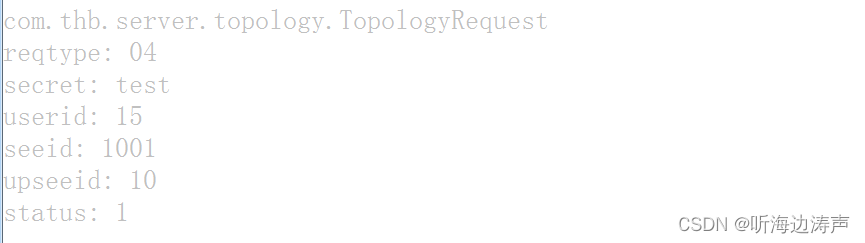
例如,下面这段请求的xml代码,在元素body下面又多了一层,嵌套了4个元素:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<request>
<reqtype>04</reqtype>
<secret>test</secret>
<body>
<userid>15</userid>
<seeid>1001</seeid>
<upseeid>10</upseeid>
<status>1</status>
</body>
</request>
可以使用下面的JAXB注解来跟上面的xml映射。其中属性seeContent映射到xml的body元素,seeContent属性的类型不再是一个简单类型,而是一个Java类:
package com.thb.server.topology;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement;
/**
* 该类映射到http请求的xml
* @author thb
*
*/
// 使用了JAXB注解,映射到xml中的request元素
@XmlRootElement(name = "request")
public class TopologyRequest {
private String reqtype;
private String secret;
private SeeContent seeContent;
// 使用了JAXB注解,映射到xml中的reqtype元素
@XmlElement(name="reqtype", required = true)
public String getReqtype() {
return this.reqtype;
}
// 此处的setter函数要有,否则从xml反序列到java对象的时候无法赋值
public void setReqtype(String reqtype) {
this.reqtype = reqtype;
}
// 使用了JAXB注解,映射到xml中的secret元素
@XmlElement(name="secret", required = true)
public String getSecret() {
return this.secret;
}
// 此处的setter函数要有,否则从xml反序列到java对象的时候无法赋值
public void setSecret(String secret) {
this.secret = secret;
}
// 使用了JAXB注解,映射到xml中的body元素
@XmlElement(name="body", required = true)
public SeeContent getSeeContent() {
return this.seeContent;
}
public void setSeeContent(SeeContent seeContent) {
this.seeContent = seeContent;
}
}
下面定义Java属性seeContent引用的类型SeeContent,这个类的属性映射到xml中body元素下面的四个元素:
package com.thb.server.topology;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
import jakarta.xml.bind.annotation.XmlType;
@XmlType(propOrder = {"userid", "seeid", "upseeid", "status"})
class SeeContent{
private String userid;
private String seeid;
private String upseeid;
private String status;
// 使用了JAXB注解,映射到xml中body元素下面的userid元素
@XmlElement(name="userid", required = true)
String getUserid() {
return this.userid;
}
void setUserid(String userid) {
this.userid = userid;
}
// 使用了JAXB注解,映射到xml中body元素下面的seeid元素
@XmlElement(name="seeid", required = true)
String getSeeid() {
return this.seeid;
}
void setSeeid(String seeid) {
this.seeid = seeid;
}
// 使用了JAXB注解,映射到xml中body元素下面的upseeid元素
@XmlElement(name="upseeid", required = true)
String getUpseeid() {
return this.upseeid;
}
void setUpseeid(String upseeid) {
this.upseeid = upseeid;
}
// 使用了JAXB注解,映射到xml中body元素下面的status元素
@XmlElement(name="status", required = true)
String getStatus() {
return this.status;
}
void setStatus(String status) {
this.status = status;
}
}
生成XML schema看看:

生成的XML schema文件内容:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<xs:schema version="1.0" xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema">
<xs:element name="request" type="topologyRequest"/>
<xs:complexType name="topologyRequest">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="reqtype" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="secret" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="body" type="seeContent"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="seeContent">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="userid" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="seeid" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="upseeid" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="status" type="xs:string"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:schema>
用Postman请求web服务,收到了正常的响应:
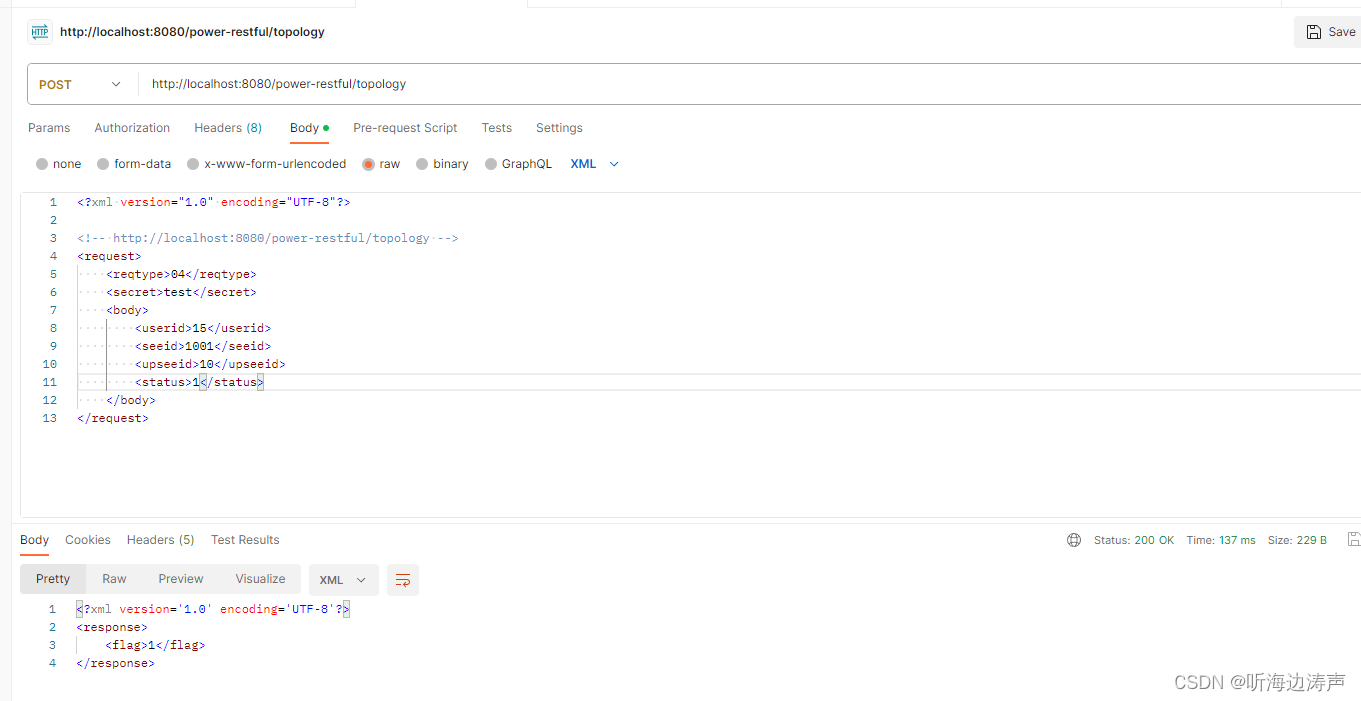
在服务端把收到的信息打印出来,成功将请求的xml内容反序列化到了java对象,内容正确: