文章目录
- 题目
- 方法一:暴力哈希
- 方法二:利用二叉搜索树的特性(递归+双指针)
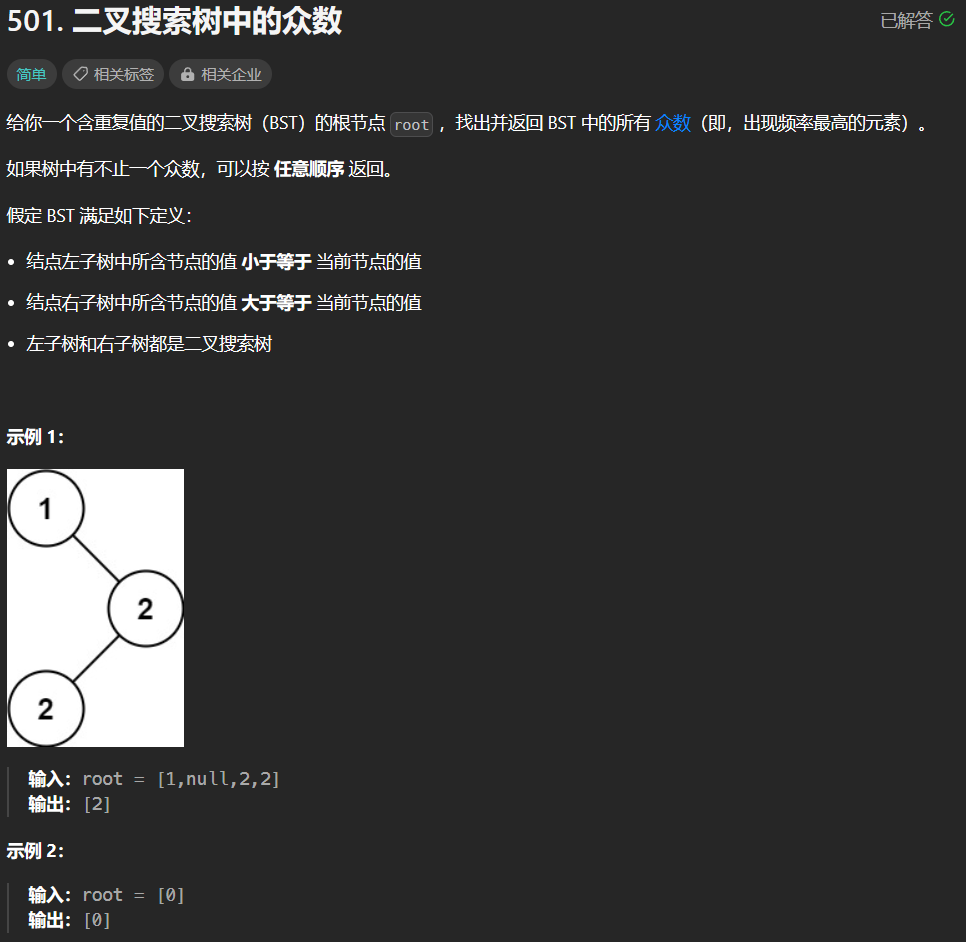
题目
方法一:暴力哈希
这是针对于普通二叉树的解法 统计number出现次数 然后将次数最大的众数集 取出来
Map<Integer , Integer > map = new HashMap<>();
PriorityQueue<int[]> priori = new PriorityQueue<>((a,b)->b[1]-a[1]);//优先队列 按数组第二个元素从大到小排
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
for(Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> num : map.entrySet()) priori.offer(new int[]{num.getKey(),num.getValue()});
int max = priori.peek()[1];
int size =priori.size();
for(int i = 0 ; i<size ; i++){
int [] a1 = priori.poll();
if(max == a1[1]) list.add(a1[0]);
}
return list.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) return;
map.put(root.val,map.getOrDefault(root.val, 0)+1);
dfs(root.left);
dfs(root.right);
}
方法二:利用二叉搜索树的特性(递归+双指针)
关键在于本层逻辑的处理
维护一个最大频率maxcount、单数字统计频率count、当前节点root的前一个节点 pre、
class Solution {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
TreeNode pre = null;// 记录前一个节点
int maxcount = 0; // 最大频率
int count = 0;// 统计频率
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return list.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) return;
dfs(root.left);
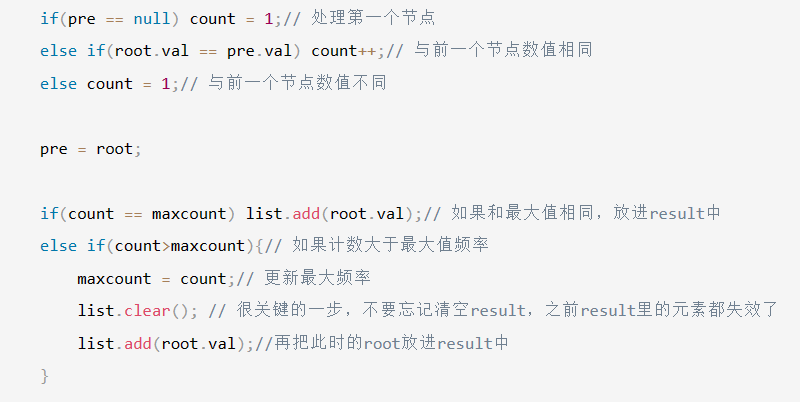
if(pre == null) count = 1;// 处理第一个节点
else if(root.val == pre.val) count++;// 与前一个节点数值相同
else count = 1;// 与前一个节点数值不同
pre = root;
if(count == maxcount) list.add(root.val);// 如果和最大值相同,放进result中
else if(count>maxcount){// 如果计数大于最大值频率
maxcount = count;// 更新最大频率
list.clear(); // 很关键的一步,不要忘记清空result,之前result里的元素都失效了
list.add(root.val);//再把此时的root放进result中
}
dfs(root.right);
}
}