论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.11907v2
代码地址:https://github.com/huawei-noah/Efficient-AI-Backbones/blob/master/ghostnet_pytorch/ghostnet.py
1.是什么?
Ghost module是一种模型压缩的方法,它可以在保证网络精度的同时减少网络参数和计算量,从而提升计算速度和降低延时。Ghost模块可以代替现有卷积网络中的每一个卷积层。Ghost module的核心思想是将一个卷积层分解成两个较小的卷积层,其中一个卷积层被称为ghost卷积层,它只使用原始卷积层的一小部分通道来计算输出,而另一个卷积层则被称为剩余卷积层,它使用剩余的通道来计算输出。这种分解方式可以大大减少计算量和参数数量,同时保持网络的精度。Ghost module已经被应用于GhostNet等网络架构中,并取得了出色的表现。
2.为什么?
由于硬件资源以及计算量的限制,在嵌入式设备当中部署卷积神经网络是很困难的。想要解决这个问题,就要想方设法的使网络模型更加的轻量化。现存的网络模型轻量化方法一般有两种:模型压缩和轻量化网络设计。
模型压缩:
pruning connection: 减去一些不重要的神经元连接;
channel pruning: 通道剪枝,减去一些无用的通道,以便加速运算;
model quantization: 模型量化,在具有离散值的神经网络中对权重或激活函数进行压缩和计算加速;
tensor decomposition: 张量分解,通过权重的冗余性和low-link来减少参数或计算;
knowledge distillation: 知识蒸馏, 利用大模型来教小模型,提高小模型的性能
轻量化网络设计:
Xception: depthwise conv operation
MobileNet 系列: 深度可分离卷积 depthwise separable conv、inverted resdual block、AutoML technology
ShuffleNet 系列: channel shuffle operation
尽管这些模型获得了良好的性能,但是feature map之间的相关性和冗余性一直没有得到很好的利用。
那么什么是feature map之间的相关性和冗余性呢?
作者在实验过程中将ResNet50的第一个残差组的feature map进行可视化,发现里面有三对feature map(如下图中的红绿蓝三对feature map)它们极其相似,作者认为这些feature map对之间是冗余的(相关的)。
每张图代表一个通道,图中三组颜色相连的图非常相似。论文将一组中的一张图称为本征图(intrinsic),其他和本征图相似的图称为本征图的魅影(ghost)。那么,既然ghost和Intrinsic非常相似,我们是否可以通过一种相对简单的、计算量较少的运算代替运算量大的卷积操作生成ghost图?ghost模块就是基于这种想法,提出用简单的线性运算生成ghost,但总共的通道数(# intrinsic+ghost)以及生成特征图的大小和原来保持一致。

作者考虑到这些feature map层中的冗余信息可能是一个成功模型的重要组成部分,正是因为这些冗余信息才能保证输入数据的全面理解,所以作者在设计轻量化模型的时候并没有试图去除这些冗余feature map,而是尝试使用更低成本的计算量来获取这些冗余feature map。
作者生动的将这些冗余的feature map称为 Ghost(幽灵) 。
3.怎么样?
3.1 Ghost Module
生成ghost图的过程采用简单的线性运算Φ,代替原本的卷积操作。如下图所示,假设原始卷积操作中输入Input与n组k x k的Kernel卷积后生成通道数为n,尺寸为h’ x w’大小的输出。在ghost模型中,我们用m组k x k的Kernel与input进行卷积,生成m x h’ x w’的本征图intrinsic,之后本征图进行线性变换Φ产生ghost图,将intrinsic和ghost一起作为输出。
3.2 模型压缩量定量计算
下面计算用一个ghost模块取代原始的一层卷积操作带来多少计算量、参数量上的优势。
加速比(rs:speed up ratio):这里用计算量来近似代替速度。

压缩比(compression ratio):

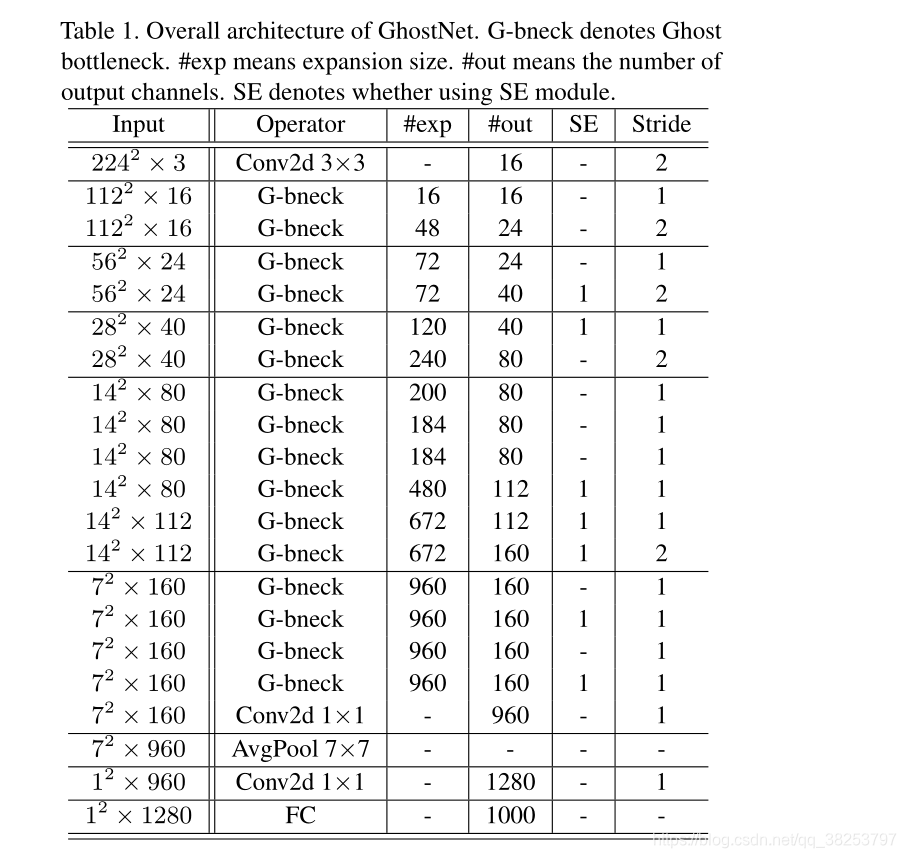
3.3 GhostNet

网络参数
3.4 代码实现
GhostModule
class GhostModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inp, oup, kernel_size=1, ratio=2, dw_size=3, stride=1, relu=True):
super(GhostModule, self).__init__()
self.oup = oup
init_channels = math.ceil(oup / ratio)
new_channels = init_channels*(ratio-1)
self.primary_conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(inp, init_channels, kernel_size, stride, kernel_size//2, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(init_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True) if relu else nn.Sequential(),
)
self.cheap_operation = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(init_channels, new_channels, dw_size, 1, dw_size//2, groups=init_channels, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(new_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True) if relu else nn.Sequential(),
)
def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.primary_conv(x)
x2 = self.cheap_operation(x1)
out = torch.cat([x1,x2], dim=1)
return out[:,:self.oup,:,:]GhostNet
# 2020.06.09-Changed for building GhostNet
# Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. <foss@huawei.com>
"""
Creates a GhostNet Model as defined in:
GhostNet: More Features from Cheap Operations By Kai Han, Yunhe Wang, Qi Tian, Jianyuan Guo, Chunjing Xu, Chang Xu.
https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.11907
Modified from https://github.com/d-li14/mobilenetv3.pytorch and https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models
"""
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import math
__all__ = ['ghost_net']
def _make_divisible(v, divisor, min_value=None):
"""
This function is taken from the original tf repo.
It ensures that all layers have a channel number that is divisible by 8
It can be seen here:
https://github.com/tensorflow/models/blob/master/research/slim/nets/mobilenet/mobilenet.py
"""
if min_value is None:
min_value = divisor
new_v = max(min_value, int(v + divisor / 2) // divisor * divisor)
# Make sure that round down does not go down by more than 10%.
if new_v < 0.9 * v:
new_v += divisor
return new_v
def hard_sigmoid(x, inplace: bool = False):
if inplace:
return x.add_(3.).clamp_(0., 6.).div_(6.)
else:
return F.relu6(x + 3.) / 6.
class SqueezeExcite(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_chs, se_ratio=0.25, reduced_base_chs=None,
act_layer=nn.ReLU, gate_fn=hard_sigmoid, divisor=4, **_):
super(SqueezeExcite, self).__init__()
self.gate_fn = gate_fn
reduced_chs = _make_divisible((reduced_base_chs or in_chs) * se_ratio, divisor)
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.conv_reduce = nn.Conv2d(in_chs, reduced_chs, 1, bias=True)
self.act1 = act_layer(inplace=True)
self.conv_expand = nn.Conv2d(reduced_chs, in_chs, 1, bias=True)
def forward(self, x):
x_se = self.avg_pool(x)
x_se = self.conv_reduce(x_se)
x_se = self.act1(x_se)
x_se = self.conv_expand(x_se)
x = x * self.gate_fn(x_se)
return x
class ConvBnAct(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_chs, out_chs, kernel_size,
stride=1, act_layer=nn.ReLU):
super(ConvBnAct, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_chs, out_chs, kernel_size, stride, kernel_size//2, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_chs)
self.act1 = act_layer(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.act1(x)
return x
class GhostModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inp, oup, kernel_size=1, ratio=2, dw_size=3, stride=1, relu=True):
super(GhostModule, self).__init__()
self.oup = oup
init_channels = math.ceil(oup / ratio)
new_channels = init_channels*(ratio-1)
self.primary_conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(inp, init_channels, kernel_size, stride, kernel_size//2, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(init_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True) if relu else nn.Sequential(),
)
self.cheap_operation = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(init_channels, new_channels, dw_size, 1, dw_size//2, groups=init_channels, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(new_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True) if relu else nn.Sequential(),
)
def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.primary_conv(x)
x2 = self.cheap_operation(x1)
out = torch.cat([x1,x2], dim=1)
return out[:,:self.oup,:,:]
class GhostBottleneck(nn.Module):
""" Ghost bottleneck w/ optional SE"""
def __init__(self, in_chs, mid_chs, out_chs, dw_kernel_size=3,
stride=1, act_layer=nn.ReLU, se_ratio=0.):
super(GhostBottleneck, self).__init__()
has_se = se_ratio is not None and se_ratio > 0.
self.stride = stride
# Point-wise expansion
self.ghost1 = GhostModule(in_chs, mid_chs, relu=True)
# Depth-wise convolution
if self.stride > 1:
self.conv_dw = nn.Conv2d(mid_chs, mid_chs, dw_kernel_size, stride=stride,
padding=(dw_kernel_size-1)//2,
groups=mid_chs, bias=False)
self.bn_dw = nn.BatchNorm2d(mid_chs)
# Squeeze-and-excitation
if has_se:
self.se = SqueezeExcite(mid_chs, se_ratio=se_ratio)
else:
self.se = None
# Point-wise linear projection
self.ghost2 = GhostModule(mid_chs, out_chs, relu=False)
# shortcut
if (in_chs == out_chs and self.stride == 1):
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential()
else:
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_chs, in_chs, dw_kernel_size, stride=stride,
padding=(dw_kernel_size-1)//2, groups=in_chs, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(in_chs),
nn.Conv2d(in_chs, out_chs, 1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_chs),
)
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
# 1st ghost bottleneck
x = self.ghost1(x)
# Depth-wise convolution
if self.stride > 1:
x = self.conv_dw(x)
x = self.bn_dw(x)
# Squeeze-and-excitation
if self.se is not None:
x = self.se(x)
# 2nd ghost bottleneck
x = self.ghost2(x)
x += self.shortcut(residual)
return x
class GhostNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, cfgs, num_classes=1000, width=1.0, dropout=0.2):
super(GhostNet, self).__init__()
# setting of inverted residual blocks
self.cfgs = cfgs
self.dropout = dropout
# building first layer
output_channel = _make_divisible(16 * width, 4)
self.conv_stem = nn.Conv2d(3, output_channel, 3, 2, 1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(output_channel)
self.act1 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
input_channel = output_channel
# building inverted residual blocks
stages = []
block = GhostBottleneck
for cfg in self.cfgs:
layers = []
for k, exp_size, c, se_ratio, s in cfg:
output_channel = _make_divisible(c * width, 4)
hidden_channel = _make_divisible(exp_size * width, 4)
layers.append(block(input_channel, hidden_channel, output_channel, k, s,
se_ratio=se_ratio))
input_channel = output_channel
stages.append(nn.Sequential(*layers))
output_channel = _make_divisible(exp_size * width, 4)
stages.append(nn.Sequential(ConvBnAct(input_channel, output_channel, 1)))
input_channel = output_channel
self.blocks = nn.Sequential(*stages)
# building last several layers
output_channel = 1280
self.global_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
self.conv_head = nn.Conv2d(input_channel, output_channel, 1, 1, 0, bias=True)
self.act2 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.classifier = nn.Linear(output_channel, num_classes)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv_stem(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.act1(x)
x = self.blocks(x)
x = self.global_pool(x)
x = self.conv_head(x)
x = self.act2(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
if self.dropout > 0.:
x = F.dropout(x, p=self.dropout, training=self.training)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
def ghostnet(**kwargs):
"""
Constructs a GhostNet model
"""
cfgs = [
# k, t, c, SE, s
# stage1
[[3, 16, 16, 0, 1]],
# stage2
[[3, 48, 24, 0, 2]],
[[3, 72, 24, 0, 1]],
# stage3
[[5, 72, 40, 0.25, 2]],
[[5, 120, 40, 0.25, 1]],
# stage4
[[3, 240, 80, 0, 2]],
[[3, 200, 80, 0, 1],
[3, 184, 80, 0, 1],
[3, 184, 80, 0, 1],
[3, 480, 112, 0.25, 1],
[3, 672, 112, 0.25, 1]
],
# stage5
[[5, 672, 160, 0.25, 2]],
[[5, 960, 160, 0, 1],
[5, 960, 160, 0.25, 1],
[5, 960, 160, 0, 1],
[5, 960, 160, 0.25, 1]
]
]
return GhostNet(cfgs, **kwargs)
if __name__=='__main__':
model = ghostnet()
model.eval()
print(model)
input = torch.randn(32,3,320,256)
y = model(input)
print(y.size())原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38253797/article/details/118487753
参考:
GhostNet(CVPR 2020) 原理与代码解析