在
java
中定义类时需要用到
class
关键字
,具体语法如下
// 创建类
class ClassName{
field; // 字段(属性) 或者 成员变量
method; // 行为 或者 成员方法
}
class
为
定义类的关键字,
ClassName
为类的名字,
{}
中为类的主体。
类中包含的内容称为类的成员。属性主要是用来描述类的,称之为类的成员属性或者类成员变量。方法主要说明类 具有哪些功能,称为类的成员方法。
例如定义一个狗类:
class PetDog {
public String name;//名字
public String color;//颜色
// 狗的属性
public void barks() {
System.out.println(name + ": 旺旺旺~~~");
}
// 狗的行为
public void wag() {
System.out.println(name + ": 摇尾巴~~~");
}
}
注意事项:
- 一般一个文件当中只定义一个类
- main方法所在的类一般要使用public修饰(注意:Eclipse默认会在public修饰的类中找main方法)
- public修饰的类必须要和文件名相同
- 不要轻易去修改public修饰的类的名称,如果要修改,通过开发工具修改
类的实例化
定义了一个类,就相当于在计算机中定义了一种新的类型
用类类型创建对象的过程,称为类的实例化
,在
java
中采用
new
关键字,配合类名来实例化对象。
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
PetDog dogh = new PetDog(); //通过new实例化对象
dogh.name = "阿黄";
dogh.color = "黑黄";
dogh.barks();
dogh.wag();
PetDog dogs = new PetDog();
dogs.name = "阿黄";
dogs.color = "黑黄";
dogs.barks();
dogs.wag();
}
}
输出结果:
阿黄: 旺旺旺~~~
阿黄: 摇尾巴~~~
赛虎: 旺旺旺~~~
赛虎: 摇尾巴~~~
注意事项
- new 关键字用于创建一个对象的实例.
- 使用 . 来访问对象中的属性和方法.
- 同一个类可以创建对个实例.
this引用
this
引用指向当前对象
(
成员方法运行时调用该成员方法的对象
)
,在成员方法中所有成员变量的操作,都是通过该
引用去访问
。只不过所有的操作对用户是透明的,即用户不需要来传递,编译器自动完成。
this
引用的是调用成员方法的对象
。
this
引用的特性
- this的类型:对应类类型引用,即哪个对象调用就是哪个对象的引用类型
- this只能在"成员方法"中使用
- 在"成员方法"中,this只能引用当前对象,不能再引用其他对象
- this是“成员方法”第一个隐藏的参数,编译器会自动传递,在成员方法执行时,编译器会负责将调用成员方法 对象的引用传递给该成员方法,this负责来接收

对象的构造及初始化
构造方法
(
也称为构造器
)
是一个特殊的成员方法,
名字必须与类名相同,在创建对象时,由编译器自动调用,并且
在整个对象的生命周期内只调用一次
。
public class Date {
public int year;
public int month;
public int day;
// 构造方法:
// 名字与类名相同,没有返回值类型,设置为void也不行
// 一般情况下使用public修饰
// 在创建对象时由编译器自动调用,并且在对象的生命周期内只调用一次
public Date(int year, int month, int day){
this.year = year;
this.month = month;
this.day = day;
System.out.println("Date(int,int,int)方法被调用了");
}
public void printDate(){
System.out.println(year + "-" + month + "-" + day);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 此处创建了一个Date类型的对象,并没有显式调用构造方法
Date d = new Date(2021,6,9); // 输出Date(int,int,int)方法被调用了
d.printDate(); // 2021-6-9
}
}
特性
- 名字必须与类名相同
- 没有返回值类型,设置为void也不行
- 创建对象时由编译器自动调用,并且在对象的生命周期内只调用一次
- 构造方法可以重载(用户根据自己的需求提供不同参数的构造方法)
构造方法中,可以通过
this
调用其他构造方法来简化代码
public class Date {
public int year;
public int month;
public int day;
// 无参构造方法--内部给各个成员赋值初始值,该部分功能与三个参数的构造方法重复
// 此处可以在无参构造方法中通过this调用带有三个参数的构造方法
// 但是this(1900,1,1);必须是构造方法中第一条语句
public Date(){
//System.out.println(year); 注释取消掉,编译会失败
this(1900, 1, 1);
//this.year = 1900;
//this.month = 1;
//this.day = 1;
}
// 带有三个参数的构造方法
public Date(int year, int month, int day) {
this.year = year;
this.month = month;
this.day = day;
}
}
注意:
- this(...)必须是构造方法中第一条语句
- 不能形成环
就地初始化
public class Date {
public int year = 1900;
public int month = 1;
public int day = 1;
public Date(){
}
public Date(int year, int month, int day) {
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date d1 = new Date(2021,6,9);
Date d2 = new Date();
}
}封装
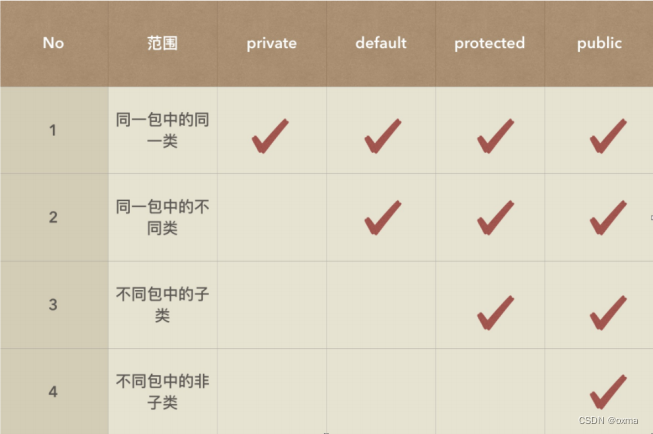
访问限定符
public class Computer {
private String cpu; // cpu
private String memory; // 内存
public String screen; // 屏幕
String brand; // 品牌---->default属性
public Computer(String brand, String cpu, String memory, String screen) {
this.brand = brand;
this.cpu = cpu;
this.memory = memory;
this.screen = screen;
}
public void Boot(){
System.out.println("开机~~~");
}
public void PowerOff(){
System.out.println("关机~~~");
}
public void SurfInternet(){
System.out.println("上网~~~");
}
}
public class TestComputer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Computer p = new Computer("HW", "i7", "8G", "13*14");
System.out.println(p.brand); // default属性:只能被本包中类访问
System.out.println(p.screen); // public属性: 可以任何其他类访问
// System.out.println(p.cpu); // private属性:只能在Computer类中访问,不能被其他类访问
}
}







![2023年中国医疗传感器行业现状分析:市场国有化率低[图]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/39ef84436d0174bb4f8eb966c3952a6c.png)