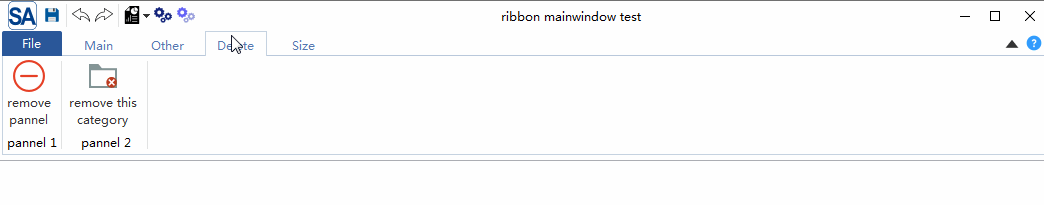
(1)把类成员函数作为参数传递给thread类 一般地,在调用类的非静态函数时,编译器会隐式添加一参数,它是所操作对象的地址, 用于绑定对象和成员函数,并且位于所有其他实际参数之前。例如,类example具有成员函数func(int x),而obj是该类的对象,则调用obj.func(2)等价于调用example::func(&obj,2)。请参阅《深度探索 C++对象模型》。 using namespace std;
class Student
{
public:
void get(const string &sName,const size_t& nAge)
{
cout << "姓名:"<< sName << "\n年龄:"<< nAge <<"\n";
}
};
int main()
{
Student student;
std::thread t(&Student::get,&student,"陈平安", 15);
t.join();
}输出:
(2)把主线程内存移动到子线程 using namespace std;
using namespace lf;
void do_something(std::unique_ptr<string> pAuto)
{
}
void main()
{
std::unique_ptr<string> pAutoFree(new string("test"));
cout << "之前内存地址:" << pAutoFree << "\n";
cout << *pAutoFree << "\n";
std::thread t(do_something, std::move(pAutoFree));
t.join();
cout << "之后内存地址:" << pAutoFree << "\n";
if (pAutoFree == NULL)
{
cout << "内存已移到新线程!";
}
}输出: