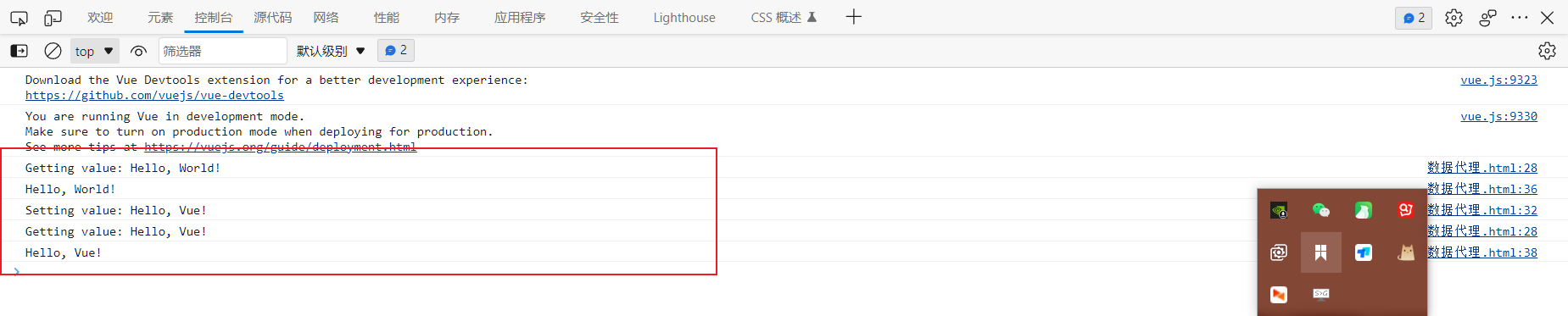
1 map自定义排序
#include <map>
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
int main() {
function<bool(pair<int, int>, pair<int, int>)> cmp = [&](pair<int, int> p1, pair<int, int> p2) -> bool {
return p1.second < p2.second;
};
map< pair<int, int>, int, decltype(cmp)> mp({ {{5, 1}, 2}, {{1, 7}, 3}, {{7, 3}, 2}, {{2, 2}, 1} },cmp);
//map<pair<int, int>, int> mp = { {{5, 2}, 2}, {{1, 2}, 3}, {{7, 2}, 2}, {{2, 2}, 1} };
for (auto& p : mp) {
cout << p.first.first << ' ' << p.first.second << ' ' << p.second << '\n';
}
}
map的类模板参数

map的构造函数

2 map/unordered_map的下标操作
2.1 at()
访问关键字为k的元素,带参数检查:若k不存在容器中,抛出一个out_of_range异常
2.2 下标运算符与解引用迭代器的区别
下标运算符:调用insert返回pair<iterator, bool>用返回的迭代器访问mapped_type
V& operator[](const K& key) {
pair<iterator, bool> ret = _t.insert(make_pair(key, V()));
return ret.first->second;
}
解引用迭代器返回pair<key_type, mapped_type>
2.3 对比vector与map的下标运算符
map<int, int> m;
m[0] = 1;
vector<int> v;
v[0] = 1;
2.4 对map使用find替代下标操作
使用下标操作有一个严重的副作用:如果关键字还未在map中,下标操作会插入一个具有给定关键字的元素(具体原因可以参考2.2节给出的代码),其值为0;
3 用lower_bound、upper_bound、equal_range查找multimap中的元素
- 用lower_bound与upper_bound锁定范围
//authoers的key为作者,mapped为书名
//search_item表示要查找的作者
for (auto beg = authors.lower_bound(search_item), end = authors.upper_bound(search_item); beg != end; ++beg) {
cout << beg->second << endl;
}
- 用equal_range锁定范围
equal_range接受一个关键字,返回一个迭代器pair,若关键字存在,则第一个迭代器指向第一个与关键字匹配的元素,第二个迭代器指向最后一个匹配元素之后的位置。若未找到匹配元素,则两个迭代器都指向关键字可以插入的位置
for (auto pos = authors.equal_range(search_item); pos.first != pos.second; ++pos.first) {
cout << pos.first.second << endl;
}
4 将自定义类型作为无序容器的关键字
默认情况下,无序容器使用关键字类型的==运算符来比较元素,他们还使用一个hash<key_type>类型的对象(仿函数)来生成每个元素的哈希值。标准库为内置类型(包括指针)提供了hash模板,还为一些标准库类型,比如string和智能指针类型定义了hash。
那么如何定义关键字为自定义类型的无序容器呢?
4.1类模板特化
namespace std {
template<>
struct hash<Sales_data> {
//用来散列一个无需容器的类型必须要定义下列类型
typedef size_t result_type;
typedef Sales_data argument_type; //默认情况下,此类型需要operator==
size_t operator()(const Sales_data& s) const {
return hash<string>() (s.bookNo) ^ //构造匿名对象调用operator()返回一个哈希值
hash<unsigned>() (s.units_sold) ^
hash<double>() (s.revenue);
}
}
} //关闭std命名空间
4.2 通过类模板传参
size_t hasher(const Sales_data& sd) {
return hash<string>() (sd.isbn());
}
//如果类中定义了operator==则只需重载哈希函数
bool eqOp(const Sales_data& lhs, const Sales_data& rhs) {
return lhs.isbn() == rhs.isbn();
}
int main() {
using SD_multiset = unordered_multiset<Sales_data, decltype(hahser)*, decltype(eqOp)*>; //C++11
//参数是桶大小、哈希函数指针和相等性判断运算符指针
SD_multiset bookstore(42, hasher, eqOp);
}
- 为什么能通过上述代码完成自定义类型作为无序容器的关键字呢?
- 模板参数

以下是unordered_multiset类的成员类型,其中key_equal是typedef的第三个模板参数,该类创建的对象用于调用operator==比较两关键字是否相等。
| member type | definition | notes |
|---|---|---|
key_type | the first template parameter (Key) | |
mapped_type | the second template parameter (T) | |
value_type | pair<const key_type,mapped_type> | |
hasher | the third template parameter (Hash) | defaults to: hash<key_type> |
key_equal | the fourth template parameter (Pred) | defaults to: equal_to<key_type> |
allocator_type | the fifth template parameter (Alloc) | defaults to: allocator<value_type> |
reference | Alloc::reference | |
const_reference | Alloc::const_reference | |
pointer | Alloc::pointer | for the default allocator: value_type* |
const_pointer | Alloc::const_pointer | for the default allocator: const value_type* |
iterator | a forward iterator to value_type | |
const_iterator | a forward iterator to const value_type | |
local_iterator | a forward iterator to value_type | |
const_local_iterator | a forward iterator to const value_type | |
size_type | an unsigned integral type | usually the same as size_t |
difference_type | a signed integral type | usually the same as ptrdiff_t |
- equal_to类模板的实现:

equal_to类在容器中创建的对象:key_eq(其他无序容器均有)


- 对于unordered系列的构造函数,都有一个接受unsigned int参数的构造函数,表示哈希桶的大小,且不能被隐式类型转换

5 无序容器的管理操作
-
Buckets
-
bucket_count
Return number of buckets (public member function)
-
max_bucket_count
Return maximum number of buckets (public member function)
-
bucket_size
Return bucket size (public member type)
-
bucket
Locate element’s bucket (public member function)
Hash policy
-
load_factor
Return load factor (public member function)
-
max_load_factor
Get or set maximum load factor (public member function )
-
rehash
Set number of buckets (public member function )
-
reserve
Request a capacity change (public member function)
-
#include <unordered_map>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
unordered_map<int, int> mp(8);
cout << mp.bucket_count() << endl; //output: 8
mp.insert({ 1, 1 });
mp.insert({ 2, 1 });
mp.insert({ 3, 1 });
mp.insert({ 11, 1 });
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
cout << mp.bucket_size(i) << ' '; //output:0 0 0 0 1 0 2 1
}
}
6 总结
-
有序容器(
set multiset map multimap)底层为红黑树,使用比较函数来比较关键字,从而将元素按顺序存储。默认情况下,比较操作是采用关键字类型的**<运算符(operator <)** -
无序容器(
unordered_set unordered_multiset unordered_map unordered_multimap)底层是哈希桶,使用关键字类型的**==运算符(operator ==)和一个hash<key_type>类型的对象来计算哈希值从而组织对象(放入哪个哈希桶中)
,使用比较函数来比较关键字,从而将元素按顺序存储。默认情况下,比较操作是采用关键字类型的<运算符(operator <)* -
无序容器(
unordered_set unordered_multiset unordered_map unordered_multimap)底层是哈希桶,使用关键字类型的**==运算符(operator ==)**和一个hash<key_type>类型的对象来计算哈希值从而组织对象(放入哪个哈希桶中)