vector用法详解
- vector定义
- vector容器的构造函数
- vector容器内元素的访问
- 1.通过下标 + [ ]来访问
- 2.通过迭代器来访问
- 3.通过范围for来访问
- vector常用函数的用法解析
- 1.size()
- 2.clear()
- 3.capacity()
- 4.reserve()
- 5.resize()
- 6.shrink_to_fit()
- 7.pop_back()
- 8.push_back()
- 9.erase()
- 10.insert()
- 补充:算法库中的find()
- 11.vector iterator适用
- 1. begin() + end()
- 2.rbegin() + rend()
铁汁们,今天给大家分享一篇vector用法详解,来吧,开造⛳️
vector定义
💡 vector< typename> name ;
-
vector本质是顺序表,是可以更改大小的"变长数组"。
-
typename为任意类型,例如:int、char、double、string、vector。
💡 Tips:vector是可变大小数组的序列容器。vector使用动态分配数组来存储它的元素,物理空间连续,可以采用下标+[ ]对vector中的元素进行访问。在末尾插入或者删除一个元素时间复杂度为O(1),效率高,而在其他位置处进行插入或者删除一个元素时间复杂度为O(n),效率低,而对于其他物理空间不连续的容器采用迭代器或者引用的方式来访问元素效率高。
vector容器的构造函数
- 1.构造一个没有元素的空数组a, 元素类型为typename。
💡1. vector a ;
- 2.构造一个与容器c内元素相同的数组d, 元素类型为typename。
💡2.vector d(const vector& c) ;
- 3.构造一个与[first, last)范围一样多元素的容器c。
💡3.vector c(iterator first, iterator last ) ;
- 4.构造一个包含n个元素,每个元素的值为val的数组b, 元素类型为typename。
💡4.vector b(size_t n, const typename& val ) ;
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> a;
for (auto it : a)
{
cout << it << ' ';
}
vector<int> b(5, 1);
for (auto it : b)
{
cout << it << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
string s("abcd");
vector<int> c(s.begin(), s.end());
//编码表-字符与ASCII值对应的表,内存中实际存储的是字符所对应的ASCII值
for (auto it : c)
{
cout << it << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
vector<int> d(b);
for (auto it : d)
{
cout << it << ' ';
}
return 0;
}

vector容器内元素的访问
1.通过下标 + [ ]来访问
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
{
cout << v[i] << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
2.通过迭代器来访问
vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin();
while (it != v.end())
{
cout << *it << ' ';
it++;
}
cout << endl;
3.通过范围for来访问
for (auto it : v) //只要该容器支持迭代器,就支持范围for,原因:范围for的底层实现为迭代器
{
cout << it << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
💡 Tips:只要某个容器支持迭代器,就支持范围for, 原因:范围for的底层实现为迭代器。
vector常用函数的用法解析
1.size()
💡 1.size_t size( )const ;
- 功能:获得vector中元素的总个数,元素类型为typename。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<string> v1(5, "1111"); //
cout << v1.size() << endl;
vector<int> v2;
v2.push_back(1);
v2.push_back(2);
v2.push_back(3);
vector<int> v3(v2.begin() + 1, v2.end());
cout << v2.size() << endl << v3.size() << endl;
return 0;
}

2.clear()
💡2.void clear( ) ;
- 功能:使vector中元素的总个数size变为0,但容量capacity不变。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v(4, 2);
cout << v.size() << ' ' << v.capacity() << endl;
v.clear();
cout << v.size() << ' ' << v.capacity() << endl;
return 0;
}

3.capacity()
💡3.size_t capacity( )const ;
- 功能:获得当前分配给vector存储空间的大小。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v; //测试vs下vector默认的扩容机制 -》1.5倍
size_t sz = v.capacity();
cout << "start capacity:" << sz << endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
if (sz != v.capacity())
{
sz = v.capacity();
cout << "changed capacity:" << sz << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}

💡 Tips:在vs下capacity呈1.5倍增长的,vs是PJ版本的STL、在g++(linux)下capacity呈2倍增长的,g++是 SGI版本的STL。vector的增容,具体增多少,不能固化,在不同编译器下增容的定义是不同的。
4.reserve()
4.void reserve(size_t n) ;
- 功能:使得vector容器存储空间的大小为n。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v;
for (size_t i = 1; i < 15; i++)
v.push_back(i);
cout << v.size() << ' ' << v.capacity() << endl;
v.reserve(16); //情况一: size < n < capacity ->size不变,capacity不变
cout << v.size() << ' ' << v.capacity() << endl;
v.reserve(22); //情况二: n > capacity ->size不变,capacity改变,扩容
cout << v.size() << ' ' << v.capacity() << endl;
for (auto it : v)
{
cout << it << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
v.reserve(5); //情况三: size > n ->size改变,size不变,capacity不变
cout << v.size() << ' ' << v.capacity() << endl;
return 0;
}
-
相当于扩容,不会初始化。
-
不会改变数据,只会改变容量。当n < size 或 size < n < capacity,在vs下不会缩容,在g++下会缩容。
-
reserve(n),是否会开辟n个空间,取决于编译器,仅仅是向编译器做了个请求工作。
-
已知需开辟空间的大小为n,可以使用reserve(n),从而减少扩容的次数,提高效率,因为扩容有损耗。

5.resize()
💡5.void resize(size_t n, const typename& val = typename( ) ) ;
- 功能:调整vector容器的大小,使其内元素个数变为n。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v;
for (size_t i = 1; i < 15; i++)
v.push_back(i);
cout << v.size() << ' ' << v.capacity() << endl;
v.resize(16); //情况一: size < n < capacity ->size改变,capacity不变,插入数据
cout << v.size() << ' ' << v.capacity() << endl;
v.resize(22); //情况二: n > capacity ->size改变,capacity改变,扩容+插入数据
cout << v.size() << ' ' << v.capacity() << endl;
for (auto it : v)
{
cout << it << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
v.resize(5); //情况三: size > n ->size改变,capacity不变,删除数据
cout << v.size() << ' ' << v.capacity() << endl;
return 0;
}

- 相当于扩容 + 初始化。
- 既改变容量,又改变数据。当n < size 或 size < n < capacity,在vs下不会缩容,在g++下会缩容。
- 情况一: size > n ->size改变,capacity不变,删除数据 ;情况二: size < n < capacity
->size改变,capacity不变,插入数据 ; 情况三: n > capacity ->size改变,capacity改变,扩容+插入数据 。 - 初始化处默认给缺省值,缺省值为无参构造函数,自定义类型会去调它自己的默认构造函数,c++11为了兼容模板,使得内置类型也有构造函数,内置类型得无参构造函数初始化为0eg:int
val = int(), val = 0、double val = double(),val = 0.0,int* val =
int*() , val = nullptr、char val = char(), val = ‘\0’。
6.shrink_to_fit()
💡void shrink_to_fit( ) ;
- 功能:缩容,使capacity()减小到与size()大小相同。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v;
for (size_t i = 1; i < 15; i++)
v.push_back(i);
cout << v.size() << ' ' << v.capacity() << endl;
v.resize(5);
cout << v.size() << ' ' << v.capacity() << endl;
v.shrink_to_fit();
cout << v.size() << ' ' << v.capacity() << endl;
return 0;
}

7.pop_back()
💡void pop_back( ) ;
💡void push_back( ) ;
- 功能:在末尾插入一个元素。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3);
for (auto it : v)
{
cout << it << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
v.pop_back();
for (auto it : v)
{
cout << it << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}

9.erase()
💡void erase(iterator position) ;
- 功能:删除指定位置(迭代器)处的值。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3);
v.erase(v.begin() + 1);
for (auto it : v)
{
cout << it << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}

10.insert()
💡void insert(iterator position , const typename& x) ;
- 功能:在指定的位置(迭代器)前插入元素x。
💡void insert(iterator position , iterator first , iterator end) ;
- 功能: 在指定位置(迭代器)前插入与范围[first , end)一样多元素的容器
补充:算法库中的find()
💡iterator find(iterator first, iterator end, const typename& x) ;
- 功能:在范围[first, end)容器中查找与x相同的元素,若查找到了,则返回查找到的元素所在的位置(迭代器),否则返回end(迭代器)。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v1(5, 2);
vector<int> v2(3, 6);
v1.insert(v1.begin() + 2, 3);
v1.insert(v1.begin(), v2.begin(), v2.end());
for (auto it : v1)
{
cout << it << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
vector<int>::iterator p = find(v1.begin() + 1, v1.end(), 3);
if (p != v1.end())
cout << "查找到了" << endl;
else
cout << "查找不到" << endl;
return 0;
}

- 头文件为#include。
- 是函数模板,泛型编程,不是针对于某个容器的迭代器实现的,而是针对于所有容器的迭代器实现的。
11.vector iterator适用
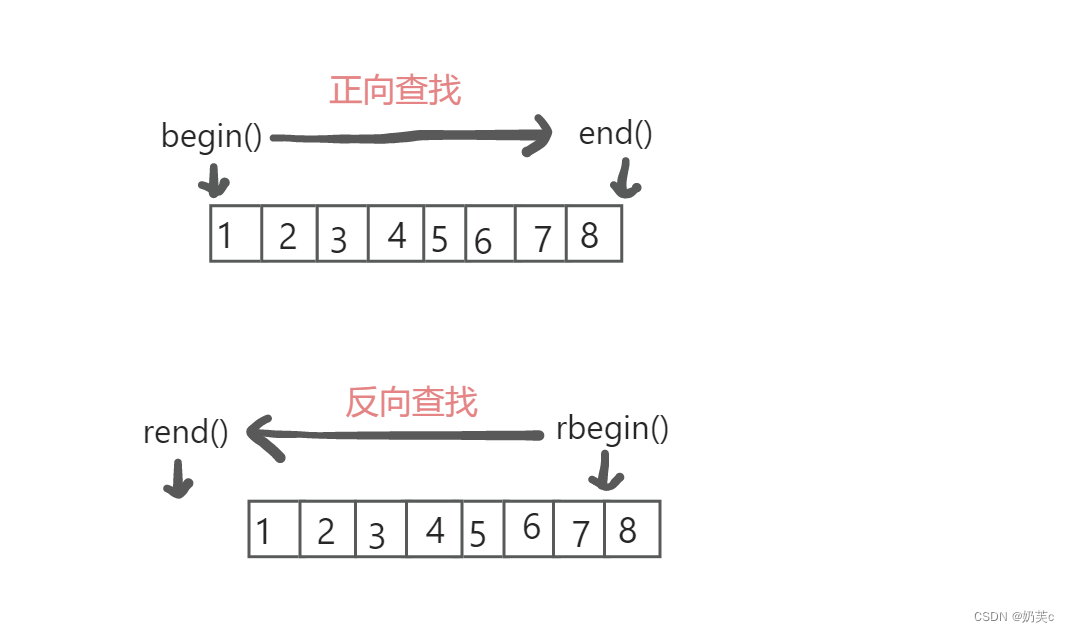
1. begin() + end()
💡iterator begin( )、const_iterator begin( )const ;
- 功能:返回第一个元素的位置(迭代器)。
Tips:const_iterator 修饰的是迭代器所指向的元素不能被修改,而迭代器本身可以被修改。const修饰this指针,表示在该成员函数中成员变量不允许被修改,此处const的用法只能用于类中的成员函数。
💡iterator end( )、const_iterator end( )const ;
- 功能:返回最后一个元素的下一个位置(迭代器)。
2.rbegin() + rend()
💡iterator rbegin( )、const_iterator rbegin( )const ;
- 功能:返回最后一个元素的位置(迭代器)。
💡iterator rend( )、const_iterator rend( )const ;
- 功能:返回第一个元素的前一个位置(迭代器)。
铁铁们,vector用法详解就到此结束啦,若博主有不好的地方,请指正,欢迎铁铁们留言,请动动你们的手给作者点个👍鼓励吧,你们的鼓励就是我的动力✨


![[python]基于LSTR车道线实时检测onnx部署](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/dd5fdf020fa24047a670682dc42cae9d.jpeg)