导 读
本文将手把手教你用Python和OpenCV搭建一个半自动标注工具(包含详细步骤 + 源码)。
背景介绍

样本标注是深度学习项目中最关键的部分,甚至在模型学习效果上起决定性作用。但是,标注工作往往非常繁琐且耗时。一种解决方案是使用自动图像标注工具,它可以大大减少标注的时间。
本文主要介绍的半自动标注工具为pyOpenAnnotate,此工具是基于Python和OpenCV实现,最新版本为0.4.0,可通过下面指令安装使用:
pip install pyOpenAnnotate详细介绍与使用步骤参考链接:
https://pypi.org/project/pyOpenAnnotate/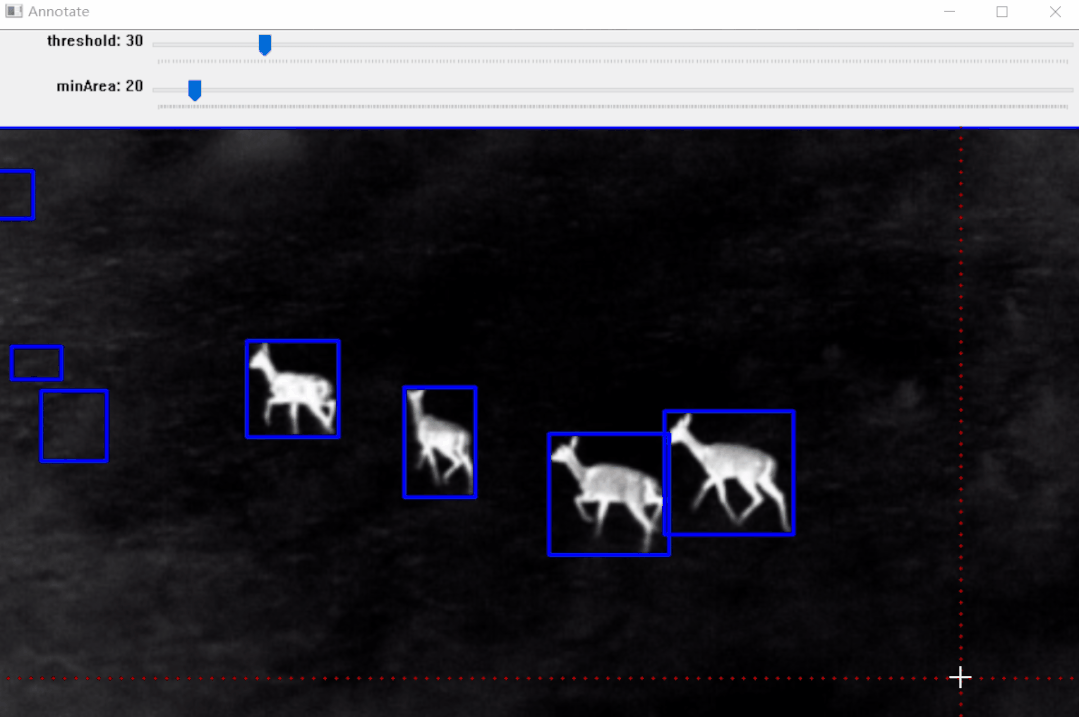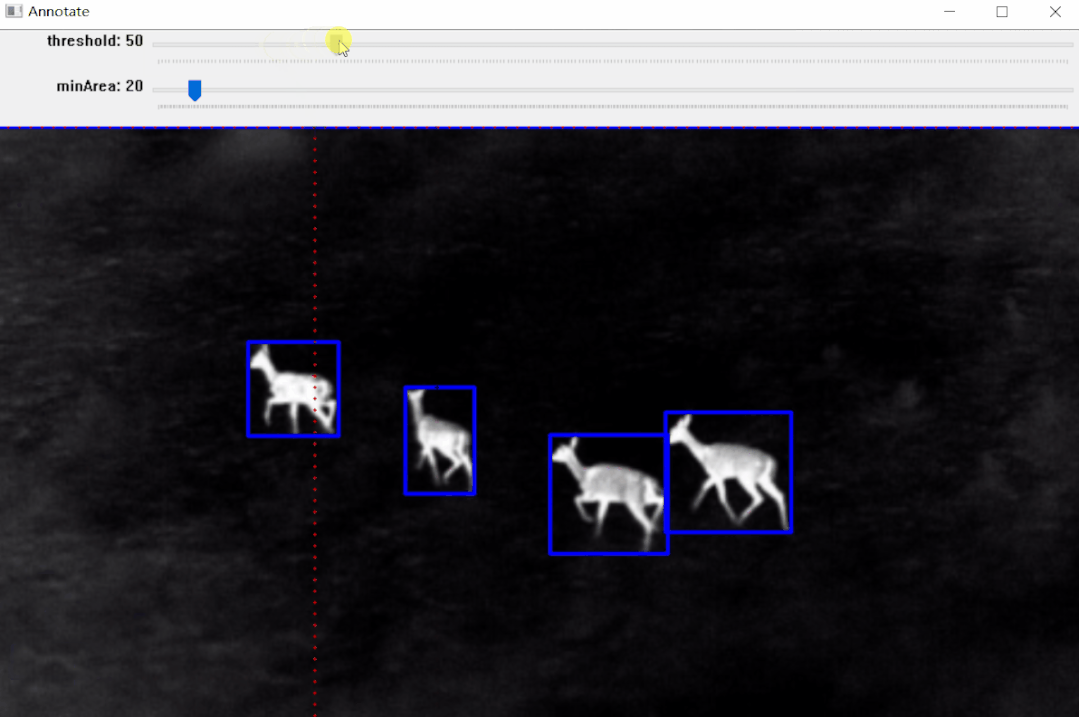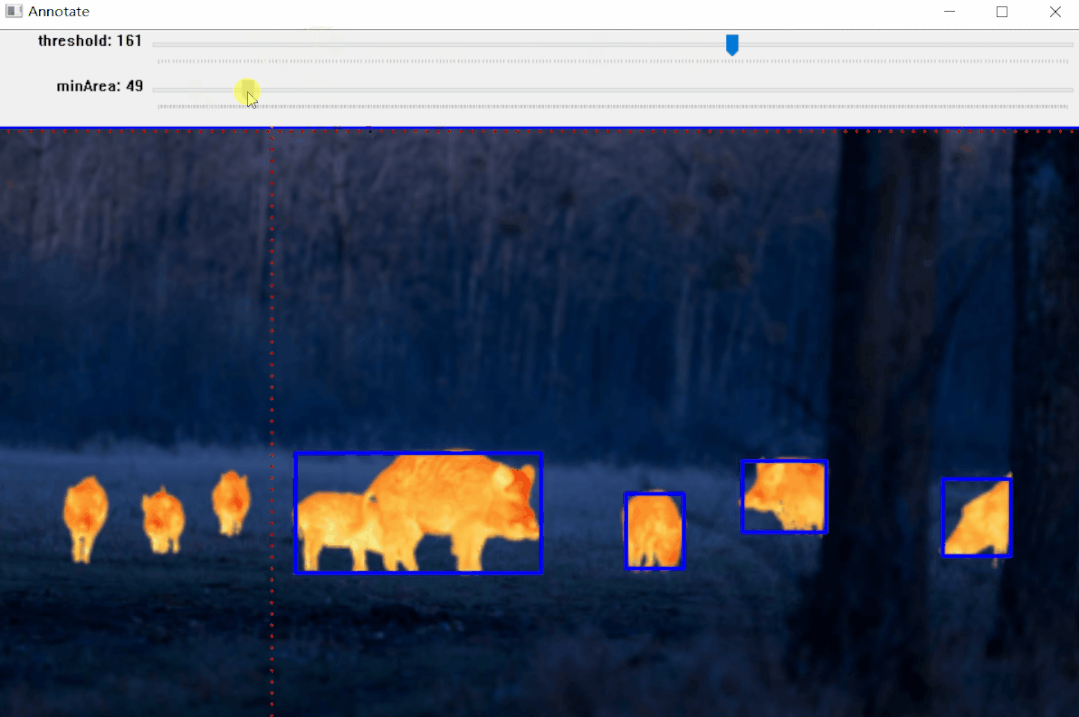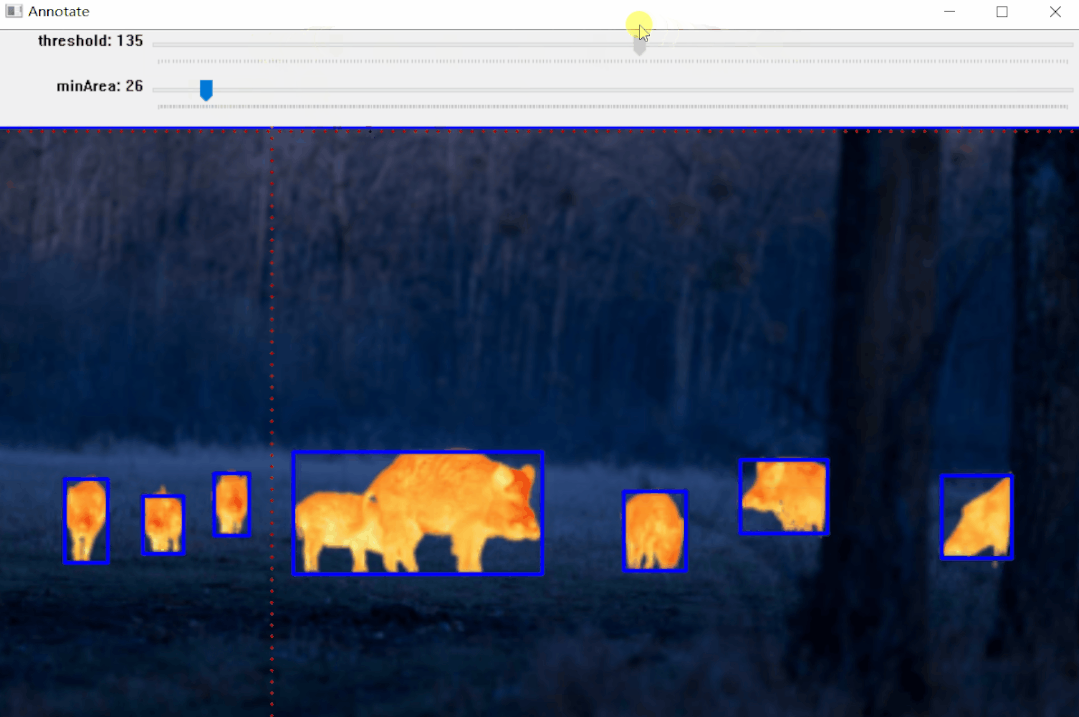
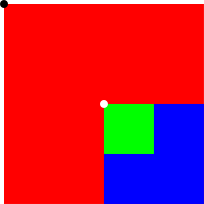
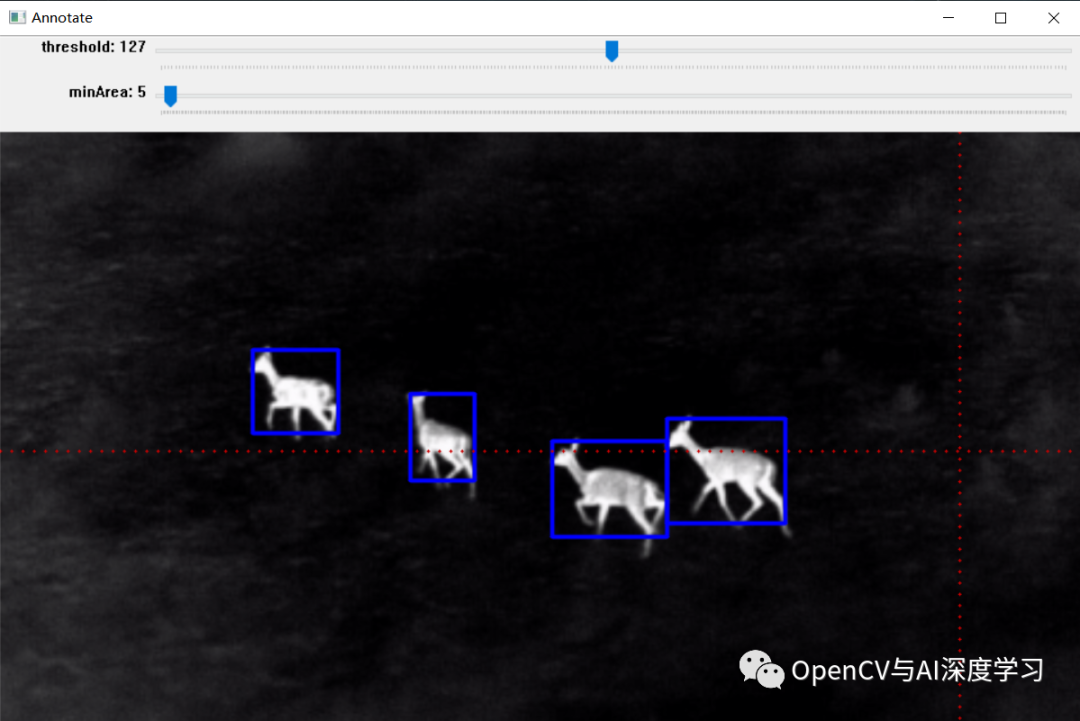
标注效果:
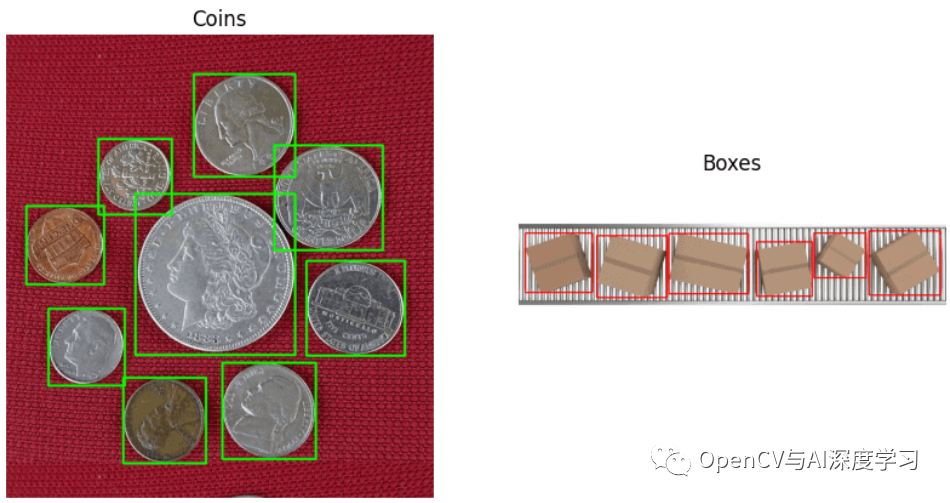

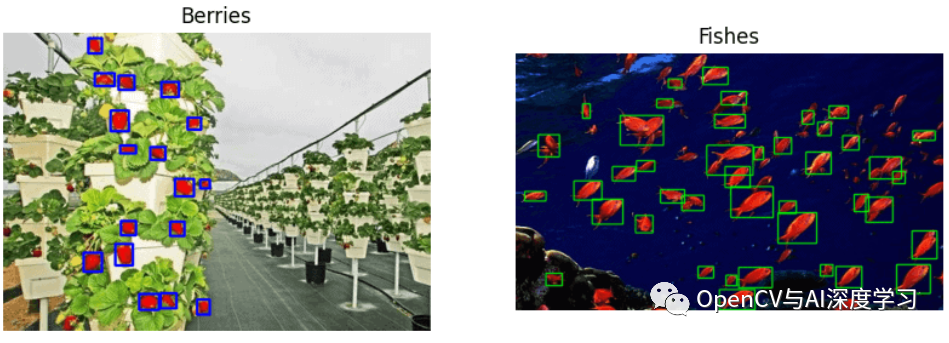

效果如上图所示,标注完成后可以生成标注文件,后面部分将详细介绍其实现步骤。
实现步骤
实现原理流程:
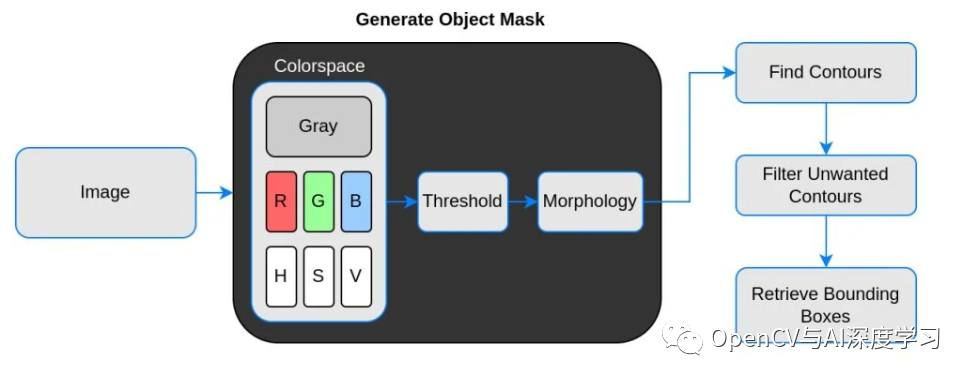
说明:
【1】Threshold(二值化)只接受单通道图像,但这里并不是直接使用灰度转换图来处理,而是从灰度图、R、G、B、H、S、V通道图像中找到对比度最高的图像来做二值化。
【2】二值化之后并不能保证总是得到我们需要的掩码,有时会有噪声、斑点、边缘的干扰,所以加入了膨胀、腐蚀等形态学处理。
【3】最后通过轮廓分析得到对象的边界框,也就是左上角和右下角坐标。
代码讲解与演示
首先需要导入所需库:
import cv2import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltplt.rcParams['image.cmap'] = 'gray'
加载图像:
stags = cv2.imread('stags.jpg')boars = cv2.imread('boar.jpg')berries = cv2.imread('strawberries.jpg')fishes = cv2.imread('fishes.jpg')coins = cv2.imread('coins.png')boxes = cv2.imread('boxes2.jpg')
选择色彩空间(这里添加了 RGB和HSV,存储在字典中,方便验证使用):
def select_colorsp(img, colorsp='gray'):# Convert to grayscale.gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)# Split BGR.red, green, blue = cv2.split(img)# Convert to HSV.im_hsv = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)# Split HSV.hue, sat, val = cv2.split(im_hsv)# Store channels in a dict.channels = {'gray':gray, 'red':red, 'green':green,'blue':blue, 'hue':hue, 'sat':sat, 'val':val}return channels[colorsp]
显示 1×2 图像的实用函数(display()函数接受两个图像并并排绘制。可选参数是绘图的标题和图形大小):
def display(im_left, im_right, name_l='Left', name_r='Right', figsize=(10,7)):# Flip channels for display if RGB as matplotlib requires RGB.im_l_dis = im_left[...,::-1] if len(im_left.shape) > 2 else im_leftim_r_dis = im_right[...,::-1] if len(im_right.shape) > 2 else im_rightplt.figure(figsize=figsize)plt.subplot(121); plt.imshow(im_l_dis);plt.title(name_l); plt.axis(False);plt.subplot(122); plt.imshow(im_r_dis);plt.title(name_r); plt.axis(False);
阈值处理(thresh()函数接受1通道灰度图像,默认阈值设置为 127。执行逆阈值处理,方便轮廓分析,它返回单通道阈值图像):
def threshold(img, thresh=127, mode='inverse'):im = img.copy()if mode == 'direct':thresh_mode = cv2.THRESH_BINARYelse:thresh_mode = cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INVret, thresh = cv2.threshold(im, thresh, 255, thresh_mode)return thresh
实例:雄鹿红外图像标注
整体实现步骤:
【1】选择色彩空间
# Select colorspace.gray_stags = select_colorsp(stags)# Perform thresholding.thresh_stags = threshold(gray_stags, thresh=110)# Display.display(stags, thresh_stags,name_l='Stags original infrared',name_r='Thresholded Stags',figsize=(20,14))
【2】执行阈值

【3】执行形态学操作
def morph_op(img, mode='open', ksize=5, iterations=1):im = img.copy()kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_ELLIPSE,(ksize, ksize))if mode == 'open':morphed = cv2.morphologyEx(im, cv2.MORPH_OPEN, kernel)elif mode == 'close':morphed = cv2.morphologyEx(im, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)elif mode == 'erode':morphed = cv2.erode(im, kernel)else:morphed = cv2.dilate(im, kernel)return morphed
# Perform morphological operation.morphed_stags = morph_op(thresh_stags)# Display.display(thresh_stags, morphed_stags,name_l='Thresholded Stags',name_r='Morphological Operations Result',figsize=(20,14))

【4】轮廓分析以找到边界框
bboxes = get_bboxes(morphed_stags)ann_morphed_stags = draw_annotations(stags, bboxes, thickness=5, color=(0,0,255))# Display.display(ann_stags, ann_morphed_stags,name_l='Annotating Thresholded Stags',name_r='Annotating Morphed Stags',figsize=(20,14))

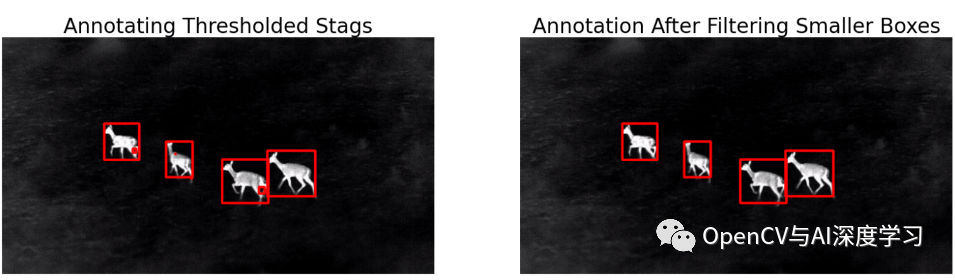
【5】过滤不需要的轮廓
def get_filtered_bboxes(img, min_area_ratio=0.001):contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(img, cv2.RETR_LIST, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)# Sort the contours according to area, larger to smaller.sorted_cnt = sorted(contours, key=cv2.contourArea, reverse = True)# Remove max area, outermost contour.sorted_cnt.remove(sorted_cnt[0])# Container to store filtered bboxes.bboxes = []# Image area.im_area = img.shape[0] * img.shape[1]for cnt in sorted_cnt:x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(cnt)cnt_area = w * h# Remove very small detections.if cnt_area > min_area_ratio * im_area:bboxes.append((x, y, x+w, y+h))return bboxes
【6】绘制边界框
bboxes = get_filtered_bboxes(thresh_stags, min_area_ratio=0.001)filtered_ann_stags = draw_annotations(stags, bboxes, thickness=5, color=(0,0,255))# Display.display(ann_stags, filtered_ann_stags,name_l='Annotating Thresholded Stags',name_r='Annotation After Filtering Smaller Boxes',figsize=(20,14))
视频标注:

【7】以需要的格式保存
Pascal VOC、YOLO和COCO 是对象检测中使用的三种流行注释格式。让我们研究一下它们的结构。
I. Pascal VOC 以 XML 格式存储注释
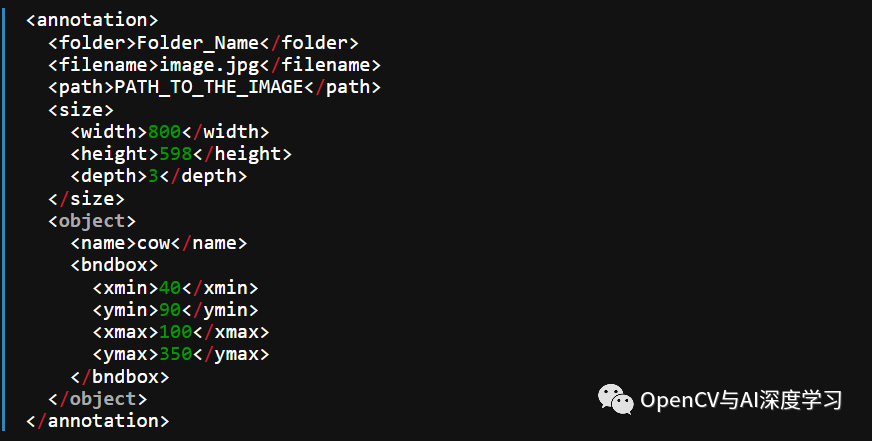
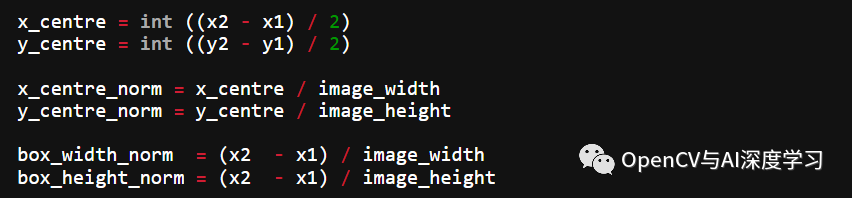
II. YOLO标注结果保存在文本文件中。对于每个边界框,它看起来如下所示。这些值相对于图像的高度和宽度进行了归一化。
0 0.0123 0.2345 0.123 0.754<object-class> <x_centre_norm> <y_centre_norm> <box_width_norm> <box_height_norm>让边界框的左上角和右下角坐标表示为(x1, y1)和(x2, y2)。然后:
III. MS COCO

这里以YOLO Darknet保存格式为例(当然,你可以保存其他格式):
def save_annotations(img, bboxes):img_height = img.shape[0]img_width = img.shape[1]with open('image.txt', 'w') as f:for box in boxes:x1, y1 = box[0], box[1]x2, y2 = box[2], box[3]if x1 > x2:x1, x2 = x2, x1if y1 > y2:y1, y2 = y2, y1width = x2 - x1height = y2 - y1x_centre, y_centre = int(width/2), int(height/2)norm_xc = x_centre/img_widthnorm_yc = y_centre/img_heightnorm_width = width/img_widthnorm_height = height/img_heightyolo_annotations = ['0', ' ' + str(norm_xc),' ' + str(norm_yc),' ' + str(norm_width),' ' + str(norm_height), '\n']f.writelines(yolo_annotations)
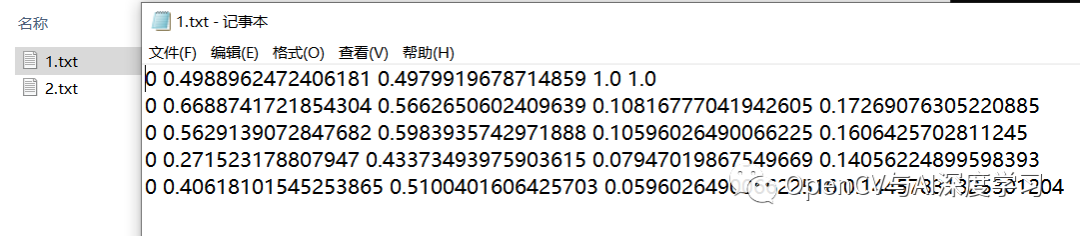
标注结果显示与保存:
简单演示:

—THE END—