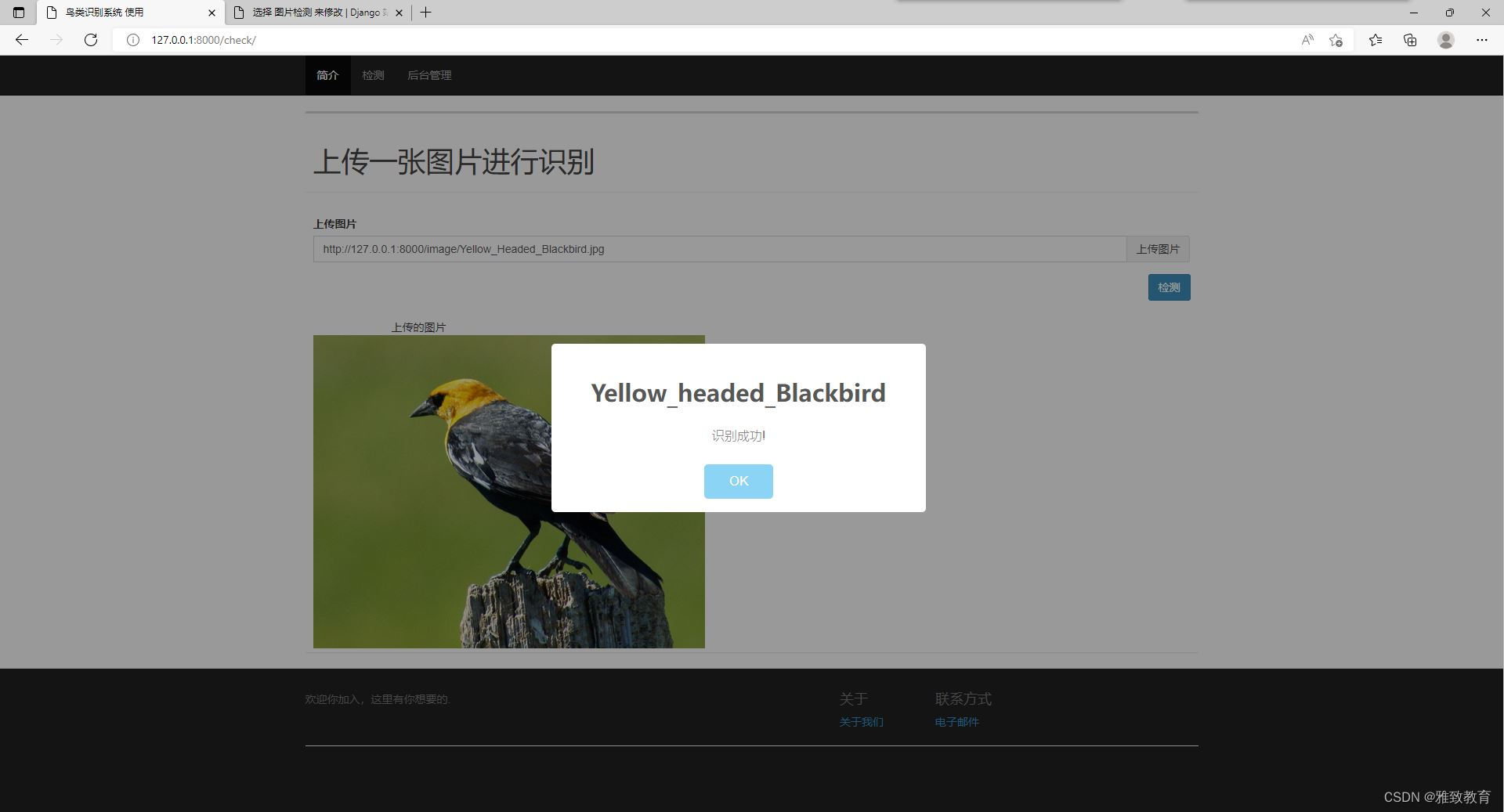
优先级队列
完整可编译运行代码见:Github::Data-Structures-Algorithms-and-Applications/_25Priority queue
定义
优先级队列(priority queue)是0个或多个元素的集合,每个元素都有一个优先权或值,对优先级队列执行的操作有1)查找一个元素;2)插入一个新元素;3)删除一个元素。与这些操作分别对应的函数是top、push和pop。在最小优先级队列(min priority queue)中,查找和删除的元素都是优先级最小的元素;在最大优先级队列(max priority queue)中,查找和删除的元素都是优先级最大的元素。优先级队列的元素可以有相同的优先级,对这样的元素,查找与删除可以按任意顺序处理。
抽象数据类型
最大优先级队列的抽象数据类型说明如ADT 12-1所示,最小优先级队列的抽象数据类型说明与之类似,只是top的pop函数不同,查找和删除的都是优先级最小的元素。

堆
定义
定义 12-1 一棵大根树(小根树)是这样一棵树,其中每个节点的值都大于(小于)或等于其子节点(如果有子节点的话)的值。
定义 12-2 一个大根堆(小根堆)既是大根树(小根树)也是完全二叉树。
在大根树或小根树中,节点的子节点个数可以任意,不一定是二叉树。
必须满足是大(小)根树同时是完全二叉树才能称为大(小)根堆。
堆是完全二叉树,具有n个元素的堆的高度为 ⌈ l o g 2 ( n + 1 ) ⌉ \lceil log_2(n+1)\rceil ⌈log2(n+1)⌉。因此,如果能够在 O ( h e i g h t ) O(height) O(height)时间内完成插入和删除操作,那么这些操作的复杂性为 O ( l o g n ) O(logn) O(logn)。
大(小)根堆使用数组存储。以层序遍历的顺序存储元素。
大根堆的插入
由于大根堆是完全二叉树,所以在插入元素时,一定会在完全二叉树的最后一层的最后一个元素后添加一个节点。插入元素的步骤是新元素插入新节点,然后沿着从新节点到根节点的路径,执行一趟起泡操作,将新元素与其父节点的元素比较交换,直到后者大于或等于前者为止。如下图所示,如果插入元素1,可以将其直接作为节点2的左孩子。但是如果插入元素5,就需要执行起泡操作。
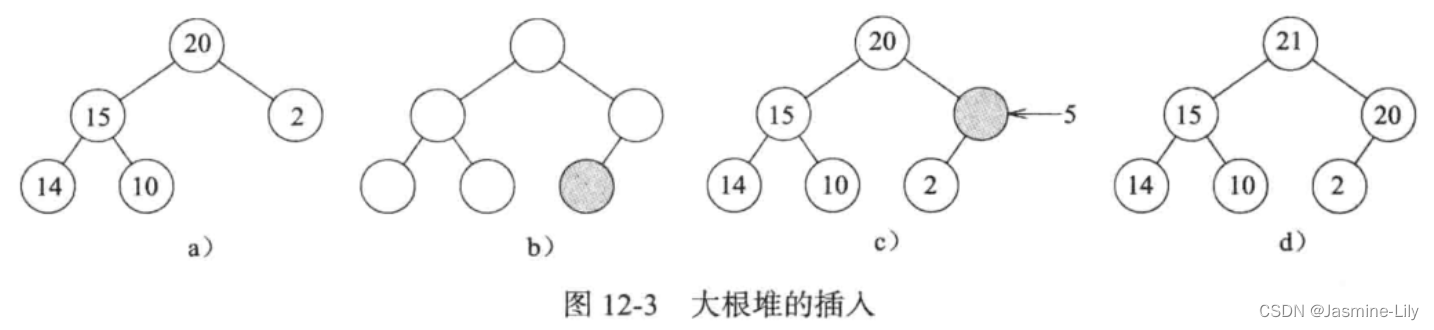
大根堆的删除
在大根堆中删除一个元素,就是删除根节点的元素。
大根堆使用数组存储,以层序遍历的顺序存储,因此数组存储的第一个节点就是最大元素。删除操作顺序为,首先找到数组存储的最后一个元素,将该元素使用temp变量暂存起来,并删除最后一个元素。然后尝试将temp放到第一个元素,这样不满足大根堆的定义,因此把根元素的左右元素的大者移到根节点。移动后形成一个空位,尝试将temp放到该空位,如果满足该节点元素大于等于其孩子节点元素,那么放置成功,删除操作完成;否则,继续选择空位的左右孩子的大者移动到空位,以此类推,直到找到合适的位置放置temp,删除操作完成。
如图12-4删除图12-3 d)的根节点。
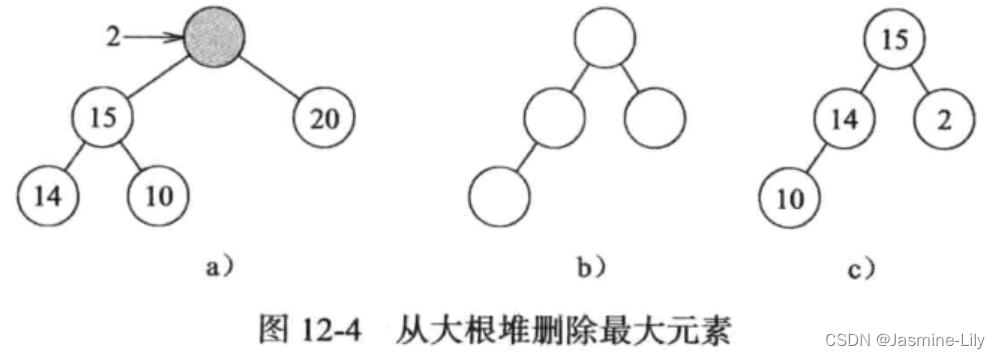
大根堆的初始化
初始时,要向堆中插入n(n>0)个元素。插入操作所需的总时间为 O ( n l o g n ) O(nlogn) O(nlogn)。也可以用不同的策略在 O ( n ) O(n) O(n)时间内完成堆的初始化。
首先是拿到一个数组,数组的元素按任意顺序。该数组可以转化为一个完全二叉树,需要做的是将完全二叉树转化为大根堆。从最后一个具有孩子的节点开始,如果以这个元素为根的子树是大根堆,则不做操作;如果以这个元素为根的子树不是大根堆,则需要将这个子树调整为大根堆。然后一次检查倒数第二个、倒数第三个子树,直到检查到第一个元素为根的树为止。
代码
template<class T>
void maxHeap<T>::initialize(T *theHeap, int theSize)
{
delete [] heap;
heap = theHeap;// 数组已经指定了
heapSize = theSize;
// 从最后一个有孩子节点的节点开始
for (int root = heapSize / 2; root >= 1; root--)
{
T rootElement = heap[root];
int child = 2 * root; // 当前节点的左孩子节点
while (child <= heapSize)
{
// 找到孩子节点中的较大者
if (child < heapSize && heap[child] < heap[child + 1])
child++;
// 如果rootElement大于等于孩子节点的较大者,那么就终止循环
if (rootElement >= heap[child])
break;
// 如果rootElement小于孩子节点的较大者,就在父亲节点放置孩子节点
heap[child / 2] = heap[child];
child *= 2;// 找到较大孩子节点的孩子节点
}
// 如果孩子节点的较大者小于rootElement,就将rootElement作为孩子节点的父亲
heap[child / 2] = rootElement;
}
}
复杂性
在大根堆的初始化程序 initialize函数中,如果元素个数为 n(即theSize=n),那么for 循环的每次迭代所需时间为 O ( l o g n ) O(logn) O(logn),迭代次数为 n / 2 n/2 n/2,因此initialize函数的复杂性为 O ( n l o g n ) O(nlogn) O(nlogn)。注意,O表示法提供算法复杂性的上限。实际应用中,initialize的复杂性要比上限 O ( n l o g n ) O(nlogn) O(nlogn)好一些。经过更仔细的分析,我们得出真正的复杂性为 Θ ( n ) Θ(n) Θ(n)。
在 initialize 函数中,while 循环的每一次迭代所需时间为 O ( h i ) O(h_i) O(hi),其中 h i h_i hi是以位置i 为根节点的子树的高度。完全二叉树heap[1:n]的高度为 h = ⌈ l o g 2 ( n + 1 ) ⌉ h=\lceil log_2(n+1)\rceil h=⌈log2(n+1)⌉。在树的第j层,最多有 2 j − 1 2^{j-1} 2j−1个节点。因此最多有 2 j − 1 2^{j-1} 2j−1个节点具有相同的高度 h i = h − j + 1 h_i=h-j+1 hi=h−j+1。于是大根堆的初始化时间为:
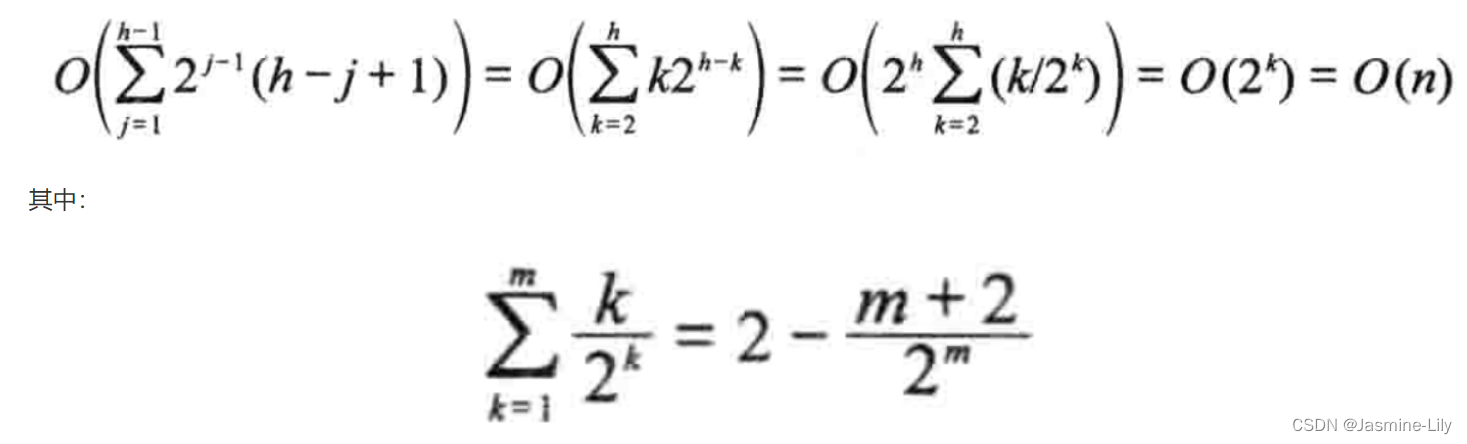
因为for循环执行n/2次迭代,所以复杂性为2(n)。将两者综合考虑,得到initialize的复杂性为 Θ ( n ) Θ(n) Θ(n)。
堆与STL
STL的类 priority_queue利用了基于向量的堆来实现大根堆,它允许用户自己制定优先级的比较函数,因此,这个类也可以用于实现小根堆。
代码
main.cpp
/*
Project name : _25Priority_queue
Last modified Date: 2023年11月29日21点08分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 优先级队列——大根堆main函数
*/
#include "maxHeap.h"
int main() {
maxHeapTest();
return 0;
}
maxHeap.h
/*
Project name : _25Priority_queue
Last modified Date: 2023年11月29日21点08分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 优先级队列——大根堆模板头文件
*/
/*[[nodiscard]]标记符可以用于提示程序员在调用有返回值的函数时不要忘记接收改函数的返回值*/
#ifndef _25PRIORITY_QUEUE_MAXHEAP_H
#define _25PRIORITY_QUEUE_MAXHEAP_H
#include "maxPriorityQueue.h"
#include "_1myExceptions.h"
#include "_2myFunctions.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
int maxHeapTest();
template<class T>
class maxHeap : public maxPriorityQueue<T>
{
public:
explicit maxHeap(int initialCapacity = 10);
~maxHeap() {heap = nullptr;}
[[nodiscard]] bool empty() const {return heapSize == 0;}
[[nodiscard]] int size() const {return heapSize;}
const T& top()
{// 返回最大元素,也就是堆顶的值
if (heapSize == 0)
throw queueEmpty();
return heap[1];
}
void pop();// 向堆中弹出元素
void push(const T&);// 向堆中插入元素
void initialize(T *, int);// 初始化堆
void deactivateArray()// 禁用数组,这个还没搞清楚怎么用
{heap = nullptr; arrayLength = heapSize = 0;}
void output(ostream& out) const;// 输出大根堆的所有元素
private:
int heapSize; // 存储大根堆中有多少元素
int arrayLength; // 存储大根堆的容量大小
T* heap; // 存储大根堆元素的数组
};
template<class T>
maxHeap<T>::maxHeap(int initialCapacity)
{// 构造函数,容量必须>=1
if (initialCapacity < 1)
{
ostringstream s;
s << "Initial capacity = " << initialCapacity << " Must be > 0";
throw illegalParameterValue(s.str());
}
arrayLength = initialCapacity + 1;
heap = new T(arrayLength);
heapSize = 0;
}
// 向大顶堆中插入元素
template<class T>
void maxHeap<T>::push(const T& theElement)
{
// 如果容量不够的话需要增加容量
if (heapSize == arrayLength - 1)
{
changeLength1D(heap, arrayLength, 2 * arrayLength);
arrayLength *= 2;
}
// 从叶子节点开始起泡,将元素插入
int currentNode = ++heapSize;
// 如果编号i不是根节点,则其父节点的编号为[i/2](向下取整)
while (currentNode != 1 && heap[currentNode / 2] < theElement)
{
// 父节点小于子节点,不能将元素放到此处
heap[currentNode] = heap[currentNode / 2]; // 将父节点放到currentNode出
currentNode /= 2; // 当前节点的index转移到父节点
}
// 直到父节点大于等于theElement,将theElement放到当前位置
heap[currentNode] = theElement;
}
// 删除大顶堆的最大元素
// 在大根堆是二叉树时可以这样弄
template<class T>
void maxHeap<T>::pop()
{
// 如果大顶堆元素个数为0,那么抛出queueEmpty异常
if (heapSize == 0)
throw queueEmpty();
// 删除数组中第一个元素,也就是根节点的元素
heap[1].~T();
// 找到大顶堆的最后一排的最后一个元素
T lastElement = heap[heapSize--];
// 当前节点与其孩子节点的index
int currentNode = 1,
child = 2;
while (child <= heapSize)
{
// 找到孩子节点中的较大者
if (child < heapSize && heap[child] < heap[child + 1]) // 这里只考虑了两个孩子,因此大根堆是二叉树
child++;
// 如果lastElement大于等于孩子节点的较大者,就终止循环,说明找到了lastElement可以放置的位置
if (lastElement >= heap[child])
break;
// 如果没找到放置lastElement的位置,就在currentNode放置孩子节点中的较大者
heap[currentNode] = heap[child];
currentNode = child;// 现在空位就变成了刚刚移动的孩子节点
child *= 2;// 其孩子的index就是2倍的child
}
heap[currentNode] = lastElement;// 如果找到位置了就直接将最后一个元素放置到找到的位置上
}
template<class T>
void maxHeap<T>::initialize(T *theHeap, int theSize)
{
delete [] heap;// 数组已经指定了
heap = theHeap;
heapSize = theSize;
// 从最后一个有孩子节点的节点开始
for (int root = heapSize / 2; root >= 1; root--)
{
T rootElement = heap[root];
int child = 2 * root; // 当前节点的左孩子节点
while (child <= heapSize)
{
// 找到孩子节点中的较大者
if (child < heapSize && heap[child] < heap[child + 1])
child++;
// 如果rootElement大于等于孩子节点的较大者,那么就终止循环
if (rootElement >= heap[child])
break;
// 如果rootElement小于孩子节点的较大者,就在父亲节点放置孩子节点
heap[child / 2] = heap[child];
child *= 2;// 找到较大孩子节点的孩子节点
}
// 如果孩子节点的较大者小于rootElement,就将rootElement作为孩子节点的父亲
heap[child / 2] = rootElement;
}
}
template<class T>
void maxHeap<T>::output(ostream& out) const
{// 输出大顶堆中的所有元素
for(T* i = heap + 1; i < heap + heapSize + 1; i++)
cout << *i << " ";
cout << endl;
}
// 重载输出操作符 <<
template <class T>
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const maxHeap<T>& x)
{x.output(out); return out;}
#endif //_25PRIORITY_QUEUE_MAXHEAP_H
maxHeap.cpp
/*
Project name : _25Priority_queue
Last modified Date: 2023年11月29日21点08分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 优先级队列——大根堆模板源文件
*/
#include "maxHeap.h"
using namespace std;
int maxHeapTest()
{
// test constructor and push
maxHeap<int> h(3);
h.push(10);
h.push(20);
h.push(5);
cout << "Heap size is " << h.size() << endl;
cout << "Elements in array order are" << endl;
cout << h << endl;
h.push(15);
h.push(30);
cout << "Heap size is " << h.size() << endl;
cout << "Elements in array order are" << endl;
cout << h << endl;
// test top and pop
cout << "The max element is " << h.top() << endl;
h.pop();
cout << "The max element is " << h.top() << endl;
h.pop();
cout << "The max element is " << h.top() << endl;
h.pop();
cout << "Heap size is " << h.size() << endl;
cout << "Elements in array order are" << endl;
cout << h << endl;
// test initialize
int z[10];
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++)
z[i] = i;
h.initialize(z, 9);
cout << "Elements in array order are" << endl;
cout << h << endl;
return 0;
}
maxPriorityQueue.h
/*
Project name : _25Priority_queue
Last modified Date: 2023年11月29日21点08分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 优先级队列——大根堆抽象数据类型
*/
#ifndef _25PRIORITY_QUEUE_MAXPRIORITYQUEUE_H
#define _25PRIORITY_QUEUE_MAXPRIORITYQUEUE_H
template<class T>
class maxPriorityQueue
{
public:
virtual ~maxPriorityQueue() = default;
[[nodiscard]] virtual bool empty() const = 0;
// return true iff queue is empty
[[nodiscard]] virtual int size() const = 0;
// return number of elements in queue
virtual const T& top() = 0;
// return reference to the max element
virtual void pop() = 0;
// remove the top element
virtual void push(const T& theElement) = 0;
// add theElement to the queue
};
#endif //_25PRIORITY_QUEUE_MAXPRIORITYQUEUE_H
_1myExceptions.h
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月13日17点38分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 综合各种异常
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef _MYEXCEPTIONS_H_
#define _MYEXCEPTIONS_H_
#include <string>
#include<iostream>
#include <utility>
using namespace std;
// illegal parameter value
class illegalParameterValue : public std::exception
{
public:
explicit illegalParameterValue(string theMessage = "Illegal parameter value")
{message = std::move(theMessage);}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// illegal input data
class illegalInputData : public std::exception
{
public:
explicit illegalInputData(string theMessage = "Illegal data input")
{message = std::move(theMessage);}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// illegal index
class illegalIndex : public std::exception
{
public:
explicit illegalIndex(string theMessage = "Illegal index")
{message = std::move(theMessage);}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// matrix index out of bounds
class matrixIndexOutOfBounds : public std::exception
{
public:
explicit matrixIndexOutOfBounds
(string theMessage = "Matrix index out of bounds")
{message = std::move(theMessage);}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// matrix size mismatch
class matrixSizeMismatch : public std::exception
{
public:
explicit matrixSizeMismatch(string theMessage =
"The size of the two matrics doesn't match")
{message = std::move(theMessage);}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// stack is empty
class stackEmpty : public std::exception
{
public:
explicit stackEmpty(string theMessage =
"Invalid operation on empty stack")
{message = std::move(theMessage);}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// queue is empty
class queueEmpty : public std::exception
{
public:
explicit queueEmpty(string theMessage =
"Invalid operation on empty queue")
{message = std::move(theMessage);}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// hash table is full
class hashTableFull : public std::exception
{
public:
explicit hashTableFull(string theMessage =
"The hash table is full")
{message = std::move(theMessage);}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// edge weight undefined
class undefinedEdgeWeight : public std::exception
{
public:
explicit undefinedEdgeWeight(string theMessage =
"No edge weights defined")
{message = std::move(theMessage);}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
// method undefined
class undefinedMethod : public std::exception
{
public:
explicit undefinedMethod(string theMessage =
"This method is undefined")
{message = std::move(theMessage);}
void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:
string message;
};
#endif
_2myFunctions.h
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月13日17点38分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 综合各种非成员函数
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef _MYFUNCTIONS_H_
#define _MYFUNCTIONS_H_
#include<iostream>
#include "_1myExceptions.h"
#include<cmath>
#include <exception>
#include <memory>
using std::min;
using std::endl;
using std::cout;
using std::bad_alloc;
/*交换两数据*/
template<class V>
void Swap(V& a, V& b)
{
V temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
/*
作用:将数组的长度加倍
输入:指针a指向需要改变长度的数组,oldLength表示数组原来的长度,newLength表示需要改变的新长度
结果:将数组扩容/缩容 为newLength
*/
template<class T>
void changeLength(T*& a, int oldLength, int newLength)
{
if (newLength < 0)
throw illegalParameterValue("new length must be >= 0");
T* temp = new T[newLength];
int number = min(oldLength, newLength);
copy(a, a + number, temp);
delete[] a;
a = temp;
}
/*遍历一维数组*/
template<class T>
void traverse1dArray(T* x, int length)
{
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
cout << x[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
/*创建二维数组*/
template <class T>
bool make2dArray(T**& x, int numberOfRows, int numberOfColumns)
{
try {
//行指针
x = new T * [numberOfRows];
//为每一行分配内存
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfRows; i++)
x[i] = new int[numberOfColumns];
return true;
}
catch (bad_alloc) { return false; }
}
/*遍历二维数组*/
template<class T>
void traverse2dArray(T**& x, int numberOfRows, int numberOfColumns)
{
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfRows; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < numberOfColumns; j++)
{
cout.width(4);
cout << x[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
template<class T>
void changeLength1D(T*& a, int oldLength, int newLength)
{
if (newLength < 0)
throw illegalParameterValue("new length must be >= 0");
T* temp = new T[newLength]; // new array
int number = min(oldLength, newLength); // number to copy
copy(a, a + number, temp);
a = temp;
}
#endif
运行结果
"C:\Users\15495\Documents\Jasmine\prj\_Algorithm\Data Structures, Algorithms and Applications in C++\_25Priority queue\cmake-build-debug\_25Priority_queue.exe"
Heap size is 3
Elements in array order are
20 10 5
Heap size is 5
Elements in array order are
30 20 5 10 15
The max element is 30
The max element is 20
The max element is 15
Heap size is 2
Elements in array order are
10 5
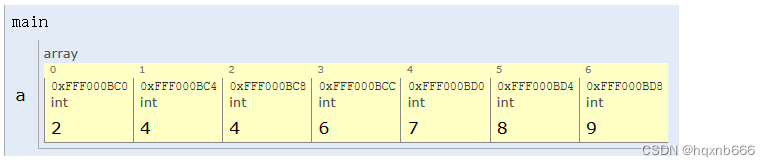
Elements in array order are
9 8 7 4 5 6 3 2 1
Process finished with exit code 0