前言
Dubbo 框架采用分层设计,最底下的 Serialize 层负责把对象序列化为字节序列,再经过 Transport 层网络传输到对端。一次 RPC 调用,在 Dubbo 看来其实就是一段请求报文和一段响应报文的传输过程。
理解Transport
Transport 层即网络传输层,它在 Serialize 的上层,Exchange 的下层,起到一个承上启下的作用。
有很多网络库可以做网络传输,比如 Netty、Mina、甚至是 JDK 原生的 Socket,但是这些库的使用方式和对外接口都不一样,如果直接依赖三方库开发,后续更换实现方案就非常麻烦了,违背了开闭原则。
所以 Transport 层对网络传输做了抽象,它把 Netty、Mina 封装成统一接口,上层面向接口编程,具体实现可以轻松替换。
Transport 层只负责数据的传输,至于要传输什么数据它是不关心的,也不应该关心。传输的数据格式和通信协议息息相关,应该由协议层去定义。
设计实现
Transport 层和 Exchange 层的代码都位于dubbo-remoting模块,同样的,dubbo-remoting-api模块只定义抽象接口,其它子模块负责具体实现。
Dubbo 官方内置的 remoting 模块:
<modules>
<module>dubbo-remoting-api</module>
<module>dubbo-remoting-netty</module>
<module>dubbo-remoting-mina</module>
<module>dubbo-remoting-grizzly</module>
<module>dubbo-remoting-p2p</module>
<module>dubbo-remoting-http</module>
<module>dubbo-remoting-zookeeper</module>
<module>dubbo-remoting-netty4</module>
<module>dubbo-remoting-etcd3</module>
</modules>
抽象层
Transport 层的核心SPI接口是 Transporter,默认实现是 Netty。
@SPI("netty")
public interface Transporter {
@Adaptive({Constants.SERVER_KEY, Constants.TRANSPORTER_KEY})
RemotingServer bind(URL url, ChannelHandler handler) throws RemotingException;
@Adaptive({Constants.CLIENT_KEY, Constants.TRANSPORTER_KEY})
Client connect(URL url, ChannelHandler handler) throws RemotingException;
}
接口定义了两个方法,bind()用于服务端绑定本地接口,connect()用于客户端和服务器建立连接。
ChannelHandler 接口用来定义 Channel 事件,Dubbo 目前定义了五个事件,分别是:
- connected:连接事件
- disconnected:连接断开事件
- sent:数据发送事件
- received:数据接收事件
- caught:异常事件
@SPI
public interface ChannelHandler {
void connected(Channel channel) throws RemotingException;
void disconnected(Channel channel) throws RemotingException;
void sent(Channel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException;
void received(Channel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException;
void caught(Channel channel, Throwable exception) throws RemotingException;
}
Channel 接口抽象的是一个tcp连接,它继承自 Endpoint,代表它也是一个端点。既然是连接,那自然就拥有发送数据、主动断开、读写属性等能力。
public interface Channel extends Endpoint {
// 远程地址
InetSocketAddress getRemoteAddress();
// 是否连接
boolean isConnected();
/****属性的读写****/
boolean hasAttribute(String key);
Object getAttribute(String key);
void setAttribute(String key, Object value);
void removeAttribute(String key);
}
public interface Endpoint {
URL getUrl();
// Channel事件处理器
ChannelHandler getChannelHandler();
// 本地地址
InetSocketAddress getLocalAddress();
// 发送数据
void send(Object message) throws RemotingException;
void send(Object message, boolean sent) throws RemotingException;
// 关闭连接
void close();
void close(int timeout);
void startClose();
boolean isClosed();
}
RemotingServer 抽象的是服务器接口,通过绑定本地接口可以获得一个服务器对象,它会维护所有和它建立连接的 Channel。
public interface RemotingServer extends Endpoint, Resetable, IdleSensible {
// 是否绑定
boolean isBound();
// 拿所有连接
Collection<Channel> getChannels();
// 根据远程地址拿连接
Channel getChannel(InetSocketAddress remoteAddress);
@Deprecated
void reset(org.apache.dubbo.common.Parameters parameters);
}
Client 接口抽象的是客户端,它继承自 Channel,所以它也是一个连接,可以向远程发送数据。
public interface Client extends Endpoint, Channel, Resetable, IdleSensible {
// 重连
void reconnect() throws RemotingException;
@Deprecated
void reset(org.apache.dubbo.common.Parameters parameters);
}
除了围绕 Transporter 的这些接口,传输层还有一个很重要的接口。
Codec2 是网络编解码器的抽象接口,我们代码里发送的是 Object,对象本身不能通过网络传输,得经过编码器把它编码为字节序列才能发送。同样的,对端收到的也是一段字节序列,得经过解码器按照相同的规则解码为 Object。
@SPI
public interface Codec2 {
// 编码
@Adaptive({Constants.CODEC_KEY})
void encode(Channel channel, ChannelBuffer buffer, Object message) throws IOException;
// 解码
@Adaptive({Constants.CODEC_KEY})
Object decode(Channel channel, ChannelBuffer buffer) throws IOException;
enum DecodeResult {
NEED_MORE_INPUT,
SKIP_SOME_INPUT
}
}
实现层
直接看默认实现,基于 Netty4 的 org.apache.dubbo.remoting.transport.netty4.NettyTransporter。
public class NettyTransporter implements Transporter {
public static final String NAME = "netty";
@Override
public RemotingServer bind(URL url, ChannelHandler handler) throws RemotingException {
return new NettyServer(url, handler);
}
@Override
public Client connect(URL url, ChannelHandler handler) throws RemotingException {
return new NettyClient(url, handler);
}
}
NettyServer
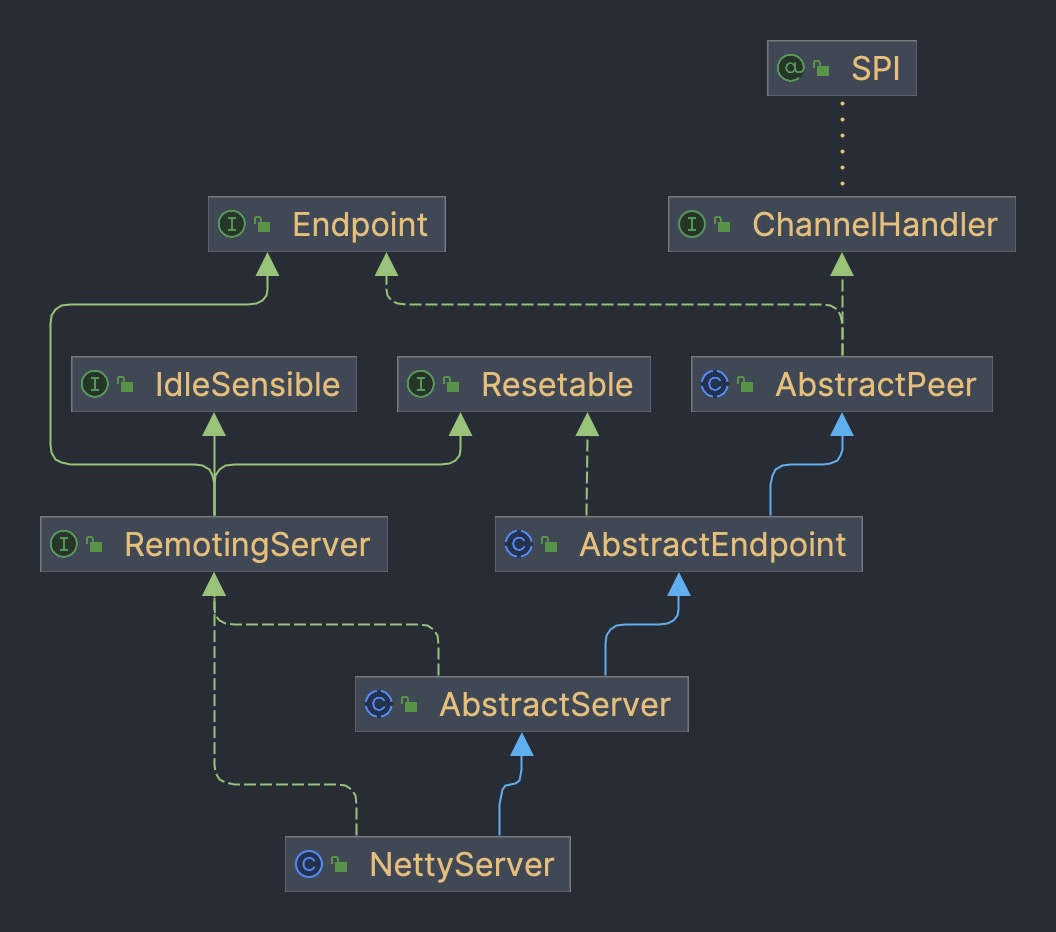
基于 Netty 实现的服务器类是 NettyServer,继承关系比较复杂,看看每一层构造函数都干了啥。
AbstractPeer 主要是保存 URL 和 ChannelHandler
public AbstractPeer(URL url, ChannelHandler handler) {
this.url = url;
this.handler = handler;
}
AbstractEndpoint 通过 SPI 加载编解码器 Codec2 的实现
public AbstractEndpoint(URL url, ChannelHandler handler) {
super(url, handler);
this.codec = getChannelCodec(url);
this.timeout = url.getPositiveParameter(TIMEOUT_KEY, DEFAULT_TIMEOUT);
this.connectTimeout = url.getPositiveParameter(Constants.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_CONNECT_TIMEOUT);
}
AbstractServer 构造函数是个模板方法,调用子类的doOpen开启服务,然后创建线程池
public AbstractServer(URL url, ChannelHandler handler) throws RemotingException {
super(url, handler);
localAddress = getUrl().toInetSocketAddress();
// 获取绑定的IP和端口
String bindIp = getUrl().getParameter(Constants.BIND_IP_KEY, getUrl().getHost());
int bindPort = getUrl().getParameter(Constants.BIND_PORT_KEY, getUrl().getPort());
if (url.getParameter(ANYHOST_KEY, false) || NetUtils.isInvalidLocalHost(bindIp)) {
bindIp = ANYHOST_VALUE;
}
bindAddress = new InetSocketAddress(bindIp, bindPort);
// 最大连接数、连接空闲超时时间
this.accepts = url.getParameter(ACCEPTS_KEY, DEFAULT_ACCEPTS);
this.idleTimeout = url.getParameter(IDLE_TIMEOUT_KEY, DEFAULT_IDLE_TIMEOUT);
try {
doOpen(); // 开启服务
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Start " + getClass().getSimpleName() + " bind " + getBindAddress() + ", export " + getLocalAddress());
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new RemotingException(url.toInetSocketAddress(), null, "Failed to bind " + getClass().getSimpleName()
+ " on " + getLocalAddress() + ", cause: " + t.getMessage(), t);
}
// 业务线程池
executor = executorRepository.createExecutorIfAbsent(url);
}
NettyServer 是具体实现,主要是基于 Netty 开启服务,常规的 ServerBootstrap 启动流程,我们重点关注的是 Dubbo 对 ChannelPipeline 的编排。
- 如果开启 ssl,会插入一个 SslServerTlsHandler
- 接着插入编解码器
- IdleStateHandler 用于关闭超时闲置的连接
- NettyServerHandler 主要是对我们的业务处理器 handler 再包装了一层
@Override
protected void doOpen() throws Throwable {
bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
// Accept线程
bossGroup = NettyEventLoopFactory.eventLoopGroup(1, "NettyServerBoss");
// IO线程 CPU核心数+1 最大不会超过32
workerGroup = NettyEventLoopFactory.eventLoopGroup(
getUrl().getPositiveParameter(IO_THREADS_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_IO_THREADS),
"NettyServerWorker");
final NettyServerHandler nettyServerHandler = new NettyServerHandler(getUrl(), this);
channels = nettyServerHandler.getChannels();
bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NettyEventLoopFactory.serverSocketChannelClass())
.option(ChannelOption.SO_REUSEADDR, Boolean.TRUE)
.childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, Boolean.TRUE)
.childOption(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
// FIXME: should we use getTimeout()?
int idleTimeout = UrlUtils.getIdleTimeout(getUrl());
NettyCodecAdapter adapter = new NettyCodecAdapter(getCodec(), getUrl(), NettyServer.this);
if (getUrl().getParameter(SSL_ENABLED_KEY, false)) {
// 开启ssl
ch.pipeline().addLast("negotiation",
SslHandlerInitializer.sslServerHandler(getUrl(), nettyServerHandler));
}
// 编排ChannelPipeline
ch.pipeline()
.addLast("decoder", adapter.getDecoder())
.addLast("encoder", adapter.getEncoder())
.addLast("server-idle-handler", new IdleStateHandler(0, 0, idleTimeout, MILLISECONDS))
/**
* @see HeaderExchanger#bind(URL, ExchangeHandler)
*/
.addLast("handler", nettyServerHandler);
}
});
// 绑定端口,同步等待完成
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.bind(getBindAddress());
channelFuture.syncUninterruptibly();
channel = channelFuture.channel();
}
NettyClient
基于 Netty 实现的客户端类是 org.apache.dubbo.remoting.transport.netty4.NettyClient。
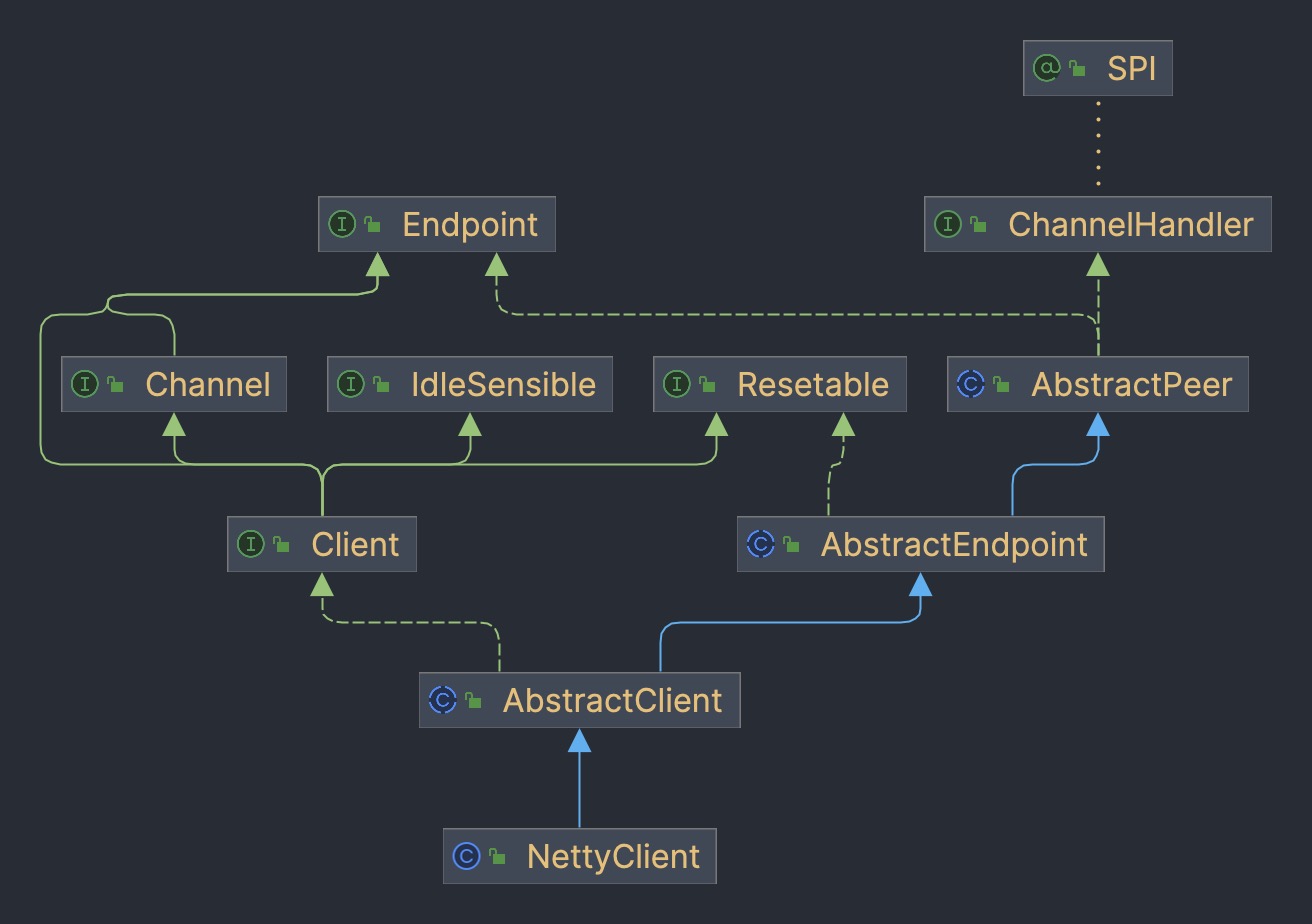
基类是一样的,用于初始化编解码器 Codec2。AbstractClient 会调用子类doOpen开启客户端,紧接着调用connect和服务器建立连接。
public AbstractClient(URL url, ChannelHandler handler) throws RemotingException {
super(url, handler);
needReconnect = url.getParameter(Constants.SEND_RECONNECT_KEY, false);
// 初始化线程池
initExecutor(url);
doOpen();// 开启客户端
connect(); // 建立连接
}
doOpen也是常规的 Netty Bootstrap 启动流程,ChannelPipeline 的编排和 Server 端一致。
@Override
protected void doOpen() throws Throwable {
final NettyClientHandler nettyClientHandler = new NettyClientHandler(getUrl(), this);
bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(NIO_EVENT_LOOP_GROUP)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.option(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT)
//.option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, getTimeout())
.channel(socketChannelClass());
bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, Math.max(3000, getConnectTimeout()));
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
int heartbeatInterval = UrlUtils.getHeartbeat(getUrl());
if (getUrl().getParameter(SSL_ENABLED_KEY, false)) {
ch.pipeline().addLast("negotiation", SslHandlerInitializer.sslClientHandler(getUrl(), nettyClientHandler));
}
NettyCodecAdapter adapter = new NettyCodecAdapter(getCodec(), getUrl(), NettyClient.this);
ch.pipeline()//.addLast("logging",new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))//for debug
.addLast("decoder", adapter.getDecoder())
.addLast("encoder", adapter.getEncoder())
.addLast("client-idle-handler", new IdleStateHandler(heartbeatInterval, 0, 0, MILLISECONDS))
.addLast("handler", nettyClientHandler);
String socksProxyHost = ConfigUtils.getProperty(SOCKS_PROXY_HOST);
if(socksProxyHost != null) {
int socksProxyPort = Integer.parseInt(ConfigUtils.getProperty(SOCKS_PROXY_PORT, DEFAULT_SOCKS_PROXY_PORT));
Socks5ProxyHandler socks5ProxyHandler = new Socks5ProxyHandler(new InetSocketAddress(socksProxyHost, socksProxyPort));
ch.pipeline().addFirst(socks5ProxyHandler);
}
}
});
}
doConnect会调用Bootstrap#connect和服务端建立连接,连接成功后会得到一个 Channel 对象,Dubbo 可以通过它给服务端发数据。
@Override
protected void doConnect() throws Throwable {
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect(getConnectAddress());
boolean ret = future.awaitUninterruptibly(getConnectTimeout(), MILLISECONDS);
if (ret && future.isSuccess()) {
Channel newChannel = future.channel();
NettyClient.this.channel = newChannel;
}
}









![[HTML]Web前端开发技术12(HTML5、CSS3、JavaScript )——喵喵画网页](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/3459348837da4004922ca6eba73cbfcf.png)