738. Monotone Increasing Digits
An integer has monotone increasing digits单调递增数字 if and only if each pair of adjacent digits x and y satisfy x <= y.
Given an integer n, return the largest number that is less than or equal to n with monotone increasing digits.

violent solution:
Time complexity: O(n × m) m is the length of the number n
Space complexity: O(1)
class Solution:
def monotoneIncreasingDigits(self, n: int) -> int:
for i in range(n, -1, -1):
if self.check_num(i):
return i
#return 0
def check_num(self, n):
max = 10
while n:
t = n % 10
if max >= t:
max = t
else:
return False
n = n//10
return True
greedy:
1. A local optimum leads to a global
2. traversal from right to the left
class Solution:
def monotoneIncreasingDigits(self, n: int) -> int:
n_str = list(str(n))
for i in range(len(n_str) - 1, 0, -1):
if n_str[i] < n_str[i - 1]: #string can compare the value, but you can still use int()
n_str[i - 1] = str(int(n_str[i - 1]) - 1)
for j in range(i, len(n_str)):
n_str[j] = '9'
return int(''.join(n_str))Time complexity: O(n), n is the length of the number
Space complexity: O(n), need a string, it is more convenient to convert to string operation
968. Binary Tree Cameras
You are given the root of a binary tree. We install cameras on the tree nodes where each camera at a node can monitor监控 its parent, itself, and its immediate children.
Return the minimum number of cameras needed to monitor all nodes of the tree.
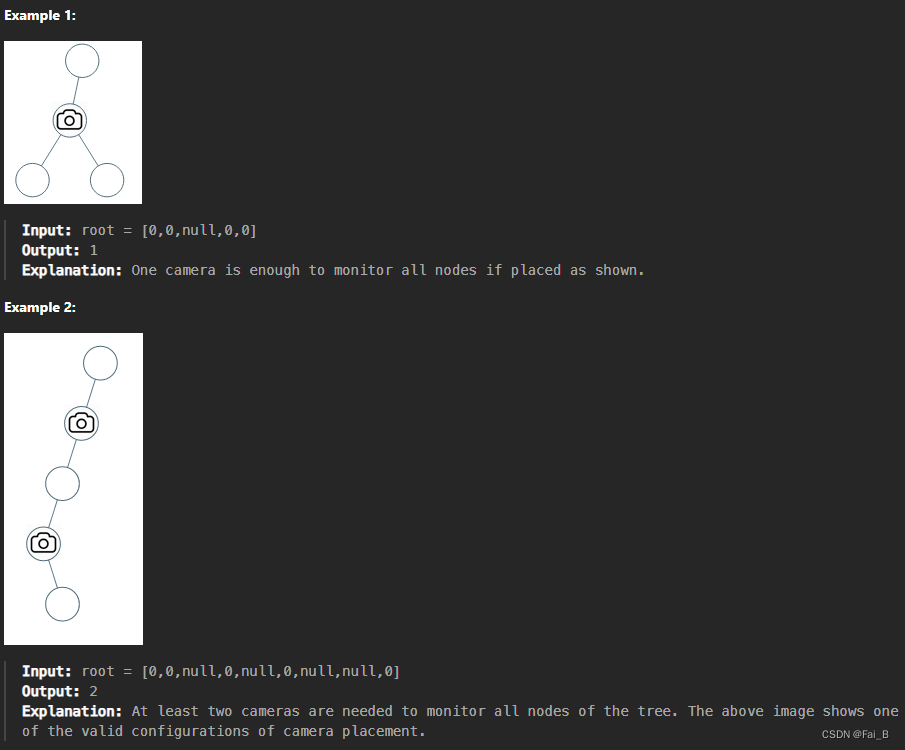
Local optimization: let the parent of a leaf node plant a camera, the least number of cameras used.
Overall optimization: minimize the number of cameras used for all.
Case 1: Both left and right nodes are covered
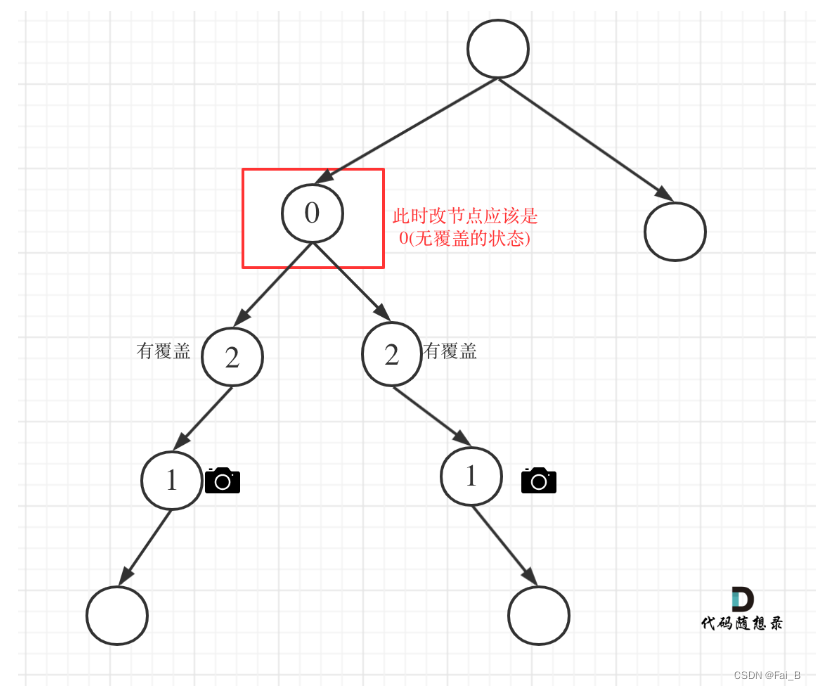
Case 2: At least one of the left and right nodes is uncovered
Case 3: At least one of the left and right nodes has a camera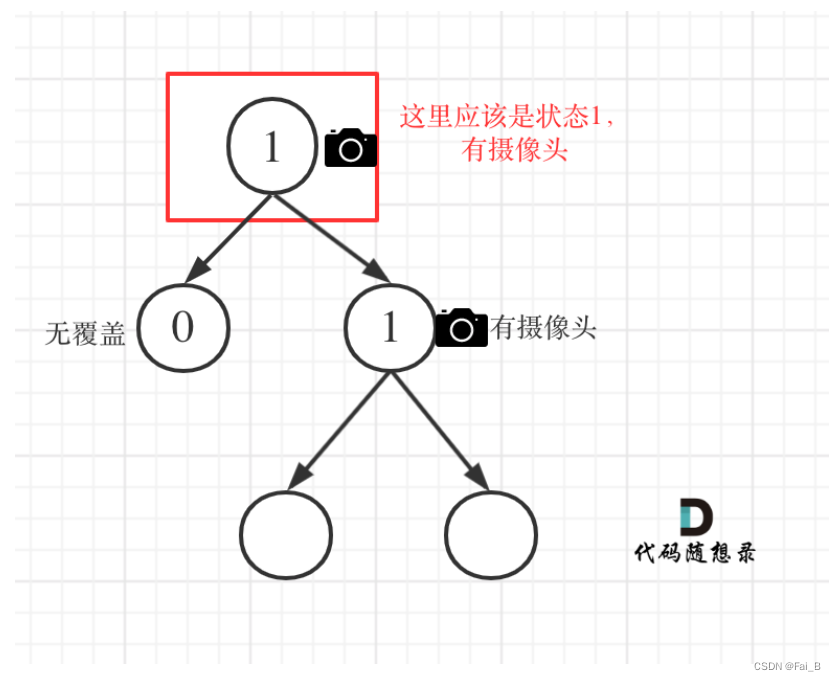
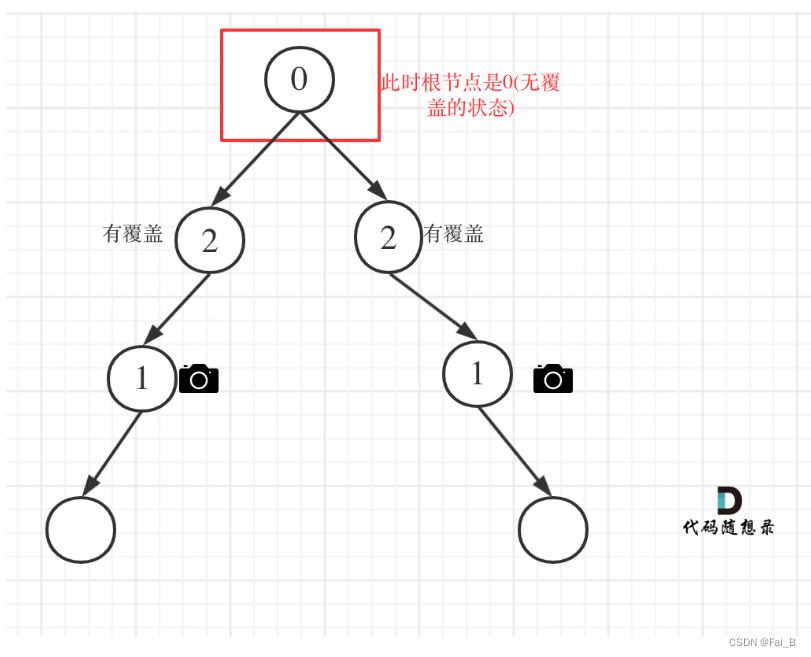
Case 4: Header node not covered
class Solution:
# Greedy Algo:
# 从下往上安装摄像头:跳过leaves这样安装数量最少,局部最优 -> 全局最优
# 先给leaves的父节点安装,然后每隔两层节点安装一个摄像头,直到Head
# 0: 该节点未覆盖
# 1: 该节点有摄像头
# 2: 该节点有覆盖
def minCameraCover(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
# 定义递归函数
result = [0] # 用于记录摄像头的安装数量
if self.traversal(root, result) == 0:
result[0] += 1
return result[0]
def traversal(self, cur: TreeNode, result: List[int]) -> int:
if not cur:
return 2
left = self.traversal(cur.left, result)
right = self.traversal(cur.right, result)
# 情况1: 左右节点都有覆盖
if left == 2 and right == 2:
return 0
# 情况2:
# left == 0 && right == 0 左右节点无覆盖
# left == 1 && right == 0 左节点有摄像头,右节点无覆盖
# left == 0 && right == 1 左节点无覆盖,右节点有摄像头
# left == 0 && right == 2 左节点无覆盖,右节点覆盖
# left == 2 && right == 0 左节点覆盖,右节点无覆盖
if left == 0 or right == 0:
result[0] += 1
return 1
# 情况3:
# left == 1 && right == 2 左节点有摄像头,右节点有覆盖
# left == 2 && right == 1 左节点有覆盖,右节点有摄像头
# left == 1 && right == 1 左右节点都有摄像头
if left == 1 or right == 1:
return 2