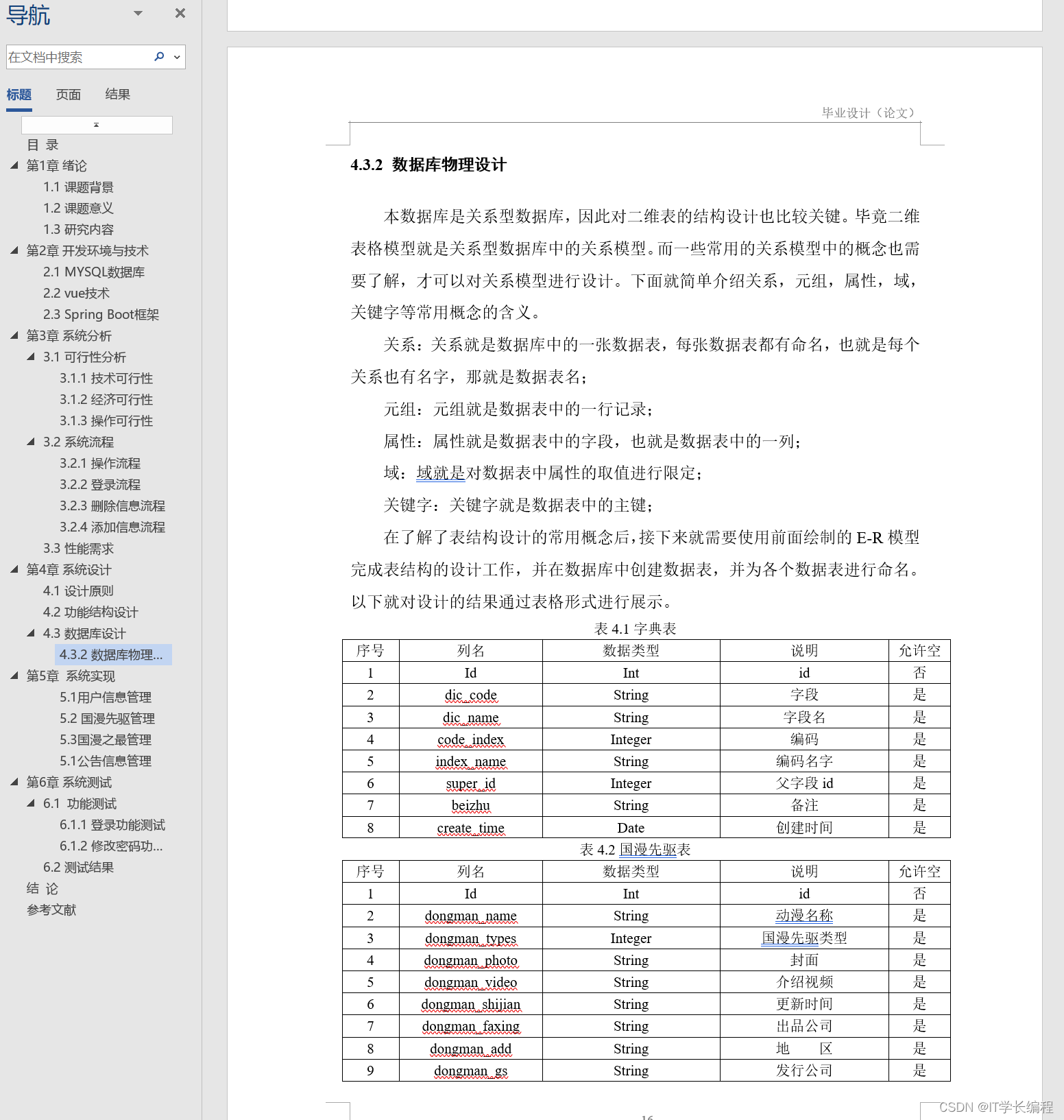
状态管理
看下面这张图

Components部分的装饰器为组件级别的状态管理,Application部分为应用的状态管理。开发者可以通过@StorageLink/@LocalStorageLink 实现应用和组件状态的双向同步,通过@StorageProp/@LocalStorageProp 实现应用和组件状态的单向同步。
@Prop
static Prop(propName: string): any
与 AppStorage 中对应的 propName 建立单向属性绑定。如果给定的 propName 在 AppStorage 中存在,则返回与 AppStorage 中 propName 对应属性的单向绑定数据。如果 AppStorage 中不存在 propName,则返回 undefined。单向绑定数据的修改不会被同步回 AppStorage 中。
prop 是单向绑定,但父级不会跟子集进行相应
@Prop 是单向传递。
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
// State必须要进行初始化
@State message: string ='Southern Wind'
build() {
Row() {
Column() {
Text(this.message)
.textStyle()
Button('点击')
.backgroundColor(Color.Black)
.onClick(()=>{
this.message= this.message === 'Southern Wind'? '你好' : 'Southern Wind';
})
StateProp({content:this.message})
}
.width('100%')
}
}
}
// 子组件
@Component
struct StateProp{
@Prop content:string
build(){
Column(){
Text('prop:'+this.content)
.textStyle()
.fontColor(Color.Green)
Button('修改数据')
.btnStyle(()=>{
this.content = 'HarmonyOS4.0'
})
}
}
}
// 文本公共样式
@Extend(Text) function textStyle() {
.fontSize(30)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
}
// 按钮公共样式
@Extend(Button) function btnStyle(click:Function) {
.backgroundColor(Color.Green)
.fontSize(25)
.margin(10)
.onClick(()=>{
click()
})
}
效果:

关于多个页面使用相同组件重名报错问题:
可以自己定义一个规范:
我这里用结构体名称加下划线的形式命名函数,如果文件名为 Index,那么我的按钮组件可以用Index_btnStyle
@Link
static Link(propName: string): any
与 AppStorage 中对应的 propName 建立双向数据绑定。如果给定的 propName 在 AppStorage 中存在,返回与 AppStorage 中 propName 对应属性的双向绑定数据。
双向绑定数据的修改会同步回 AppStorage 中,AppStorage 会将变化同步到所有绑定该 propName 的数据和自定义组件中。
如果 AppStorage 中不存在 propName,则返回 undefined。
以上是官方的说明,其实说白了Prop就是单项数据绑定,Link是双向数据绑定。
@Link 和@Prop 的区别
继续往下看个例子就明白了:
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
// State必须要进行初始化
@State message: string = 'Southern Wind'
build() {
Row() {
Column() {
Text(this.message)
.textStyle()
Button('点击')
.backgroundColor(Color.Black)
.onClick(() => {
this.message = this.message === 'Southern Wind' ? '你好' : 'Southern Wind';
})
StateProp({ content: this.message })
// Index_link({content_link:this.message})
// 如果是Link,则使用$+变量名进行传递
Index_link({content_link: $message})
}
.width('100%')
}
}
}
// 子组件
@Component
struct StateProp {
@Prop content: string
build() {
Column() {
Text('prop:' + this.content)
.textStyle()
.fontColor(Color.Green)
Button('修改Prop数据')
.btnStyle(() => {
this.content = '我是Prop数据'
})
}
}
}
@Component
struct Index_link {
@Link content_link: string
build() {
Column() {
Text('link:' + this.content_link)
.textStyle()
.fontColor(Color.Red)
Button('修改Link数据').btnStyle(()=>{
this.content_link = '我是Link数据'
})
.backgroundColor(Color.Red)
}
}
}
// 文本公共样式
@Extend(Text) function textStyle() {
.fontSize(30)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
}
// 按钮公共样式
@Extend(Button) function btnStyle(click: Function) {
.backgroundColor(Color.Green)
.fontSize(25)
.margin(10)
.onClick(() => {
click()
})
// .click()
}
效果:

父孙组件传递 @Provide和 @Consume 与后代组件双向同步
父孙组件可以使用@Link来进行双向绑定,但是和子组件来说的话没法进行区分,所以需要使用@Provide和@Consume来进行区分。
例:
@Entry
@Component
struct Index{
@Provide message:string = '我是父组件'
build(){
Row(){
Column({space:20}){
Text(this.message).IndexTextStyle()
.onClick(()=>{
this.message = 'Southern Wind'
})
Divider()
Index_son()
}.width('100%')
}.height('100%')
}
}
@Component
struct Index_son{
build(){
Column({space:30}){
Text('子组件').IndexTextStyle()
Divider()
Index_sun()
}
}
}
@Component
struct Index_sun{
@Consume message:string
build(){
Column(){
Text('孙组件' + this.message).IndexTextStyle()
.onClick(()=>{
this.message = 'HarmonyOS 4.0'
})
}
}
}
@Extend(Text) function IndexTextStyle() {
.fontSize(30)
}
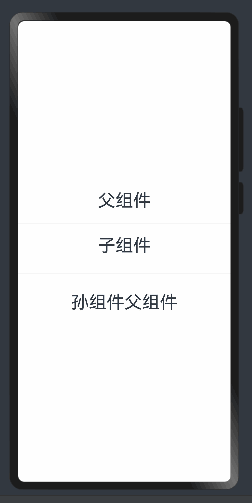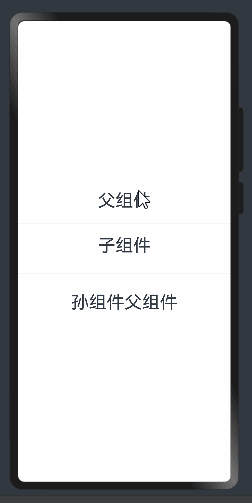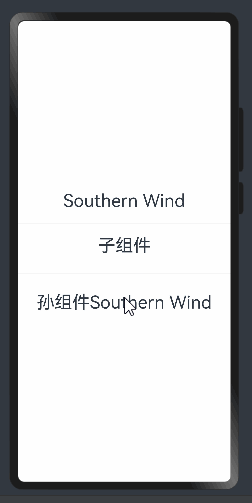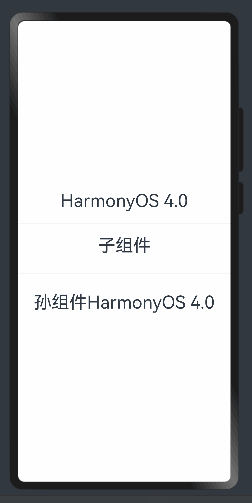
其中@Provide装饰的变量是在祖先节点中,可以理解为被“提供”给后代的状态变量。@Consume装饰的变量是在后代组件中,去“消费(绑定)”祖先节点提供的变量。
** @Provide/@Consume装饰的状态变量有以下特性:**
@Provide装饰的状态变量自动对其所有后代组件可用,即该变量被“provide”给他的后代组件。由此可见,@Provide的方便之处在于,开发者不需要多次在组件之间传递变量。- 后代通过使用
@Consume去获取@Provide提供的变量,建立在@Provide和@Consume之间的双向数据同步,与@State/@Link不同的是,前者可以在多层级的父子组件之间传递。 @Provide和@Consume可以通过相同的变量名或者相同的变量别名绑定,变量类型必须相同。
// 通过相同的变量名绑定
@Provide a: number = 0;
@Consume a: number;
// 通过相同的变量别名绑定
@Provide('a') b: number = 0;
@Consume('a') c: number;
如果@Provide和@Consume绑定的变量名不相同,则可以通过变量别名来区分。
// 通过相同的变量别名绑定
@Provide('a') b: number = 0;
@Consume('d') c: number
@Watch:状态变量更改通知
@Watch应用于对状态变量的监听。如果开发者需要关注某个状态变量的值是否改变,可以使用@Watch为状态变量设置回调函数。
@Watch用于监听状态变量的变化,当状态变量变化时,@Watch的回调方法将被调用。@Watch在ArkUI框架内部判断数值有无更新使用的是严格相等(===),遵循严格相等规范。当在严格相等为false的情况下,就会触发@Watch的回调。
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State @Watch('change') count:number = 0
@State num:number = 2
@State total:number = 0
change(){
this.total = Math.pow(this.count,this.num)
}
build() {
Row(){
Column({space:20}) {
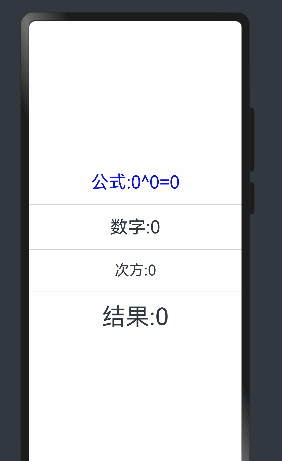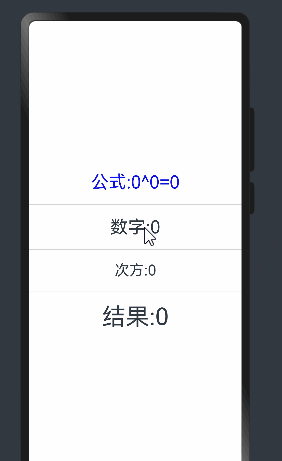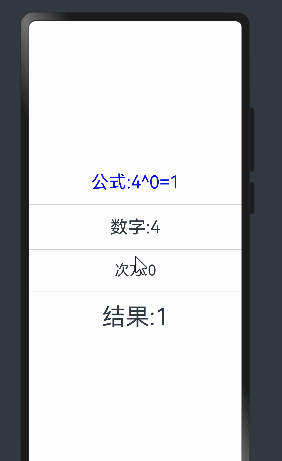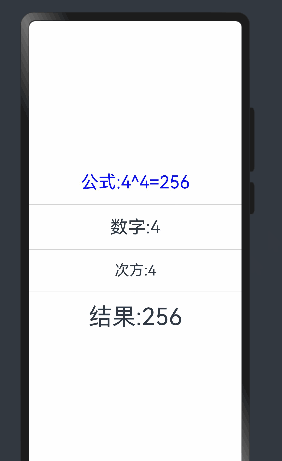
Text(`公式:${this.count}^${this.num}=${this.total}`).fontSize(30).fontColor(Color.Blue)
Divider()
Text('数字:'+this.count)
.fontSize(30)
.onClick(()=>{
this.count ++
})
Divider()
Text('次方:' + this.num).fontSize(25)
.onClick(()=>{
this.num ++
})
Divider()
Text('结果:'+this.total).fontSize(40)
}.width('100%')
}.height('100%')
}
}
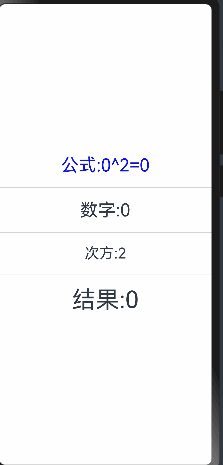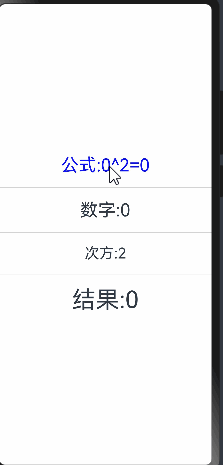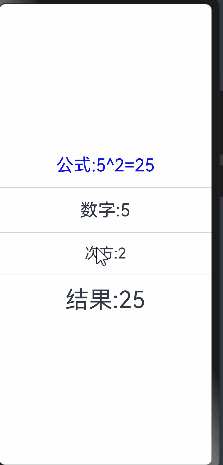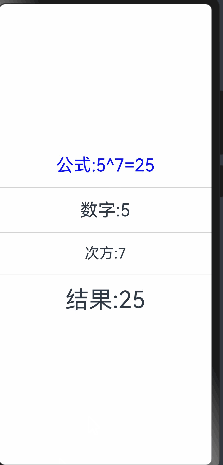
当点击次方为文本时无法进行监听,这是因为num只是定义了双向绑定,没有设置状态监听
这时需要将num 添加监听器
@State @Watch('change') num:number = 0
效果:
当点击次方为文本时无法进行监听,这是因为num只是定义了双向绑定,没有设置状态监听
这时需要将num 添加监听器
@State @Watch('change') num:number = 0
效果: