Java - JDK演变之路和JDK21新特性
- 前言
- 一. JDK演变之路
- JDK9 新特性(2017年9月)
- JDK10 新特性(2018年3月)
- JDK11 新特性(2018年9月 - LTS版本)☆
- JDK12 新特性(2019年3月)
- JDK13 新特性(2019年9月)
- JDK14 新特性(2020年3月)
- JDK15 新特性(2020年9月)
- JDK16 新特性(2021年3月)
- JDK17 新特性(2021年9月 - LTS版本)☆
- 二. JDK21 新特性
- String Templates(字符串模板)☆
- Record Patterns(记录模式)
- Pattern Matching for switch ☆
- Generational ZGC
- 虚拟线程 ☆☆
前言
2023年9月19日,Oracle 正式推出了 JDK21 ,并且将为JDK21提供至少八年的支持。JDK21 是 Java 平台的12个功能版本之一,该版本包含了数千项性能、稳定性和安全更新,以及 15 项重大的新特性和增强。在介绍 JDK21之前,我们先看下JDK的演变之路。
一. JDK演变之路
JDK8是我们经常用的版本号,这里就不说了。我们从JDK9开始。只说几个重点的特性。
JDK9 新特性(2017年9月)
- 提供了
List.of()、Set.of()、Map.of()和Map.ofEntries()等工厂方法。 - 模块系统。
- 设置
G1为JVM默认垃圾收集器。 - 支持
http2.0和websocket的API。
JDK10 新特性(2018年3月)
- 可以通过
var关键字实现局部变量的类型推断。 JVM的G1垃圾收集器由单线程改成多线程。
JDK11 新特性(2018年9月 - LTS版本)☆
LTS版本:Long Term Support,也就是官方保证会长期支持的版本。
- 新增
ZGC垃圾收集器。 - 对
Stream、集合相关的API进行增强。
JDK12 新特性(2019年3月)
Switch表达式扩展,可以有返回值。G1收集器的优化,将GC的垃圾分为强制部分和可选部分,强制部分会被回收,可选部分可能不会被回收,提高GC的效率。- 新增
NumberFormat对复杂数字的格式化 - 字符串支持
transform、indent操作
switch语法可以使用箭头语法,并且可以有返回值。
int size = 3;
String cn = switch (size) {
case 1 -> "111";
case 2 -> "222";
case 3, 4 -> "333";
default -> "000";
};
System.out.println(cn);
JDK13 新特性(2019年9月)
- 文本块的引入:使用
"""三个双引号表示文本块,文本块内部就不需要使用换行的转义字符。 ZGC优化,将标记长时间空闲的堆内存空间返还给操作系统。socket底层实现引入NIO。
文本块的案例:
// 改进前
String json = "{\"name\":\"LJJ\",\"age\":\"123\"}"
// 改进后
String json = """
{
"name" : "LJJ",
"age" : "123"
}
""";
JDK14 新特性(2020年3月)
instanceof模式匹配,instanceof类型匹配语法简化,可以直接给对象赋值。- 引入
Record类型,用于标记不可变的数据类型,类似于Lombok的@Data注解。可以自动生成构造和get/set函数。 - 删除
CMS垃圾回收器。
instanceof匹配案例:
// 老写法
Object obj = "你好";
if (obj instanceof String) {
String str = (String) obj;
System.out.println(str);
}
// 新写法
Object obj = "你好";
if (obj instanceof String str) {
// 此时的str不再是 Object 类型,而是 String 类型
System.out.println(str);
}
Record使用案例:
// 老写法
public class User {
private String name = null;
private String password = null;
public User(String name, String password) {
this.name = name;
this.password = password;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
//用于判断是否相等
if (this == o) return true;
if (!(o instanceof User)) return false;
User user = (User) o;
return name.equals(user.name) && password.equals(user.password);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
//hash算法
return Objects.hash(name, password);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "user{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
// 新写法
public record User1(String name, String password) {}
JDK15 新特性(2020年9月)
Sealed Classes(封闭类,预览),通过sealed关键字修饰抽象类限定只允许指定的子类才可以实现或继承抽象类,避免抽象类被滥用。
JDK16 新特性(2021年3月)
Pattern匹配:引入了Pattern匹配特性,使得对对象的模式匹配更加简洁和灵活。(也就是instanceof模式匹配过程中直接给你转型好了)- 对
JDK14和JDK15的一些特性进行正式引入(instanceof模式匹配和Record类)。
JDK17 新特性(2021年9月 - LTS版本)☆
- 移除实验性的
AOT和JIT编译器。 - 恢复始终执行严格模式 (
Always-Strict) 的浮点定义。 - 统一日志异步刷新,先将日志写入缓存,然后再异步刷新。
Spring6和SpringBoot3需要JDK17,算是开源框架对JDK版本升级的一个推动。- 主要也是对前几个版本的功能整合以及完善。
二. JDK21 新特性
这里介绍几个重要的特性:
String Templates(字符串模板)☆
官网案例。在Java当中,往往对于字符串模板,我们都是采取以下几种方式来拼接:
+号拼接。StringBuilder拼接。String.format拼接。- 等等
int x = 10, y = 20;
System.out.println(x + " + " + y + " = " + (x + y));
System.out.println(new StringBuilder().append(x).append(" + ").append(y).append(" = ").append(x + y));
System.out.println(String.format("%1$d + %2$d = %3$d", x, y, x + y));
System.out.println(new MessageFormat("").format("{0} + {1} = {2}", x, y, x + y));
但是有了字符串模板之后,我们就可以更加方便的进行字符串的拼接,例如:
System.out.println(STR. "\{ x } + \{ y } = \{ x + y }" );
有几个特点:
-
用
STR为开头标识。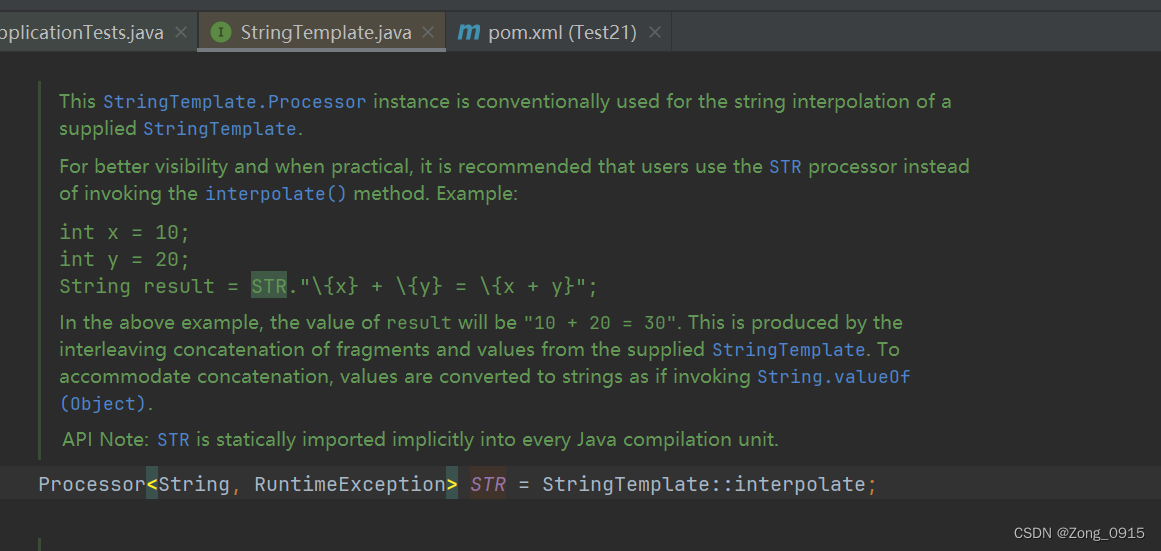
-
每个变量前面需要加
\转义。
其他用法例如:
@Test
public void testStringTemplates() {
int index = 0;
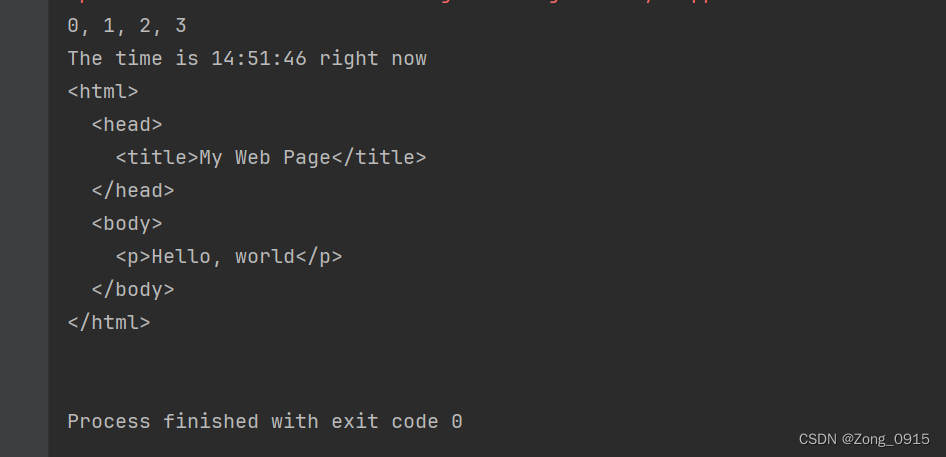
String data = STR. "\{ index++ }, \{ index++ }, \{ index++ }, \{ index++ }" ;
System.out.println(data);
System.out.println(STR. "The time is \{
// The java.time.format package is very useful
DateTimeFormatter
.ofPattern("HH:mm:ss")
.format(LocalTime.now())
} right now" );
//
String title = "My Web Page";
String text = "Hello, world";
String html = STR."""
<html>
<head>
<title>\{title}</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>\{text}</p>
</body>
</html>
""";
System.out.println(html);
}
结果如下:
Record Patterns(记录模式)
官网案例。允许开发人员使用模式来解构记录类的实例,从而简化数据查询。例如:
@Test
public void testRecordPatterns() {
Test21ApplicationTests.printSum16(new Point(1, 2));
Test21ApplicationTests.printSum21(new Point(1, 2));
}
record Point(int x, int y) {
}
static void printSum16(Object obj) {
if (obj instanceof Point p) {
int x = p.x();
int y = p.y();
System.out.println(x + y);
}
}
static void printSum21(Object obj) {
if (obj instanceof Point(int x, int y)) {
System.out.println(x + y);
}
}
两种方式都打印:3。
Pattern Matching for switch ☆
官网案例
static String formatter(Object obj) {
String formatted = "unknown";
if (obj instanceof Integer i) {
formatted = String.format("int %d", i);
} else if (obj instanceof Long l) {
formatted = String.format("long %d", l);
} else if (obj instanceof Double d) {
formatted = String.format("double %f", d);
} else if (obj instanceof String s) {
formatted = String.format("String %s", s);
}
return formatted;
}
@Test
public void testSwitch() {
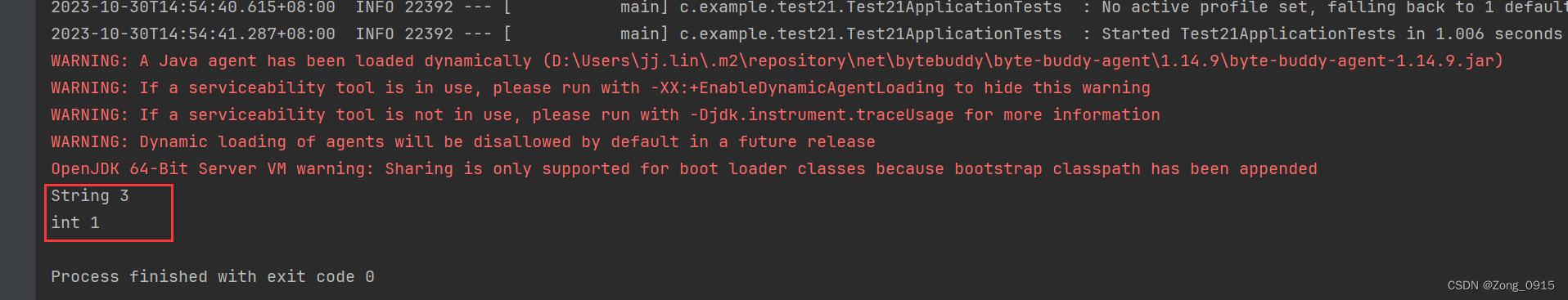
System.out.println(Test21ApplicationTests.formatter("3"));
System.out.println(Test21ApplicationTests.formatter(1));
}
结果如下:
Generational ZGC
官网案例。通过扩展 Z 垃圾收集器(ZGC),为新旧对象分别保留不同的世代,从而提高应用程序的性能。这将允许 ZGC 更频繁地收集年轻代的对象。
虚拟线程 ☆☆
官网案例。可以参考:JDK19 - Virtual Thread 虚拟线程探究
剩余的一些特性可以参考 官网