一、单表查询
素材: 表名:worker-- 表中字段均为中文,比如 部门号 工资 职工号 参加工作 等
1、显示所有职工的基本信息。
select * from worker;
2、查询所有职工所属部门的部门号,不显示重复的部门号。
select distinct 部门号 from worker;
3、求出所有职工的人数。
select count("职工号") as 人数 from worker;
4、列出最高工和最低工资。
select min(工资),max(工资) from worker;
5、列出职工的平均工资和总工资。
select avg(工资) 平均工资,sum(工资) 总工资 from worker;
6、创建一个只有职工号、姓名和参加工作的新表,名为工作日期表。
create table work_day(
职工号 int(11) not null,
姓名 varchar(20) not null,
参加工作 text not null,
primary key(职工号)
);
mysql> insert into work_day(职工号,姓名,参加工作,性别) values(1001,'张三','会计','男');
mysql> insert into work_day(职工号,姓名,参加工作,性别) values(1002,'李四','Java工程师','男');
mysql> insert into work_day(职工号,姓名,参加工作,性别) values(1003,'王亮','Java工程师','男');
mysql> insert into work_day(职工号,姓名,参加工作,性别) values(1004,'赵六','网络工程师','男');
mysql> insert into work_day(职工号,姓名,参加工作,性别) values(1005,'钱七','会计','女');
mysql> insert into work_day(职工号,姓名,参加工作,性别) values(1006,'孙八','运维工程师','女');
7、显示所有女职工的年龄。
select worker.姓名,year(now())-year(出生日期) as 年龄 from worker inner join work_day on(worker.职工号=work_day.职工号) where 性别='女';
8、列出所有姓张的职工的职工号、姓名和出生日期。
select 职工号,姓名,工作时间 from worker where 姓名 like '张%';
select 职工号,姓名,工作时间 from worker where left(姓名,1)='张';
9、列出1960年以前出生s职工的姓名、参加工作日期。
select 姓名,工作时间 from worker where year(出生日期)<1960;
10、列出工资在1000-2000之间的所有职工姓名。
select 姓名 from worker where 工资>1000 and 工资<2000;
11、列出所有陈姓和李姓的职工姓名。
select 职工号,姓名,工作时间 from worker where left(姓名,1)='陈'or left(姓名,1)='李';
select 职工号,姓名,工作时间 from worker where 姓名 like '李%' or '陈%';
12、列出所有部门号为102和103的职工号、姓名、党员否。
select 职工号,姓名,政治面貌 from worker where 部门号=102 or 部门号=103;
13、将职工表worker中的职工按出生的先后顺序排序。
select * from worker order by 出生日期 asc;
14、显示工资最高的前3名职工的职工号和姓名。
select 职工号,姓名 from worker order by 工资 desc limit 3;
15、求出各部门党员的人数。
select distinct(部门号),count(政治面貌) as 党员人数 from worker where 政治面貌='党员' group by 部门号;
16、统计各部门的工资和平均工资
select distinct(部门号),sum(工资) as 工资,avg(工资) as 平均工资 from worker group by 部门号;
17、列出总人数大于4的部门号和总人数。
select distinct(部门号),count(职工号) as 总人数 from worker group by 部门号 having count(职工号)>=4;
二、多表查询
1.创建student和score表
CREATE TABLE student (
id INT(10) NOT NULL UNIQUE PRIMARY KEY ,
name VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL ,
sex VARCHAR(4) ,
birth YEAR,
department VARCHAR(20) ,
address VARCHAR(50)
);
创建score表。SQL代码如下:
CREATE TABLE score (
id INT(10) NOT NULL UNIQUE PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT ,
stu_id INT(10) NOT NULL ,
c_name VARCHAR(20) ,
grade INT(10)
);
2.为student表和score表增加记录
向student表插入记录的INSERT语句如下:
INSERT INTO student VALUES( 901,'张老大', '男',1985,'计算机系', '北京市海淀区');
INSERT INTO student VALUES( 902,'张老二', '男',1986,'中文系', '北京市昌平区');
INSERT INTO student VALUES( 903,'张三', '女',1990,'中文系', '湖南省永州市');
INSERT INTO student VALUES( 904,'李四', '男',1990,'英语系', '辽宁省阜新市');
INSERT INTO student VALUES( 905,'王五', '女',1991,'英语系', '福建省厦门市');
INSERT INTO student VALUES( 906,'王六', '男',1988,'计算机系', '湖南省衡阳市');
向score表插入记录的INSERT语句如下:
INSERT INTO score VALUES(NULL,901, '计算机',98);
INSERT INTO score VALUES(NULL,901, '英语', 80);
INSERT INTO score VALUES(NULL,902, '计算机',65);
INSERT INTO score VALUES(NULL,902, '中文',88);
INSERT INTO score VALUES(NULL,903, '中文',95);
INSERT INTO score VALUES(NULL,904, '计算机',70);
INSERT INTO score VALUES(NULL,904, '英语',92);
INSERT INTO score VALUES(NULL,905, '英语',94);
INSERT INTO score VALUES(NULL,906, '计算机',90);
INSERT INTO score VALUES(NULL,906, '英语',85);
3.查询student表的所有记录
select * from student;
4.查询student表的第2条到4条记录
select * from student limit 1,3;
5.从student表查询所有学生的学号(id)、姓名(name)和院系(department)的信息
select id,name,department from student;
6.从student表中查询计算机系和英语系的学生的信息
select * from student where department='计算机系' or department='英语系';
7.从student表中查询年龄18~22岁的学生信息
select * from student where (year(now())-birth)>18 and (year(now())-birth)<22;
8.从student表中查询每个院系有多少人
select distinct(department),count(id) as 人数 from student group by department;
9.从score表中查询每个科目的最高分
select c_name ,max(grade) as 最高分 from score group by c_name;
10.查询李四的考试科目(c_name)和考试成绩(grade)
> select score.c_name,score.grade from score inner join student on(student.id=score.stu_id) where student.name='李四';
11.用连接的方式查询所有学生的信息和考试信息
select * from score inner join student on(student.id=score.stu_id);
12.计算每个学生的总成绩select student.name,sum(score.grade) as 总成绩 from score inner join student on(student.id=score.stu_id) group by student.name;
13.计算每个考试科目的平均成绩
select c_name,avg(grade) as average from score group by c_name;
14.查询计算机成绩低于95的学生信息
select * from score inner join student on(score.stu_id=student.id) where score.c_name='计算机'and score.grade<95;
15.查询同时参加计算机和英语考试的学生的信息
select * from student,(select * from score where c_name='英语') as s1 inner join (select * from score where c_name='计算机') as s2 on s1.stu_id=s2.stu_id where student.id=s1.stu_id;
16.将计算机考试成绩按从高到低进行排序
select grade from score where c_name='计算机' order by grade desc;
17.从student表和score表中查询出学生的学号,然后合并查询结果
select * from score inner join student on(student.id=score.stu_id);
18.查询姓张或者姓王的同学的姓名、院系和考试科目及成绩
select student.name,student.department,score.c_name,score.grade from score inner join student on(student.id=score.stu_id) where student.name like '张%' or student.name like '王%';
19.查询都是湖南的学生的姓名、年龄、院系和考试科目及成绩
select student.name,student.birth,student.department,score.c_name,score.grade from score inner join student on(student.id=score.stu_id) where student.address like '湖南%';
select student.name,student.birth,student.department,score.c_name,score.grade from score inner join student on(student.id=score.stu_id) where left(student.address,2)= '湖南';
三.面试题
create table student2(
s_id int(10) not null unique primary key comment '学号',
s_name varchar(20) not null comment '姓名',
s_birth date not null comment '生日',
s_sex enum("男", "女") default "男" comment '性别'
)comment ='学生表';
INSERT INTO student2 (s_id,s_name,s_birth,s_sex) VALUES (001, '潘帅', '2002-9-14', '男');
INSERT INTO student2 (s_id,s_name,s_birth,s_sex) VALUES (002, '王美丽', '2004-1-14', '女');
INSERT INTO student2 (s_id,s_name,s_birth,s_sex) VALUES (003, '张帅', '2012-5-4', '男');
INSERT INTO student2 (s_id,s_name,s_birth,s_sex) VALUES (004, '李帅', '2002-5-4', '男');
INSERT INTO student2 (s_id,s_name,s_birth,s_sex) VALUES (005, '吴美', '1999-4-10', '女');
INSERT INTO student2 (s_id,s_name,s_birth,s_sex) VALUES (006, '李七', '2006-7-14', '男');
INSERT INTO student2 (s_id,s_name,s_birth,s_sex) VALUES (007, '张六', '2001-9-14', '男');
INSERT INTO student2 (s_id,s_name,s_birth,s_sex) VALUES (008,'吴雪', '2008-1-24', '女');
create table course(
c_id int(10) not null unique primary key AUTO_INCREMENT comment '课程编号',
c_name varchar(20) not null comment '课程名称',
t_id int(10) not null comment '教师编号',
foreign key(t_id) references teacher(t_id)
)comment ='课程表';
INSERT INTO course(c_id,c_name,t_id) VALUES (null, '计算机',01 );
INSERT INTO course(c_id,c_name,t_id) VALUES (null, '英语',02 );
INSERT INTO course(c_id,c_name,t_id) VALUES (null, '数学',03 );
create table teacher(
t_id int(10) not null unique primary key comment '教师编号',
t_name varchar(20) not null comment '姓名'
)comment='教师表';
insert into teacher values('01' , '张三');
insert into teacher values('02' , '李四');
insert into teacher values('03' , '王五');
create table score2(
s_id int(10) comment '学号',
c_id int(10) comment '课程编号',
s_score decimal(18,1) comment '成绩'
)comment='成绩表';
insert into score2 values('001' , '01' , 80);
insert into score2 values('001' , '02' , 90);
insert into score2 values('001' , '03' , 99);
insert into score2 values('002' , '01' , 70);
insert into score2 values('002' , '02' , 60);
insert into score2 values('002' , '03' , 80);
insert into score2 values('003' , '01' , 80);
insert into score2 values('003' , '02' , 80);
insert into score2 values('003' , '03' , 80);
insert into score2 values('004' , '01' , 50);
insert into score2 values('004' , '02' , 30);
insert into score2 values('004' , '03' , 20);
insert into score2 values('005' , '01' , 76);
insert into score2 values('005' , '02' , 87);
insert into score2 values('006' , '01' , 31);
insert into score2 values('006' , '03' , 34);
insert into score2 values('007' , '02' , 89);
insert into score2 values('007' , '03' , 98);
insert into score2 values('008' , '02' , 79);
insert into score2 values('008' , '03' , 68);
查询所有学生的学号、姓名、选课数、总成绩。
select student2.s_id,student2.s_name,r.选课数,r.总成绩 from student2,(select score2.s_id,sum(score2.s_score) as 总成绩,count(score2.s_score) as 选课数 from score2 group by score2.s_id) as r where student2.s_id=r.s_id;
查询学过"张三"老师所教的所有课程的同学的学号和姓名。
select student2.s_id,student2.s_name from student2,score2,teacher,course where student2.s_id=score2.s_id and course.t_id=teacher.t_id and score2.c_id=course.c_id and teacher.t_name='张三';
查询和'02'号同学学习的课程完全相同的其他同学学号和姓名。
不会写
使用分段[100-85],[85-70],[70-60],[<60]来统计各科成绩,分别统计各分数段的人数:课程ID和课程名称
select course.c_name, course.c_id,
sum(case when score2.s_score<=100 and score2.s_score>85 then 1 else 0 end) as "[100-85]",
sum(case when score2.s_score<=85 and score2.s_score>70 then 1 else 0 end) as "[85-70]",
sum(case when score2.s_score<=70 and score2.s_score>60 then 1 else 0 end) as "[70-60]",
sum(case when score2.s_score<=60 and score2.s_score>0 then 1 else 0 end) as "[60-0]"
from score2 left join course
on score2.c_id = course.c_id
group by score2.c_id;
四.

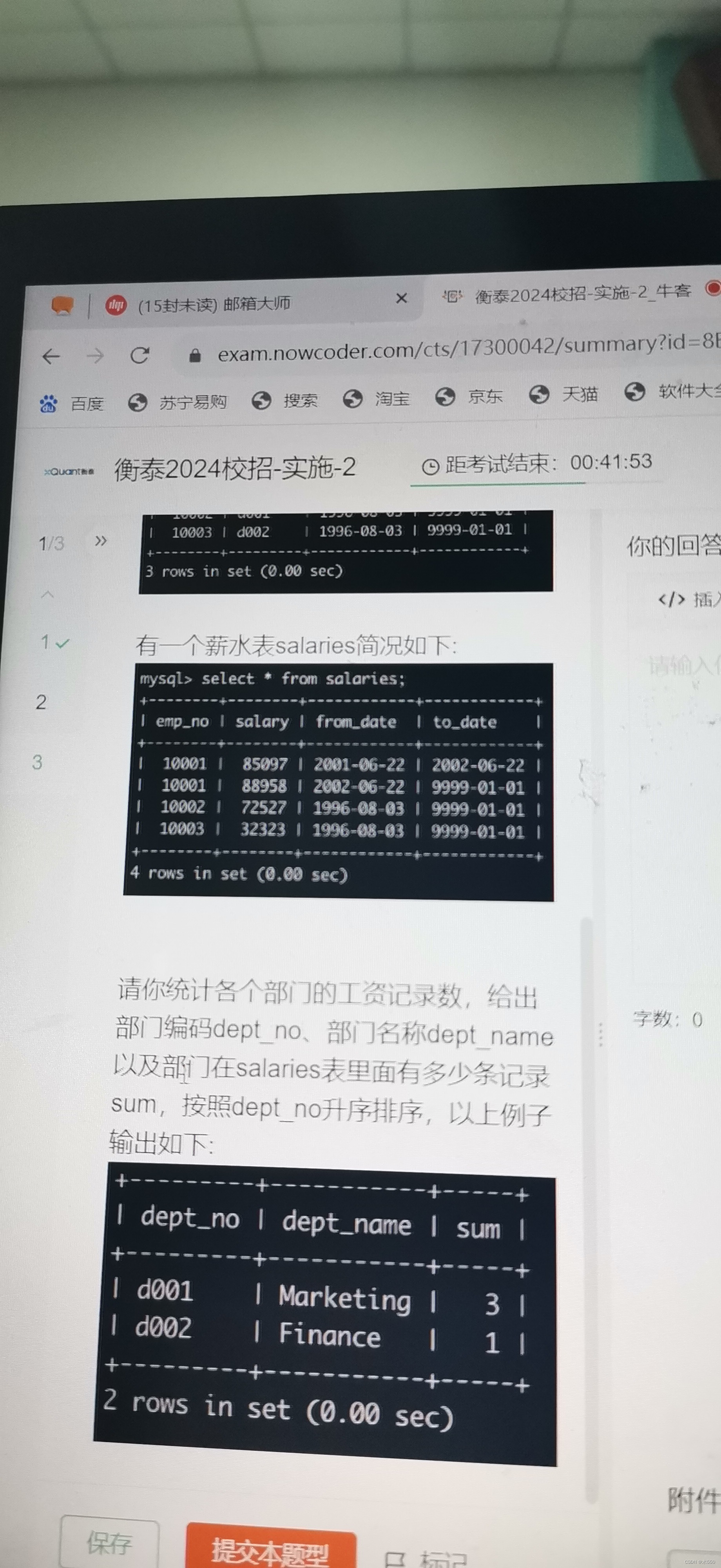
create table departments(
dept_no varchar(10) not null,
dept_name varchar(10) not null
);
insert into departments values('d001','Marketing');
insert into departments values('d002','Finance');
create table dept_emp(
emp_no int(20) not null,
dept_no varchar(10) not null,
from_date date not null,
to_date date not null
);
insert into dept_emp values(10001,'d001','2001-06-22','9999-01-01');
insert into dept_emp values(10002,'d001','1996-08-03','9999-01-01');
insert into dept_emp values(10003,'d002','1996-08-03','9999-01-01');
create table salaries(
emp_no int(20) not null,
salary int(20) not null,
from_date date not null,
to_date date not null
);
insert into salaries values(10003,85097,'2001-06-22','2002-06-22');
insert into salaries values(10001,88958,'1996-08-03','9999-01-01');
insert into salaries values(10002,72527,'1996-08-03','9999-01-01');
insert into salaries values(10003,32323,'1996-08-03','9999-01-01');