文章目录
- 1. DispatcherServlet 的 service 方法
- 1.1. processRequest 方法
- 1.2. doService 方法
背景:平时我们学习 MVC 重点关注的时DispatcherServlet 的 doDispatcher 方法,但是在 doDispatcher 方法之前 还有请求处理的前置过程,这个过程作为一个高级程序员是必须要了解的。
1. DispatcherServlet 的 service 方法
DispatcherServlet�的继承关系如下图:
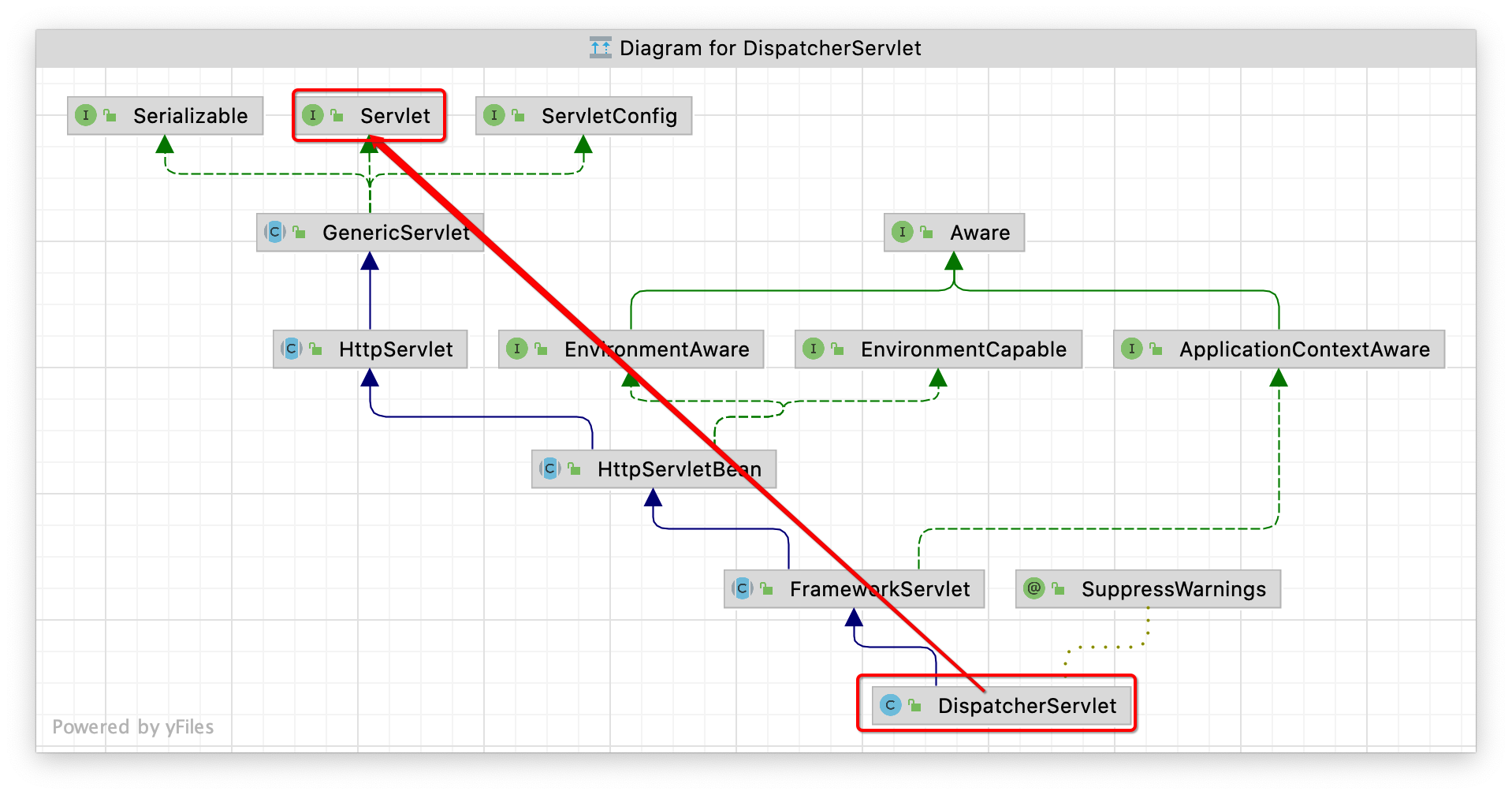
因为是 Servlet,自然看它的 service 方法
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res)
throws ServletException, IOException
{
HttpServletRequest request;
HttpServletResponse response;
if (!(req instanceof HttpServletRequest &&
res instanceof HttpServletResponse)) {
throw new ServletException("non-HTTP request or response");
}
request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
service(request, response);
}
为了处理 patch 请求
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpMethod httpMethod = HttpMethod.resolve(request.getMethod());
if (httpMethod == HttpMethod.PATCH || httpMethod == null) {
processRequest(request, response);
}
else {
super.service(request, response);
}
}
各种请求类型分发:
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException
{
String method = req.getMethod();
if (method.equals(METHOD_GET)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
if (lastModified == -1) {
// servlet doesn't support if-modified-since, no reason
// to go through further expensive logic
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
long ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader(HEADER_IFMODSINCE);
if (ifModifiedSince < lastModified) {
// If the servlet mod time is later, call doGet()
// Round down to the nearest second for a proper compare
// A ifModifiedSince of -1 will always be less
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
resp.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_MODIFIED);
}
}
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_HEAD)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doHead(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_POST)) {
doPost(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_PUT)) {
doPut(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_DELETE)) {
doDelete(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_OPTIONS)) {
doOptions(req,resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_TRACE)) {
doTrace(req,resp);
} else {
//
// Note that this means NO servlet supports whatever
// method was requested, anywhere on this server.
//
String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented");
Object[] errArgs = new Object[1];
rArgs[0] = method;
errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs);
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED, errMsg);
}
}
各种 doXxx 方法会流转到,以下以 doGet 为例子,其它类似。特殊的请求方法有特殊处理,我们不用管。
@Override
protected final void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
processRequest(request, response);
}
继续看 processRequest 方法
1.1. processRequest 方法
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Throwable failureCause = null;
// <1>
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request);
// <2>
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);
// <3>
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor());
// <4>
initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
try {
// <5>
doService(request, response);
}
catch (ServletException | IOException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex);
}
// <6>
finally {
resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if (requestAttributes != null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
}
logResult(request, response, failureCause, asyncManager);
publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause);
}
}
- 在<1>处,获取之前的语言上下文。然后构建本次的语言上下文。LocaleContext
语言上下文是可以继承的。把之前的保存下来,在请求处理完之后要“还原”。
- 在<2>处,获取之前的“请求属性上下文”RequestAttributes,具体实现类是:ServletRequestAttributes��
这个上下文不能继承,必须是当次请求的。
- 在<3>处,获取“Web 的异步管理器”
此处与异步请求相关:RequestBindingInterceptor�
- 在<4>处,绑定 2 个上下文。把 LocaleContext� 绑定到LocaleContextHolder�中,把 ServletRequestAttributes� 绑定到RequestContextHolder�中
这个上下文非常有用,Web 的很多工具类使用到这个上下文来简化编程。不需要传参数request,直接在任意位置获取request。
- 在<5>处,具体如何处理请求。后续会详细分析
- 在<6>处,清尾操作。
1、把之前的2个上下文还原。
2、记录请求的日志(此处是否就是框架提供的打印响应日志的地方?)
3、发布事件(请求处理完成事件ServletRequestHandledEvent�)
1.2. doService 方法
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
logRequest(request);
// Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include,
// to be able to restore the original attributes after the include.
Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<>();
Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
}
// Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects.
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
if (this.flashMapManager != null) {
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
}
RequestPath previousRequestPath = null;
if (this.parseRequestPath) {
previousRequestPath = (RequestPath) request.getAttribute(ServletRequestPathUtils.PATH_ATTRIBUTE);
ServletRequestPathUtils.parseAndCache(request);
}
try {
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
if (this.parseRequestPath) {
ServletRequestPathUtils.setParsedRequestPath(previousRequestPath, request);
}
}
}
不详细解释了,主要是把 Spring 框架的一些组件放入到request�的请求属性中。在后续可以根据 request 拿出 Spring 框架的组件。比如设置了如下的内容:
- Web 的上下文
- 本地语言解析器
- 主题解析器
- …