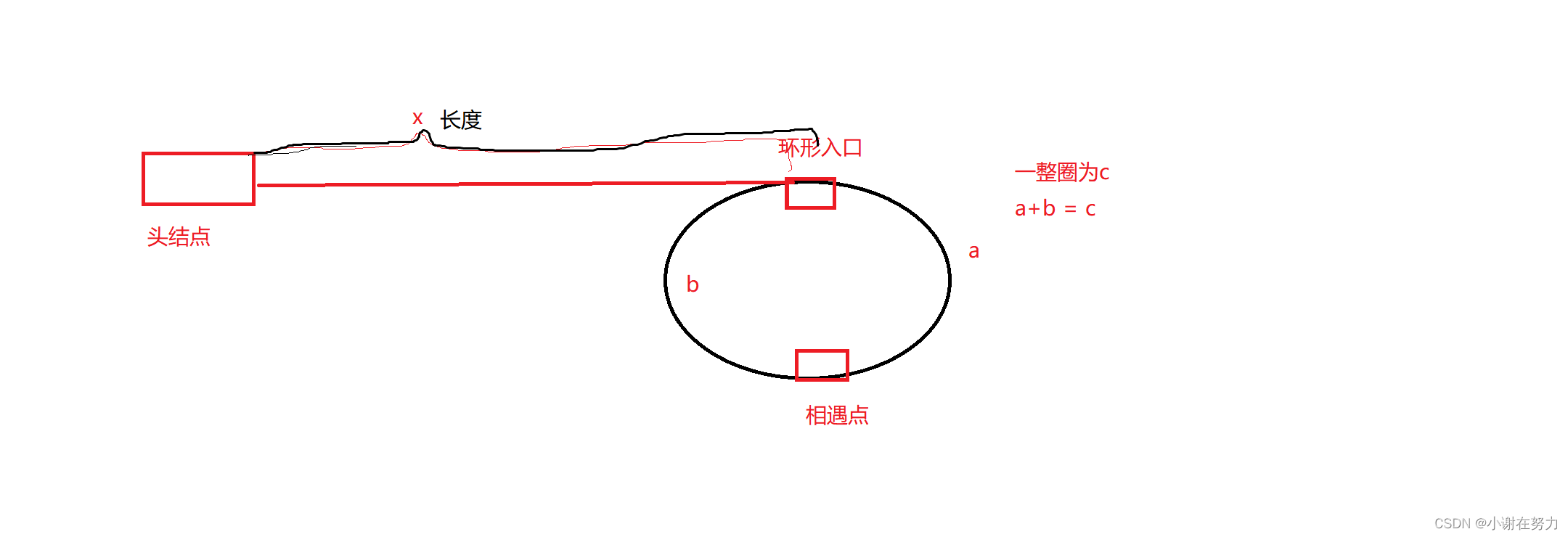
1.使用有名管道,完成两个进程的相互通信
代码:
// 使用有名管道,完成两个进程的相互通信
#include <myhead.h>
// task sender
void *tasks(void *arg)
{
printf("I am tasks\n");
int fdw = -1;
const char **ppargv = (const char **)arg; // resolve param arg get file name
printf("fifo_send=%s\n", *(ppargv + 1) );
if( (fdw =open( *(ppargv +1), O_WRONLY)) == -1)
{
//printf("3------\n");
perror("fdw open error");
return NULL;
}
//printf("4------\n");
char wbuf[128] = ""; // buffer for write
while(1)
{
printf("please input msg:\n");
fgets(wbuf, sizeof(wbuf), stdin);
wbuf[strlen(wbuf) -1] = 0;
write(fdw, wbuf, sizeof(wbuf));
if(strcmp(wbuf, "quit")==0)
{
break;
}
}
close(fdw);
printf("com closed!\n");
pthread_exit( NULL);
}
void *taskr(void *arg)
{
printf("I am taskr\n");
int fdr = -1;
const char **ppargv =(const char **)arg;
printf("fifo_recv=%s\n", *(ppargv + 2)) ;
if( (fdr = open( *(ppargv + 2) , O_RDONLY)) == -1)
{
//printf("1------\n");
perror("fdr open error");
return NULL;
}
char rbuf[128] = "";
//printf("2------\n");
while(1)
{
//printf("a------\n");
bzero(rbuf, sizeof(rbuf));
int res = read(fdr, rbuf, sizeof(rbuf));
printf("received msg: %s\n", rbuf);
if(strcmp(rbuf, "quit")==0)
{
break;
}
}
close(fdr);
pthread_exit( NULL);
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
if(argc<3)
{
printf("input param error\n");
printf("usage: ./a.out fifo(send) fifo(recv)\n");
return -1;
}
//char **ppargv = argv;
//argv 是指针数组
void *ppargv = (void *)argv;
pthread_t tidr = -1;
pthread_t tids = -1;
if((pthread_create(&tidr, NULL, taskr,(void *) ppargv))==-1 )
{
printf("thread create error!\n");
return -1;
}
if((pthread_create(&tids, NULL, tasks,(void *) ppargv))==-1 )
{
printf("thread create error!\n");
return -1;
}
pthread_join(tidr, NULL);
pthread_join(tids, NULL);
return 0;
}
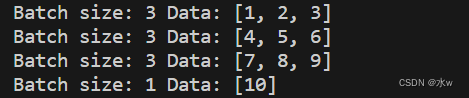
运行结果

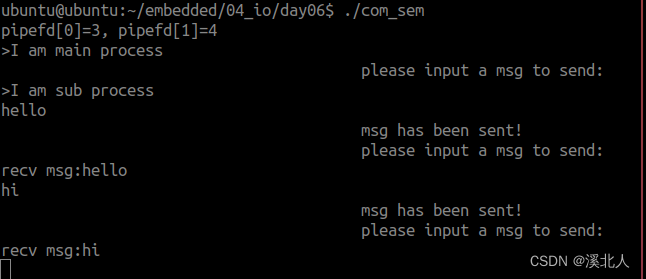
2.使用无名管道完成父子进程间的通信
代码:
#include <myhead.h>
//使用无名管道完成父子进程间的通信
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//define pid var
pid_t pidr = -1;
//define fd of pipe file array
int pipefd[2] = {0};
//create pipe file, ***please note this shall be done before fork().
if(pipe(pipefd) == -1 )
{
perror("create pipe file error");
return -1;
}
printf("pipefd[0]=%d, pipefd[1]=%d\n", pipefd[0], pipefd[1] ); //pipdfd[0]--> read; pipefd[1]-->write
//create sub process
pidr = fork(); // pipefd will be copied to subprocess after fork();
if (pidr>0) // means main process
{
printf(">I am main process\n");
// main process play as msg sender
close(pipefd[0]);
//define a write buffer
char wbuf[128] = "";
while(1)
{
printf("\t\t\t\t\tplease input a msg to send: \n");
fgets(wbuf, sizeof(wbuf), stdin); // get inputs from terminal
wbuf[strlen(wbuf) - 1] = 0; //remove retrun character
write(pipefd[1], wbuf, sizeof(wbuf) ); // write to pipe file
printf("\t\t\t\t\tmsg has been sent!\n");
if(strcmp(wbuf, "quit")==0)
{
break;
}
}
close(pipefd[1]);
}
else if(pidr == 0) // means subprocess
{
printf(">I am sub process\n");
//sub process play as read, close write port
close(pipefd[1]);
//define a read buffer
char rbuf[128] = "";
sleep(3);
while(1)
{
bzero(rbuf, sizeof(rbuf));
read(pipefd[0], rbuf, sizeof(rbuf));
printf("recv msg:%s\n", rbuf);
if(strcmp(rbuf, "quit")==0)
{
break;
}
}
// close read fd of pipe file
close(pipefd[0]);
//exit sub process
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
else
{
perror("fork error");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
运行结果
3.使用标准IO完成两个文件的拷贝
代码:
#include <myhead.h>
// 使用标准IO完成两个文件的拷贝
void cpy(const char *src, const char *dst)
{
//define FILE ptr
FILE *fdsrc = NULL;
FILE *fddst = NULL;
if( (fdsrc=fopen(src, "r")) == NULL ) // open src file as read only
{
perror("src fopen error");
return ;
}
if( (fddst=fopen(dst, "w")) == NULL ) // open dst file as wirte only
{
perror("dst fopen error");
return ;
}
while(!feof(fdsrc)) // copy until reach eof
{
char buf[128] = {0};
int res = fread(buf, sizeof(char), sizeof(buf), fdsrc);
fwrite(buf, sizeof(char), res, fddst); // *** shall only write what read, not buffer
}
fclose(fdsrc);
fclose(fddst);
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
if(argc!=3)
{
printf("input error");
printf("usage: ./aout srcfile, dstfile\n");
return -1;
}
cpy(argv[1], argv[2]);
return 0;
}
运行结果
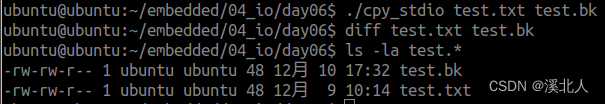
4.使用文件IO实现两个文件的拷贝
代码:
#include <myhead.h>
void cpy(const char *src, const char *dst)
{
//define fd
int fdr = -1;
int fdw = -1;
//open file
if( (fdr=open(src, O_RDONLY)) == -1)
{
perror("open error");
return ;
}
if( (fdw=open(dst, O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0664)) == -1 )
{
perror("open error");
return ;
}
//file size
int len = lseek(fdr, 0, SEEK_END);
//define a buffer
char buf[8] = "";
lseek(fdr, 0, SEEK_SET);
while(len > 0)
{
int res = read(fdr, buf, sizeof(buf));
write(fdw, buf, res);
len -= sizeof(buf);
//printf("buf=%s, len=%d, res=%d\n", buf, len, res);
}
close(fdr);
close(fdw);
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
if(argc!=3)
{
printf("input error\n");
printf("usage: ./a.out srcfile, dstfile\n");
}
cpy(argv[1], argv[2]);
return 0;
}
运行结果
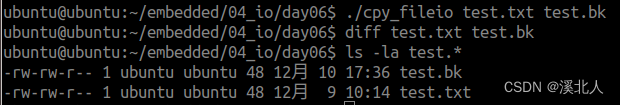
5.使用多进程完成两个文件的拷贝
代码:
#include <myhead.h>
// 使用多进程完成两个文件的拷贝
// get file size
int len(const char *src)
{
int fds = -1;
if( (fds=open(src, O_RDONLY))==-1 )
{
perror("open error");
return -1;
}
int len = lseek(fds, 0, SEEK_END); // move cursor to the file end
if(len==-1)
{
return -1;
}
close(fds);
return len;
}
//copy func
int cpy(const char *src, const char *dst, int start, int size)
{
int fdr = -1;
int fdw = -1;
if( (fdr=open(src, O_RDONLY)) == -1 )
{
perror("open error");
return -1;
}
if( (fdw=open(dst, O_WRONLY )) == -1 )
{
perror("open error");
return -1;
}
//buffer
char buf[128] = "";
// there are 2 processes working for copy job,
// move cursor to self start
lseek(fdr, start, SEEK_SET);
lseek(fdw, start, SEEK_SET);
while(size > 0 )
{
int res = read(fdr, buf , sizeof(buf));
//printf("size=%d, start=%d, res=%d, buf=%s\n", size, start, res, buf);
write(fdw, buf, res);
size -= sizeof(size);
}
close(fdr);
close(fdw);
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
if(argc!=3)
{
printf("input error\n");
printf("usage: ./a.out srcfile, dstfile\n");
return -1;
}
// get file names from params
const char *src = argv[1];
const char *dst = argv[2];
int fsize = len(src);
//create dst file for following cpy job in 2 process
int fdw = -1;
if( (fdw=open(dst, O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0664)) == -1 )
{
perror("open error");
return -1;
}
close(fdw);
//define pid
pid_t pidr = -1;
//create a sub process
pidr = fork();
if(pidr > 0)
{
//parent process
cpy(src, dst, 0, fsize/2);
}
else if(pidr == 0)
{
//sub process
cpy(src, dst, fsize/2 , fsize - (fsize/2));
//exit with flush buffer
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
// exit without flush buffer
//_exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
else
{
perror("fork error");
return -1;
}
wait(NULL); // recycle process resources
return 0;
}
运行结果:

6.使用多线程完成两个文件的拷贝
代码:
// 使用多线程完成两个文件的拷贝
#include <myhead.h>
typedef struct Param
{
const char *src;
const char *dst;
int start;
int size;
} param_t, *ptr_param_t;
int get_file_size(const char *src)
{
int fdr = -1;
if( (fdr=open(src, O_RDONLY)) == -1 )
{
perror("open error");
return -1;
}
int fsize = lseek(fdr, 0, SEEK_END);
return fsize;
}
int cpy(const char *src, const char *dst, int start, int size)
{
//printf("1---\n");
int fdr = -1;
int fdw = -1;
if( (fdr=open(src, O_RDONLY)) == -1 )
{
perror("open error");
return -1;
}
if( (fdw=open(dst, O_WRONLY)) == -1 )
{
perror("open error");
return -1;
}
int len = get_file_size(src);
char buf[128] = "";
lseek(fdr, start, SEEK_SET);
lseek(fdw, start, SEEK_SET);
while(len > 0)
{
//printf("2---\n");
int res = read(fdr, buf, sizeof(buf) );
//printf("start=%d, len=%d, buf=%s\n", start, len, buf);
write(fdw, buf, res);
len -= sizeof(buf);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
return 0;
}
void *task_copy(void *arg)
{
//resolve params
ptr_param_t ptrparam = (ptr_param_t)arg; // convert void * to struct Param *
//printf("src=%s, dst=%s, start=%d, size=%d\n", ptrparam->src, ptrparam->dst, ptrparam->start, ptrparam->size );
cpy(ptrparam->src, ptrparam->dst, ptrparam->start, ptrparam->size );
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
if(argc != 3)
{
perror("input error\n");
return -1;
}
const char *src = argv[1];
const char *dst = argv[2];
int fsize =get_file_size(src);
printf("fsize=%d\n", fsize);
//create dst file
int fdw = -1;
if( (fdw=open(dst, O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0664)) == -1 )
{
perror("open error");
return -1;
}
param_t param1 = {src, dst, 0, fsize/2};
param_t param2 = {src, dst, fsize/2 , fsize - (fsize/2)};
ptr_param_t pparam1 = ¶m1;
ptr_param_t pparam2 = ¶m2;
pthread_t tid = -1;
//create a thread
if( (tid = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, task_copy, (void *)pparam1 ) ) != 0 )
{
return -1;
}
task_copy((void *)pparam2 );
pthread_join(tid, NULL);
return 0;
}
运行结果运行结果

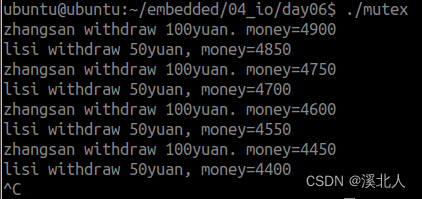
7.将互斥锁的案例
代码:
// 互斥锁的案例
#include <myhead.h>
// public resources
int money = 5000;
//1.define mutex
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
void *task(void *task)
{
while(1)
{
// 3.lock critical resource
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
money -= 50;
printf("lisi withdraw 50yuan, money=%d\n", money);
// 4.unlock critical resource
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
sleep(1);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid = -1;
// 2.init mutex
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);
if( (tid=pthread_create(&tid, NULL, task, NULL))==-1 )
{
perror("pthread_create error");
return -1;
}
while(1)
{
// 3.lock critical resource
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
money -= 100;
printf("zhangsan withdraw 100yuan. money=%d\n", money);
// 4.unlock critical resource
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
sleep(1);
}
pthread_join(tid, NULL);
// 5. destroy mutex
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
return 0;
}
运行结果
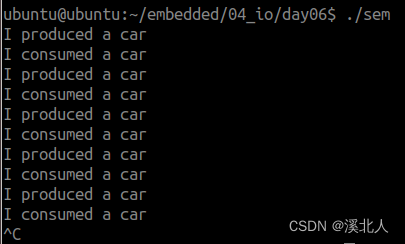
8.无名信号量实现生产者消费者程序
代码:
// 无名信号量实现生产者消费者程序
#include <myhead.h>
// 1. define a sem
sem_t sem;
void *task_c(void *arg)
{
while(1)
{
sleep(1);
// wait for available value, >0: value dec and continue, =0: waiting
sem_wait(&sem);
printf("I consumed a car\n");
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void *task_p(void *arg)
{
while(1)
{
sleep(2);
printf("I produced a car\n");
// after production, sem value inc
sem_post(&sem);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid_c = -1;
pthread_t tid_p = -1;
// 2. init sem
sem_init(&sem , 0, 0);
//param 2 value 0 means thread; non 0 means process(has to be in relative processes)
//param 3 value 0 means value
if( pthread_create(&tid_c, NULL, task_c, NULL) != 0 )
{
printf("thread create error!\n");
return -1;
}
if( pthread_create(&tid_p, NULL, task_p, NULL) != 0 )
{
printf("thread create error!\n");
return -1;
}
pthread_join(tid_c, NULL);
pthread_join(tid_p, NULL);
// 5. destroy sem
sem_destroy(&sem);
return 0;
}
运行结果
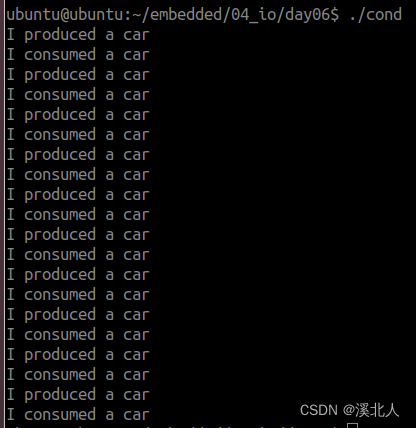
9.条件变量实现生产者消费者程序
代码:
// 将条件变量实现生产者消费者程序
#include <myhead.h>
// 1.1 define a cond var
pthread_cond_t cond;
// 1.2 define a mutex
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
void *task_c(void *arg)
{
int n = 2;
while(n--)
{
// 3.1 lock critical resource --> cond FIFO
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
//3.2 critiacl code waiting in cond quere
//inside cond, will unlock mutex -> put this into queue -> lock again
pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex);
//3.3 unlock
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
printf("I consumed a car\n");
sleep(1);
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void *task_p(void *arg)
{
int n = 10;
while(n--)
{
printf("I produced a car\n");
// 4. after production, release a signal to consumer
pthread_cond_signal(&cond);
sleep(1);
}
printf("production closed!\n");
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
#include <myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
int n=2;
pthread_t tid_p = -1;
pthread_t tid_arr[n];
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
tid_arr[i] = -1;
}
// 2.1init cond
pthread_cond_init(&cond, NULL);
// 2.2 init mutex
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);
if(pthread_create(&tid_p, NULL, task_p, NULL ) !=0 )
{
printf("thread p create error\n");
return -1;
}
for (int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
if(pthread_create(&tid_arr[i], NULL, task_c, NULL ) !=0 )
{
printf("thread [%d] create error\n", i);
return -1;
}
}
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
pthread_join(tid_arr[i] , NULL );
}
// 5.1
pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);
//5.2
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
return 0;
}
运行结果