FFT加速计算两个图的协方差
文章目录
- <center> FFT加速计算两个图的协方差
- 1. 傅里叶变换和卷积
- 1.1 卷积定理
- 1.2 空域卷积和频域乘积的复杂度
- 2. opencv中的DFT
- 3. FFT用于NCC
- 4. 测试结果
- 部分代码
1. 傅里叶变换和卷积
1.1 卷积定理

图片来源
在空域上的卷积就是上面的动图所展示的过程,把两个图重叠的部分相乘再相加,不断滑动一个图到所有可重叠的地方,计算完后得到卷积的结果。
根据卷积定理:两个函数的卷积等于两个函数在频率域相乘。用式子表示如下:
f
(
x
)
∗
g
(
x
)
=
F
(
ω
)
⋅
G
(
ω
)
f(x)*g(x)=F(\omega)\cdot G(\omega)
f(x)∗g(x)=F(ω)⋅G(ω)
也就是说如果我们把上面的两个图像转换到频率域,上述的卷积过程就可以变成两个频率域图像对应点的相乘(频率域的两个图大小相同)。转到频域再相乘的方式主要的耗时都在傅里叶变换和逆变换那里,因为最后的频域图相乘那里复杂度只有平方项,而傅里叶变换和逆变换的的复杂度的阶数高于2,傅里叶变换这一步有非常成熟的快速傅里叶变换(FFT)可以使用来加速这一个过程。
1.2 空域卷积和频域乘积的复杂度
假设两个图像分别为 A N × N , B M × M , M ≤ N A_{N\times N},B_{M\times M},M\leq N AN×N,BM×M,M≤N,则在空域的卷积的时间复杂度是 O ( N 2 ∗ M 2 ) O(N^2*M^2) O(N2∗M2)
FFT的时间复杂度
O
(
N
2
log
N
)
O(N^2\log N)
O(N2logN)
注意这里的复杂度没有错,有人可能会觉得应该是
O
(
N
2
log
N
2
)
O(N^2\log N^2)
O(N2logN2),但是在表示复杂度的
O
(
)
O()
O()表示法中可以忽略系数只关注最高阶的项数,
O
(
N
2
log
N
2
)
=
O
(
2
∗
N
2
log
N
)
=
O
(
N
2
log
N
)
O(N^2\log N^2)=O(2*N^2\log N)=O(N^2\log N)
O(N2logN2)=O(2∗N2logN)=O(N2logN)。

上图来源
| 复杂度 | n=10 | n=20 |
|---|---|---|
| log n \log n logn | 1 | 2.996 |
| n n n | 10 | 20 |
| n log n n\log n nlogn | 10 | 59.9 |
| n 2 n^2 n2 | 100 | 400 |
| 2 n 2^n 2n | 1024 | 1048576 |
| n ! n! n! | 3628800 | 2,432,902,008,176,640,000 |
上面两种方式的复杂度可以看成是 n 2 , n log n n^2 ,n\log n n2,nlogn的差别,可以看到当两个要卷积图像都比较大时采用FFT加速的方式还是可以获得非常可观的效果。
2. opencv中的DFT
opencv dft 官网介绍
void cv::dft ( InputArray src,
OutputArray dst,
int flags = 0,
int nonzeroRows = 0
)
- src input array that could be real or complex.
- dst output array whose size and type depends on the flags .
- flags transformation flags, representing a combination of the DftFlags
- nonzeroRows when the parameter is not zero, the function assumes that only the first nonzeroRows rows of the input array (DFT_INVERSE is not set) or only the first nonzeroRows of the output array (DFT_INVERSE is set) contain non-zeros, thus, the function can handle the rest of the rows more efficiently and save some time; this technique is very useful for calculating array cross-correlation or convolution using DFT.
根据官网的示例和learning opencv3中的示例实现的卷积如下
/**
* @brief 用FFT实现两个图像的卷积,src: H*W ,kernel: h*w,
* 把卷积的过程想象成kernel在src上滑动,记在src上和kernel对应的子图像块为Sxy,
* conv(x,y) = \sigma \sigma Sxy(i,j)*kernel(i,j),i in [0,h) ,j in [0,w)
* output: (H-h+1)*(W-w+1)
*
* @param src : CV_8UC1的图像
* @param kernel : CV_8UC1的图像
* @param output : CV_32FC1的图像
* @return int
*/
int convFFT(const cv::Mat &src, const cv::Mat &kernel, cv::Mat& output)
{
if (src.empty() || kernel.empty())
{
MYCV_ERROR(kImageEmpty,"input is empty");
return kImageEmpty;
}
int dft_h = cv::getOptimalDFTSize(src.rows + kernel.rows - 1);
int dft_w = cv::getOptimalDFTSize(src.cols + kernel.cols - 1);
cv::Mat dft_src = cv::Mat::zeros(dft_h, dft_w, CV_32F);
cv::Mat dft_kernel = cv::Mat::zeros(dft_h, dft_w, CV_32F);
cv::Mat dft_src_part = dft_src(cv::Rect(0, 0, src.cols, src.rows));
cv::Mat dft_kernel_part = dft_kernel(cv::Rect(0, 0, kernel.cols, kernel.rows));
//把src,kernel分别拷贝放到dft_src,dft_kernel左上角
src.convertTo(dft_src_part, dft_src_part.type());
kernel.convertTo(dft_kernel_part, dft_kernel_part.type());
cv::dft(dft_src, dft_src, 0, dft_src.rows);
cv::dft(dft_kernel, dft_kernel, 0, dft_kernel.rows);
cv::mulSpectrums(dft_src, dft_kernel, dft_src, 0, true);
int output_h = abs(src.rows - kernel.rows) + 1;
int output_w = abs(src.cols - kernel.cols) + 1;
cv::dft(dft_src, dft_src, cv::DFT_INVERSE + cv::DFT_SCALE, output_h);;
cv::Mat corr = dft_src(cv::Rect(0, 0, output_w,output_h));
output = corr;
return kSuccess;
}
3. FFT用于NCC
NCC前情提要
记
T
m
×
n
为目标图
(
t
a
r
g
e
t
)
记T_{m\times n}为目标图(target)
记Tm×n为目标图(target),
S
M
×
N
S_{M\times N}
SM×N为源搜索图(source),
S
x
,
y
S_{x,y}
Sx,y为S中以点
(
x
,
y
)
(x,y)
(x,y)为左上角的和T大小相同的子图,
R
(
M
−
m
+
1
)
×
(
N
−
n
+
1
)
R_{(M-m+1)\times (N-n+1)}
R(M−m+1)×(N−n+1)为匹配的结果图,则
R
(
x
,
y
)
=
c
o
v
(
S
x
,
y
,
T
)
σ
(
S
x
,
y
)
σ
(
T
)
R(x,y)=\frac{cov(S_{x,y},T)}{\sigma(S_{x,y})\sigma(T)}
R(x,y)=σ(Sx,y)σ(T)cov(Sx,y,T)
其中
c
o
v
(
S
x
,
y
,
T
)
=
E
(
S
x
,
y
T
)
−
E
(
S
x
,
y
)
E
(
T
)
=
Σ
i
=
1
m
Σ
j
=
1
n
S
x
,
y
(
i
,
j
)
T
(
i
,
j
)
m
n
−
S
x
,
y
ˉ
T
ˉ
\begin{aligned} cov(S_{x,y},T) &=E(S_{x,y}T)-E(S_{x,y})E(T)\\ &=\frac{\Sigma_{i=1}^{m}\Sigma_{j=1}^{n}S_{x,y}(i,j)T(i,j)}{mn} - \bar{S_{x,y}}\bar{T} \end{aligned}
cov(Sx,y,T)=E(Sx,yT)−E(Sx,y)E(T)=mnΣi=1mΣj=1nSx,y(i,j)T(i,j)−Sx,yˉTˉ
图像块
S
x
,
y
S_{x,y}
Sx,y的均值计算过程已经用积分图加速过了,NCC的速度从opencv的八百分之一提升到三百分之一。在协方差的计算过程中一直会用到模板图和
S
x
,
y
S_{x,y}
Sx,y的逐像素相乘再求和的结果,就是下式
Σ
i
=
1
m
Σ
j
=
1
n
S
x
,
y
(
i
,
j
)
T
(
i
,
j
)
\Sigma_{i=1}^{m}\Sigma_{j=1}^{n}S_{x,y}(i,j)T(i,j)
Σi=1mΣj=1nSx,y(i,j)T(i,j)
从整个图像的计算过程来看这就是卷积!而卷积天然就适合用FFT来加速。用一个矩阵来存储模板和源图的卷积结果,上面的计算式就变为访问卷积结果某个位置的值。
4. 测试结果
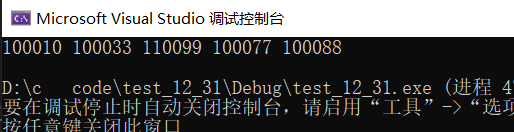
source image size w,h = (500,500)
target image size w,h = (100,100)
my NCC run 10 times,average use 12.000000 ms
min_value=-0.045359 , min_loc(x,y)=(316,121), max_value=0.044341,max_loc(x,y)=(213,264)
opencv NCC run 10 times,average use 4.000000 ms
min_value=-0.045360 , min_loc(x,y)=(316,121), max_value=0.044340,max_loc(x,y)=(213,264)
source image size w,h = (600,600)
target image size w,h = (100,100)
my NCC run 10 times,average use 16.000000 ms
min_value=-0.046514 , min_loc(x,y)=(186,308), max_value=0.044515,max_loc(x,y)=(444,178)
opencv NCC run 10 times,average use 7.000000 ms
min_value=-0.046515 , min_loc(x,y)=(186,308), max_value=0.044514,max_loc(x,y)=(444,178)
source image size w,h = (700,700)
target image size w,h = (100,100)
my NCC run 10 times,average use 24.000000 ms
min_value=-0.044219 , min_loc(x,y)=(428,192), max_value=0.042701,max_loc(x,y)=(347,262)
opencv NCC run 10 times,average use 8.000000 ms
min_value=-0.044219 , min_loc(x,y)=(428,192), max_value=0.042701,max_loc(x,y)=(347,262)
source image size w,h = (800,800)
target image size w,h = (100,100)
my NCC run 10 times,average use 30.000000 ms
min_value=-0.045473 , min_loc(x,y)=(452,292), max_value=0.044728,max_loc(x,y)=(298,175)
opencv NCC run 10 times,average use 10.000000 ms
min_value=-0.045473 , min_loc(x,y)=(452,292), max_value=0.044728,max_loc(x,y)=(298,175)
source image size w,h = (900,900)
target image size w,h = (100,100)
my NCC run 10 times,average use 39.000000 ms
min_value=-0.046390 , min_loc(x,y)=(716,347), max_value=0.043345,max_loc(x,y)=(591,252)
opencv NCC run 10 times,average use 13.000000 ms
min_value=-0.046390 , min_loc(x,y)=(716,347), max_value=0.043345,max_loc(x,y)=(591,252)
source image size w,h = (1000,1000)
target image size w,h = (100,100)
my NCC run 10 times,average use 52.000000 ms
min_value=-0.046292 , min_loc(x,y)=(727,726), max_value=0.048027,max_loc(x,y)=(664,237)
opencv NCC run 10 times,average use 18.000000 ms
min_value=-0.046293 , min_loc(x,y)=(727,726), max_value=0.048028,max_loc(x,y)=(664,237)
source image size w,h = (1100,1100)
target image size w,h = (100,100)
my NCC run 10 times,average use 57.000000 ms
min_value=-0.047824 , min_loc(x,y)=(116,699), max_value=0.049075,max_loc(x,y)=(319,546)
opencv NCC run 10 times,average use 21.000000 ms
min_value=-0.047824 , min_loc(x,y)=(116,699), max_value=0.049075,max_loc(x,y)=(319,546)
source image size w,h = (1200,1200)
target image size w,h = (100,100)
my NCC run 10 times,average use 75.000000 ms
min_value=-0.048051 , min_loc(x,y)=(1095,47), max_value=0.051388,max_loc(x,y)=(95,634)
opencv NCC run 10 times,average use 25.000000 ms
min_value=-0.048050 , min_loc(x,y)=(1095,47), max_value=0.051388,max_loc(x,y)=(95,634)
请按任意键继续. . .
我实现的NCC耗时从opencv的800多倍,用积分图降到300多倍,用FFT降到现在的2-3倍。没想到FFT加速这么多!FFT YYDS!
部分代码
/**
* @brief 模板匹配,归一化交叉相关算法。衡量模板和待匹配图像的相似性时
* 用(Pearson)相关系数来度量。
* r=cov(X,Y)/(sigma(X) * sigma(Y))
* 其中cov(X,Y): 表示两个变量的协方差
* cov(X,Y) = E[(X-E(x)) * (Y-E(Y))] = E(XY) - E(x)E(Y)
* sigma(X): 表示X变量的标准差
* sigma(Y): 表示Y变量的标准差
*
* @param source : 搜索图CV_8UC1格式
* @param target :模板图CV_8UC1格式
* @param result : 匹配结果的map图
* @return int : 程序运行的状态码
*/
int NormalizedCrossCorrelationFFT(
const cv::Mat &source,
const cv::Mat &target,
cv::Mat &result
)
{
if (source.empty() || target.empty())
{
MYCV_ERROR(kImageEmpty, "NCC empty input image");
return kImageEmpty;
}
int H = source.rows;
int W = source.cols;
int t_h = target.rows;
int t_w = target.cols;
if (t_h > H || t_w > W)
{
MYCV_ERROR(kBadSize, "NCC source image size should larger than targe image");
return kBadSize;
}
//r = cov(X,Y)/(sigma(X) * sigma(Y))
//sigma(X) = sqrt(var(X))
int r_h = H - t_h + 1; //结果图的高度
int r_w = W - t_w + 1;
cv::Mat integral_image;//source的积分图
cv::Mat sq_integral;//source 的像素平方的积分图
integral(source, integral_image, sq_integral);
//cv::integral(source, integral_image, sq_integral, CV_64FC1, CV_64FC1);
//计算模板图在source上的卷积
cv::Mat conv;
convFFT(source, target, conv);
const double target_size = t_h * t_w;
double target_mean = calculateMean(target);
double target_var = calculateVariance(target, target_mean);
double target_std_var = std::sqrt(target_var);
result = cv::Mat::zeros(cv::Size(r_w, r_h), CV_32FC1);
double region_sum = 0;
double region_sq_sum = 0;
for (int row = 0; row < r_h; row++)
{
float * p = result.ptr<float>(row);
float * convp = conv.ptr<float>(row);
for (int col = 0; col < r_w; col++)
{
cv::Rect ROI(col, row, t_w, t_h);//source上和目标图匹配的子图
cv::Mat temp = source(ROI);
//计算source中对应子块的均值
getRegionSumFromIntegralImage(integral_image, col, row, col + t_w - 1, row + t_h - 1, region_sum);
double temp_mean = region_sum / target_size;
//计算两个图的协方差
//cov(X,Y) = E(X*Y) - E(X)*E(Y)
double cov = (*(convp + col)) / target_size - temp_mean * target_mean;
//double cov = calculateCovariance(temp, target, temp_mean, target_mean);
//计算source中对应子块的方差
getRegionSumFromIntegralImage(sq_integral, col, row, col + t_w - 1, row + t_h - 1, region_sq_sum);
double temp_var = (region_sq_sum - temp_mean * region_sum) / target_size;
double temp_std_var = std::sqrt(temp_var);
p[col] = cov / ((temp_std_var + 0.0000001) * (target_std_var + 0.0000001));
}
}
return kSuccess;
}
void test_NCC_speed()
{
const int TIMES = 10;
std::string src_path = "data\\source.jfif";
std::string target_path = "data\\target.jfif";
std::string log_path = "ncc_speed.txt";
cv::Mat source, target, result;
//source = cv::imread(src_path, cv::IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
//target = cv::imread(target_path, cv::IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
std::chrono::steady_clock::time_point start_time,end_time;
double myncc_runtime = 0, opencv_runtime = 0;
auto logger = spdlog::basic_logger_mt("NCC", log_path);
logger->set_level(spdlog::level::critical);
// location
double min_value, max_value;
cv::Point min_loc, max_loc;
for (int src_size = 500; src_size <= 1200; src_size += 100)
{
source = cv::Mat(cv::Size(src_size, src_size), CV_8UC1);
target = cv::Mat(cv::Size(100, 100), CV_8UC1);
cv::randu(source,cv::Scalar(0),cv::Scalar(255));
cv::randu(target,cv::Scalar(0),cv::Scalar(255));
logger->info("src_size:(h,w)=({0},{1}), target_size:(h,w)=({2},{3})",
source.rows,source.cols,target.rows,target.cols);
// my NCC test
printf("source image size w,h = (%d,%d) \n", source.cols, source.rows);
printf("target image size w,h = (%d,%d) \n", target.cols, target.rows);
//warm up
//mycv::NormalizedCrossCorrelation(source, target, result);
mycv::NormalizedCrossCorrelationFFT(source, target, result);
start_time = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();;
for (int n = 0; n < TIMES; n++)
{
//mycv::NormalizedCrossCorrelation(source, target, result);
mycv::NormalizedCrossCorrelationFFT(source, target, result);
}
end_time = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();;
myncc_runtime = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(end_time - start_time).count() / TIMES;
printf("my NCC run %d times,average use %f ms \n", TIMES, myncc_runtime);
cv::minMaxLoc(result, &min_value, &max_value, &min_loc, &max_loc);
printf("min_value=%f , min_loc(x,y)=(%d,%d), \t max_value=%f,max_loc(x,y)=(%d,%d)\n",
min_value, min_loc.x, min_loc.y, max_value, max_loc.x, max_loc.y);
logger->info("my NCC run {0} times,average use {1} ms \n", TIMES, myncc_runtime);
logger->info("my NCC min_value = {0}, min_loc(x, y) = ({1}, {2}), \t max_value = {3}, max_loc(x, y) = ({4}, {5})\n",
min_value, min_loc.x, min_loc.y, max_value, max_loc.x, max_loc.y);
//warm up
cv::matchTemplate(source, target, result, cv::TM_CCOEFF_NORMED);
// opencv NCC test
start_time = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();;
for (int n = 0; n < TIMES; n++)
{
cv::matchTemplate(source, target, result, cv::TM_CCOEFF_NORMED);
}
end_time = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();;
opencv_runtime = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(end_time - start_time).count() / TIMES;
printf("opencv NCC run %d times,average use %f ms \n", TIMES, opencv_runtime);
cv::minMaxLoc(result, &min_value, &max_value, &min_loc, &max_loc);
printf("min_value=%f , min_loc(x,y)=(%d,%d), \t max_value=%f,max_loc(x,y)=(%d,%d)\n",
min_value, min_loc.x, min_loc.y, max_value, max_loc.x, max_loc.y);
logger->info("opencv NCC run {0} times,average use {1} ms \n", TIMES, opencv_runtime);
logger->info("opencv NCC min_value = {0}, min_loc(x, y) = ({1}, {2}), \t max_value = {3}, max_loc(x, y) = ({4}, {5})\n",
min_value, min_loc.x, min_loc.y, max_value, max_loc.x, max_loc.y);
logger->info("speed : myncc_runtime / opencv_runtime = {}", (int)(myncc_runtime / opencv_runtime));
}
}

![[Leetcode] 将二叉搜索树变平衡](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/8719412fae8441247d155ebd151469f6.png)