愿你出走半生,归来仍是少年!
在人机交互中,最常用的就是鼠标。获取鼠标在三维场景中的空间位置是保证交互结果正确的保障。
1.LabelControl
文本标签控件,可方便的添加在场景顶层。
设置编码及字体可正确的显示出中文。
setFont(osgText::readFontFile("Fonts/simhei.ttf"));
setEncoding(osgText::String::ENCODING_UTF8);
bottomStateLabel = new osgEarth::Util::Controls::LabelControl("底部状态栏", osg::Vec4f(1, 1, 1, 1), 14);
bottomStateLabel->setHorizAlign(osgEarth::Util::Controls::Control::ALIGN_CENTER);
bottomStateLabel->setVertAlign(osgEarth::Util::Controls::Control::ALIGN_BOTTOM);
bottomStateLabel->setBackColor(0, 0, 0, 0.8);
bottomStateLabel->setFont(osgText::readFontFile("Fonts/simhei.ttf"));
bottomStateLabel->setEncoding(osgText::String::ENCODING_UTF8);
bottomStateLabel->setPadding(5);
ref_ptr<osgEarth::Util::Controls::ControlCanvas> canvas = osgEarth::Util::Controls::ControlCanvas::get(this);
canvas->addControl(bottomStateLabel);2.MousePositionEvenHandler
通过继承osgGA::GUIEventHandler进行实现,仅用于鼠标移动时进行鼠标的空间位置解算。分别解算了鼠标所在的地形位置以及空间位置。
#include "MousePositionEvenHandler.h"
Cv::EventHandlers::MousePositionEvenHandler::MousePositionEvenHandler(MapNode* node, osgEarth::Util::Controls::LabelControl* control)
{
this->mapNode = node;
this->label = control;
}
bool Cv::EventHandlers::MousePositionEvenHandler::handle(const osgGA::GUIEventAdapter& ea, osgGA::GUIActionAdapter& aa)
{
osgViewer::Viewer* viewer = dynamic_cast<osgViewer::Viewer*>(&aa);
if (viewer)
{
std::string positionStr;
//鼠标移动
if (ea.getEventType()==ea.MOVE)
{
osg::Vec3d world;
if (mapNode->getTerrain()->getWorldCoordsUnderMouse(aa.asView(), ea.getX(), ea.getY(), world))
{
GeoPoint pt;
pt.fromWorld(mapNode->getMapSRS(), world);
positionStr.append(" 经度:");
positionStr.append(boost::lexical_cast<std::string>(pt.x()));
positionStr.append(" 纬度:");
positionStr.append(boost::lexical_cast<std::string>(pt.y()));
positionStr.append(" 地形高程:");
positionStr.append(boost::lexical_cast<std::string>(pt.z()));
}
osgUtil::LineSegmentIntersector::Intersections hits;
if (viewer->computeIntersections(ea.getX(),ea.getY(),hits))
{
auto first = hits.begin()->getWorldIntersectPoint();
GeoPoint pt;
pt.fromWorld(mapNode->getMapSRS(), first);
positionStr.append(" 交点经度:");
positionStr.append(boost::lexical_cast<std::string>(pt.x()));
positionStr.append(" 交点纬度:");
positionStr.append(boost::lexical_cast<std::string>(pt.y()));
positionStr.append(" 交点高程:");
positionStr.append(boost::lexical_cast<std::string>(pt.z()));
}
this->label->setText(positionStr);
}
}
return false;
}
3.坐标获取原理
一个屏幕坐标通过两种方式获取到的平面位置相差不大,主要集中在高程上。
3.1.地形坐标
通过mapNode->getTerrain()->getWorldCoordsUnderMouse获取屏幕位置在地形中的世界位置,然后转换为空间位置。当场景中有倾斜等地物时,无法捕捉到在倾斜表面作为鼠标的位置。
3.2.空间位置
通过viewer->computeIntersections计算交点位置,当场景中有倾斜等地物时,可捕捉到在倾斜表面的交点作为鼠标的位置。
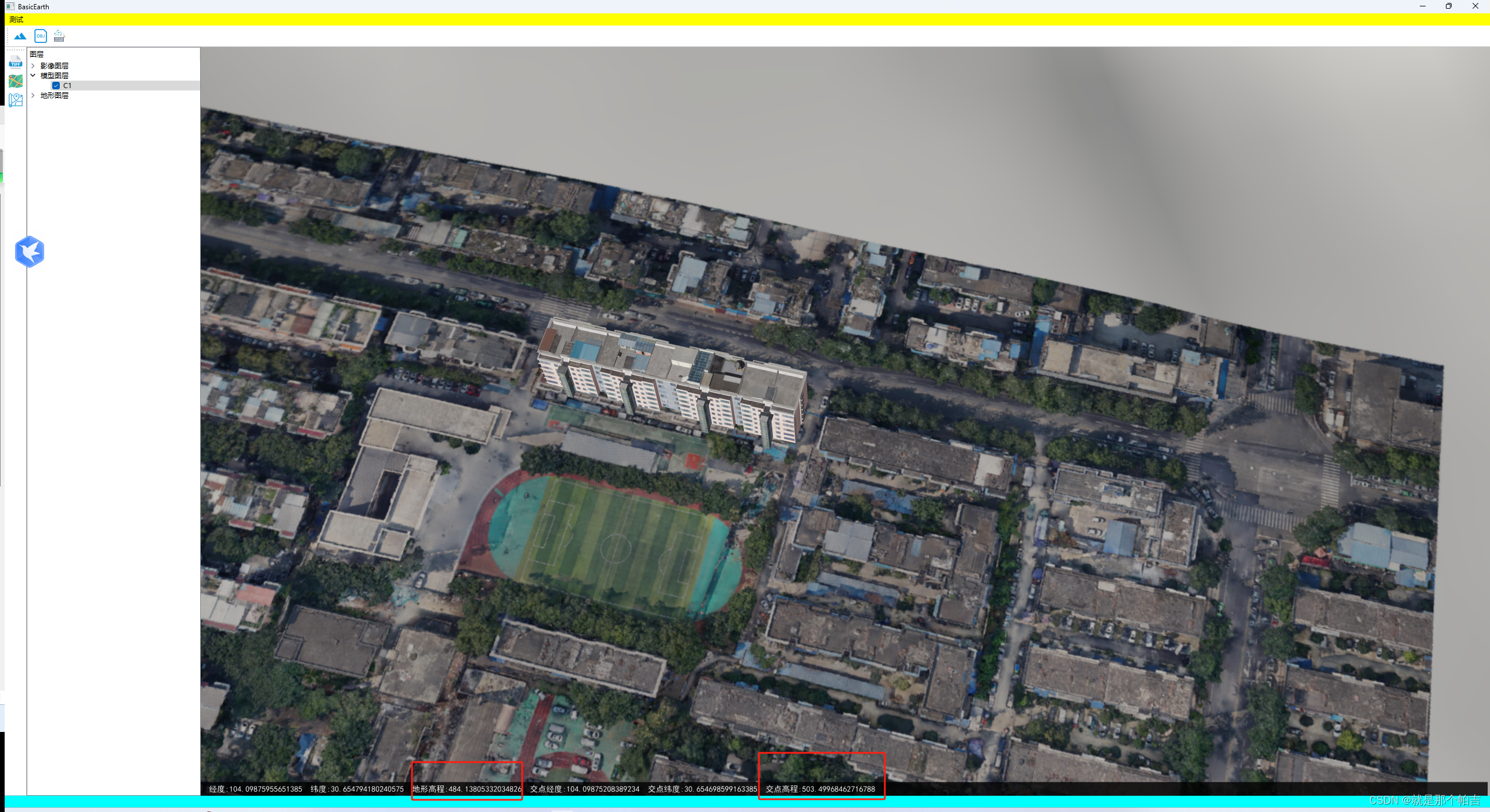
4.效果
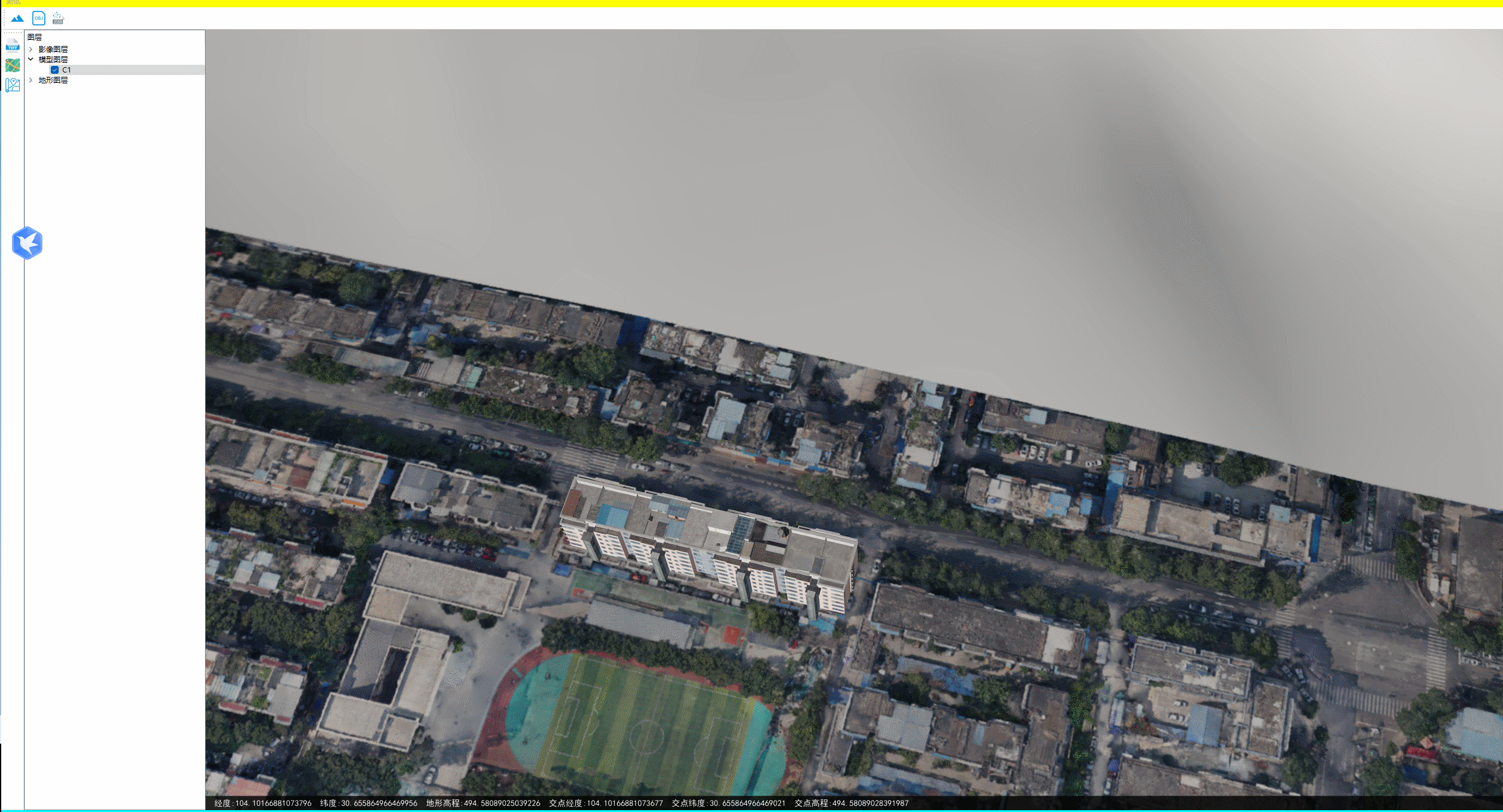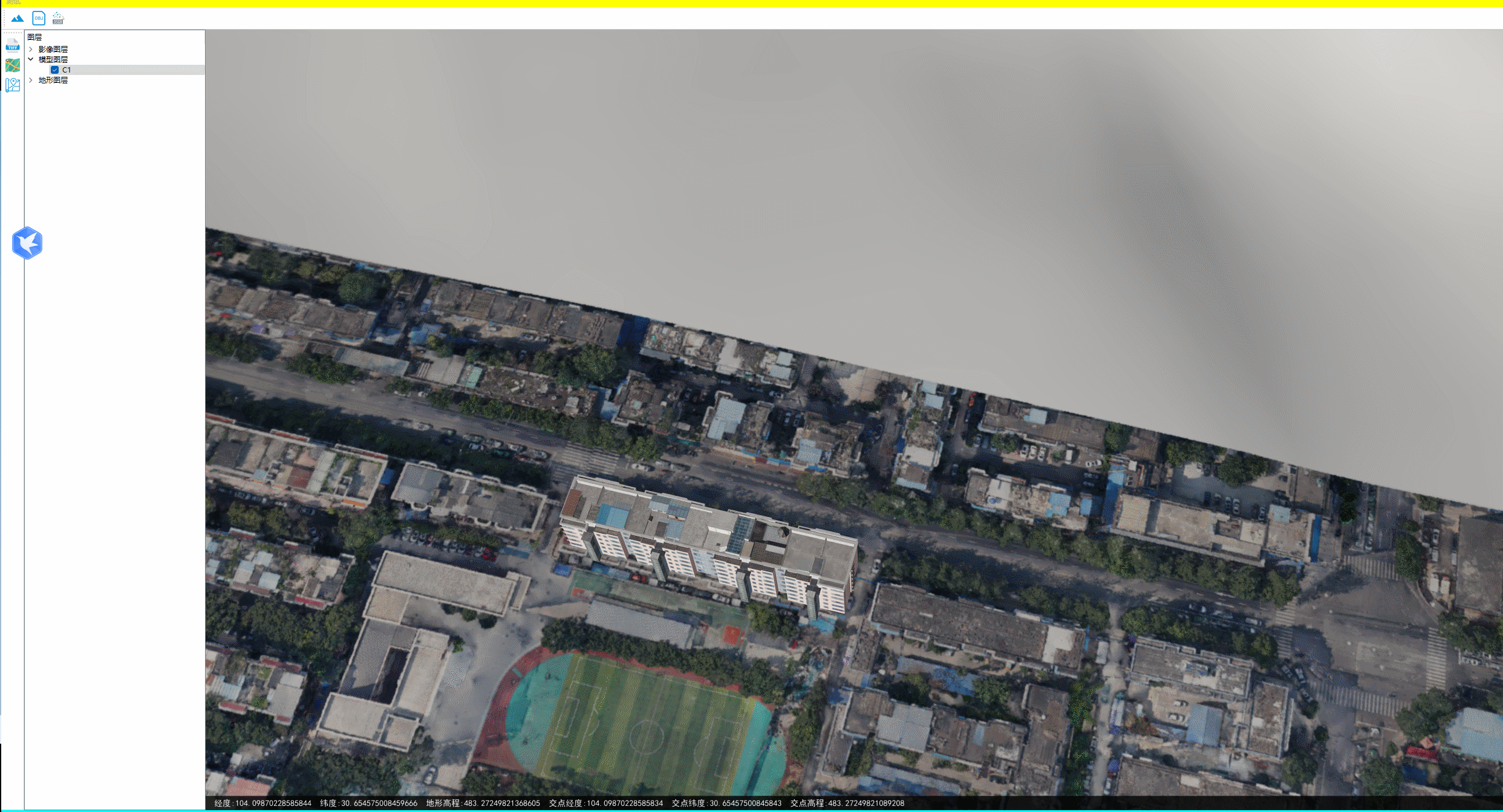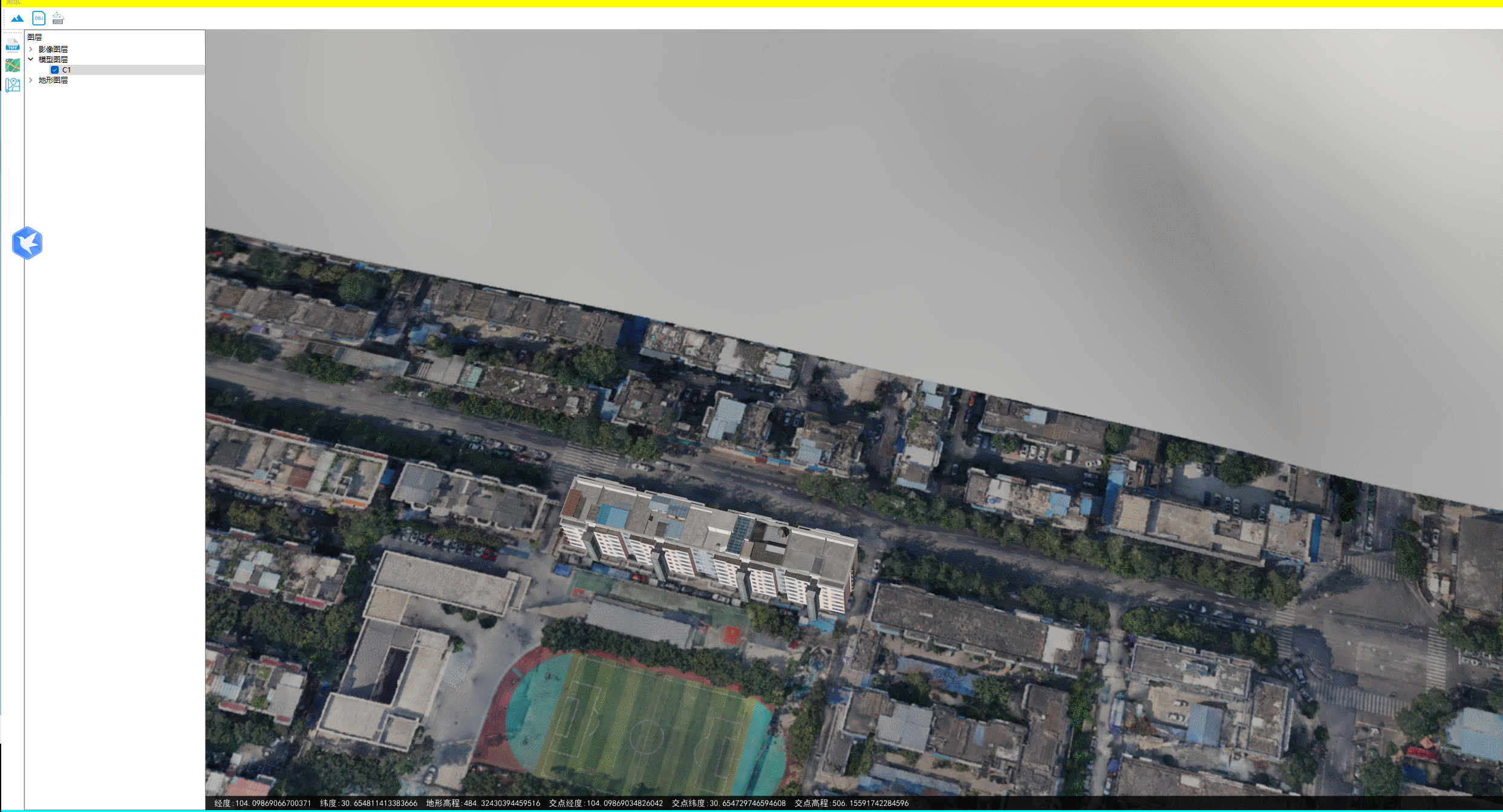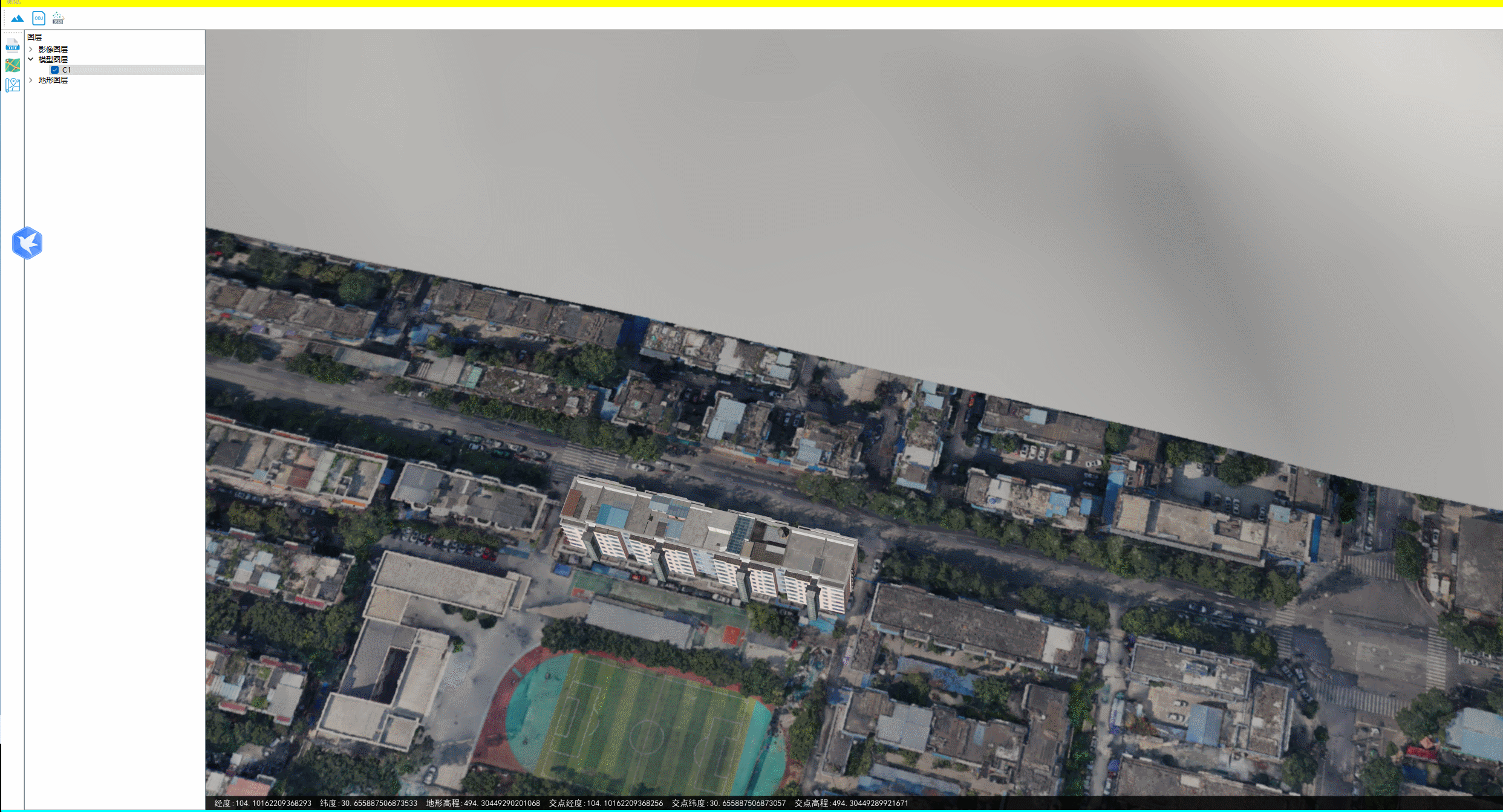
下图为地面无地物情况的情况下,两种方式获取的坐标、高程相差很小。
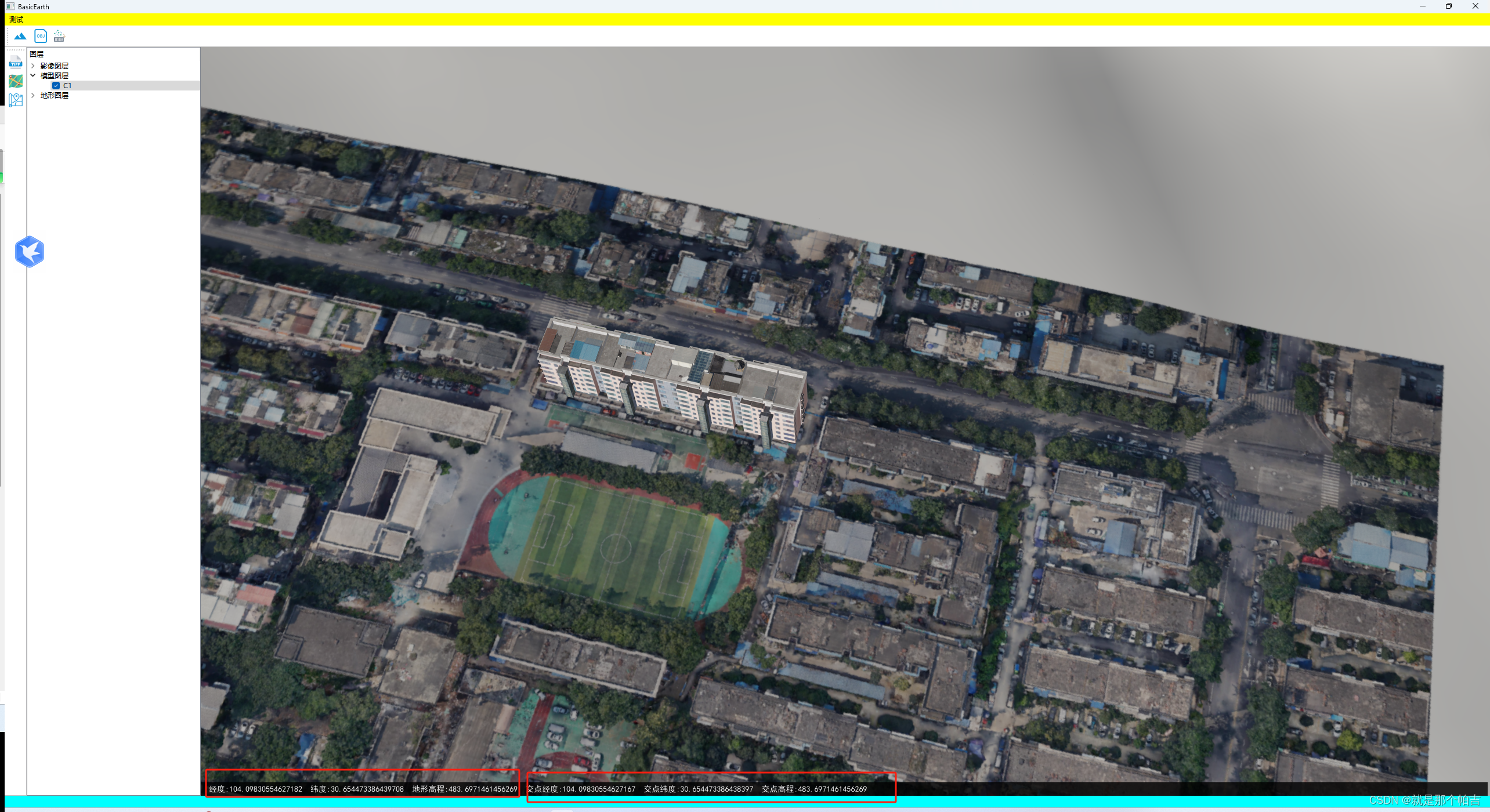
下图为地面存在地物(模型)的情况下。两种方式获取的坐标相差很小,但是高程相差很大。一种只是获取到地形高度,一种获取到了模型的顶面高度。