二叉树中序遍历
- 题解1 递归
- 题解2 迭代
给定一个二叉树的根节点
root ,返回它的
中序 遍历 。
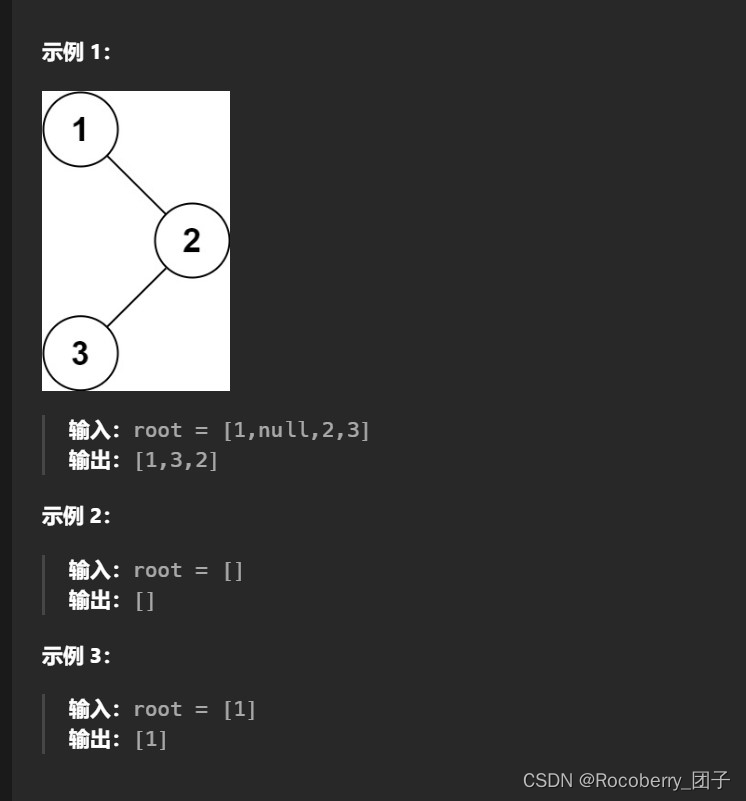
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围 [0, 100] 内
- -100 <=
Node.val<= 100
进阶: 递归算法很简单,你可以通过迭代算法完成吗?
题解1 递归
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> finalR;
void inorder(TreeNode* root){
if(! root) return;
inorder(root->left);
finalR.push_back(root->val);
inorder(root->right);
}
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
if(! root ) return vector<int>();
inorder(root);
return finalR;
}
};
题解2 迭代
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> finalR;
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
if(! root ) return vector<int>();
// 弹栈符合中序遍历顺序
stack<TreeNode*> kk;
TreeNode* Lroot = root;
while(Lroot){
kk.push(Lroot);
Lroot = Lroot->left;
}
while(kk.size()){
auto k = kk.top();
finalR.emplace_back(k->val);
kk.pop();
// 对每个点查右结点
//(不需要再考虑左结点,因为此时该点左侧的点都已经检查完了)
if(k->right){
k = k->right;
// 依旧是先左
while(k){
kk.push(k);
k = k->left;
}
}
}
return finalR;
}
};










![[红明谷CTF 2021]write_shell %09绕过过滤空格 ``执行](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d4689eed5afe4de4a687cd0cd2eb865d.png)