1. 题目链接:30. 串联所有单词的子串
2. 题目描述:
给定一个字符串
s和一个字符串数组words。words中所有字符串 长度相同。
s中的 串联子串 是指一个包含words中所有字符串以任意顺序排列连接起来的子串。
- 例如,如果
words = ["ab","cd","ef"], 那么"abcdef","abefcd","cdabef","cdefab","efabcd", 和"efcdab"都是串联子串。"acdbef"不是串联子串,因为他不是任何words排列的连接。返回所有串联子串在
s中的开始索引。你可以以 任意顺序 返回答案。示例 1:
输入:s = "barfoothefoobarman", words = ["foo","bar"] 输出:[0,9] 解释:因为 words.length == 2 同时 words[i].length == 3,连接的子字符串的长度必须为 6。 子串 "barfoo" 开始位置是 0。它是 words 中以 ["bar","foo"] 顺序排列的连接。 子串 "foobar" 开始位置是 9。它是 words 中以 ["foo","bar"] 顺序排列的连接。 输出顺序无关紧要。返回 [9,0] 也是可以的。示例 2:
输入:s = "wordgoodgoodgoodbestword", words = ["word","good","best","word"] 输出:[] 解释:因为 words.length == 4 并且 words[i].length == 4,所以串联子串的长度必须为 16。 s 中没有子串长度为 16 并且等于 words 的任何顺序排列的连接。 所以我们返回一个空数组。示例 3:
输入:s = "barfoofoobarthefoobarman", words = ["bar","foo","the"] 输出:[6,9,12] 解释:因为 words.length == 3 并且 words[i].length == 3,所以串联子串的长度必须为 9。 子串 "foobarthe" 开始位置是 6。它是 words 中以 ["foo","bar","the"] 顺序排列的连接。 子串 "barthefoo" 开始位置是 9。它是 words 中以 ["bar","the","foo"] 顺序排列的连接。 子串 "thefoobar" 开始位置是 12。它是 words 中以 ["the","foo","bar"] 顺序排列的连接。提示:
1 <= s.length <= 1041 <= words.length <= 50001 <= words[i].length <= 30words[i]和s由小写英文字母组成
3. 算法思路:
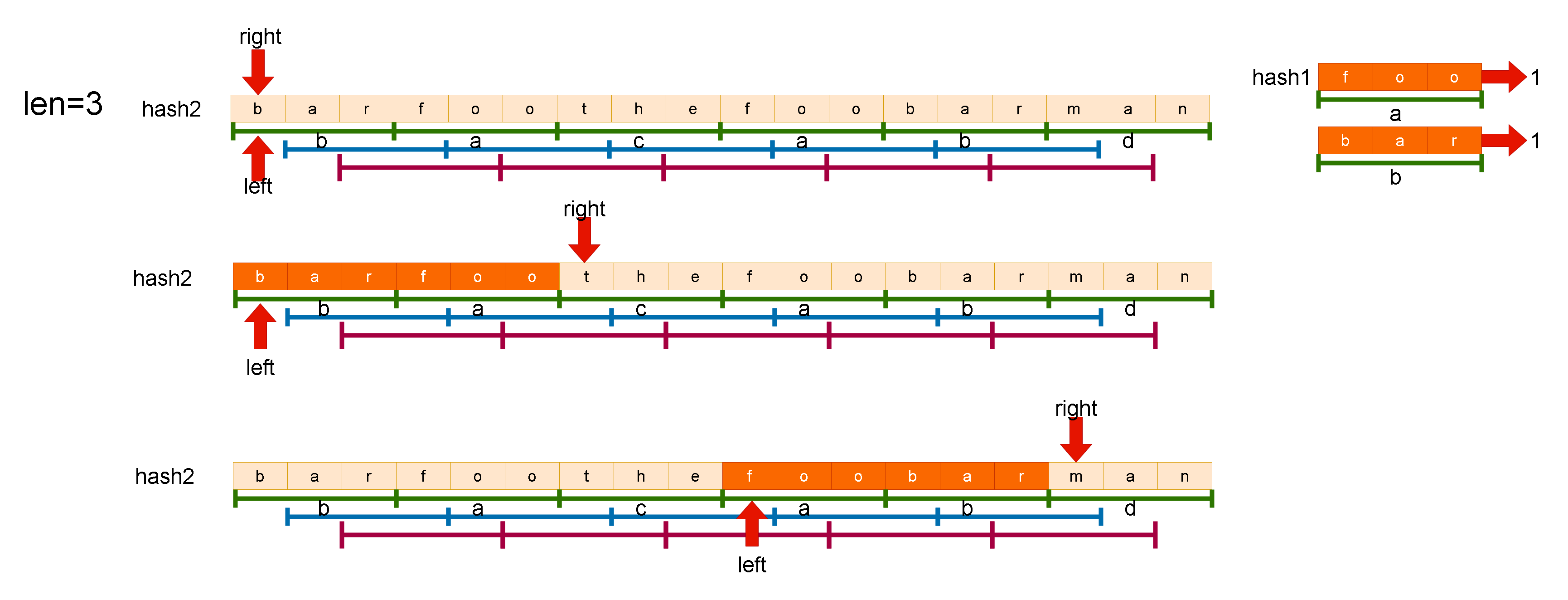
-
这段代码使用滑动窗口的思想来解决字符串匹配的问题。给定一个主串s和一个模式串
words,如果s中存在一个子串,该子串包含words中所有单词且顺序一致,那么这个子串就是words的一个"串联子串"。代码的目标是在s中寻找所有的串联子串的起始位置。 -
首先,用一个哈希表
hash1来保存模式串words中所有单词的频次。然后遍历字符串s的所有可能起始位置,记为x。 -
接下来,构建一个新的哈希表
hash2,用于维护滑动窗口内的单词频次。滑动窗口的起始位置为x,终止位置为y,窗口的长度是len(words中单词长度的总和)。每次移动窗口时,将窗口右边的单词加入到hash2中,并更新对应单词的频次和计数count。如果窗口内的单词频次在hash1中存在且小于等于hash1中的频次,则count加1。 -
如果窗口的长度超过
len*m(m是words中单词的个数),说明窗口左边的单词已经不在窗口范围内,需要移出窗口并更新hash2和count。具体操作是:将窗口左边的单词移出窗口,并更新对应单词的频次和count。 -
最后,当
count等于m时,将窗口左边的起始位置加入到结果集ret中。 -
最后返回
ret,即为所有串联子串的起始位置。
4. C++算法代码:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findSubstring(string s, vector<string>& words) {
vector<int> ret;
unordered_map<string,int > hash1;//保存words里面所有单词的频次
for(auto&s:words)hash1[s]++;
int len=words[0].size();
int m=words.size();
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)//执行len次
{
unordered_map<string,int>hash2;//维护窗口内单词的频次
for(int left=i,right=i,count=0;right+len<=s.size();right+=len)
{
//进窗口+维护count
string in=s.substr(right,len);
hash2[in]++;
if(hash1.count(in)&&hash2[in]<=hash1[in])count++;
//判断
if(right-left+1>len*m)
{
//出窗口+维护count
string out=s.substr(left,len);
if(hash1.count(out)&&hash2[out]<=hash1[out])count--;
hash2[out]--;
left+=len;
}
//更新结果
if(count==m) ret.push_back(left);
}
}
return ret;
}
};







![【LeetCode】144. 二叉树的前序遍历 [ 根结点 左子树 右子树 ]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/7b0de88a1d024efbac59d159655d7de6.png)
![【LeetCode】94. 二叉树的中序遍历 [ 左子树 根结点 右子树 ]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/a0dd44bb339a48828b562c80b25b3fe2.png)