文章目录
- 前记
- AOT测试
- 反序列化
- Emit
前记
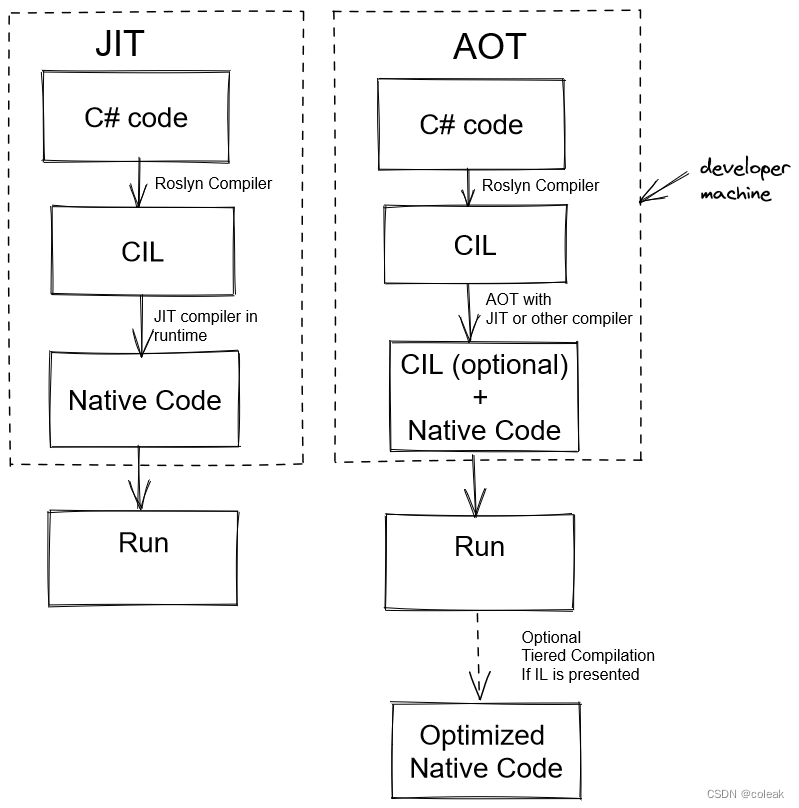
JIT\AOT
JIT编译器(Just-in-Time Complier),AOT编译器(Ahead-of-Time Complier)。
AOT测试
首先编译一段普通代码
using System;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace coleak
{
class winfun
{
[DllImport("User32.dll")]
public static extern int MessageBox(IntPtr h, string m, string c, uint type);
[DllImport("kernel32.dll", EntryPoint = "Beep")]
public static extern bool mymethod(uint frequency, uint duration);
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
winfun winfun = new winfun();
winfun.MessageBox((IntPtr)0, "yueyy", "coleak",(uint) 0);
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
{
winfun.mymethod((uint)random.Next(10000), 100);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
和csc直接编译相比,AOT发布确实可以防止dnspy出源码,但不能解决反汇编,该加壳还是得加壳
优点
不依赖.net框架环境也可以运行
不会被直接反编译而导致代码泄露
缺点
不能Assembly.Load进行动态加载
不支持32位程序
示例如下
using System;
using System.Reflection;
namespace LoadExe
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string base64string = @"";
byte[] Buffer = Convert.FromBase64String(base64string);
Assembly assembly = Assembly.Load(Buffer);
Type type = assembly.GetType("DemoExe.Test");
MethodInfo method = type.GetMethod("TestMethod");
Object obj = assembly.CreateInstance(method.Name);
method.Invoke(obj, null);
}
}
}
Unhandled Exception: System.PlatformNotSupportedException: Operation is not supported on this platform.
at Internal.Reflection.Execution.AssemblyBinderImplementation.Bind(ReadOnlySpan`1, ReadOnlySpan`1, AssemblyBindResult&, Exception&) + 0x39
at System.Reflection.Runtime.Assemblies.RuntimeAssemblyInfo.GetRuntimeAssemblyFromByteArray(ReadOnlySpan`1, ReadOnlySpan`1) + 0x58
at System.Reflection.Assembly.Load(Byte[], Byte[]) + 0xbe
at LoadExe.Program.Main(String[] args) + 0x25
at nativeAOT!<BaseAddress>+0x114a40
但是部分反射api仍然有效
using System;
using System.Reflection;
namespace LoadExe
{
class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
Console.Write("Name of type: ");
string typeName = "LoadExe.Program";
string methodName = "SayHello";
Type.GetType(typeName).GetMethod(methodName).Invoke(null, null);
Console.ReadKey();
}
public static void SayHello()
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello!");
}
}
}
具体规则如下
1.APIs that don’t work and will not work
- APIs that require dynamic code generation:
Reflection.Emit,Assembly.Loadand friends - Obvious program introspection APIs: APIs on
TypeandAssemblynot mentioned above,MethodBase,MethodInfo,ConstructorInfo,FieldInfo,PropertyInfo,EventInfo. These APIs will throw at runtime. - APIs building on top of reflection APIs. Too many to enumerate.
2.Reflection-free mode supports a limited set of reflection APIs that keep their expected semantics.
typeof(SomeType)will return aSystem.Typethat can be compared with results of othertypeofexpressions or results ofObject.GetType()calls. The patterns commonly used in perf optimizations of generic code (e.g.typeof(T) == typeof(byte)) will work fine, and so willobj.GetType() == typeof(SomeType).- Following APIs on
System.Typework:TypeHandle,UnderlyingSystemType,BaseType,IsByRefLike,IsValueType,GetTypeCode,GetHashCode,GetElementType,GetInterfaces,HasElementType,IsArray,IsByRef,IsPointer,IsPrimitive,IsAssignableFrom,IsAssignableTo,IsInstanceOfType. Activator.CreateInstance()will work. The compiler statically analyzes and expands this to efficient code at compile time. No reflection is involved at runtime.Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly()will return aSystem.Reflection.Assemblythat can be compared with other runtimeAssemblyinstances. This is mostly to make it possible to use theNativeLibrary.SetDllImportResolverAPI.
反序列化
JSON格式
using System;
using System.Runtime.Serialization.Json;//添加的引用
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
public class Book
{
public int ID { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public float Price { get; set; }
}
public class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//序列化json
Book book = new Book() { ID = 101, Name = "C#程序设计", Price = 79.5f };
DataContractJsonSerializer formatter = new DataContractJsonSerializer(typeof(Book));
using (MemoryStream stream = new MemoryStream())
{
formatter.WriteObject(stream, book);
string result = System.Text.Encoding.UTF8.GetString(stream.ToArray());
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
Console.WriteLine();
//反序列化json
string oriStr = "{\"ID\":102,\"Name\":\"C# wpf程序设计\",\"Price\":100}";
DataContractJsonSerializer formatter1 = new DataContractJsonSerializer(typeof(Book));
using (MemoryStream stream = new MemoryStream(System.Text.Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(oriStr)))
{
Book outBook = formatter1.ReadObject(stream) as Book;
Console.WriteLine(outBook.ID);
Console.WriteLine(outBook.Name);
Console.WriteLine(outBook.Price);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Emit
using System;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Reflection.Emit;
using System.Text;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
CreateAssembly();
Console.ReadKey();
}
public static void CreateAssembly()
{
StringBuilder asmFileNameBldr = new StringBuilder();
//定义一个程序集的名称
var asmName = new AssemblyName("MyAssembly");
//首先就需要定义一个程序集
AssemblyBuilder defAssembly = AssemblyBuilder.DefineDynamicAssembly(asmName, AssemblyBuilderAccess.RunAndCollect);
//定义一个构建类DefineDynamicModule
ModuleBuilder defModuleBuilder = defAssembly.DefineDynamicModule("MyModule");
//定义一个类
TypeBuilder typeBuilder = defModuleBuilder.DefineType("MyModule.MyClass", TypeAttributes.Public);
//定义一个方法
var defMethodBuilder = typeBuilder.DefineMethod("MyMethod",
MethodAttributes.Public,
null,//返回类型
null//参数类型
);
Console.WriteLine($"程序集信息:{typeBuilder.Assembly.FullName}");
Console.WriteLine($"命名空间:{typeBuilder.Namespace} , 类型:{typeBuilder.Name}");
//获取IL生成器
var il = defMethodBuilder.GetILGenerator();
//定义一个字符串
il.Emit(OpCodes.Ldstr, "coleak");
//调用一个函数
il.Emit(OpCodes.Call, typeof(Console).GetMethod("WriteLine", new Type[] { typeof(string) }));
//返回到方法开始(返回)
il.Emit(OpCodes.Ret);
//创建类型
Type dynamicType = typeBuilder.CreateType();
object ass = Activator.CreateInstance(dynamicType);
dynamicType.GetMethod("MyMethod").Invoke(ass, null);
}
}
}
.NET Framework 中,有 RunAndSave 、Save 等枚举,可用于保存构建的程序集,但是在 .NET Core 中,是没有这些枚举的,也就是说,Emit 构建的程序集只能在内存中,是无法保存成 .dll 文件的