目录
- 前言
- 题目
- 1.使用队列
- 思路(定义变量)
- 2. 本题思路分析:
- 3. 算法实现
- 4. pop函数的算法复杂度
- 5. 算法坑点
前言
在本科毕设结束后,我开始刷卡哥的“代码随想录”,每天一节。自己的总结笔记均会放在“算法刷题-代码随想录”该专栏下。
代码随想录此题链接
题目
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,翻转这棵二叉树,并返回其根节点。
示例 1:
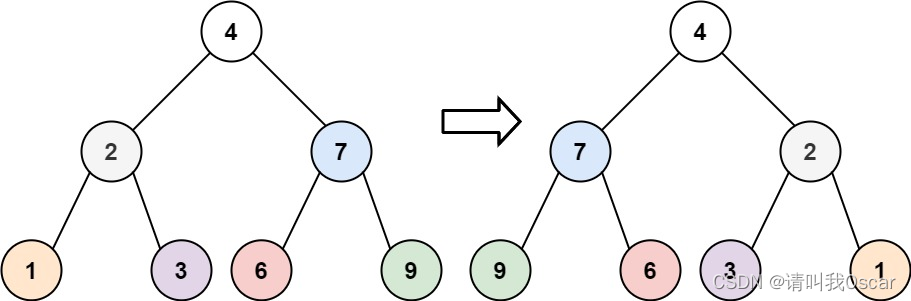
输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3,6,9]
输出:[4,7,2,9,6,3,1]
示例 2:
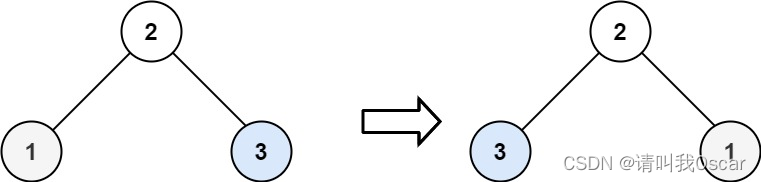
输入:root = [2,1,3]
输出:[2,3,1]
示例 3:
输入:root = []
输出:[]
提示:
树中节点数目范围在 [0, 100] 内
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
1.使用队列
思路(定义变量)
- 有三种方式,递归、深度优先遍历的迭代、广度优先遍历。
遍历每个节点,更换当前节点的左右孩子。
2. 本题思路分析:
广度优先遍历全部的节点,然后之前记录节点值的操作改换成更换当前节点的左右孩子操作即可
3. 算法实现
- 代码:
递归:
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return null;
swap(root);
invertTree(root.left);
invertTree(root.right);
return root;
}
public void swap(TreeNode cur){
TreeNode tmp = cur.left;
cur.left = cur.right;
cur.right = tmp;
}
深度优先遍历:
(前序,非统一迭代法)
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return null;
Deque<TreeNode> stack = new ArrayDeque<>();
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
TreeNode cur = stack.pop();
if(cur.left != null){
stack.push(cur.left);
}
if(cur.right != null){
stack.push(cur.right);
}
}
return root;
}
public void swap(TreeNode cur){
TreeNode tmp = cur.left;
cur.left = cur.right;
cur.right = tmp;
}
(后序,统一迭代法)
ArrayDeque中不能加入null,所以通过Stack实现栈,而不是ArrayDeque
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return null;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
TreeNode cur = stack.pop();
if(cur != null){
stack.push(cur);
stack.push(null);
if(cur.right != null){stack.push(cur.right);}
if(cur.left != null){stack.push(cur.left);}
}else{
cur = stack.pop();
swap(cur);
}
}
return root;
}
public void swap(TreeNode cur){
TreeNode tmp = cur.left;
cur.left = cur.right;
cur.right = tmp;
}
广度优先遍历解法:
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
Deque<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
if(root == null) return null;
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int size = queue.size();
for(int i = 0;i < size;i++){
TreeNode cur = queue.remove();
swap(cur);
if(cur.left != null){
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
if(cur.right != null){
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
}
return root;
}
public void swap(TreeNode cur){
TreeNode tmp = cur.left;
cur.left = cur.right;
cur.right = tmp;
}
4. pop函数的算法复杂度
略
5. 算法坑点
略