本章概要
- mapMutations
- mapState
- getter
16.4 mapMutations
继续完善购物车程序,为购物车添加删除商品功能。删除商品同样要修改 store 中保存的购物车商品数据,因此继续在 mutations 选项中定义一个 deleteItem mutation。编辑 store 目录下的 index.js 文件,如下:
store/index.js
import { createStore } from "vuex";
import books from "@/data/books.js";
const store = createStore({
// 状态数据通过 state() 函数返回
state() {
return {
items: books // 使用导入的 books 对 items 进行格式化
}
},
mutations:{
pushItemToCart (state,book){
state.items.push(book);
},
deleteItem (state,id){
// 根据提交的 id 载荷,查找是否存在相同 id 的商品,返回商品的索引
let index = state.items.findIndex(item => item.id === id);
if(index>0){
state.items.splice(index,1);
}
}
}
})
export default store;
编辑 Cart.vue,为“删除”按钮添加 click 事件处理,提交 deleteItem mutation。如下:
Cart.vue
<td><button @click="$store.commit('deleteItem',book.id)">删除</button></td>
此时再次运行项目,单击“删除”,可以看到购物车中的商品项被成功删除。
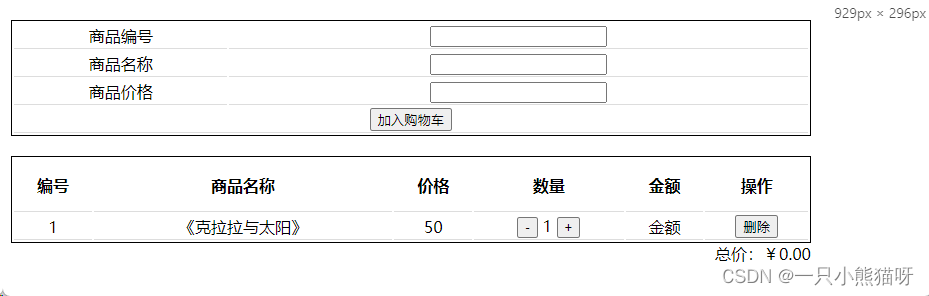
如果组件中需要提交的 mutation 较多,使用 this.$store.commit() 方法提交就会很烦琐,为了简化 mutation 提交,可以使用 mapMutations() 辅助函数将组件中的方法映射为 store.commit() 调用。如下:
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'
methods:mapMutations([
// 将 this.increment() 映射为 this.$store.commit('increment')
'increment',
// 将 this.incrementBy(amount) 映射为 this.$store.commit('incrementBy',amount)
'incrementBy'
])
除了使用字符串数组外,mapMutations() 函数的参数也可以是一个对象。如下:
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'
methods:mapMutations({
// 将 this.add() 映射为 this.$store.commit('increment')
add:'increment'
})
在大多数情况下,组件还有自己的方法,在这种情况下,可以使用 ES6 的展开运算符提取 mapMutation() 函数返回的对象属性,赋值到 methods 选项中。如下:
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'
export default {
// ...
methods:{
...mapMutations([
// 将 this.increment() 映射为 this.$store.commit('increment')
'increment',
// mapMutations 也支持载荷
// 将 this.incrementBy(amount) 映射为 this.$store.commit('increment',amount)
'incrementBy'
]),
...mapMutations({
// 将this.add() 映射为 this.$store.commit('increment')
add:'increment'
})
}
}
修改 Cart.vue ,使用 mapMutations() 辅助函数简化 mutation 的提交。如下:
Cart.vue
<template>
<div>
<table>
<tr>
<td>商品编号</td>
<td><input type="text" v-model.number="id" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>商品名称</td>
<td><input type="text" v-model.number="title" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>商品价格</td>
<td><input type="text" v-model.number="price" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="2"><button @click="addCart">加入购物车</button></td>
</tr>
</table>
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>编号</th>
<th>商品名称</th>
<th>价格</th>
<th>数量</th>
<th>金额</th>
<th>操作</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr v-for="book in books" :key="book.id">
<td>{{ book.id }}</td>
<td>{{ book.title }}</td>
<td>{{ book.price }}</td>
<td>
<button>-</button>
{{ book.count }}
<button>+</button>
</td>
<td>金额</td>
<!-- <td><button @click="$store.commit('deleteItem',book.id)">删除</button></td> -->
<td><button @click="deleteItem(book.id)">删除</button></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<span>总价:¥0.00</span>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex';
export default {
data() {
return {
id: null,
title: '',
price: '',
quantity: 1
}
},
computed: {
books() {
// return this.$store.state.items;
return this.$store.state.items;
}
},
methods: {
...mapMutations({
addItemToCart:'pushItemToCart'
}),
...mapMutations([
'deleteItem'
]),
addCart() {
// this.$store.commit('pushItemToCart', {
this.addItemToCart({
id: this.id,
title: this.title,
price: this.price,
count: this.quantity
})
this.id = '';
this.title = '';
this.price = '';
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
div {
width: 800px;
}
table {
border: 1px solid black;
width: 100%;
margin-top: 20px;
}
th {
height: 50px;
}
th,
td {
border-bottom: 1px solid #ddd;
text-align: center;
}
span {
float: right;
}
</style>
代码中为了演示 mapMutations() 辅助函数的用法,采用了两种方式映射 mutation,实际开发中不必如此,采用统一的映射方式更有助于代码的维护和修改。
16.5 mapState
当一个组件需要使用多个 store 状态属性时,将这些状态都声明为计算属性就会有些重复和冗余。为了解决这个问题,可以使用 mapState() 辅助函数生成计算属性。例如,在 store 中定义了两个状态。如下:
const store = createStore({
state() {
return {
count:0,
message:'biubiubiu'
}
}
})
在组件中使用 mapState() 辅助函数生成计算属性。如下:
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
// ...
computed:mapState({
count:'count',
msg:'message'
})
}
mapState 代码块中,冒号前是计算属性的名字,冒号后是 store 中状态属性的名字,以字符串形式给出。上述代码等价于下面的代码:
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
// ...
computed:mapState({
count:function(state){
return state.count;
},
msg:(state) => state.message
})
}
可以看到,不管是使用普通函数,还是箭头函数,都没有直接使用字符串方便。但如果在计算属性中还要访问组件内的数据属性,那么就只能使用普通函数的方式。如下:
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
data(){
return {
price:99
}
},
computed:mapState({
totalPrice(state){
return this.price * state.count
}
})
}
如果计算属性的名字和 store 中状态属性的名字相同,那么还可以进一步简化,直接给 mapState() 函数传递一个字符串数组即可。如下:
computed:mapState([
// 映射 this.count 为 store.state.count
'count',
// 映射 this.message 为 store.state.message
'message'
])
与 mapMutations() 一样,mapState() 函数返回的也是一个对象,因此可以使用展开运算符将它和组件内的本地计算属性结合一起使用。如下:
computed:{
localComputed(){
// ...
},
// 使用对象展开运算符将此对象混入外部对象中
...mapState({
// ...
})
}
接下来修改 Cart.vue ,使用 mapState() 辅助函数生成 books 计算属性。如下:
Cart.vue
import { mapMutations,mapState } from 'vuex'
...
computed:{
// books() {
// return this.$store.state.items;
// },
...mapState({
books: 'items'
}),
}
16.6 getter
假如在 store 的状态中定义了一个图书数组。如下:
const store = createStore({
state(){
return {
books:[
{id:1,title:'duangduang',siSold:false},
{id:2,title:'pengpeng',siSold:true},
{id:3,title:'biubiu',siSold:true}
]
}
}
})
在组件内需要得到正在销售的图书,于是定义一个计算属性 sellingBooks,对 state 中的 books 进行过滤。如下:
computed:{
sellingBooks(){
return this.$store.state.books.filter(book => book.isSold === true)
}
}
这没有什么问题,但如果多个组件都需要用到 sellingBooks 属性,那么应该怎么办呢?是复制代码,还是抽取为共享函数在多处导入?显然,这都不理想。
Vuex 允许我们在 store 中定义 getters(可以认为是 store 的计算属性)。与计算属性一样,getter 的返回值会根据它的依赖被缓存起来,且只有在它的依赖项发生改变时才会重新计算。
getter 接收 state 作为其第一个参数。如下:
const store = createState({
state(){
return {
books:[
{id:1,title:'duangduang',siSold:false},
{id:2,title:'pengpeng',siSold:true},
{id:3,title:'biubiu',siSold:true}
]
}
},
getters:{
sellingBooks:state => state.books.filter(book => book.isSold === true)
}
})
我们定义的 getter 将作为 store.getter 对象的属性来访问。如下:
<ul>
<li v-for="book in this.$store.getter.sellingBooks" :key="book.id">
{{ book.title }}
</li>
</ul>
getter 也可以接收其他 getter 作为第二个参数。如下:
getters:{
sellingBooks: state => state.books.filter(book => book.isSold === true),
sellingBooksCount:(state,getters) => {
return getters.sellingBooks.length
}
}
在组件内,要简化 getter 的调用,同样可以使用计算属性。如下:
computed:{
sellingBooks(){
return this.$store.getters.sellingBooks;
},
sellingBooksCount(){
return this.$store.getters.sellingBooksCount;
}
}
要注意,作为属性访问的 getter 作为 Vue 响应式系统的一部分被缓存。
如果想简化上述 getter 在计算属性中的访问形式,则可以使用 mapGetter() 辅助函数,这个辅助函数的用法和 mapMutations() 、mapState() 类似,如下:
computed:{
// 使用对象展开运算符将 getter 混入 computed 中
// 传递数组作为参数
...mapGetters([
'sellingBooks',
'sellingBooksCount',
// ...
]),
// 传递对象作为参数
...mapGetters({
// 将 this.booksCount 映射为 this.$store.getters.sellingBooksCount
booksCount:'sellingBooksCount'
})
}
getter 还有更灵活的用法,通过让 getter 返回一个函数来实现给 getter 传参。例如,下面的 getter 根据图书 id 查找图书对象。
getters:{
...
getBookById:function(state){
return function(id){
return state.books.find(book => book.id === id);
}
}
}
也可以使用箭头函数简化上述代码的编写。如下:
getters:{
...
getBookById:state => id => state.books.find(book => book.id === id)
}
下面在组件模板中的调用将返回 {“id”:2,“title”:“pengpeng”,“isSold”:true}。
<p>{{ $store.getters.getBookById(2) }}</p>
下面完成购物车中单项商品价格和所有商品总价的计算,单项商品价格是商品的价格乘以数量,总价是单项商品价格相加的结果。
由于购物车中的商品是存储在 store 中的,因此单项商品价格和所有商品总价的计算应该通过 getter 完成,而不是直接在 组件内 定义计算属性来完成。
编辑 store 目录下的 index.js ,添加计算单项商品价格和所有商品总价的 getter。如下:
store/index.js
import { createStore } from "vuex";
import books from "@/data/books.js";
const store = createStore({
// 状态数据通过 state() 函数返回
state() {
return {
items: books // 使用导入的 books 对 items 进行格式化
}
},
mutations:{
pushItemToCart (state,book){
state.items.push(book);
},
deleteItem (state,id){
// 根据提交的 id 载荷,查找是否存在相同 id 的商品,返回商品的索引
let index = state.items.findIndex(item => item.id === id);
if(index>0){
state.items.splice(index,1);
}
}
},
getters:{
cartItemPrice(state){
return function (id){
let item = state.items.find(item => item.id === id);
if(item){
return item.price * item.count;
}
}
},
cartTotalPrice(state){
return state.items.reduce((total,item) => {
return total + item.price * item.count;
},0)
}
}
})
export default store;
如果 getter 要接收参数,则需要 getter 返回一个函数来实现给 getter 传参。
编辑 Cart.vue ,在computed 选项中使用 mapGetters() 映射上述两个 getter ,然后修改模板代码,完善单项商品价格计算和购物车中所有商品总价的计算。如下:
Cart.vue
...
<!-- <td>金额</td> -->
<td>{{ itemPrice(book.id) }}</td>
<!-- <td><button @click="$store.commit('deleteItem',book.id)">删除</button></td> -->
<td><button @click="deleteItem(book.id)">删除</button></td>
...
<span>总价:¥{{ totalPrice }}</span>
...
import { mapMutations,mapState,mapGetters } from 'vuex';
...
computed: {
// books() {
// return this.$store.state.items;
// },
...mapState({
books: 'items'
}),
...mapGetters({
itemPrice: 'cartItemPrice',
totalPrice: 'cartTotalPrice'
}),
},
...
下面实现购物车中商品数量加 1 和 减 1 的功能,这个功能的实现与 getter 无关,因为要修改 store 中所存储的商品的数量,因此是通过 mutation 实现商品数量的变化。
编辑 store 目录下的 index.js 文件,修改后的代码如下:
store/index.js
...
mutations:{
pushItemToCart (state,book){
state.items.push(book);
},
deleteItem (state,id){
// 根据提交的 id 载荷,查找是否存在相同 id 的商品,返回商品的索引
let index = state.items.findIndex(item => item.id === id);
if(index>0){
state.items.splice(index,1);
}
},
incrementItemCount(state,{id,count}){
let item = state.items.find(item => item.id === id);
if(item){
item.count += count; //如果count 为1,则加1;如果 count 为 -1 则减 1
}
}
},
...
编辑 Cart.vue ,在 methods 选项中使用 mapMutations() 辅助函数映射 incrementItemCount,并为减号按钮添加 click 事件的处理代码。如下:
Cart.vue
...
<td>
<button :disabled="book.count === 0" @click="increment({id:book.id,count:-1})">-</button>
{{ book.count }}
<button @click="increment({id:book.id,count:1})">+</button>
</td>
...
...mapMutations({
addItemToCart:'pushItemToCart',
increment:'incrementItemCount'
}),
...
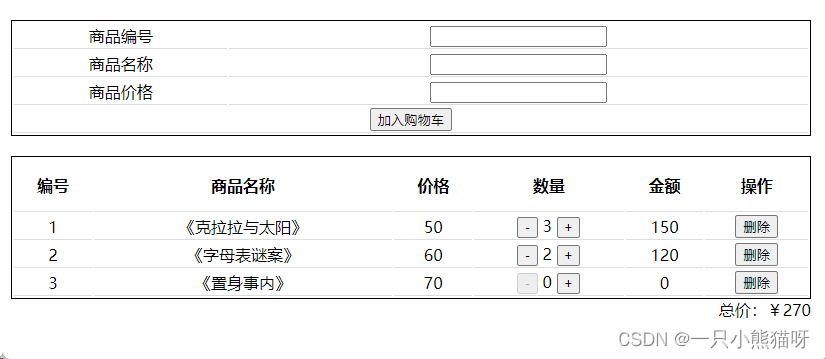
运行项目,访问 localhost:8080 ,随意增加某项商品的数量,如下:

![[Kettle] Kettle界面介绍](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d0569bcdaf4844ca9b28c12063d1fc59.png)