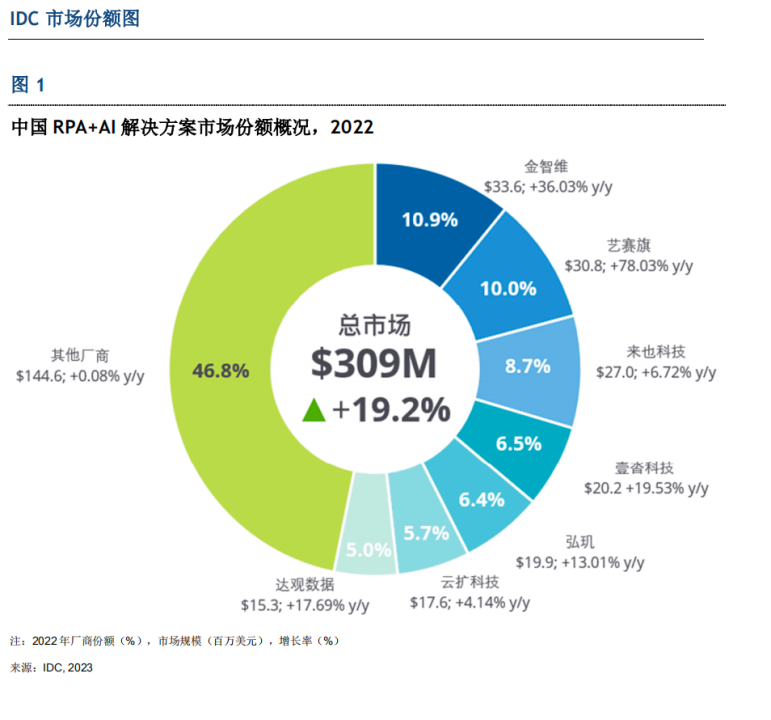
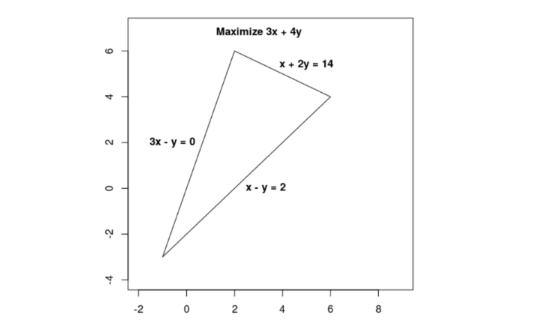
画出可行域如图所示:
Python调用ortools求解
导入求解器
# 导入(或包含)or - tools线性求解器包装器,这是MIP求解器和线性求解器的接口,如下所示
from ortools.linear_solver import pywraplp
声明线性规划求解器
MPsolver is a wrapper for several different solvers, including Glop. The code below declares the GLOP solver.
solver = pywraplp.Solver.CreateSolver("GLOP")
创建决策变量
x = solver.NumVar(0, solver.infinity(), "x")
y = solver.NumVar(0, solver.infinity(), "y")
f"Number of variables ={solver.NumVariables()}"
'Number of variables =2'
约束条件
# Constraint 0: x + 2y <= 14.
solver.Add(x + 2 * y <= 14.0)
# Constraint 1: 3x - y >= 0.
solver.Add(3 * x - y >= 0.0)
# Constraint 2: x - y <= 2.
solver.Add(x - y <= 2.0)
print("Number of constraints =", solver.NumConstraints())
定义目标函数
# Objective function: 3x + 4y.
solver.Maximize(3 * x + 4 * y)
调用求解器
status = solver.Solve()
### 打印结果
if status == pywraplp.Solver.OPTIMAL:
print("Solution:")
print("Objective value =", solver.Objective().Value())
print("x =", x.solution_value())
print("y =", y.solution_value())
else:
print("The problem does not have an optimal solution.")
Solution:
Objective value = 0.0
x = 0.0
y = 0.0
Java调用ortools求解
package org.example;
import com.google.ortools.Loader;
import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPConstraint;
import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPObjective;
import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPSolver;
import com.google.ortools.linearsolver.MPVariable;
/**
* Simple linear programming example.
*/
public final class LinearProgrammingExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Loader.loadNativeLibraries();
MPSolver solver = MPSolver.createSolver("GLOP");
double infinity = java.lang.Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
// x and y are continuous non-negative variables.
MPVariable x = solver.makeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "x");
MPVariable y = solver.makeNumVar(0.0, infinity, "y");
System.out.println("Number of variables = " + solver.numVariables());
// x + 2*y <= 14.
MPConstraint c0 = solver.makeConstraint(-infinity, 14.0, "c0");
c0.setCoefficient(x, 1);
c0.setCoefficient(y, 2);
// 3*x - y >= 0.
MPConstraint c1 = solver.makeConstraint(0.0, infinity, "c1");
c1.setCoefficient(x, 3);
c1.setCoefficient(y, -1);
// x - y <= 2.
MPConstraint c2 = solver.makeConstraint(-infinity, 2.0, "c2");
c2.setCoefficient(x, 1);
c2.setCoefficient(y, -1);
System.out.println("Number of constraints = " + solver.numConstraints());
// Maximize 3 * x + 4 * y.
MPObjective objective = solver.objective();
objective.setCoefficient(x, 3);
objective.setCoefficient(y, 4);
objective.setMaximization();
final MPSolver.ResultStatus resultStatus = solver.solve();
if (resultStatus == MPSolver.ResultStatus.OPTIMAL) {
System.out.println("Solution:");
System.out.println("Objective value = " + objective.value());
System.out.println("x = " + x.solutionValue());
System.out.println("y = " + y.solutionValue());
} else {
System.err.println("The problem does not have an optimal solution!");
}
System.out.println("\nAdvanced usage:");
System.out.println("Problem solved in " + solver.wallTime() + " milliseconds");//运行时间
System.out.println("Problem solved in " + solver.iterations() + " iterations");//迭代次数
}
private LinearProgrammingExample() {
}
}