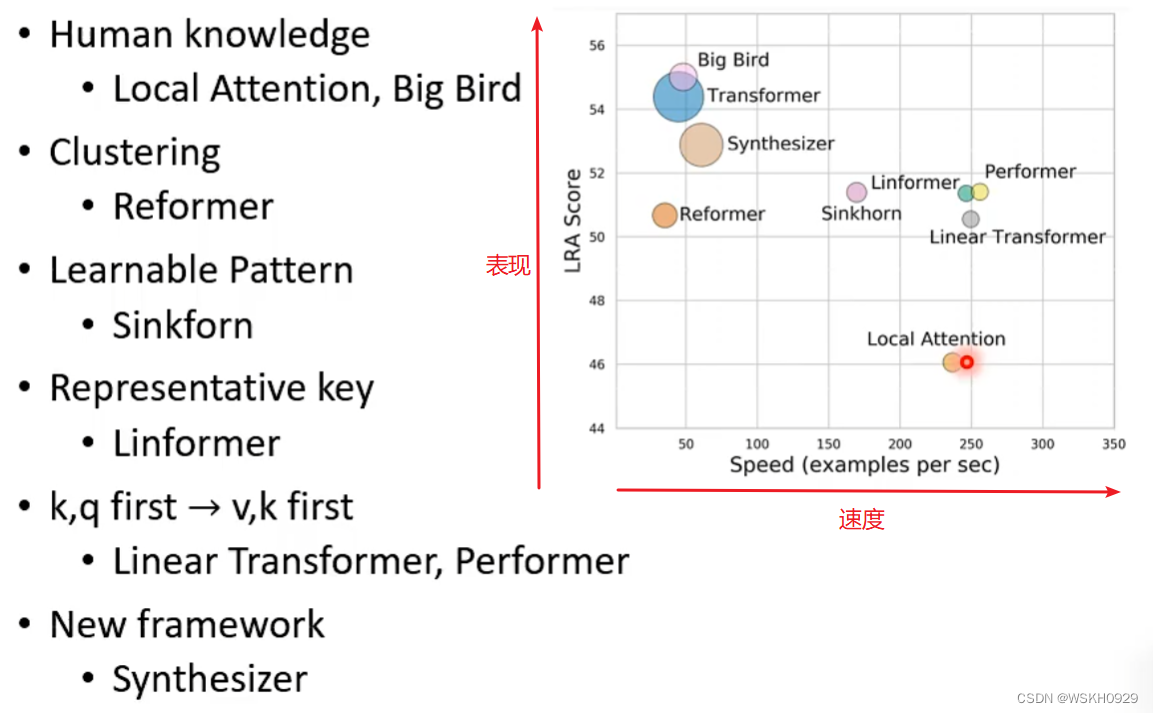
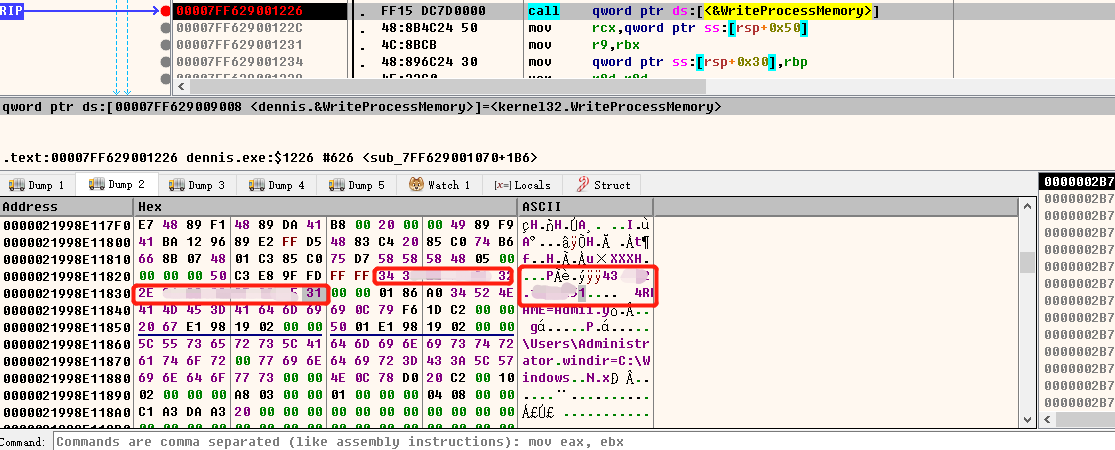
一般地,进入循环体后,在下次循环判断之前程序执行循环体中所有语句
一、continue语句
continue:循环中,当运行到该语句时,其将导致剩余的迭代部分被忽略,开始下一次迭代
如果continue处于嵌套结构中,其仅影响包含它的最里层的结构
continue语句可用于3中循环形式中(while、for、do-while)
示例代码:
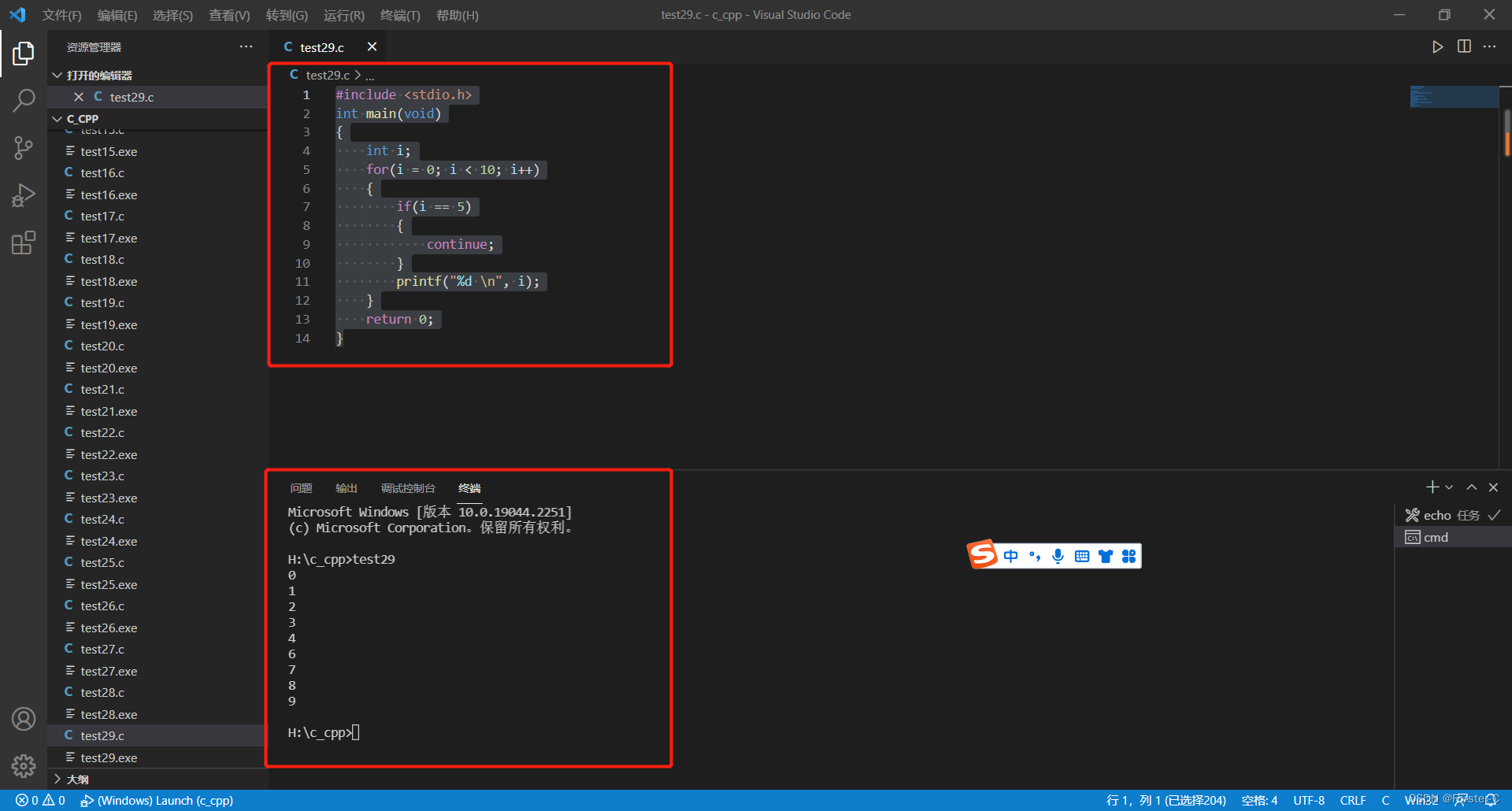
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int i;
for(i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
if(i == 5)
{
continue;
}
printf("%d \n", i);
}
return 0;
}运行结果:
对于while循环和do-while循环,continue语句之后发生的动作是求循环判断表达式的值
对于for循环,continue语句之后发生的动作是先求更新表达式的值,然后再求循环表达式的值
二、break语句
循环中,break语句导致程序终止包含它的循环,并进行程序的下一阶段
示例代码:
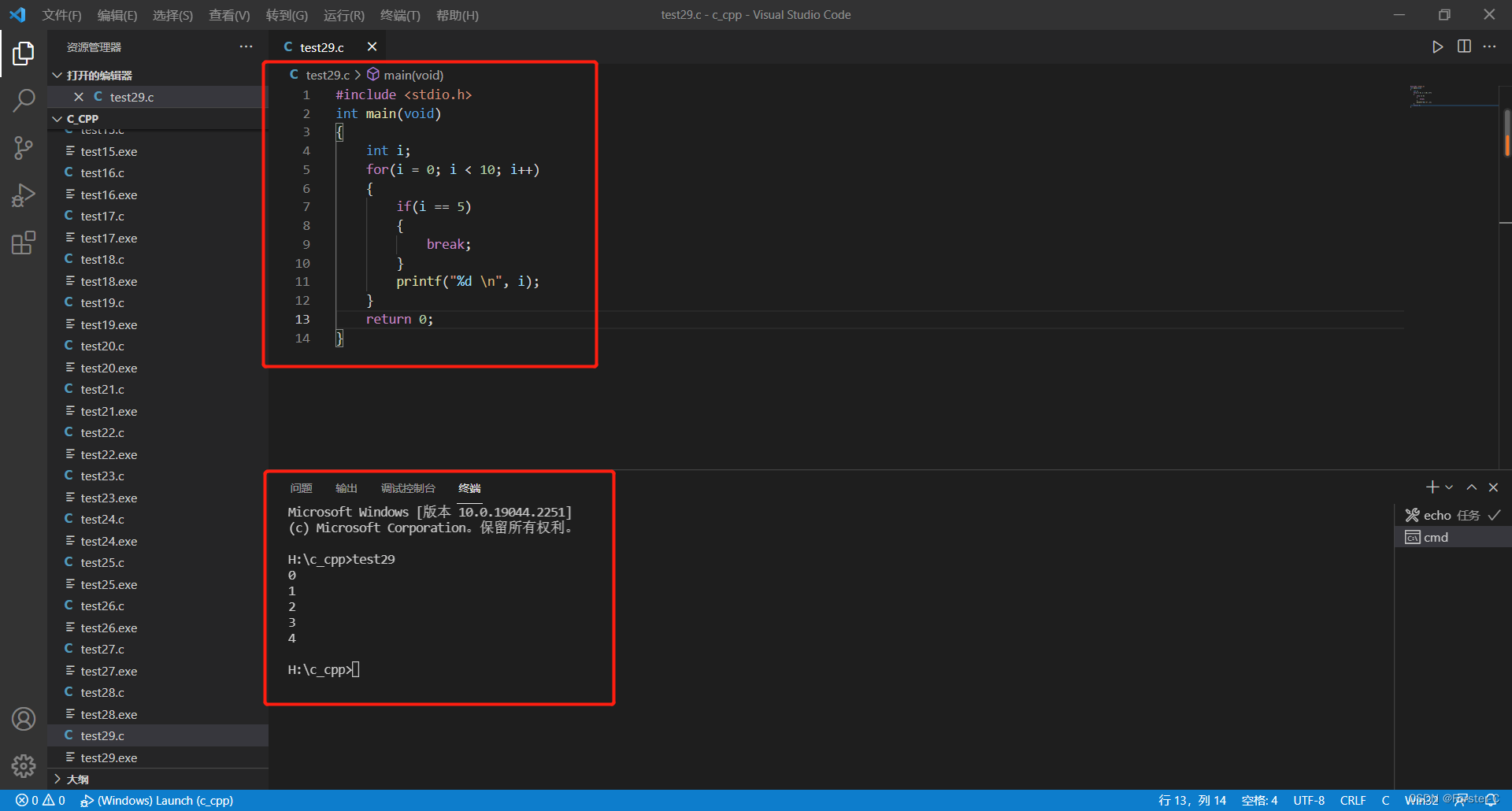
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int i;
for(i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
if(i == 5)
{
break;
}
printf("%d \n", i);
}
return 0;
}运行结果:
如果break语句位于嵌套循环里,其只影响包含它的最里层的循环
与continue一样,break的使用是为了简化代码,当其反而使代码更复杂时,不要使用
break语句使程序直接转到紧接着该循环后的第一条语句继续执行
三、switch语句
相比if-else if-else if...这样的语句,使用switch更加方便
示例代码:猜奖系统
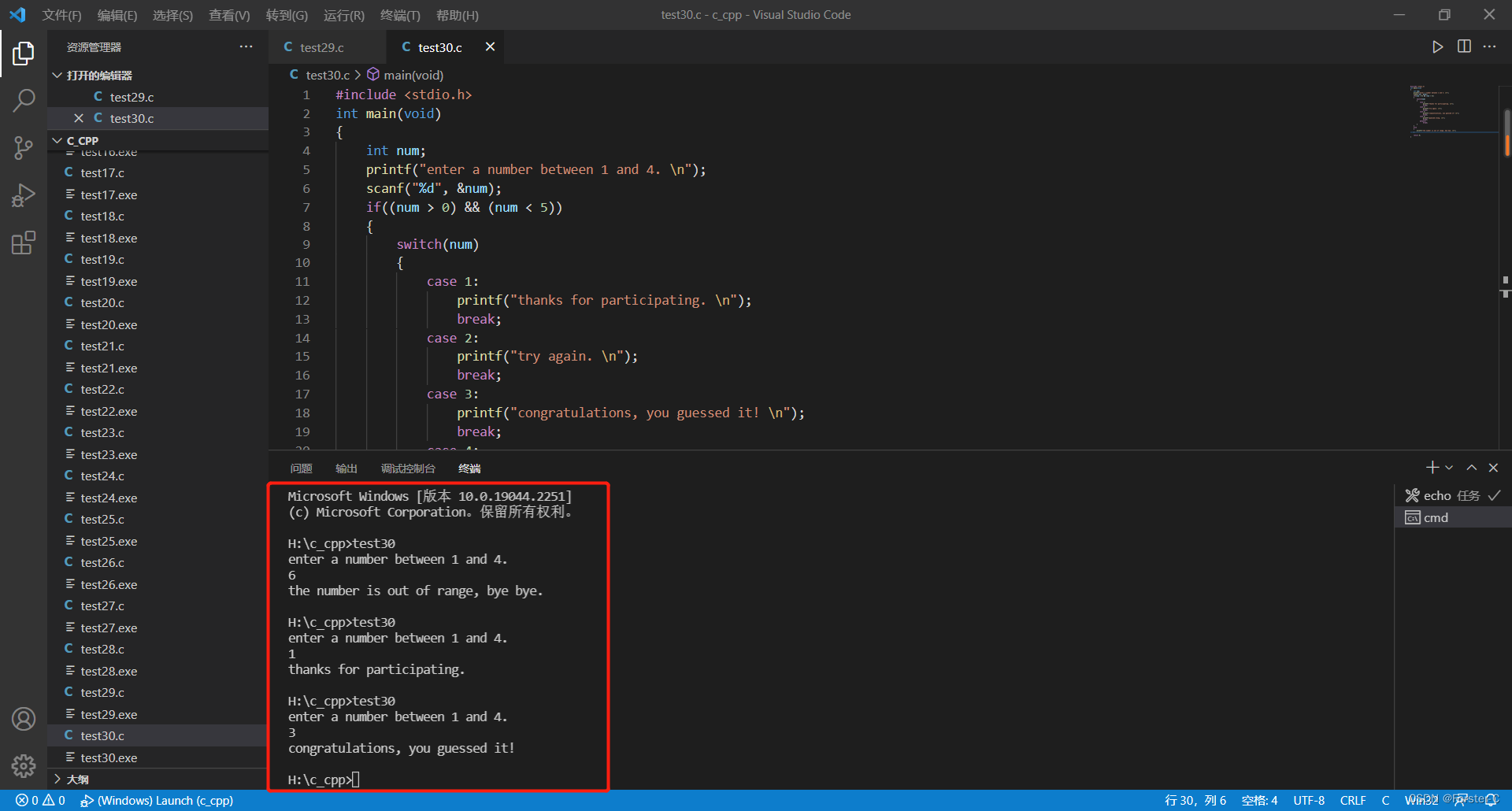
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int num;
printf("enter a number between 1 and 4. \n");
scanf("%d", &num);
if((num > 0) && (num < 5))
{
switch(num) // 搜索与num匹配的标签,然后程序跳到那一行
{
case 1:
printf("thanks for participating. \n");
break;
case 2:
printf("try again. \n");
break;
case 3:
printf("congratulations, you guessed it! \n");
break;
case 4:
printf("guessed wrong. \n");
break;
default:
break;
}
}
else
{
printf("the number is out of range, bye bye. \n");
}
return 0;
}运行结果:
break的作用:引导程序脱离switch语句,跳到switch之后的下一条语句;如果没有break语句,从相匹配的标签到switch末尾的每一条语句都将被执行
示例代码:
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int num;
printf("enter a number between 1 and 4. \n");
scanf("%d", &num);
if((num > 0) && (num < 5))
{
switch(num)
{
case 1: // 标签
printf("thanks for participating. \n");
break;
case 2:
printf("try again. \n");
break;
case 3:
printf("congratulations, you guessed it! \n");
//break;
case 4:
printf("guessed wrong. \n");
break;
default:
break;
}
}
else
{
printf("the number is out of range, bye bye. \n");
}
return 0;
}运行结果:

break语句用于循环和switch,continue语句仅用于循环
圆括号中的switch判断表达式应该具有整数值(包括char类型)
case标签必须是整形(包括char)常量或者整数常量表达式,不能使用变量作为case标签
switch结构的一般形式:
switch(interger expression)
{
case constant1:
statements
case constant2:
statements
default:
statements
}switch和else if:
如果选择是基于求一个浮点型变量或表达式的值,就不能使用switch
如果变量必须落入某个范围,使用switch也不方便