文章目录
- 1. 相关概念
- 2. 代码中理解
- 4. 子类访问父类的修饰符权限说明
1. 相关概念
- 定义:
在子类中可以根据需要对从父类中继承来的方法进行改造,也称方法的重置、覆盖。在程序执行时,子类的方法将覆盖父类的方法。 - 要求:
(1)重写方法必须和被重写方法具有相同的方法名称、参数列表和返回值类型。
(2)重写方法不能使用比被重写方法更严格的访问权限。(如果父类方法的修饰符时public,那么子类方法的修饰符只能是public了)
注意:如果现在父类的一个方法定义成 private 访问权限,在子类中将此方法声明为 default 访问权限,那么这样还叫重写吗? :不叫重写,因为子类不能访问父类的私有东西 。
(3)重写和被重写的方法须同时为 static 的,或同时为非 static 的
(4)子类方法抛出的异常不能大于父类被重写方法的异常
2. 代码中理解
创建一个父类Person,创建一个子类Student,在子类中重写父类的方法与不重写父类的方法及进行比较
父类Person代码:
package day07;
public class Person {
int age;
String name;
int sex;
public void showInfo() {
System.out.println(this.age);
System.out.println(this.name);
System.out.println(this.sex);
}
public void setInfo(int age, String name, int sex) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
}
}
子类Student代码:
情况一:不重写父类代码的showInfo方法
package day07;
public class Student extends Person {
String school;
// @Override
// public void showInfo() {
// System.out.println("以下是student类对Person类的showInfo方法的重写");
// System.out.println(this.age);
// System.out.println(this.name);
// System.out.println(this.sex);
//
// }
public static void main(String[] args) { //主函数
Student stu = new Student(); //创建本类中的对象Student
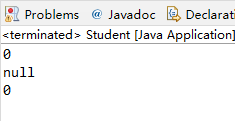
stu.showInfo(); // 本类中没有showInfo方法,而父类有该方法,故调用父类方法
}
}
运行结果:
情况二:重写父类代码的showInfo方法
package day07;
public class Student extends Person {
String school;
@Override
public void showInfo() {
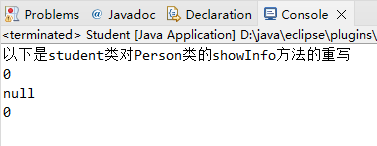
System.out.println("以下是student类对Person类的showInfo方法的重写");
System.out.println(this.age);
System.out.println(this.name);
System.out.println(this.sex);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student stu = new Student();
stu.showInfo();
}
}
运行结果:
4. 子类访问父类的修饰符权限说明
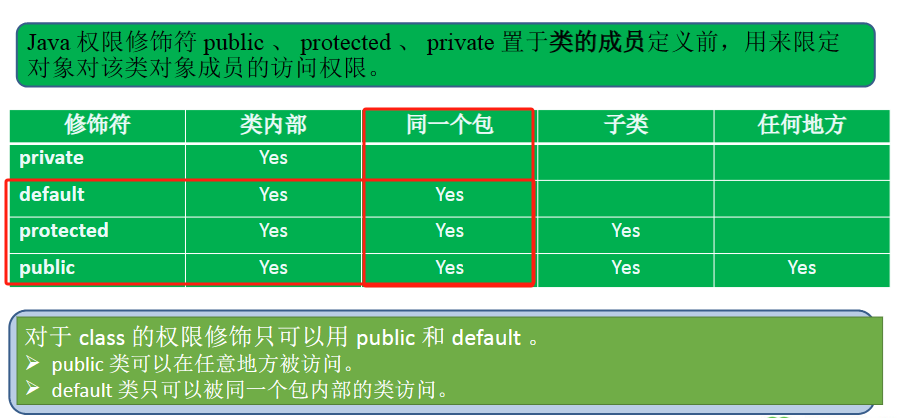
(1)如果子类和父类在同一个包下,那么对于父类的成员修饰符只要不是private,那就可以使用

(2)如果子类和父类不在同一个包下,那么子类只能使用父类中的protected和public修饰的成员






![[计算机提升] Windows系统权限](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/182d2ed4ed114041a9806ee0a4f5fad0.png)