文章目录
- **概述**
- **使用方式**
- 基于配置文件的注入
- 基于非配置文件的注入
- 注入普通字符串
- 注入操作系统属性
- 注入表达式结果
- 注入其他bean属性
- 注入URL资源
概述
本文配置文件为yml文件
在使用spring框架的项目中,@Value是经常使用的注解之一。其功能是将与配置文件中的键对应的值分配给其带注解的属性。在日常使用中,我们常用的功能相对简单。本文使您系统地了解@Value的用法。
@Value 注解可以用来将外部的值动态注入到 Bean 中,在 @Value 注解中,可以使${} 与 #{} ,它们的区别如下:
(1)@Value(“${}”):可以获取对应属性文件中定义的属性值。
(2)@Value(“#{}”):表示 SpEl 表达式通常用来获取 bean 的属性,或者调用 bean 的某个方法。
使用方式
根据注入的内容来源,@ Value属性注入功能可以分为两种:通过配置文件进行属性注入和通过非配置文件进行属性注入。
非配置文件注入的类型如下:
1.注入普通字符串
2.注入操作系统属性
3.注入表达式结果
4.注入其他bean属性
5.注入URL资源
基于配置文件的注入
首先,让我们看一下配置文件中的数据注入,无论它是默认加载的application.yml还是自定义my.yml文档(需要@PropertySource额外加载)。
application.yml文件配置,获得里面配置的端口号

程序源代码
package cn.wideth.controller;
import cn.wideth.PdaAndIpadApplication;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest()
@ContextConfiguration(classes = PdaAndIpadApplication.class)
public class ValueController {
/**
*Get in application.yml
*/
@Value("${server.port}")
private String port;
@Test
public void getPort(){
System.out.println(port);
}
}
程序结果

自定义yml文件,application-config.yml文件配置,获得里面配置的用户密码值
注意,如果想导入自定义的yml配置文件,应该首先把自定义文件在application.yml文件中进行注册,自定义的yml文件要以application开头,形式为application-fileName

配置信息
测试程序
package cn.wideth.controller;
import cn.wideth.PdaAndIpadApplication;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest()
@ContextConfiguration(classes = PdaAndIpadApplication.class)
public class ValueController {
/**
*Get in application-config.yml
*/
@Value("${user.password}")
private String password;
@Test
public void getPassword(){
System.out.println(password);
}
}
程序结果
基于配置文件一次注入多个值
配置信息
测试程序
package cn.wideth.controller;
import cn.wideth.PdaAndIpadApplication;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import java.util.List;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest()
@ContextConfiguration(classes = PdaAndIpadApplication.class)
public class ValueController {
/**
*Injection array (automatically split according to ",")
*/
@Value("${tools}")
private String[] toolArray;
/**
*Injection list form (automatic segmentation based on "," and)
*/
@Value("${tools}")
private List<String> toolList;
@Test
public void getTools(){
System.out.println(toolArray);
System.out.println(toolList);
}
}
程序结果

基于非配置文件的注入
在使用示例说明基于非配置文件注入属性的实例之前,让我们看一下SpEl。
Spring Expression Language是Spring表达式语言,可以在运行时查询和操作数据。使用#{…}作为操作符号,大括号中的所有字符均视为SpEl。
让我们看一下特定实例场景的应用:
注入普通字符串
测试程序
package cn.wideth.controller;
import cn.wideth.PdaAndIpadApplication;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import java.util.List;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest()
@ContextConfiguration(classes = PdaAndIpadApplication.class)
public class ValueController {
// 直接将字符串赋值给 str 属性
@Value("hello world")
private String str;
@Test
public void getValue(){
System.out.println(str);
}
}
程序结果
注入操作系统属性
可以利用 @Value 注入操作系统属性。
测试程序
package cn.wideth.controller;
import cn.wideth.PdaAndIpadApplication;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest()
@ContextConfiguration(classes = PdaAndIpadApplication.class)
public class ValueController {
@Value("#{systemProperties['os.name']}")
private String osName; // 结果:Windows 10
@Test
public void getValue(){
System.out.println(osName);
}
}
程序结果
注入表达式结果
在 @Value 中,允许我们使用表达式,然后自动计算表达式的结果。将结果复制给指定的变量。如下
测试程序
package cn.wideth.controller;
import cn.wideth.PdaAndIpadApplication;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest()
@ContextConfiguration(classes = PdaAndIpadApplication.class)
public class ValueController {
// 生成一个随机数
@Value("#{ T(java.lang.Math).random() * 1000.0 }")
private double randomNumber;
@Test
public void getValue(){
System.out.println(randomNumber);
}
}
程序结果
注入其他bean属性
其他Bean
package cn.wideth.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
//其他bean,自定义名称为 myBeans
@Component("myBeans")
public class OtherBean {
@Value("OtherBean的NAME属性")
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
测试程序
package cn.wideth.controller;
import cn.wideth.PdaAndIpadApplication;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest()
@ContextConfiguration(classes = PdaAndIpadApplication.class)
public class ValueController {
@Value("#{myBeans.name}")
private String fromAnotherBean;
@Test
public void getValue(){
System.out.println(fromAnotherBean);
}
}
程序结果
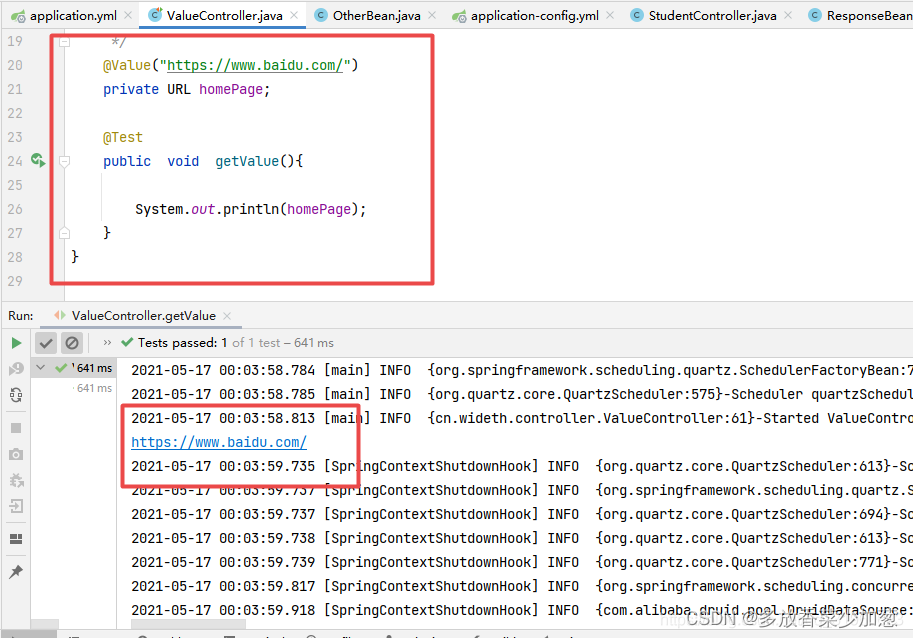
注入URL资源
测试程序
package cn.wideth.controller;
import cn.wideth.PdaAndIpadApplication;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import java.net.URL;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest()
@ContextConfiguration(classes = PdaAndIpadApplication.class)
public class ValueController {
/**
*注入 URL 资源
*/
@Value("https://www.baidu.com/")
private URL homePage;
@Test
public void getValue(){
System.out.println(homePage);
}
}
程序结果