + 1, inRight, postorder, postLeft + (loc - inLeft), postRight - 1)
return thisNode
def buildTree(self, inorder: List[int], postorder: List[int]) -> TreeNode:
self.ma = dict()
for i in range(len(inorder)):
self.ma[inorder[i]] = i
return self.dfs(inorder, 0, len(inorder), postorder, 0, len(postorder))
同步发文于CSDN,原创不易,转载经作者同意后请附上原文链接哦~
Tisfy:https://letmefly.blog.csdn.net/article/details/136204741