文章目录
- linux日志与日志的查询方法
- 更多journalctl用法
- journalctl用法案例
- 部分日志路径说明
- 推荐阅读
linux日志与日志的查询方法
在Linux系统中,日志文件用于记录系统的各种运行信息和错误消息。常见的日志文件包括但不限于/var/log/下的各种日志,如message、secure、maillog、cron等。
对于采用Systemd作为初始化系统的Linux,除了传统的文本日志文件外,还提供了Journal存储机制,可以通过journalctl命令进行复杂且高效的查询操作:
journalctl [OPTIONS...] [MATCHES...]
| 命令 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| journalctl -x | 查看日志 |
| journalctl -xe | 跳到尾部查看日志 |
更多journalctl用法
Options:
| options | description |
|---|---|
| –system | Show the system journal |
| –user | Show the user journal for the current user |
| -M --machine=CONTAINER | Operate on local container |
| -S --since=DATE | Show entries not older than the specified date |
| -U --until=DATE | Show entries not newer than the specified date |
| -c --cursor=CURSOR | Show entries starting at the specified cursor |
| –after-cursor=CURSOR | Show entries after the specified cursor |
| –show-cursor | Print the cursor after all the entries |
| –cursor-file=FILE | Show entries after cursor in FILE and update FILE |
| -b --boot[=ID] | Show current boot or the specified boot |
| –list-boots | Show terse information about recorded boots |
| -k --dmesg | Show kernel message log from the current boot |
| -u --unit=UNIT | Show logs from the specified unit |
| –user-unit=UNIT | Show logs from the specified user unit |
| -t --identifier=STRING | Show entries with the specified syslog identifier |
| -p --priority=RANGE | Show entries with the specified priority |
| –facility=FACILITY… | Show entries with the specified facilities |
| -g --grep=PATTERN | Show entries with MESSAGE matching PATTERN |
| –case-sensitive[=BOOL] | Force case sensitive or insenstive matching |
| -e --pager-end | Immediately jump to the end in the pager |
| -f --follow | Follow the journal |
| -n --lines[=INTEGER] | Number of journal entries to show |
| –no-tail | Show all lines, even in follow mode |
| -r --reverse | Show the newest entries first |
| -o --output=STRING | Change journal output mode (short, short-precise, |
| -x --catalog | Add message explanations where available |
| -a --all | Show all fields, including long and unprintable |
| -q --quiet | Do not show info messages and privilege warning |
| -m --merge | Show entries from all available journals |
| -D --directory=PATH | Show journal files from directory |
Commands:
| commands | description |
|---|---|
| –help | Show this help text |
| –version | Show package version |
| –fields | List all field names currently used |
| –field=FIELD | List all values that a specified field takes |
| –disk-usage | Show total disk usage of all journal files |
| –vacuum-size=BYTES | Reduce disk usage below specified size |
| –vacuum-files=INT | Leave only the specified number of journal files |
| –vacuum-time=TIME | Remove journal files older than specified time |
| –verify | Verify journal file consistency |
| –sync | Synchronize unwritten journal messages to disk |
| –relinquish-var | Stop logging to disk, log to temporary file system |
| –smart-relinquish-var | Similar, but NOP if log directory is on root mount |
| –flush | Flush all journal data from /run into /var |
| –rotate | Request immediate rotation of the journal files |
| –header | Show journal header information |
| –list-catalog | Show all message IDs in the catalog |
| –dump-catalog | Show entries in the message catalog |
| –update-catalog | Update the message catalog database |
| –setup-keys | Generate a new FSS key pair |
journalctl用法案例
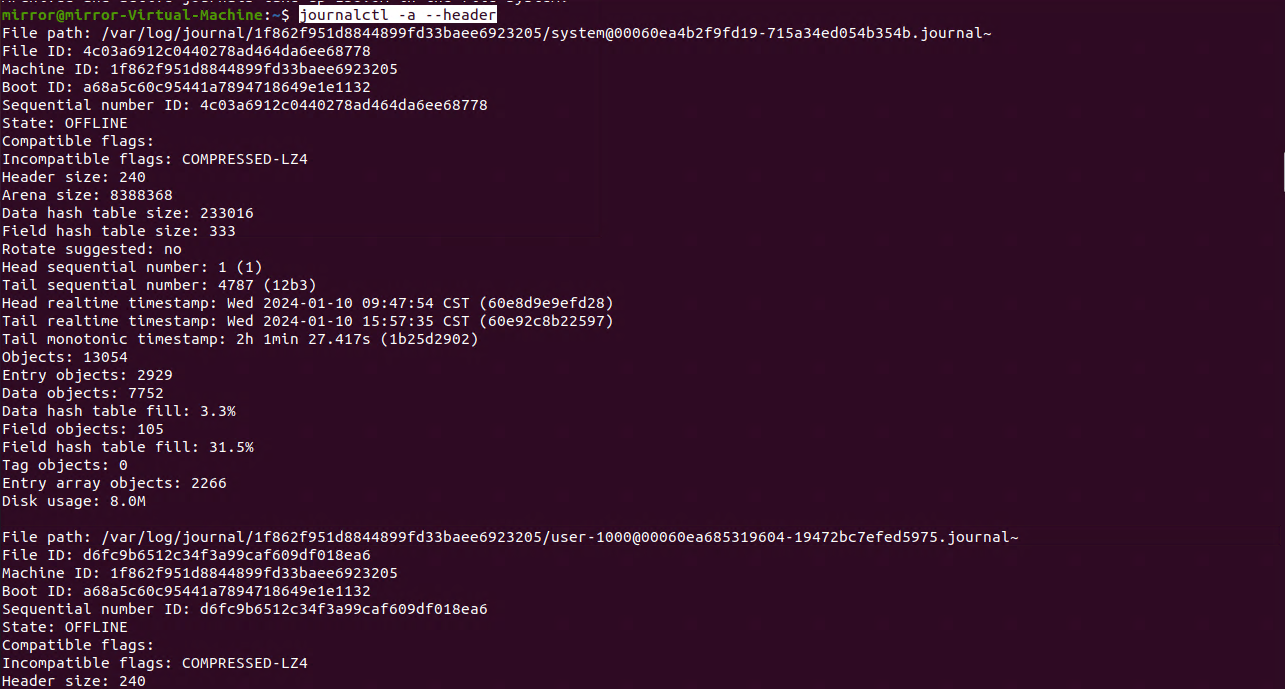
journalctl -a --header
journalctl -a --header会展示系统日志中的所有记录,并且每条记录前面都会带有详细的头部信息。
journalctl -a
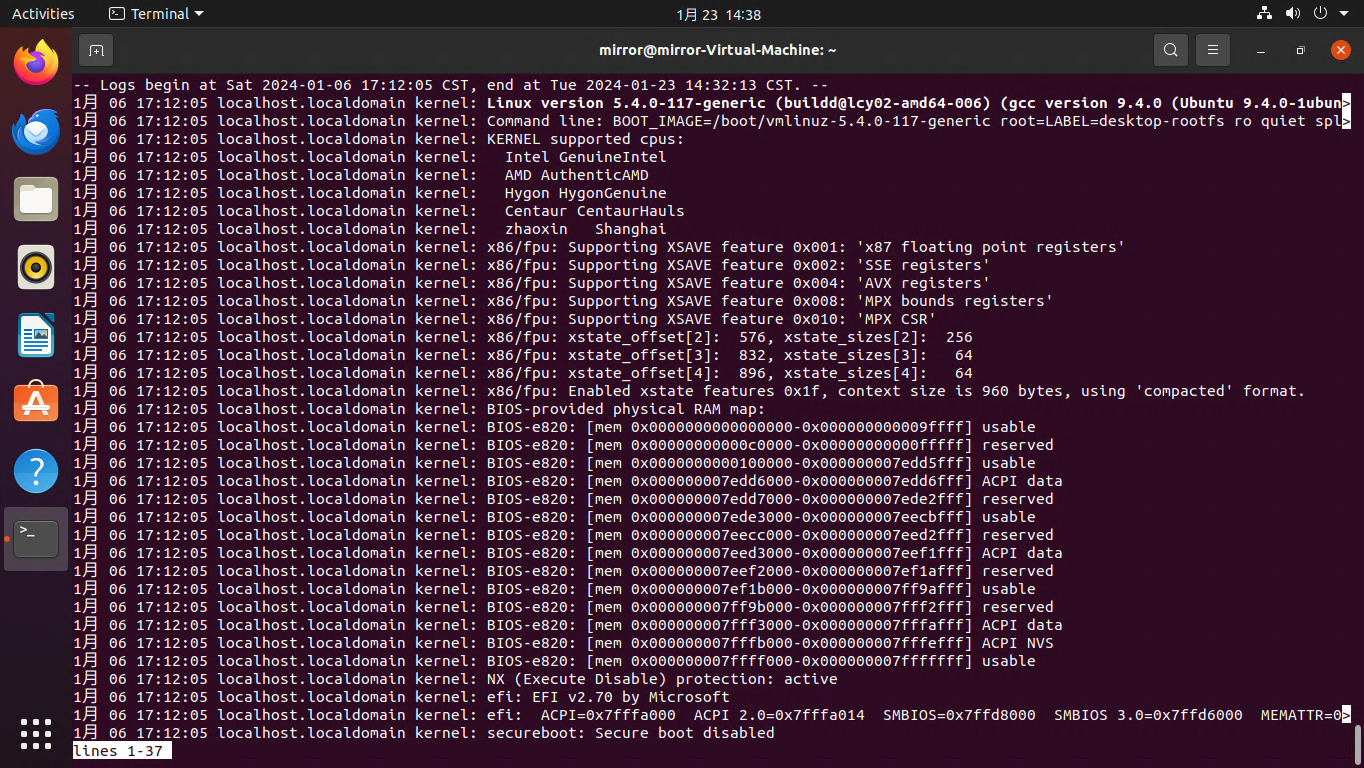
执行此命令会查看存储在系统 journal 中的完整日志历史。包括过去和现在的、与当前控制台关联的以及不关联的所有日志条目,不论它们的日志级别(优先级)如何。
journalctl -xe
journalctl -xe命令主要用于查看系统最新的、详尽的日志信息,且这些信息会直接输出到终端屏幕,方便用户实时监控系统的最新状态和事件。
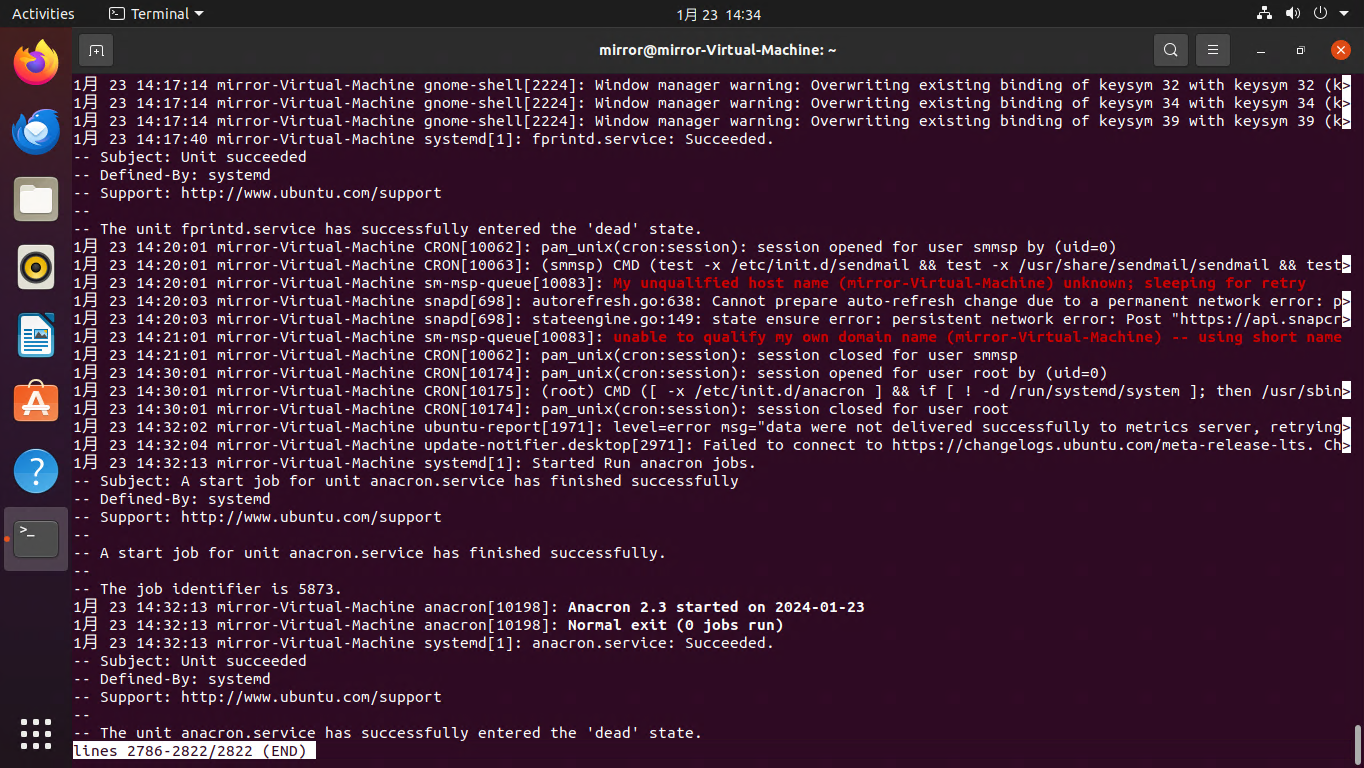
id mirror
journalctl _UID=1000 -n 20
从系统日志中查找并显示由用户ID为1000的用户产生的最近20条日志条目。
journalctl --since "2024-01-23 12:00:00" --until "2024-01-23 14:00:00"
-
--since "2024-01-23 12:00:00":这个选项用于从特定时间点开始显示日志记录,即从2024年1月23日的中午12点开始。 -
--until "2024-01-23 14:00:00":这个选项用于限制输出的日志条目范围,仅显示直到特定时间点的日志记录,此处指到同一天下午2点为止。

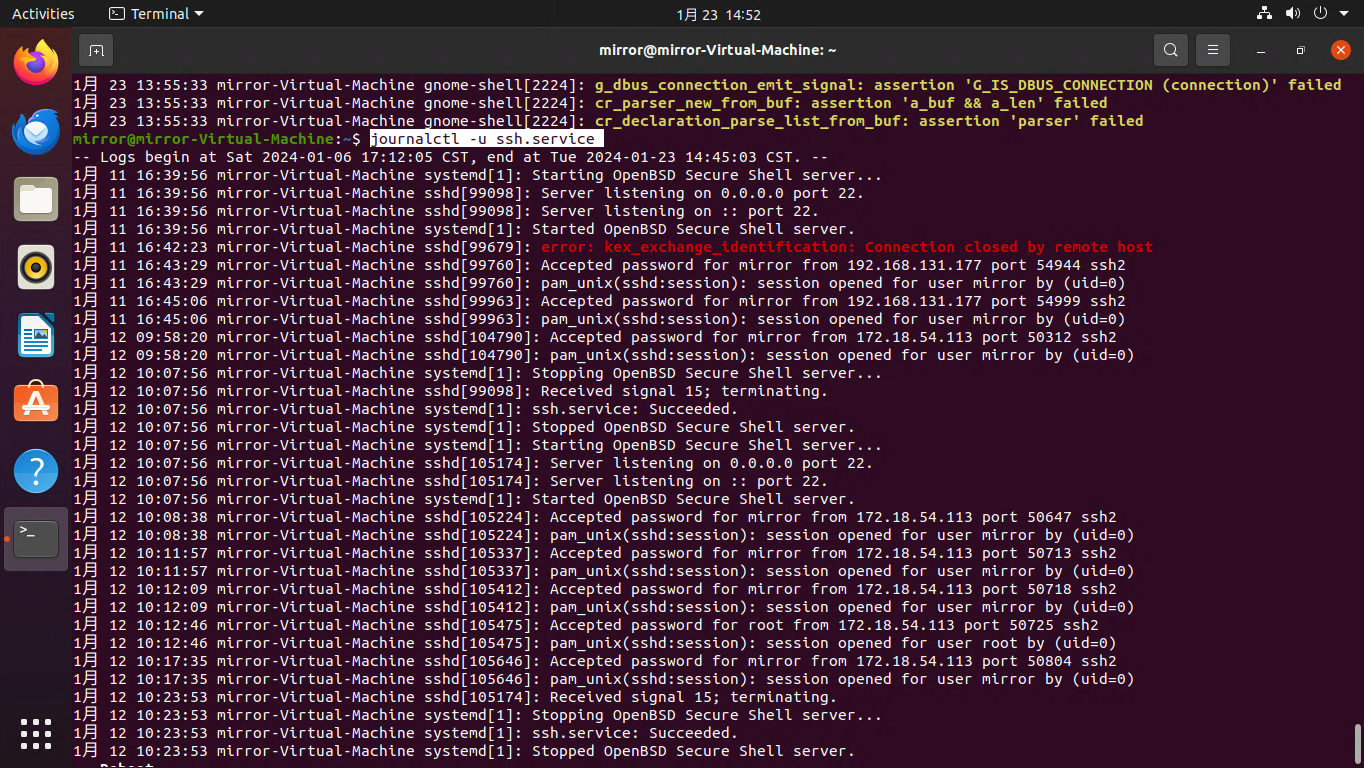
journalctl -u ssh.service
或者
journalctl --unit ssh.service
查看某个服务的日志,这里举例的是ssh服务。
部分日志路径说明
| 日志路径 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| /var/log/message | 全局系统日志,包括登录,对服务启停认证等 |
| /var/log/lastlog | 不是一个文本文件,需要用lastlog命令读,保存了用户最近的登录信息 |
| /var/log/yun.log | 最近通过yum安装的程序的日志 |
| /var/log/cron | 定时任务的日志 |
| /var/log/boot.log | 启动日志 |
| /var/log/kern | 内核日志,也可以通过dmesg查看 |
推荐阅读
- 分布式文件系统协议:NFS(Network File System)网络文件系统
- 云服务器基于Centos创建个人云盘实践经验分享
- Tcpdump 抓包分析指令使用方法
- 进程已结束,退出代码为 -1073741819 (0xC0000005)
- 【漏洞修复】Cisco IOS XE软件Web UI权限提升漏洞及修复方法