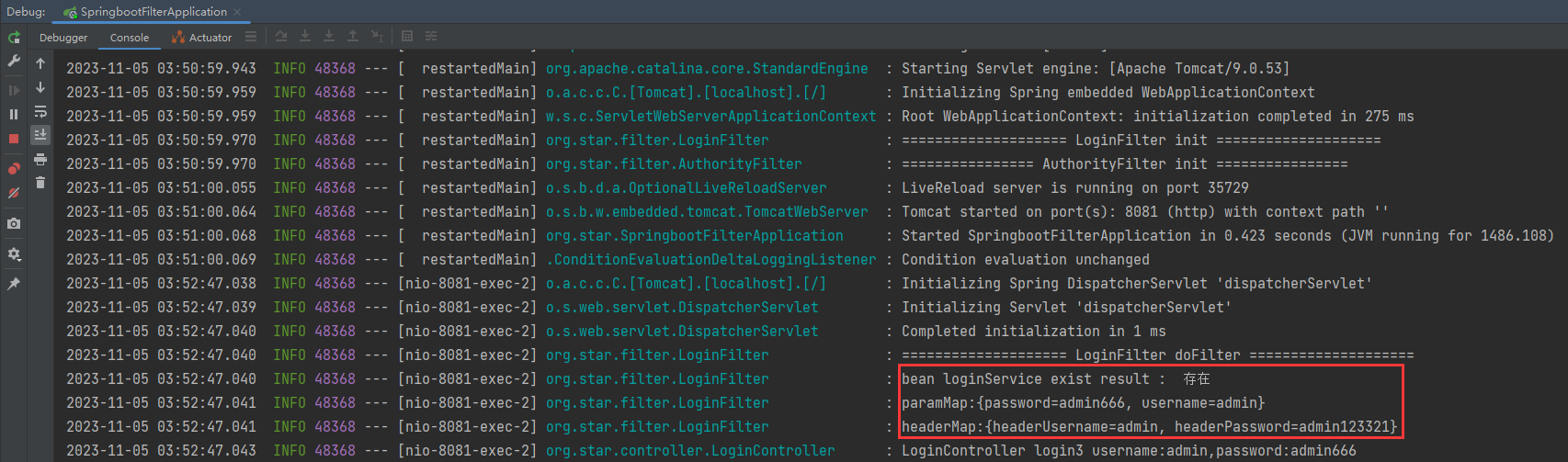
Zygote(孵化器)进程启动
在init进程中有解析.rc文件,在这个rc文件中配置了一个重要的服务service–zygote,这是app程序的鼻祖
zygote进程主要负责创建Java虚拟机,加载系统资源,启动SystemServer进程,以及在后续运行过程中启动普通的应用程序。
import /init.environ.rc
import /init.usb.rc
import /init.${ro.hardware}.rc
import /vendor/etc/init/hw/init.${ro.hardware}.rc
import /init.usb.configfs.rc
import /init.${ro.zygote}.rc
on early-init
# Set init and its forked children's oom_adj.
write /proc/1/oom_score_adj -1000
# Disable sysrq from keyboard
write /proc/sys/kernel/sysrq 0
不同机器 zygote.rc 的文件个数可能有不同,这里有四种
- init.zygote32.rc :进程对应的执行程序是 app_process (纯 32bit 模式)
- init.zygote32_64.rc :启动两个 zygote 进程 (名为 zygote 和 zygote_secondary),对应的执行程序分别是 app_process32 (主模式)、app_process64
- init.zygote64.rc:进程对应的执行程序是 app_process64 (纯 64bit 模式)
- init.zygote64_32.rc:启动两个 zygote 进程 (名为 zygote 和 zygote_secondary),对应的执行程序分别是 app_process64 (主模式)、app_process32
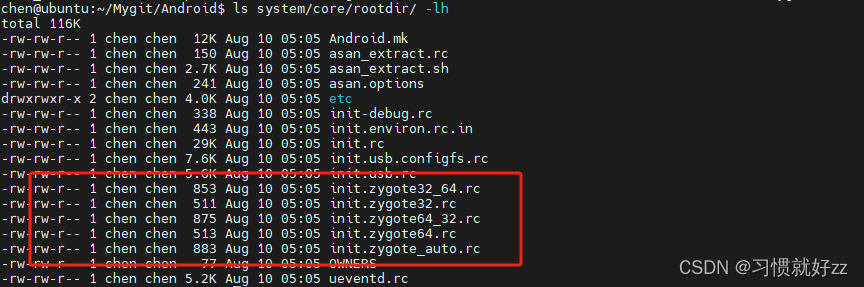
service zygote /system/bin/app_process32 -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server --socket-name=zygote
class main
priority -20
user root
group root readproc reserved_disk
socket zygote stream 660 root system #创建一个socket,名字为zygote,以tcp的形式
onrestart write /sys/android_power/request_state wake
onrestart write /sys/power/state on
onrestart restart audioserver
onrestart restart cameraserver
onrestart restart media
onrestart restart netd
onrestart restart wificond
writepid /dev/cpuset/foreground/tasks #创建子进程,向/dev/cpuset/foreground/tasks写入pid
service zygote_secondary /system/bin/app_process64 -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --socket-name=zygote_secondary
class main
priority -20 #另一个service名字为zygote_secondary
user root
group root readproc reserved_disk
socket zygote_secondary stream 660 root system
onrestart restart zygote
writepid /dev/cpuset/foreground/tasks
之前注释九的位置,在init 最后会加入 late-init 的 trigger,当late-init 触发时,会触发zygote-start的操作,start zygote就会创建zygote进程并运行
位置system/core/init/init.cpp
// Don't mount filesystems or start core system services in charger mode.
std::string bootmode = GetProperty("ro.bootmode", "");
if (bootmode == "charger") {
am.QueueEventTrigger("charger");
} else {
am.QueueEventTrigger("late-init");
}
位置system/core/rootdir/init.rc
# Mount filesystems and start core system services.
on late-init
trigger early-fs
# Mount fstab in init.{$device}.rc by mount_all command. Optional parameter
# '--early' can be specified to skip entries with 'latemount'.
# /system and /vendor must be mounted by the end of the fs stage,
# while /data is optional.
trigger fs
trigger post-fs
# Mount fstab in init.{$device}.rc by mount_all with '--late' parameter
# to only mount entries with 'latemount'. This is needed if '--early' is
# specified in the previous mount_all command on the fs stage.
# With /system mounted and properties form /system + /factory available,
# some services can be started.
trigger late-fs
# Now we can mount /data. File encryption requires keymaster to decrypt
# /data, which in turn can only be loaded when system properties are present.
trigger post-fs-data
# Now we can start zygote for devices with file based encryption
trigger zygote-start #这里触发zygote-start
# Load persist properties and override properties (if enabled) from /data.
trigger load_persist_props_action
# Remove a file to wake up anything waiting for firmware.
trigger firmware_mounts_complete
trigger early-boot
trigger boot
#............
# It is recommended to put unnecessary data/ initialization from post-fs-data
# to start-zygote in device's init.rc to unblock zygote start.
on zygote-start && property:ro.crypto.state=unencrypted
# A/B update verifier that marks a successful boot.
exec_start update_verifier_nonencrypted
start netd
start zygote
start zygote_secondary
on zygote-start && property:ro.crypto.state=unsupported
# A/B update verifier that marks a successful boot.
exec_start update_verifier_nonencrypted
start netd
start zygote
start zygote_secondary
on zygote-start && property:ro.crypto.state=encrypted && property:ro.crypto.type=file
# A/B update verifier that marks a successful boot.
exec_start update_verifier_nonencrypted
start netd
start zygote
start zygote_secondary
在解析init.rc文件时会创建解析器解析init.rc里面的命令,而start命令是由ActionParser 解析器解析。
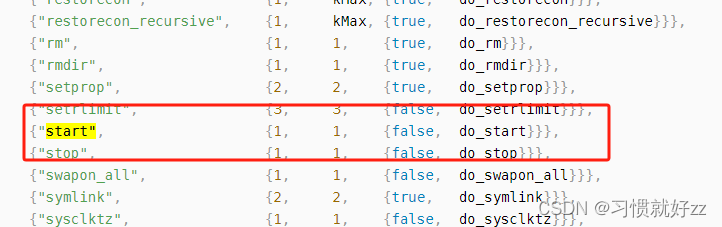
可知 start 命令对应的执行函数为 do_start,do_start函数首先通过 FindService 去service 数组中遍历,根据信息匹配出对应的service,然后调用这个 service 的 Start 方法

#位置system/core/rootdir/init.zygote64.rc
service zygote /system/bin/app_process64 -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server
class main
priority -20
user root
group root readproc reserved_disk
socket zygote stream 660 root system
onrestart write /sys/android_power/request_state wake
onrestart write /sys/power/state on
onrestart restart audioserver
onrestart restart cameraserver
onrestart restart media
onrestart restart netd
onrestart restart wificond
writepid /dev/cpuset/foreground/tasks
zygote 服务对应的二进制文件是 /system/bin/app_processXXX,对应的源文件在:/frameworks/base/cmds/app_process/app_main.cpp
int main(int argc, char* const argv[])
{
//将参数argc放到argv_String字符串中
//上面可知,传入的参数是-Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server
if (!LOG_NDEBUG) {
String8 argv_String;
for (int i = 0; i < argc; ++i) {
argv_String.append("\"");
argv_String.append(argv[i]);
argv_String.append("\" ");
}
ALOGV("app_process main with argv: %s", argv_String.string());
}
//构建 AppRuntime 对象,并将参数传入
AppRuntime runtime(argv[0], computeArgBlockSize(argc, argv));
// Process command line arguments
// ignore argv[0]
argc--;
argv++;
// Everything up to '--' or first non '-' arg goes to the vm.
//
// The first argument after the VM args is the "parent dir", which
// is currently unused.
//
// After the parent dir, we expect one or more the following internal
// arguments :
//
// --zygote : Start in zygote mode
// --start-system-server : Start the system server.
// --application : Start in application (stand alone, non zygote) mode.
// --nice-name : The nice name for this process.
//
// For non zygote starts, these arguments will be followed by
// the main class name. All remaining arguments are passed to
// the main method of this class.
//
// For zygote starts, all remaining arguments are passed to the zygote.
// main function.
//
// Note that we must copy argument string values since we will rewrite the
// entire argument block when we apply the nice name to argv0.
//
// As an exception to the above rule, anything in "spaced commands"
// goes to the vm even though it has a space in it.
//这两个参数是Java程序需要依赖的Jar包,相当于import
const char* spaced_commands[] = { "-cp", "-classpath" };
// Allow "spaced commands" to be succeeded by exactly 1 argument (regardless of -s).
bool known_command = false;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < argc; i++) {
//将spaced_commands中的参数额外加入VM
if (known_command == true) {
runtime.addOption(strdup(argv[i]));
// The static analyzer gets upset that we don't ever free the above
// string. Since the allocation is from main, leaking it doesn't seem
// problematic. NOLINTNEXTLINE
ALOGV("app_process main add known option '%s'", argv[i]);
known_command = false;
continue;
}
for (int j = 0;
j < static_cast<int>(sizeof(spaced_commands) / sizeof(spaced_commands[0]));
++j) {
//参数是否是spaced_commands中的参数
if (strcmp(argv[i], spaced_commands[j]) == 0) {
known_command = true;
ALOGV("app_process main found known command '%s'", argv[i]);
}
}
//如果参数第一个字符是”-“,直接跳出循环,之前传入的第一个参数是 -Xzygote,所以执行到这里就跳出了,i=0
if (argv[i][0] != '-') {
break;
}
if (argv[i][1] == '-' && argv[i][2] == 0) {
++i; // Skip --.
break;
}
runtime.addOption(strdup(argv[i]));
// The static analyzer gets upset that we don't ever free the above
// string. Since the allocation is from main, leaking it doesn't seem
// problematic. NOLINTNEXTLINE
ALOGV("app_process main add option '%s'", argv[i]);
}
// Parse runtime arguments. Stop at first unrecognized option.
bool zygote = false;
bool startSystemServer = false;
bool application = false;
String8 niceName;
String8 className;
++i; // Skip unused "parent dir" argument.
//跳过一个参数,之前跳过了 -Xzygote,这里跳过 /system/bin
while (i < argc) {
const char* arg = argv[i++];
if (strcmp(arg, "--zygote") == 0) { //表示zygote启动模式
zygote = true;
niceName = ZYGOTE_NICE_NAME;
} else if (strcmp(arg, "--start-system-server") == 0) { //需要启动SystemServer
startSystemServer = true;
} else if (strcmp(arg, "--application") == 0) { //表示application启动模式,普通的应用程序
application = true;
} else if (strncmp(arg, "--nice-name=", 12) == 0) { //进程别名
niceName.setTo(arg + 12);
} else if (strncmp(arg, "--", 2) != 0) { //application启动的class
className.setTo(arg);
break;
} else {
--i;
break;
}
}
Vector<String8> args;
if (!className.isEmpty()) { //className不为空,说明是application启动模式
// We're not in zygote mode, the only argument we need to pass
// to RuntimeInit is the application argument.
//
// The Remainder of args get passed to startup class main(). Make
// copies of them before we overwrite them with the process name.
args.add(application ? String8("application") : String8("tool"));
runtime.setClassNameAndArgs(className, argc - i, argv + i); //将className和参数设置给runtime
if (!LOG_NDEBUG) {
String8 restOfArgs;
char* const* argv_new = argv + i;
int argc_new = argc - i;
for (int k = 0; k < argc_new; ++k) {
restOfArgs.append("\"");
restOfArgs.append(argv_new[k]);
restOfArgs.append("\" ");
}
ALOGV("Class name = %s, args = %s", className.string(), restOfArgs.string());
}
} else { //zygote启动模式
// We're in zygote mode.
maybeCreateDalvikCache(); //创建Dalvik的缓存目录
if (startSystemServer) { //加入 start-system-server参数
args.add(String8("start-system-server"));
}
char prop[PROP_VALUE_MAX];
if (property_get(ABI_LIST_PROPERTY, prop, NULL) == 0) {
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("app_process: Unable to determine ABI list from property %s.",
ABI_LIST_PROPERTY);
return 11;
}
String8 abiFlag("--abi-list=");
abiFlag.append(prop);
args.add(abiFlag); // 加入--abi-list=参数
// In zygote mode, pass all remaining arguments to the zygote
// main() method.
for (; i < argc; ++i) {
args.add(String8(argv[i])); //将剩下的参数加入args
}
}
if (!niceName.isEmpty()) { //设置进程的别名
runtime.setArgv0(niceName.string(), true /* setProcName */);
}
if (zygote) { //zygote启动模式,加载 ZygoteInit 类
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit", args, zygote);
} else if (className) { //application 启动模式,加载 RuntimeInit 类
runtime.start("com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit", args, zygote);
} else {
fprintf(stderr, "Error: no class name or --zygote supplied.\n");
app_usage();
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("app_process: no class name or --zygote supplied.");
}
}
app_main.cpp 的 main 函数主要做的事就是参数解析,这个函数有两种启动模式
- 一种是zygote模式:初始化zygote进程,传递的参数:–start-system-server 和 --socket-name=zygote,前者表示启动SystemServer,后者指定socket的名称
- 一种是application模式:启动普通应用程序,传递的参数有class名字以及class带的参数
两种模式最终都是调用AppRuntime对象的start函数,加载 ZygoteInit 或 RuntimeInit 两个Java类,并将之前整理的参数传入进去
上面main函数最后得知,如果 zygote 为 true,说明当前在运行Zygote进程中,就会调用 AppRuntime 的 start 函数
位置:frameworks\base\core\jni\AndroidRuntime.cpp
void AndroidRuntime::start(const char* className, const Vector<String8>& options, bool zygote)
{
//.....
/* start the virtual machine */
JniInvocation jni_invocation;
jni_invocation.Init(NULL); //注释一:初始化jni
JNIEnv* env;
if (startVm(&mJavaVM, &env, zygote) != 0) { //注释二:启动JAVA虚拟机
return;
}
onVmCreated(env);
/*
* Register android functions.
*/ //注释三:为Java虚拟机注册JNI方法
if (startReg(env) < 0) {
ALOGE("Unable to register all android natives\n");
return;
}
/*
* We want to call main() with a String array with arguments in it.
* At present we have two arguments, the class name and an option string.
* Create an array to hold them.
*/
jclass stringClass; //注释四:调用ZygoteInit.java 的 main 函数
jobjectArray strArray;
jstring classNameStr;
stringClass = env->FindClass("java/lang/String");
assert(stringClass != NULL);
strArray = env->NewObjectArray(options.size() + 1, stringClass, NULL);
assert(strArray != NULL);
// 获得传递的 className 参数,如果为 zygote 则传递的参数为:com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit
classNameStr = env->NewStringUTF(className);
assert(classNameStr != NULL);
env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, 0, classNameStr);
for (size_t i = 0; i < options.size(); ++i) {
jstring optionsStr = env->NewStringUTF(options.itemAt(i).string());
assert(optionsStr != NULL);
env->SetObjectArrayElement(strArray, i + 1, optionsStr);
}
/*
* Start VM. This thread becomes the main thread of the VM, and will
* not return until the VM exits.
*/
// slashClassName 函数将className中的 “.” 替换成 “/”
char* slashClassName = toSlashClassName(className != NULL ? className : "");
// 找到 com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit.java 这个类
jclass startClass = env->FindClass(slashClassName);
if (startClass == NULL) {
ALOGE("JavaVM unable to locate class '%s'\n", slashClassName);
/* keep going */
} else {
// 找到 ZygoteInit.java 类中的main方法
jmethodID startMeth = env->GetStaticMethodID(startClass, "main",
"([Ljava/lang/String;)V");
if (startMeth == NULL) {
ALOGE("JavaVM unable to find main() in '%s'\n", className);
/* keep going */
} else {
//通过jni反射调用 zygoteInit.java 的 main 方法
env->CallStaticVoidMethod(startClass, startMeth, strArray);
#if 0
if (env->ExceptionCheck())
threadExitUncaughtException(env);
#endif
}
}
free(slashClassName);
ALOGD("Shutting down VM\n");
if (mJavaVM->DetachCurrentThread() != JNI_OK) //退出当前线程
ALOGW("Warning: unable to detach main thread\n");
if (mJavaVM->DestroyJavaVM() != 0) //创建一个线程,该线程会等待所有子线程结束后关闭虚拟机
ALOGW("Warning: VM did not shut down cleanly\n");
}
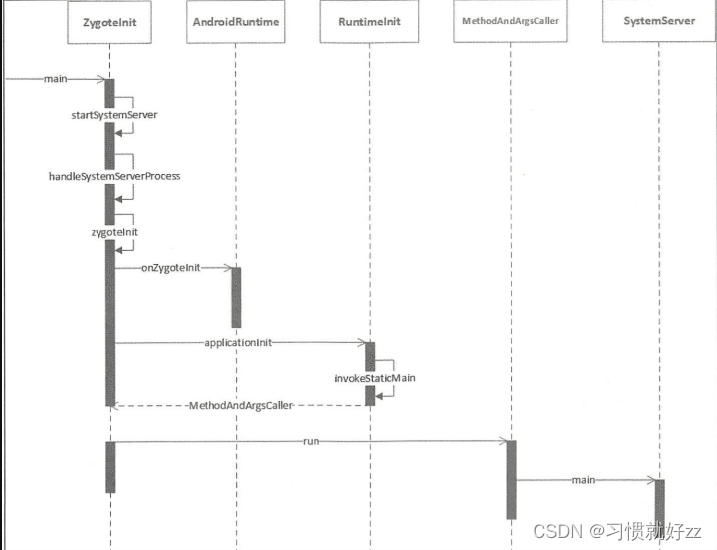
总体流程是:
- 初始化jni
- startVm函数创建java虚拟机
- startReg 函数为虚拟机注册JNI方法
- 根据传递进来的参数找到对应的java类
- 通过JNI调用对应类的main方法。通过JNI的方法zygote就从Native层进入了Java框架层了,此前没有任何代码进入Java框架层
注释一:初始化JNI
位置:libnativehelper\JniInvocation.cpp
bool JniInvocation::Init(const char* library) {
#ifdef __ANDROID__
char buffer[PROP_VALUE_MAX];
#else
char* buffer = NULL;
#endif
library = GetLibrary(library, buffer);
// Load with RTLD_NODELETE in order to ensure that libart.so is not unmapped when it is closed.
// This is due to the fact that it is possible that some threads might have yet to finish
// exiting even after JNI_DeleteJavaVM returns, which can lead to segfaults if the library is
// unloaded.
//RTLD_NOW 表示需要在dlopen返回前,解析出所有未定义的符号,如果解析不出返回NULL
//RTLD_NODELETE 表示在dlclose()期间不卸载库,并在之后使用dlopen重新加载库的时不初始化库中的静态变量
const int kDlopenFlags = RTLD_NOW | RTLD_NODELETE;
//dlopen的功能是以指定的模式打开指定的动态链接库文件,并返回一个句柄
handle_ = dlopen(library, kDlopenFlags);
if (handle_ == NULL) {
if (strcmp(library, kLibraryFallback) == 0) {
// Nothing else to try.
ALOGE("Failed to dlopen %s: %s", library, dlerror());
return false;
}
// Note that this is enough to get something like the zygote
// running, we can't property_set here to fix this for the future
// because we are root and not the system user. See
// RuntimeInit.commonInit for where we fix up the property to
// avoid future fallbacks. http://b/11463182
ALOGW("Falling back from %s to %s after dlopen error: %s",
library, kLibraryFallback, dlerror());
library = kLibraryFallback;
handle_ = dlopen(library, kDlopenFlags);
if (handle_ == NULL) {
ALOGE("Failed to dlopen %s: %s", library, dlerror());
return false;
}
}
// FindSymbol 函数内部实际调用的是dlsym
// dlsym作用是根据动态链接库 操作句柄(handle)与符号(symbol),返回对应的地址
// 这里实际就是从libart.so库中将 JNI_GetDefaultJavaVMInitArgs 等对应的地址存放到 &JNI_GetDefaultJavaVMInitArgs_
if (!FindSymbol(reinterpret_cast<void**>(&JNI_GetDefaultJavaVMInitArgs_),
"JNI_GetDefaultJavaVMInitArgs")) {
return false;
}
if (!FindSymbol(reinterpret_cast<void**>(&JNI_CreateJavaVM_),
"JNI_CreateJavaVM")) {
return false;
}
if (!FindSymbol(reinterpret_cast<void**>(&JNI_GetCreatedJavaVMs_),
"JNI_GetCreatedJavaVMs")) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
注释二:创建虚拟机 startVm
调用的函数是libnativehelper\JniInvocation.cpp下的 AndroidRuntime::startVm 函数,这个函数比较长,但做的事情单一,就是从系统属性中读取参数,然后通过 addOption 设置到 AndroidRuntime 的 mOptions 数组中存储起来,然后调用从 libart.so 中找到的 JNI_CreateJavaVM 函数,并将之前读到的参数传入
位置:frameworks/base/core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp
int AndroidRuntime::startVm(JavaVM** pJavaVM, JNIEnv** pEnv, bool zygote)
{
JavaVMInitArgs initArgs;
//....
/* route exit() to our handler */
addOption("exit", (void*) runtime_exit); //将各个参数放到mOption数组中
//....
initArgs.version = JNI_VERSION_1_4;
initArgs.options = mOptions.editArray(); //将mOptions赋值给initArgs
initArgs.nOptions = mOptions.size();
initArgs.ignoreUnrecognized = JNI_FALSE;
/*
* Initialize the VM.
*
* The JavaVM* is essentially per-process, and the JNIEnv* is per-thread.
* If this call succeeds, the VM is ready, and we can start issuing
* JNI calls.
*/
if (JNI_CreateJavaVM(pJavaVM, pEnv, &initArgs) < 0) { //调用libart.so 的JNI_CreateJavaVM 函数去创建虚拟机
ALOGE("JNI_CreateJavaVM failed\n");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
libart.so是ART虚拟机的核心库,它包含了ART虚拟机所有的核心组件,如ClassLinker、DexFile、JNI、gc等
注释三:为虚拟机注册JNI方法 startReg
/*
* Register android native functions with the VM.
*/
/*static*/ int AndroidRuntime::startReg(JNIEnv* env)
{
ATRACE_NAME("RegisterAndroidNatives");
/*
* This hook causes all future threads created in this process to be
* attached to the JavaVM. (This needs to go away in favor of JNI
* Attach calls.)
*/
//设置Android创建线程的函数javaCreateThreadEtc,这个函数内部是通过Linux的clone来创建线程的
androidSetCreateThreadFunc((android_create_thread_fn) javaCreateThreadEtc);
ALOGV("--- registering native functions ---\n");
/*
* Every "register" function calls one or more things that return
* a local reference (e.g. FindClass). Because we haven't really
* started the VM yet, they're all getting stored in the base frame
* and never released. Use Push/Pop to manage the storage.
*/
//创建一个200容量的局部引用作用域,这个局部引用其实就是局部变量
env->PushLocalFrame(200);
if (register_jni_procs(gRegJNI, NELEM(gRegJNI), env) < 0) {//注册JNI函数
env->PopLocalFrame(NULL);
return -1;
}
env->PopLocalFrame(NULL);//释放局部引用作用域
//createJavaThread("fubar", quickTest, (void*) "hello");
return 0;
}
/*********************************************************/
static int register_jni_procs(const RegJNIRec array[], size_t count, JNIEnv* env)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < count; i++) {
if (array[i].mProc(env) < 0) {
#ifndef NDEBUG
ALOGD("----------!!! %s failed to load\n", array[i].mName);
#endif
return -1;
}
}
return 0;
}
startReg 处理就是交给 RegJNIRec 的 mProc,RegJNIRec是个很简单的结构体,mProc是个函数指针
static const RegJNIRec gRegJNI[] = {
REG_JNI(register_com_android_internal_os_RuntimeInit),
REG_JNI(register_com_android_internal_os_ZygoteInit_nativeZygoteInit),
REG_JNI(register_android_os_SystemClock),
REG_JNI(register_android_util_EventLog),
REG_JNI(register_android_util_Log),
REG_JNI(register_android_util_MemoryIntArray),
REG_JNI(register_android_util_PathParser),
REG_JNI(register_android_util_StatsLog),
REG_JNI(register_android_app_admin_SecurityLog),
REG_JNI(register_android_content_AssetManager),
REG_JNI(register_android_content_StringBlock),
REG_JNI(register_android_content_XmlBlock),
REG_JNI(register_android_content_res_ApkAssets),
REG_JNI(register_android_text_AndroidCharacter),
REG_JNI(register_android_text_Hyphenator),
REG_JNI(register_android_text_MeasuredParagraph),
REG_JNI(register_android_text_StaticLayout),
REG_JNI(register_android_view_InputDevice),
REG_JNI(register_android_view_KeyCharacterMap),
REG_JNI(register_android_os_Process),
REG_JNI(register_android_os_SystemProperties),
REG_JNI(register_android_os_Binder),
REG_JNI(register_android_os_Parcel),
REG_JNI(register_android_os_HidlSupport),
//...
};
注释四:反射调用ZygoteInit类的main函数
虚拟机创建完成后,就可以运行java代码了,主要是通过jni的函数 CallStaticVoidMethod 反射调用 com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit.java 的main函数,至此 Zygote 进程已经启动
SystemServer进程启动
上面已经启动了Zygote进程,并最终调用到了ZygoteInit.java 的main函数,而SystemServer就是在这个main函数中启动的
位置:frameworks\base\core\java\com\android\internal\os\ZygoteInit.java
public static void main(String argv[]) {
ZygoteServer zygoteServer = new ZygoteServer();
// Mark zygote start. This ensures that thread creation will throw
// an error.
ZygoteHooks.startZygoteNoThreadCreation();
// Zygote goes into its own process group.
try {
Os.setpgid(0, 0);
} catch (ErrnoException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to setpgid(0,0)", ex);
}
final Runnable caller;
try {
// Report Zygote start time to tron unless it is a runtime restart
if (!"1".equals(SystemProperties.get("sys.boot_completed"))) {
MetricsLogger.histogram(null, "boot_zygote_init",
(int) SystemClock.elapsedRealtime());
}
String bootTimeTag = Process.is64Bit() ? "Zygote64Timing" : "Zygote32Timing";
TimingsTraceLog bootTimingsTraceLog = new TimingsTraceLog(bootTimeTag,
Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK);
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("ZygoteInit");
RuntimeInit.enableDdms();
// 注释一:处理传递过来的参数
boolean startSystemServer = false;
String socketName = "zygote";
String abiList = null;
boolean enableLazyPreload = false;
for (int i = 1; i < argv.length; i++) {
if ("start-system-server".equals(argv[i])) { //是否启动systemServer
startSystemServer = true;
} else if ("--enable-lazy-preload".equals(argv[i])) {
enableLazyPreload = true;
} else if (argv[i].startsWith(ABI_LIST_ARG)) { //ABI_LIST_ARG = "--abi-list=";
abiList = argv[i].substring(ABI_LIST_ARG.length());
} else if (argv[i].startsWith(SOCKET_NAME_ARG)) { //SOCKET_NAME_ARG = "--socket-name=";
socketName = argv[i].substring(SOCKET_NAME_ARG.length());
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Unknown command line argument: " + argv[i]);
}
}
if (abiList == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("No ABI list supplied.");
}
// 注释二:创建一个Server端的Socket,socketName的值为“zygote”
zygoteServer.registerServerSocketFromEnv(socketName);
// In some configurations, we avoid preloading resources and classes eagerly.
// In such cases, we will preload things prior to our first fork.
if (!enableLazyPreload) {
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("ZygotePreload");
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_START,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
// 注释三:预加载类和资源
preload(bootTimingsTraceLog);
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_END,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // ZygotePreload
} else {
Zygote.resetNicePriority();
}
// Do an initial gc to clean up after startup
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("PostZygoteInitGC");
gcAndFinalize();
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // PostZygoteInitGC
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // ZygoteInit
// Disable tracing so that forked processes do not inherit stale tracing tags from
// Zygote.
Trace.setTracingEnabled(false, 0);
Zygote.nativeSecurityInit();
// Zygote process unmounts root storage spaces.
Zygote.nativeUnmountStorageOnInit();
ZygoteHooks.stopZygoteNoThreadCreation();
if (startSystemServer) {
// 注释四:启动systemSercer进程
Runnable r = forkSystemServer(abiList, socketName, zygoteServer);
// {@code r == null} in the parent (zygote) process, and {@code r != null} in the
// child (system_server) process.
if (r != null) {
r.run();
return;
}
}
Log.i(TAG, "Accepting command socket connections");
// The select loop returns early in the child process after a fork and
// loops forever in the zygote.
//注释五:等待 AMS 请求 进入looper,等待AMS请求Zygote进程来创建新的应用程序进程
caller = zygoteServer.runSelectLoop(abiList);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "System zygote died with exception", ex);
throw ex;
} finally {
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
}
// We're in the child process and have exited the select loop. Proceed to execute the
// command.
if (caller != null) {
caller.run();
}
}
注释一:处理传递过来的参数
在frameworks\base\cmds\app_process\app_main.cpp中有传递对应的参数
int main(int argc, char* const argv[])
{
//...
maybeCreateDalvikCache();
if (startSystemServer) {
args.add(String8("start-system-server"));
}
char prop[PROP_VALUE_MAX];
if (property_get(ABI_LIST_PROPERTY, prop, NULL) == 0) {
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("app_process: Unable to determine ABI list from property %s.",
ABI_LIST_PROPERTY);
return 11;
}
String8 abiFlag("--abi-list=");
abiFlag.append(prop);
args.add(abiFlag);
// In zygote mode, pass all remaining arguments to the zygote
// main() method.
for (; i < argc; ++i) {
args.add(String8(argv[i]));
}
//...
if (!niceName.isEmpty()) {
runtime.setArgv0(niceName.string(), true /* setProcName */);
}
//...
}
注释二:创建一个Server端的Socket
位置:frameworks\base\core\java\com\android\internal\os\ZygoteServer.java
void registerServerSocketFromEnv(String socketName) {
if (mServerSocket == null) {
int fileDesc;
final String fullSocketName = ANDROID_SOCKET_PREFIX + socketName; //拼接socket的名称
try {
String env = System.getenv(fullSocketName); //得到Socket环境变量的值
fileDesc = Integer.parseInt(env); //将环境变量的值转换成文件描述符的参数(int类型)
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(fullSocketName + " unset or invalid", ex);
}
try {
FileDescriptor fd = new FileDescriptor(); //创建文件描述符
fd.setInt$(fileDesc);
mServerSocket = new LocalServerSocket(fd); //创建服务器端socket
mCloseSocketFd = true;
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Error binding to local socket '" + fileDesc + "'", ex);
}
}
}
之后创建 SystemServer 进程的时候,会将这个Socket传递进去,SystemServer 就会在这个务器端 Socket 上等待 AMS 请求 Zygote 进程来创建新的应用程序进程。
注释三:预处理
static void preload(TimingsTraceLog bootTimingsTraceLog) {
Log.d(TAG, "begin preload");
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("BeginIcuCachePinning");
beginIcuCachePinning();
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // BeginIcuCachePinning
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("PreloadClasses");
preloadClasses(); //预加载/system/etc/preloaded-classes目录下常用的类
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // PreloadClasses
preloadTextResources(); //预加载drawables、color、freeform_multi_window_drawables等常用资源
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("PreloadResources");
preloadResources();
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // PreloadResources
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK, "PreloadAppProcessHALs");
nativePreloadAppProcessHALs();
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK);
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK, "PreloadOpenGL");
preloadOpenGL(); //预加载OpenGl
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_DALVIK);
preloadSharedLibraries(); //预加载android、compiler_rt、jnigraphics库
waitForPreloadAsync(); //预加载字体资源文件
// Ask the WebViewFactory to do any initialization that must run in the zygote process,
// for memory sharing purposes.
WebViewFactory.prepareWebViewInZygote();
endIcuCachePinning();
warmUpJcaProviders();
Log.d(TAG, "end preload");
sPreloadComplete = true;
}
注释四:启动SystemSercer进程
SystemSercer进程创建
private static Runnable forkSystemServer(String abiList, String socketName, ZygoteServer zygoteServer) {
long capabilities = posixCapabilitiesAsBits(
OsConstants.CAP_IPC_LOCK,
OsConstants.CAP_KILL,
OsConstants.CAP_NET_ADMIN,
OsConstants.CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE,
OsConstants.CAP_NET_BROADCAST,
OsConstants.CAP_NET_RAW,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_MODULE,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_NICE,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_PTRACE,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_TIME,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_TTY_CONFIG,
OsConstants.CAP_WAKE_ALARM,
OsConstants.CAP_BLOCK_SUSPEND
);
/* Containers run without some capabilities, so drop any caps that are not available. */
StructCapUserHeader header = new StructCapUserHeader(
OsConstants._LINUX_CAPABILITY_VERSION_3, 0);
StructCapUserData[] data;
try {
data = Os.capget(header);
} catch (ErrnoException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to capget()", ex);
}
capabilities &= ((long) data[0].effective) | (((long) data[1].effective) << 32);
// Mediatek Android Patch Begin
/* Mediatek add 1014 to setgroups for dhcp*/
/* Hardcoded command line to start the system server */
String args[] = { // 创建args 数组,这个数组用来保存启动 SystemServer 的启动参数
"--setuid=1000",
"--setgid=1000",
"--setgroups=1001,1002,1003,1004,1005,1006,1007,1014,1008,1009,1010,1018,1021,1023,1024,1032,1065,3001,3002,3003,3006,3007,3009,3010",
"--capabilities=" + capabilities + "," + capabilities,
"--nice-name=system_server",
"--runtime-args",
"--target-sdk-version=" + VMRuntime.SDK_VERSION_CUR_DEVELOPMENT,
"com.android.server.SystemServer",
};
// Mediatek Android Patch End
ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs = null;
int pid;
try {
parsedArgs = new ZygoteConnection.Arguments(args);
ZygoteConnection.applyDebuggerSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
ZygoteConnection.applyInvokeWithSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
boolean profileSystemServer = SystemProperties.getBoolean(
"dalvik.vm.profilesystemserver", false);
if (profileSystemServer) {
parsedArgs.runtimeFlags |= Zygote.PROFILE_SYSTEM_SERVER;
}
/* Request to fork the system server process */
pid = Zygote.forkSystemServer( //创建一个子进程,也就是 SystemServer 进程
parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid,
parsedArgs.gids,
parsedArgs.runtimeFlags,
null,
parsedArgs.permittedCapabilities,
parsedArgs.effectiveCapabilities);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
/* For child process */
if (pid == 0) { //当代码逻辑运行在子进程中,既是 SystemServer 进程
if (hasSecondZygote(abiList)) {
waitForSecondaryZygote(socketName);
}
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket(); //子进程关闭 Socket
return handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs);//处理 SystemServer 进程
}
return null;
}
第一步:创建 SystemServer 的启动参数
从 args 数组,SystemServer 的启动参数可以看出 SystemServer 进程用户 id 和 用户组 id 被设置成了1000,并拥有
setgroups=1001,1002,1003,1004,1005,1006,1007,1014,1008,1009,1010,1018,1021,1023,1024,1032,1065,3001,3002,3003,3006,3007,3009,3010"
的权限,进程的名称为:–nice-name=system_server,启动的类名为com.android.server.SystemServer
第二步:forkSystemServer 创建出 SystemServer进程
注意: 这里有个pid = = 0 的判断,android
的fork机制可以理解为分裂,分裂后有两个代码一模一样的进程,分裂后会同时执行两个进程的代码,如果是在父进程中执行
fork,则会返回分裂子进程的的进程号(pid),如果是在子进程中 执行 fork,返回值为0,所以 if (pid = = 0)
里面的代码只会在子进程既 SystemServer 进程中执行
至此,就创建出了 SystemServer 进程
由于SystemServer进程 是 fork Zygote进程的,所以也会得到 Zygote 进程创建的 Socket ,但这个 Socket 对于 SystemServer 没有用处,所以关闭了这个 Socket,之后调用 handleSystemServerProcess 来初始化SystemServer 进程
//位置:"frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java"
private static Runnable handleSystemServerProcess(ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs) {
// set umask to 0077 so new files and directories will default to owner-only permissions.
Os.umask(S_IRWXG | S_IRWXO);
if (parsedArgs.niceName != null) {
Process.setArgV0(parsedArgs.niceName);
}
final String systemServerClasspath = Os.getenv("SYSTEMSERVERCLASSPATH");
if (systemServerClasspath != null) {
performSystemServerDexOpt(systemServerClasspath);
// Capturing profiles is only supported for debug or eng builds since selinux normally
// prevents it.
boolean profileSystemServer = SystemProperties.getBoolean(
"dalvik.vm.profilesystemserver", false);
if (profileSystemServer && (Build.IS_USERDEBUG || Build.IS_ENG)) {
try {
prepareSystemServerProfile(systemServerClasspath);
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.wtf(TAG, "Failed to set up system server profile", e);
}
}
}
if (parsedArgs.invokeWith != null) {
//...
} else {
ClassLoader cl = null;
if (systemServerClasspath != null) {
//创建了PathClassLoader
cl = createPathClassLoader(systemServerClasspath, parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion);
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(cl);
}
/*
* Pass the remaining arguments to SystemServer.
*/
return ZygoteInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion, parsedArgs.remainingArgs, cl);
}
/* should never reach here */
}
//位置:"frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java"
public static final Runnable zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (RuntimeInit.DEBUG) {
Slog.d(RuntimeInit.TAG, "RuntimeInit: Starting application from zygote");
}
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "ZygoteInit");
RuntimeInit.redirectLogStreams();
RuntimeInit.commonInit();
ZygoteInit.nativeZygoteInit(); //启动Binder线程池,卡方法名就知道是Native层的函数
return RuntimeInit.applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, argv, classLoader);
}
//位置:"./frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/RuntimeInit.java"
protected static Runnable applicationInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv,
ClassLoader classLoader) {
// If the application calls System.exit(), terminate the process
// immediately without running any shutdown hooks. It is not possible to
// shutdown an Android application gracefully. Among other things, the
// Android runtime shutdown hooks close the Binder driver, which can cause
// leftover running threads to crash before the process actually exits.
nativeSetExitWithoutCleanup(true);
// We want to be fairly aggressive about heap utilization, to avoid
// holding on to a lot of memory that isn't needed.
VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetHeapUtilization(0.75f);
VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetSdkVersion(targetSdkVersion);
final Arguments args = new Arguments(argv);
// The end of of the RuntimeInit event (see #zygoteInit).
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
// Remaining arguments are passed to the start class's static main
return findStaticMain(args.startClass, args.startArgs, classLoader); //寻找main
}
protected static Runnable findStaticMain(String className, String[] argv,
ClassLoader classLoader) {
Class<?> cl;
try {
cl = Class.forName(className, true, classLoader);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Missing class when invoking static main " + className,
ex);
}
Method m;
try {
//这里反射获取到systemServer的main方法
m = cl.getMethod("main", new Class[] { String[].class });
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Missing static main on " + className, ex);
} catch (SecurityException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Problem getting static main on " + className, ex);
}
int modifiers = m.getModifiers();
if (! (Modifier.isStatic(modifiers) && Modifier.isPublic(modifiers))) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Main method is not public and static on " + className);
}
/*
* This throw gets caught in ZygoteInit.main(), which responds
* by invoking the exception's run() method. This arrangement
* clears up all the stack frames that were required in setting
* up the process.
*/
return new MethodAndArgsCaller(m, argv); //返回了一个Runnable对象
}
//位置:"./frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/RuntimeInit.java"
static class MethodAndArgsCaller implements Runnable {
/** method to call */
private final Method mMethod;
/** argument array */
private final String[] mArgs;
public MethodAndArgsCaller(Method method, String[] args) {
mMethod = method;
mArgs = args;
}
public void run() {
try {
//这里执行mMethod方法,也就是传进来的systemServer的main方法
mMethod.invoke(null, new Object[] { mArgs });
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
} catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
Throwable cause = ex.getCause();
if (cause instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) cause;
} else if (cause instanceof Error) {
throw (Error) cause;
}
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
}
}
最终是得到了 SystemServer 的main方法反射
SystemSercer进程启动流程
//位置:"frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java"
public static void main(String argv[]) {
//...
if (startSystemServer) {
//得到SystemServer的main方法的Runnable对象
Runnable r = forkSystemServer(abiList, socketName, zygoteServer);
// {@code r == null} in the parent (zygote) process, and {@code r != null} in the
// child (system_server) process.
if (r != null) { //不为null说明是SystemServer子进程中,执行run方法然后return
r.run();
return;
}
}
//...
}
private static Runnable forkSystemServer(String abiList, String socketName, ZygoteServer zygoteServer) {
//...
/* For child process */
if (pid == 0) { //上面讲到,为0就是子进程SystemServer
if (hasSecondZygote(abiList)) {
waitForSecondaryZygote(socketName);
}
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket(); //子进程关闭 Socket
return handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs);//处理 SystemServer 进程
}
//...
}
位置:frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java
/**
* The main entry point from zygote.
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SystemServer().run();
}
public SystemServer() {
// Check for factory test mode.
mFactoryTestMode = FactoryTest.getMode();
// Remember if it's runtime restart(when sys.boot_completed is already set) or reboot
mRuntimeRestart = "1".equals(SystemProperties.get("sys.boot_completed"));
mRuntimeStartElapsedTime = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
mRuntimeStartUptime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
}
private void run() {
try {
traceBeginAndSlog("InitBeforeStartServices");
// If a device's clock is before 1970 (before 0), a lot of
// APIs crash dealing with negative numbers, notably
// java.io.File#setLastModified, so instead we fake it and
// hope that time from cell towers or NTP fixes it shortly.
if (System.currentTimeMillis() < EARLIEST_SUPPORTED_TIME) { //获得时间
Slog.w(TAG, "System clock is before 1970; setting to 1970.");
SystemClock.setCurrentTimeMillis(EARLIEST_SUPPORTED_TIME);
}
//
// Default the timezone property to GMT if not set.
//
String timezoneProperty = SystemProperties.get("persist.sys.timezone"); //获得时区
if (timezoneProperty == null || timezoneProperty.isEmpty()) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Timezone not set; setting to GMT.");
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.timezone", "GMT");
}
// If the system has "persist.sys.language" and friends set, replace them with
// "persist.sys.locale". Note that the default locale at this point is calculated
// using the "-Duser.locale" command line flag. That flag is usually populated by
// AndroidRuntime using the same set of system properties, but only the system_server
// and system apps are allowed to set them.
//
// NOTE: Most changes made here will need an equivalent change to
// core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp
if (!SystemProperties.get("persist.sys.language").isEmpty()) { //获得语言
final String languageTag = Locale.getDefault().toLanguageTag();
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.locale", languageTag);
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.language", "");
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.country", "");
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.localevar", "");
}
// The system server should never make non-oneway calls
Binder.setWarnOnBlocking(true);
// The system server should always load safe labels
PackageItemInfo.setForceSafeLabels(true);
// Deactivate SQLiteCompatibilityWalFlags until settings provider is initialized
SQLiteCompatibilityWalFlags.init(null);
// Here we go!
Slog.i(TAG, "Entered the Android system server!");
int uptimeMillis = (int) SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.BOOT_PROGRESS_SYSTEM_RUN, uptimeMillis);
if (!mRuntimeRestart) {
MetricsLogger.histogram(null, "boot_system_server_init", uptimeMillis);
}
// In case the runtime switched since last boot (such as when
// the old runtime was removed in an OTA), set the system
// property so that it is in sync. We can | xq oqi't do this in
// libnativehelper's JniInvocation::Init code where we already
// had to fallback to a different runtime because it is
// running as root and we need to be the system user to set
// the property. http://b/11463182
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.dalvik.vm.lib.2", VMRuntime.getRuntime().vmLibrary());
// Mmmmmm... more memory!
VMRuntime.getRuntime().clearGrowthLimit();
// The system server has to run all of the time, so it needs to be
// as efficient as possible with its memory usage.
VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetHeapUtilization(0.8f);
// Some devices rely on runtime fingerprint generation, so make sure
// we've defined it before booting further.
Build.ensureFingerprintProperty();
// Within the system server, it is an error to access Environment paths without
// explicitly specifying a user.
Environment.setUserRequired(true);
// Within the system server, any incoming Bundles should be defused
// to avoid throwing BadParcelableException.
BaseBundle.setShouldDefuse(true);
// Within the system server, when parceling exceptions, include the stack trace
Parcel.setStackTraceParceling(true);
// Ensure binder calls into the system always run at foreground priority.
BinderInternal.disableBackgroundScheduling(true);
// Increase the number of binder threads in system_server
BinderInternal.setMaxThreads(sMaxBinderThreads);
// Prepare the main looper thread (this thread).
android.os.Process.setThreadPriority(
android.os.Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_FOREGROUND);
android.os.Process.setCanSelfBackground(false);
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
Looper.getMainLooper().setSlowLogThresholdMs(
SLOW_DISPATCH_THRESHOLD_MS, SLOW_DELIVERY_THRESHOLD_MS);
// Initialize native services.
System.loadLibrary("android_servers"); //加载动态库 libandroid_servers.so
// Check whether we failed to shut down last time we tried.
// This call may not return.
performPendingShutdown();
// Initialize the system context.
createSystemContext();
// Create the system service manager.
mSystemServiceManager = new SystemServiceManager(mSystemContext); //创建SystemServiceManaager对象,会对系统服务进行创建,启动和生命周期管理
mSystemServiceManager.setStartInfo(mRuntimeRestart,
mRuntimeStartElapsedTime, mRuntimeStartUptime);
LocalServices.addService(SystemServiceManager.class, mSystemServiceManager);
// Prepare the thread pool for init tasks that can be parallelized
SystemServerInitThreadPool.get();
} finally {
traceEnd(); // InitBeforeStartServices
}
// Start services.
try {
traceBeginAndSlog("StartServices");
startBootstrapServices(); //启动引导服务
startCoreServices(); //启动核心服务
startOtherServices(); //启动其他服务
SystemServerInitThreadPool.shutdown();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Slog.e("System", "******************************************");
Slog.e("System", "************ Failure starting system services", ex);
throw ex;
} finally {
traceEnd();
}
StrictMode.initVmDefaults(null);
if (!mRuntimeRestart && !isFirstBootOrUpgrade()) {
int uptimeMillis = (int) SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
MetricsLogger.histogram(null, "boot_system_server_ready", uptimeMillis);
final int MAX_UPTIME_MILLIS = 60 * 1000;
if (uptimeMillis > MAX_UPTIME_MILLIS) {
Slog.wtf(SYSTEM_SERVER_TIMING_TAG,
"SystemServer init took too long. uptimeMillis=" + uptimeMillis);
}
}
// Loop forever.
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}
- startBootStrapServices():对应系统引导服务。我们熟悉的ATM、AMS、PMS、PKMS服务就是在这启动的
- startCoreServices():对应核心服务。如电池服务就是在这启动
- startOtherServices():对应其他服务。在这个方法中,启动的服务大概有70+个,WMS服务就是在这里启动的
| 引导服务 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| Installer | 系统安装APK时的一个服务,启动完成 Installer 服务之后才能启动其他的服务 |
| ActivityManagerService | 负责四大组件的启动,切换,调度 |
| PowerManagerService | 系统中和 Power 相关的计算,然后决策系统应该如何相应 |
| LightsService | 管理背光显示LED |
| DisplayManagerService | 管理所有显示设备 |
| UserManagerService | 多用户模式管理 |
| SensorService | 为系统提供各种感应器服务 |
| PackageManagerService | 用来对APK进行安装,解析,删除,卸载等操作 |
| … | … |
| 核心服务 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| DropBoxManagerService | 用于生成和管理系运行时的一些日志文件 |
| BatteryService | 管理电池相关服务 |
| UsageStatsService | 手机用户使用每个app的频率,时长 |
| WebViewUpdateService | WebView 更新服务 |
| … | … |
| 其他服务 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| CameraService | 摄像头相关服务 |
| AlarmManagerService | 全局定时器管理服务 |
| InputManagerService | 管理输入事件 |
| WindowManagerService | 窗口管理服务 |
| VrManagerService | VR模式夫管理服务 |
| BluetoothService | 蓝牙管理服务 |
| NotificationManagerService | 通知管理服务 |
| DeviceStorageMonitorService | 存储相关管理服务 |
| LocationManagerService | 定位相关管理服务 |
| AudioService | 音频相关服务 |
| … | … |
startBootStrapServices() startCoreServices() startOtherServices()方法里都是调用类似的方法去开启服务
private void startBootstrapServices() {
Slog.i(TAG, "Reading configuration...");
final String TAG_SYSTEM_CONFIG = "ReadingSystemConfig";
traceBeginAndSlog(TAG_SYSTEM_CONFIG);
SystemServerInitThreadPool.get().submit(SystemConfig::getInstance, TAG_SYSTEM_CONFIG);
traceEnd();
//....
}
mPowerManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(PowerManagerService.class);
以 PowerManagerService 为例,调用了SystemServiceManager 的 startService 方法开启服务
位置: frameworks\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\SystemServiceManager.java
public void startService(@NonNull final SystemService service) {
// Register it.
mServices.add(service); //将PowerManagerService添加到一个ArrayList中进行管理
// Start it.
long time = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
try {
service.onStart(); //调用PowerManagerService的onStart()方法启动系统服务
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to start service " + service.getClass().getName()
+ ": onStart threw an exception", ex);
}
warnIfTooLong(SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - time, service, "onStart");
}
Launcher 启动
系统启动的最后一步是启动一个应用程序用来显示系统中已经安装的应用程序,并作为这些安装程序的启动入口,这个应用程序就是Launcher
上面得知SystemServer 进程启动中会启动很多其他的服务,其中一个就是 ActivityManagerService,在 startOtherServices 中会调用 AMS 的 systemReady() 方法将 Lanuncher 启动起来
mActivityManagerService.systemReady(() -> { //在startOtherService()方法中
Slog.i(TAG, "Making services ready");
traceBeginAndSlog("StartActivityManagerReadyPhase");
mSystemServiceManager.startBootPhase(
SystemService.PHASE_ACTIVITY_MANAGER_READY);
traceEnd();
traceBeginAndSlog("StartObservingNativeCrashes");
try {
mActivityManagerService.startObservingNativeCrashes();
} catch (Throwable e) {
reportWtf("observing native crashes", e);
}
traceEnd();
//...
}, BOOT_TIMINGS_TRACE_LOG);
位置:frameworks\base\services\core\java\com\android\server\am\ActivityManagerService.java
public void systemReady(final Runnable goingCallback, TimingsTraceLog traceLog) {
traceLog.traceBegin("PhaseActivityManagerReady");
//...
synchronized (this) {
//...
startHomeActivityLocked(currentUserId, "systemReady");
//...
}
}
在 AMS 中的 systemReady() 方法中执行 startHomeActivityLocked()方法,传入当前用户ID
boolean startHomeActivityLocked(int userId, String reason) {
if (mFactoryTest == FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL
&& mTopAction == null) {
// We are running in factory test mode, but unable to find
// the factory test app, so just sit around displaying the
// error message and don't try to start anything.
return false;
}
Intent intent = getHomeIntent(); //获取到要启动的HomeActivity的intent对象
//通过PackageManager去获取对应符合的Activity
ActivityInfo aInfo = resolveActivityInfo(intent, STOCK_PM_FLAGS, userId);
if (aInfo != null) {
intent.setComponent(new ComponentName(aInfo.applicationInfo.packageName, aInfo.name));
// Don't do this if the home app is currently being
// instrumented.
aInfo = new ActivityInfo(aInfo);
aInfo.applicationInfo = getAppInfoForUser(aInfo.applicationInfo, userId);
ProcessRecord app = getProcessRecordLocked(aInfo.processName,
aInfo.applicationInfo.uid, true);
if (app == null || app.instr == null) {
//添加FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK启动参数,开启新栈
intent.setFlags(intent.getFlags() | FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
final int resolvedUserId = UserHandle.getUserId(aInfo.applicationInfo.uid);
// For ANR debugging to verify if the user activity is the one that actually
// launched.
final String myReason = reason + ":" + userId + ":" + resolvedUserId;
mActivityStartController.startHomeActivity(intent, aInfo, myReason);
}
} else {
Slog.wtf(TAG, "No home screen found for " + intent, new Throwable());
}
return true;
}
Intent getHomeIntent() {
Intent intent = new Intent(mTopAction, mTopData != null ? Uri.parse(mTopData) : null);
intent.setComponent(mTopComponent); //mTopAction默认为INTENT.ACTION_MAIN
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_DEBUG_TRIAGED_MISSING);
if (mFactoryTest != FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL) {
intent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_HOME); //添加CATEGORY_HOME的category标志
}
return intent;
}
private ActivityInfo resolveActivityInfo(Intent intent, int flags, int userId) {
ActivityInfo ai = null;
ComponentName comp = intent.getComponent();
try {
if (comp != null) {
// Factory test.
ai = AppGlobals.getPackageManager().getActivityInfo(comp, flags, userId);
} else {
ResolveInfo info = AppGlobals.getPackageManager().resolveIntent(
intent,
intent.resolveTypeIfNeeded(mContext.getContentResolver()),
flags, userId);
if (info != null) {
ai = info.activityInfo;
}
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// ignore
}
return ai;
}
//位置:"./frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStartController.java"
void startHomeActivity(Intent intent, ActivityInfo aInfo, String reason) {
mSupervisor.moveHomeStackTaskToTop(reason);
//调用obtainStarter()方法获取到一个ActivityStarter对象
mLastHomeActivityStartResult = obtainStarter(intent, "startHomeActivity: " + reason)
.setOutActivity(tmpOutRecord)
.setCallingUid(0)
.setActivityInfo(aInfo)
.execute();
mLastHomeActivityStartRecord = tmpOutRecord[0];
if (mSupervisor.inResumeTopActivity) {
// If we are in resume section already, home activity will be initialized, but not
// resumed (to avoid recursive resume) and will stay that way until something pokes it
// again. We need to schedule another resume.
mSupervisor.scheduleResumeTopActivities();
}
}
ActivityStarter obtainStarter(Intent intent, String reason) {
return mFactory.obtain().setIntent(intent).setReason(reason); //工厂模式创建ActivityStarter对象
}
//位置"frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStarter.java"
int execute() {
try {
// TODO(b/64750076): Look into passing request directly to these methods to allow
// for transactional diffs and preprocessing.
if (mRequest.mayWait) { //mayWait默认为false
return startActivityMayWait(mRequest.caller, mRequest.callingUid,
mRequest.callingPackage, mRequest.intent, mRequest.resolvedType,
mRequest.voiceSession, mRequest.voiceInteractor, mRequest.resultTo,
mRequest.resultWho, mRequest.requestCode, mRequest.startFlags,
mRequest.profilerInfo, mRequest.waitResult, mRequest.globalConfig,
mRequest.activityOptions, mRequest.ignoreTargetSecurity, mRequest.userId,
mRequest.inTask, mRequest.reason,
mRequest.allowPendingRemoteAnimationRegistryLookup,
mRequest.originatingPendingIntent);
} else {
//执行startActivity()进入Activity的启动流程
return startActivity(mRequest.caller, mRequest.intent, mRequest.ephemeralIntent,
mRequest.resolvedType, mRequest.activityInfo, mRequest.resolveInfo,
mRequest.voiceSession, mRequest.voiceInteractor, mRequest.resultTo,
mRequest.resultWho, mRequest.requestCode, mRequest.callingPid,
mRequest.callingUid, mRequest.callingPackage, mRequest.realCallingPid,
mRequest.realCallingUid, mRequest.startFlags, mRequest.activityOptions,
mRequest.ignoreTargetSecurity, mRequest.componentSpecified,
mRequest.outActivity, mRequest.inTask, mRequest.reason,
mRequest.allowPendingRemoteAnimationRegistryLookup,
mRequest.originatingPendingIntent);
}
} finally {
onExecutionComplete();
}
}
Launcher本身就是一个系统APP,用于显示桌面等,LauncherApp启动之后会执行其生命周期方法初始化桌面布局,至此,Launcher就启动完成了,用户进入到界面,整个Android系统也启动起来

![[自学记录08*]LDR、HDR与ToneMapping](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/4eb14a68616340a186d801650c81be20.png)