题目:
样例:
|
|
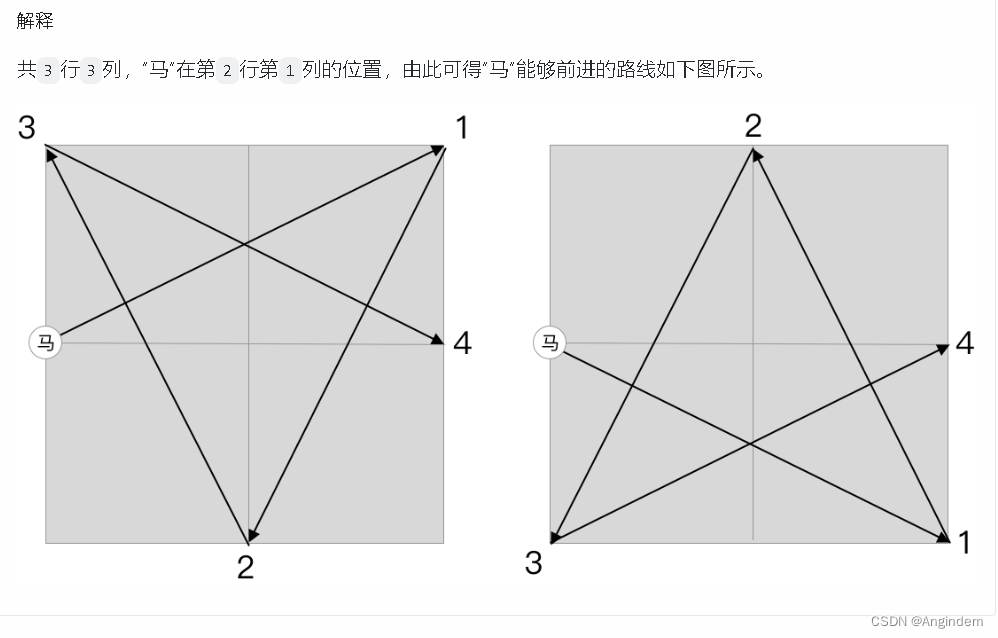
思路:
单纯的BFS走一遍即可,只是方向坐标的移动变化,需要变化一下。
代码详解如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <unordered_map>
#define endl '\n'
#define x first
#define y second
#define mk make_pair
#define YES puts("YES")
#define NO puts("NO")
#define umap unordered_map
#define All(x) x.begin(),x.end()
#pragma GCC optimize(3,"Ofast","inline")
#define IOS std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0)
using namespace std;
const int N = 500;
using PII = pair<int,int>;
// 象棋走动的方向
int dx[8] = {2,2,-2,-2,1,-1,1,-1};
int dy[8] = {1,-1,1,-1,2,2,-2,-2};
int g[N][N],n,m; // 象棋棋盘以及大小
bool st[N][N]; // 标记是否走过当前坐标
PII now; // 当前象棋坐标
inline bool isRun(int &x,int &y)
{
return (x > 0 && x <= n && y > 0 && y <= m && !st[x][y]);
}
inline void BFS()
{
// 初始化坐标所对应的最少步数
memset(g,-1,sizeof g);
g[now.x][now.y] = 0; // 初始化起点步数为 0
int step = 0;
queue<PII>q;
q.emplace(now);
while(q.size())
{
int sz = q.size();
while(sz--)
{
PII tem = q.front();
q.pop(); // 取出当前坐标
st[tem.x][tem.y] = true; // 标记当前坐标
g[tem.x][tem.y] = step; // 存储当前坐标所对应的最少步数
// 尝试往各个方向坐标走动
for(int i = 0;i < 8;++i)
{
int bx = tem.x + dx[i];
int by = tem.y + dy[i];
if(isRun(bx,by))
{
// 如果符合走动条件
// 存储下一个走动的坐标,并标记
q.emplace(mk(bx,by));
st[bx][by] = true;
}
}
}
++step;
}
}
// 打印棋盘各个坐标所对应的最少步数
inline void PrintG()
{
for(int i = 1;i <= n;++i)
{
for(int j = 1;j <= m;++j)
{
if(j > 1) cout << ' '; // 控制输入格式
cout << g[i][j];
}
cout << endl;
}
}
inline void solve()
{
cin >> n >> m >> now.x >> now.y; // 输入所对应的信息
BFS(); // BFS 搜索各个坐标所对应的最少步数
PrintG(); // 输出答案
}
int main()
{
// freopen("a.txt", "r", stdin);
IOS;
int _t = 1;
// cin >> _t;
while (_t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
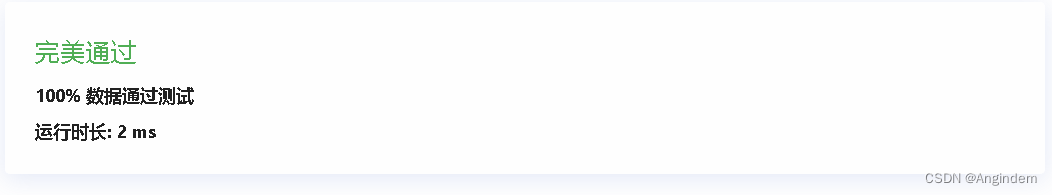
}






![[python 刷题] 287 Find the Duplicate Number](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b43348a261234d148a474a689b958ca8.jpeg#pic_center)